Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Boiler and Steam Cycle
Uploaded by
saikumarvavilla0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageb
Original Title
Boiler and steam cycle
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentb
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views1 pageBoiler and Steam Cycle
Uploaded by
saikumarvavillab
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
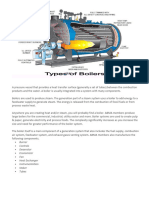
Boiler and steam cycle[edit]
Pressurized water reactor simplified schematic
In the nuclear plant field, steam generator refers to a specific type of large heat exchanger used
in a pressurized water reactor (PWR) to thermally connect the primary (reactor plant) and
secondary (steam plant) systems, which generates steam. In a nuclear reactor called a boiling
water reactor (BWR), water is boiled to generate steam directly in the reactor itself and there are
no units called steam generators.
In some industrial settings, there can also be steam-producing heat exchangers called heat
recovery steam generators (HRSG) which utilize heat from some industrial process, most
commonly utilizing hot exhaust from a gas turbine. The steam generating boiler has to produce
steam at the high purity, pressure and temperature required for the steam turbine that drives the
electrical generator.
Geothermal plants do not need boilers because they use naturally occurring steam sources. Heat
exchangers may be used where the geothermal steam is very corrosive or contains excessive
suspended solids.
A fossil fuel steam generator includes an economizer, a steam drum, and the furnace with its
steam generating tubes and superheater coils. Necessary safety valves are located at suitable
points to relieve excessive boiler pressure. The air and flue gas path equipment include: forced
draft (FD) fan, air preheater (AP), boiler furnace, induced draft (ID) fan, fly ash collectors
(electrostatic precipitator or baghouse), and the flue-gas stack.[7][8][9]
You might also like
- Jagan Steam Power PlantDocument101 pagesJagan Steam Power PlantMahender VangalaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNo ratings yet
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocument15 pagesGas Turbine Power Plantrahul100% (1)
- Thermal Power PlantDocument34 pagesThermal Power PlantRama Krishna KariNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inDocument24 pagesMechanical Engineering Project - Thermal Power Plant Study - WWW - Amie.nbcafe - inbtdoss72100% (1)
- PowerplantapplicationsDocument90 pagesPowerplantapplicationsRicky Lao100% (2)
- Physical study of the Steam-Generating UnitDocument12 pagesPhysical study of the Steam-Generating UnitIsmaeli KielNo ratings yet
- Essential Equipment of Steam Power PlantsDocument101 pagesEssential Equipment of Steam Power Plantsjamunaa83100% (1)
- 2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTDocument101 pages2013edusat Lecture On STEAM PLANTKishore KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Gajendra KumarDocument23 pagesGajendra KumarGAJENDRA KUMARNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Steam TurbineDocument32 pagesLecture 2 - Steam TurbineZulyadain Ishak100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant BasicsDocument79 pagesThermal Power Plant BasicsMukundan SwamynathanNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentDocument102 pagesEssentials of Steam Power Plant EquipmentPrakhar Shukla100% (1)
- Layout of Thermal Power PlantDocument21 pagesLayout of Thermal Power PlantRaj_Jai03100% (1)
- JJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemDocument9 pagesJJ308 REPORT Layout and Piping of The Steam Power Plant SystemAh Tiang86% (7)
- Industrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharDocument26 pagesIndustrial Training AT: Submitted By: Rishikesh (11-1-6-002) NIT, SilcharRakesh Roshan KeshriNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Rankine CycleDocument27 pagesThermal Power Plant Rankine Cyclevenki249100% (1)
- Thermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Document30 pagesThermal Power Plant: Gaini Zail Singh Punjab Technical University Campus (Bathinda)Sriram ramsNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument11 pagesThermal Power PlantAnand Kalani100% (1)
- Thermal Power StationDocument17 pagesThermal Power StationJayAr EsquilloNo ratings yet
- Report On Thermal Power PlantDocument22 pagesReport On Thermal Power PlantNitinNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument12 pagesThermal Power StationSalehAfadlehNo ratings yet
- Boiler Furnace and Steam DrumDocument4 pagesBoiler Furnace and Steam DrumGeorge AniborNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power - WikipediaDocument24 pagesThermal Power - WikipediaEusebia MaedzwaNo ratings yet
- تقرير محطات الطاقهDocument45 pagesتقرير محطات الطاقهعبد الرحمن إبراهيمNo ratings yet
- Steam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersDocument4 pagesSteam Heat Energy Water Psi Kpa: Water-Tube Boiler Fossil Fuel-Fired Boilers Heat Recovery Boilers Heat Recovery BoilersMarsNo ratings yet
- Cfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Document21 pagesCfakepathlayoutofthermalpowerplant 091031114144 Phpapp01Shruti GuptaNo ratings yet
- Abhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliDocument21 pagesAbhishek Kumar Asif Ahmad Niket Rakeshan Zeeshan AliSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument21 pagesThermal Power StationSatria WinandaNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorDocument3 pagesTypes of ReactorTariq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant Diagram ExplainedDocument21 pagesThermal Power Plant Diagram ExplainedTanveer AzizNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument16 pagesThermal Power PlanthebishtNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Stations: Electricity Production through SteamDocument13 pagesThermal Power Stations: Electricity Production through SteammuthucharaNo ratings yet
- 38 Thermal Power PlantDocument26 pages38 Thermal Power PlantSwaraj TodankarNo ratings yet
- 40.6 MW Regenerative Thermal Power PlantDocument115 pages40.6 MW Regenerative Thermal Power PlantJohn Fil PabloNo ratings yet
- Boiler TypesDocument9 pagesBoiler TypesSharif Muhammad HossainNo ratings yet
- Power PlantDocument4 pagesPower PlantNumair AshrafNo ratings yet
- Common Engineering GlossaryDocument2 pagesCommon Engineering Glossarykicchu001No ratings yet
- Thermal Power StationDocument3 pagesThermal Power StationputtloveNo ratings yet
- Industrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesIndustrial Steam Boiler: ObjectiveM. Hassan HaidderNo ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAashish SangwanNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineDocument7 pagesPower Plant Layout and Essential Feature of RankineMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Title of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantDocument98 pagesTitle of Project-: Preliminary Study On Thermal Power Plant and Detail Study On Coal Handling PlantAbir MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Plant EngDocument4 pagesPlant EngIzzat AzmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Steam GenerationDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Steam GenerationfaranimohamedNo ratings yet
- Energy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50Document3 pagesEnergy Conversion in A Nuclear Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNo ratings yet
- Jaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyDocument29 pagesJaipur: Vivekananda Institute of TechnologyAnonymous ytZsBOVNo ratings yet
- Honorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadDocument50 pagesHonorable Chief Engineer (Thermal) Genco, FaisalabadraowaleedahmadNo ratings yet
- Tugas Util (Boiler)Document4 pagesTugas Util (Boiler)AkhmadSumarnoNo ratings yet
- Harduaganj Thermal Power StationDocument21 pagesHarduaganj Thermal Power StationgeeteshsirNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Control Chapter02Document11 pagesPower Plant Control Chapter02veerendraveeru_1014No ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesThermal Power PlantSiri VenniNo ratings yet
- Types of Steam GeneratorsDocument2 pagesTypes of Steam GeneratorsAnonymous oUoJ4A8xNo ratings yet
- Major components in a steam turbine power plant process flow diagramDocument3 pagesMajor components in a steam turbine power plant process flow diagramTaqdees AhmadNo ratings yet
- Steam Power Plant 1Document17 pagesSteam Power Plant 1MohammedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Edge ComputingDocument1 pageEdge ComputingsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Artificial IntelligenceDocument2 pagesArtificial IntelligencesaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Computing PowerDocument1 pageComputing PowersaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Quantum ComputingDocument1 pageQuantum ComputingsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Extended RealityDocument1 pageExtended RealitysaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When You're Receiving Unfair Criticism.: How To Deal With HatersDocument2 pagesSay "Thank You" When You're Receiving Unfair Criticism.: How To Deal With HaterssaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- The Left Main Coronary Artery Supplies Blood To 75Document6 pagesThe Left Main Coronary Artery Supplies Blood To 75saikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When You're Receiving Helpful FeedbackDocument2 pagesSay "Thank You" When You're Receiving Helpful FeedbacksaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When Someone Gives You Unsolicited AdviceDocument1 pageSay "Thank You" When Someone Gives You Unsolicited AdvicesaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Hanoi, Vietnam: Accelerating The Uptake of E-Mobility Solutions Through Stakeholder EngagementDocument2 pagesHanoi, Vietnam: Accelerating The Uptake of E-Mobility Solutions Through Stakeholder EngagementsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When You're Comforting Someone.: Example: Your Co-Worker's Mother Passed Away RecentlyDocument2 pagesSay "Thank You" When You're Comforting Someone.: Example: Your Co-Worker's Mother Passed Away RecentlysaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When You're Running Late.: Example: You Walk in The Door 14 Minutes LateDocument1 pageSay "Thank You" When You're Running Late.: Example: You Walk in The Door 14 Minutes LatesaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Generation EfficiencyDocument2 pagesThermal Power Generation EfficiencysaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Say "Thank You" When You're Receiving A Compliment.: Example: "Your Dress Looks Great."Document2 pagesSay "Thank You" When You're Receiving A Compliment.: Example: "Your Dress Looks Great."saikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- BimboDocument1 pageBimboNaveen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- BimboDocument1 pageBimboNaveen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Where We Go From HereDocument2 pagesWhere We Go From HeresaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Types of Thermal EnergyDocument1 pageTypes of Thermal EnergysaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Electricity CostDocument1 pageElectricity CostsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Electricity CostDocument1 pageElectricity CostsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Hanoi, Vietnam: Accelerating The Uptake of E-Mobility Solutions Through Stakeholder EngagementDocument2 pagesHanoi, Vietnam: Accelerating The Uptake of E-Mobility Solutions Through Stakeholder EngagementsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- B.V. Patel Umarakh.: Guided BY: Shaunak DesaiDocument28 pagesB.V. Patel Umarakh.: Guided BY: Shaunak DesaiKristian Marlowe OleNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangerDocument14 pagesHeat ExchangersaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Queenie 140128190950 Phpapp01 PDFDocument20 pagesQueenie 140128190950 Phpapp01 PDFsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Solar Power: Group A: Yamna Tahir, Ammarah Masood, Aleena Ahmed, Asna Moiz, Mirha AsifDocument17 pagesSolar Power: Group A: Yamna Tahir, Ammarah Masood, Aleena Ahmed, Asna Moiz, Mirha AsifsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- History: Reciprocating Steam Engine James Watt Pearl Street Station Holborn Viaduct Power Station Steam TurbineDocument1 pageHistory: Reciprocating Steam Engine James Watt Pearl Street Station Holborn Viaduct Power Station Steam TurbinesaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- B.V. Patel Umarakh.: Guided BY: Shaunak DesaiDocument28 pagesB.V. Patel Umarakh.: Guided BY: Shaunak DesaiKristian Marlowe OleNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy & Solar Panels: A Presentation OnDocument40 pagesSolar Energy & Solar Panels: A Presentation OnsaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet
- Solar Power in Pakistan: Potential, Current Projects & Future ProspectsDocument17 pagesSolar Power in Pakistan: Potential, Current Projects & Future ProspectssaikumarvavillaNo ratings yet