0% found this document useful (0 votes)
496 views5 pagesAdvanced Rig Inspection Training Course
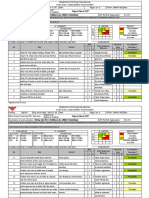
This document provides an overview and agenda for a virtual training course on advanced rig equipment inspection. The 5-day course covers inspection and maintenance procedures for key rig equipment like drawworks, rotary tables, top drives, derricks, mud pumps, and electrical systems. Attendees include drilling engineers, managers, and maintenance staff. The interactive virtual training allows participants to sharpen skills and stay current on standards to ensure equipment integrity and safety.
Uploaded by
Syed IrtazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
496 views5 pagesAdvanced Rig Inspection Training Course
This document provides an overview and agenda for a virtual training course on advanced rig equipment inspection. The 5-day course covers inspection and maintenance procedures for key rig equipment like drawworks, rotary tables, top drives, derricks, mud pumps, and electrical systems. Attendees include drilling engineers, managers, and maintenance staff. The interactive virtual training allows participants to sharpen skills and stay current on standards to ensure equipment integrity and safety.
Uploaded by
Syed IrtazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Course Overview: Describes the overview, purpose, and benefits of the rig equipment inspection training course, emphasizing safety and operational readiness.
- Course Agenda - Day 1 to Day 3: Details the training schedule and topics for the first three days, covering equipment such as drawworks, rotary table, and travelling block.
- Course Agenda - Day 4 to Day 5: Outlines mud processing and electrical equipment training scheduled for days four and five.
- Course Agenda - Day 6 to Day 7: Training on marine equipment and well control for the sixth and seventh days.
- Course Agenda - Day 8: Final day of training on well control equipment focusing on choke, kill manifolds, and BOP equipment.