0% found this document useful (0 votes)
809 views3 pagesProgressive Cavity Pump
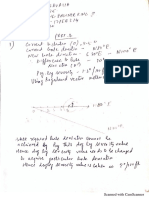
The progressive cavity pump (PCP) is a positive displacement pump that transfers the same amount of fluid that it takes in. It consists of a double helix stator attached to tubing and a single helix rotor suspended in the stator by a rod string. PCPs are suitable for high viscosity fluids, high sand content fluids, low productivity wells, and gassy wells. It works by the rotor forming cavities between it and the stator as it rotates, moving fluid within the cavities from suction to discharge. PCPs can handle high viscosities, solids, and gas with low maintenance but are sensitive to temperature and pressure changes that could damage the elastomer stator.
Uploaded by
dhrumil savaliaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
809 views3 pagesProgressive Cavity Pump
The progressive cavity pump (PCP) is a positive displacement pump that transfers the same amount of fluid that it takes in. It consists of a double helix stator attached to tubing and a single helix rotor suspended in the stator by a rod string. PCPs are suitable for high viscosity fluids, high sand content fluids, low productivity wells, and gassy wells. It works by the rotor forming cavities between it and the stator as it rotates, moving fluid within the cavities from suction to discharge. PCPs can handle high viscosities, solids, and gas with low maintenance but are sensitive to temperature and pressure changes that could damage the elastomer stator.
Uploaded by
dhrumil savaliaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd