Professional Documents
Culture Documents
After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signs
Uploaded by
roma_elonaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signs
Uploaded by
roma_elonaCopyright:
Available Formats
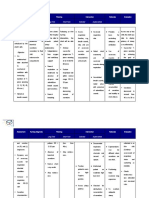
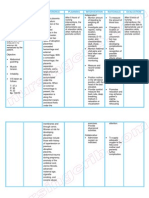
NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Postpartum After 8 hours of Independent:
Risk for Ineffective hemorrhage is nursing • monitor amount of • To measure the
tissue perfusion defined as a loss of interventions patient bleeding by weighing amount of blood loss.
related to blood in the will be able to:
all pads
postpartum period
hemorrhage as • Frequently monitor • Early recognition of
of more than 500 • Demonstrate
evidenced by: mL. The average, vital signs adverse effects allows
adequate
spontaneous perfusion. for prompt
Subjective Cues: vaginal birth will • Demonstrate interventions.
“Pira na kaadlaw an typically have a 500 stable vital
ak pag anak pero cge mL blood loss. In signs • Massage the uterus • To help expel clots of
la ghap it pag cesarean births the blood and it is also
dinugu.e haak”, as average blood loss used to check the tone
verbalized by the rises to 800-1000
of the uterus and
patient. mL. There is a
greater risk of
ensure that it is
hemorrhage in the clamping down to
first 24 hours after prevent excessive
Objective: bleeding.
the birth, called
· Restlessness
· Confusion.
primary postpartum • Place the mother in
· Irritability.
hemorrhage. A Trendelenberg • Encourages venous
secondary position return to facilitate
· V/S taken as
hemorrhage occurs circulation, and
follows:
after the first 24 prevent further
T: 36.8C
hours of birth. In
P: 90bpm bleeding.
the majority of
R: 24cpm
cases the cause of
Bp: 100/70mmhg
hemorrhage is
uterine atony, • Provide comfort • Promotes relaxation
meaning that the measures like back and may enhance
uterus is not rubs, deep breathing. patient’s coping
contracting enough Instruct in relaxation abilities by refocusing
to control theplacental or visualization attention.
site. exercise. Provide
Other reasons for a
divers ional activities.
hemorrhage would
include retained
placental fragments Collaborative • To supply adequate
(possibly including • Administer oxygen as oxygen and prevents
a placenta accreta),
indicated. further complication.
trauma of some
form, like a cervical
laceration, uterine • To promote
inversion or even • Administer contraction and
uterine rupture, and medication as prevents further
clotting disorders. indicated. (e. g bleeding.
Methergin)
MCH pp.416 by Pilliterri
vol. 1
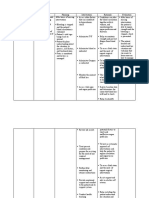
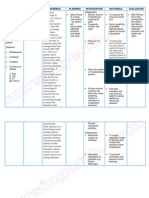
NURSING DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS OBJECTIVES NURSING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Fear related to It is difficult for a After 8 hours of Indpendent: • To establish trust and After 8 hours
outcome of woman who has nursing • Listen actively and showing interest. of nursing
pregnancy after experienced bleeding intervention the focus on the patient intervention
episode of placenta late in pregnancy to patient will be able discussed her the patient
previa bleeding wait for the baby to to: personal feelings. is relaxed
come to term, • To demonstrate and shows a
Subjective cues: wondering if her • appear • Use appropriate support. good
“ Nahadlok ako mam infant will be alright. relaxed touch with patient’s response
nga mawara na liwat Most likely she is • level of permission and
ini na ak baby kay experiencing severe anxiety be • For relaxation participates
ikaduha ko na unta ini emotional stress. She reduced to • Instructed deep well in the
hiya”, as verbalized cannot help but manageable breathing exercise. activitiesl.
by the patient. wonder if the next level • To avoid confusion and
bleeding will kill her, • discusses • Speak in brief easy to understand.
Objective cues: the infant or both. concerns statements using
• looks pale She may become so with nurse simple words.
• disturbed sleep worried about the and other
• anxious safety of her child. health care Collaborative:
providers
MCH pp 415 by • Give sedatives as * To lessen excitement,
Pillitteri vol. 1 ordered. nervousness and
irritation.
You might also like
- Hernandez NCP Drug StudyDocument7 pagesHernandez NCP Drug StudyEliza Joyce HernandezNo ratings yet
- NCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Document3 pagesNCP (Postpartum Hemmorhage)Anne DyNo ratings yet
- Altered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalDocument4 pagesAltered Tissue Perfusion UteroplacentalAlyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Airway ClearanceCaroline ChaNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 3Document3 pagesNCP Case 3boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- NCP Abruptio PlacentaDocument2 pagesNCP Abruptio PlacentaCarson Birth100% (1)
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 pagesHemorrhage NCPElishaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit PPHDocument3 pagesFluid Volume Deficit PPHEllie GartungNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPNichole Audrey Saavedra100% (1)
- Rle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyDocument6 pagesRle 107 Maternal and Child Health Nursing: University of The Assumption College of Nursing and PharmacyEvangeline Anne Macanas100% (2)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 pagesFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- NCP For Delivery RoomDocument4 pagesNCP For Delivery RoomGiselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- NCP Placenta PreviaDocument2 pagesNCP Placenta PreviaCathy CnlsNo ratings yet
- NCP On Postpartum MotherDocument9 pagesNCP On Postpartum MotherM.S.H Tube100% (1)
- Uterine AtonyDocument3 pagesUterine AtonyArsheina Paradji100% (1)
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 pagesPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- NCP - Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalDocument13 pagesNCP - Diabetes Mellitus Prepregnancy/GestationalClaudine Christophe100% (1)
- Dilatation and CurettageDocument2 pagesDilatation and CurettageBheru Lal50% (2)
- Altered Sleeping PatternDocument4 pagesAltered Sleeping PatternIan Kenneth Da SilvaNo ratings yet
- NCP PostpartumDocument3 pagesNCP Postpartumglocel88% (16)
- Assessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Interference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMelDred Cajes BolandoNo ratings yet
- Labor Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesLabor Nursing Care Plan 1Anna Mae DollenteNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionAngel Hernandez100% (1)
- SDL1 NCP Case2Document3 pagesSDL1 NCP Case2Alec AnonNo ratings yet
- NCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsDocument3 pagesNCP For Postpartum DiscomfortsCamille Maluenda - Tan0% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFambiit25No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for Diarrhea, Dehydration & Acute PainDocument13 pagesNursing Care Plans for Diarrhea, Dehydration & Acute PainRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan (Bowel Elemination)Rijane Tabonoc Omlang100% (1)
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPkristapot80% (10)
- Ncp-Imbalance NutritionDocument2 pagesNcp-Imbalance NutritionMariko BarbaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum discharge plan vitamins exercise dietDocument2 pagesPostpartum discharge plan vitamins exercise dietJude Labajo100% (1)
- ASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONDocument3 pagesASSESSMENT HEALTH NURSING INTERVENTION EVALUATIONtflorenzNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Acute Pain Managementjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- Drug Ang NCPDocument9 pagesDrug Ang NCPMelanie GaledoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannNo ratings yet
- NCP Gestational HypertensionDocument2 pagesNCP Gestational Hypertensionshila_glangNo ratings yet
- Manage Abruptio Placentae with Nursing Diagnosis, Interventions, and EvaluationDocument4 pagesManage Abruptio Placentae with Nursing Diagnosis, Interventions, and EvaluationShien Samalea Vasquez100% (1)
- Newborn Nursing Care Plan for Meconium StainingDocument6 pagesNewborn Nursing Care Plan for Meconium StainingFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Document6 pagesCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breastfeeding RT To Inadequate Milk Supply Secondary To Inverted NippleDocument3 pagesIneffective Breastfeeding RT To Inadequate Milk Supply Secondary To Inverted NippleKerny BasilioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care for 2nd Degree Perineal LacerationDocument2 pagesNursing Care for 2nd Degree Perineal LacerationDickson,Emilia Jade100% (1)
- NCP - Preeclampsia (A)Document6 pagesNCP - Preeclampsia (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Rupture of Membrames On Full Term PrimigravidaDocument7 pagesCollege of Nursing: Rupture of Membrames On Full Term PrimigravidaJulia BanagodosNo ratings yet
- NCP PPHDocument2 pagesNCP PPHmikee-berredo-9975No ratings yet
- NCP - PCGHDocument9 pagesNCP - PCGHLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Top 3 NCP For CASE-PRES PDFDocument9 pagesTop 3 NCP For CASE-PRES PDFSmartieNo ratings yet
- NCP Pain - OBDocument5 pagesNCP Pain - OBSandra Guimaray50% (2)
- PRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDDocument8 pagesPRELIMS 219 Q - uPDATEDAloha ItsmeNo ratings yet
- NCP OB Ward - Imbalanced NutritionDocument2 pagesNCP OB Ward - Imbalanced NutritionCk JosueNo ratings yet
- NCP EctopicDocument1 pageNCP Ectopicmusicath_07No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Postpartum Hemorrhagederic100% (60)
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageLei Ortega95% (21)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage ManagementDocument2 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage ManagementjsksNo ratings yet
- Aglibut Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesAglibut Nursing Care PlanTubilgaSie'jhayNo ratings yet
- NCP Vaginal BleedingDocument2 pagesNCP Vaginal Bleedingjayye.aronceNo ratings yet
- Free Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewDocument1 pageFree Gingival Graft Procedure OverviewTenzin WangyalNo ratings yet
- ICD-10 & ICD-9 codes for common medical conditions and proceduresDocument59 pagesICD-10 & ICD-9 codes for common medical conditions and procedureskiyoeugraNo ratings yet
- Concrete MSDS 1 PDFDocument5 pagesConcrete MSDS 1 PDFmanil_5100% (1)
- 4 Levels of Perio DZDocument2 pages4 Levels of Perio DZKIH 20162017No ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument1 pageConclusionSamNo ratings yet
- ActivatorDocument69 pagesActivatorParijat Chakraborty PJNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing (1) 2007Document14 pagesPerioperative Nursing (1) 2007Lorraine BuelvaNo ratings yet
- Symposiumbooklet CareerDocument36 pagesSymposiumbooklet Careerroh009No ratings yet
- Embryology GenitalDocument53 pagesEmbryology GenitalDhonat Flash100% (1)
- DylasisDocument3 pagesDylasisyuvi087No ratings yet
- MemoryDocument46 pagesMemoryMaha Al AmadNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter on ReproductionDocument4 pagesScience Chapter on ReproductionAnita GargNo ratings yet
- Evaluation MyocarditisDocument5 pagesEvaluation MyocarditisRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A ReviewDocument6 pagesStevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Reviewイアン リムホト ザナガNo ratings yet
- Thallophytes 2Document32 pagesThallophytes 2Starnley TemboNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment ReportDocument16 pagesAccomplishment ReportIsaias BigolNo ratings yet
- HPLC - 4Document24 pagesHPLC - 4Melisa Soledad Barco Jara100% (1)
- F.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. AryabiantaraDocument35 pagesF.A.S.T.H.U.G: I W. Aryabiantaraarnawaiputu60No ratings yet
- Procedure ListDocument20 pagesProcedure ListsoyrolandoNo ratings yet
- Bagian AwalDocument17 pagesBagian AwalCitra Monalisa LaoliNo ratings yet
- Guardian Angel ReikiDocument9 pagesGuardian Angel Reikikoochimetal100% (4)
- Nutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansDocument26 pagesNutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansFitriNo ratings yet
- A Novel Visual Clue For The Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Lichen PlanusDocument1 pageA Novel Visual Clue For The Diagnosis of Hypertrophic Lichen Planus600WPMPONo ratings yet
- Indian ListenerDocument103 pagesIndian ListenerTareq Aziz100% (1)
- Femoral Fractures in Children: Surgical Treatment. Miguel Marí Beltrán, Manuel Gutierres, Nelson Amorim, Sérgio Silva, JorgeCoutinho, Gilberto CostaDocument5 pagesFemoral Fractures in Children: Surgical Treatment. Miguel Marí Beltrán, Manuel Gutierres, Nelson Amorim, Sérgio Silva, JorgeCoutinho, Gilberto CostaNuno Craveiro LopesNo ratings yet
- Assignment On PrionsDocument22 pagesAssignment On PrionsRinta Moon100% (2)
- 4926-02 L2 Certificate Qualification Handbook v1 PDFDocument116 pages4926-02 L2 Certificate Qualification Handbook v1 PDFforumuse3bNo ratings yet
- VP ShuntDocument5 pagesVP ShuntPradeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care With ChecklistDocument5 pagesTracheostomy Care With ChecklistHollan GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMADocument5 pagesCase Study: MYXEDEMATOUS COMAjisooNo ratings yet