Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Davis Budget
Uploaded by
api-505775092Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Davis Budget
Uploaded by
api-505775092Copyright:
Available Formats
Planning a budget
Curriculum Topics
• Purpose of budgeting
• Types of budget
• Assumptions
• Use of budgets
Introduction Despite the severe recession of 2008-09, Davis continued to be a
profitable company. This has been the result of careful budgeting.
Davis Service Group is a large public limited company employing Budgeting involves making detailed financial plans for every aspect
around 17,000 people. Its shares are quoted on the London Stock of the business, identifying risks and ensuring that managers are
Exchange. The business is based on service contracts to source, committed to the outcomes that they have agreed.
clean and maintain industrial textiles, such as protective clothing
and linens. This is across four key sectors: workwear, healthcare, Budgets are forward financial plans. They show financial targets
hotels and restaurants, and general facilities, such as washroom over a given period of time for income, expenditure and cash
linen. The company’s headquarters are in London but its flows within a business. Davis uses budgets to plan the future use
operations are spread across the UK and Ireland, continental of its resources, either in the short or long term. For example,
Europe and Scandinavia. These are managed by two separate operational areas need to assess the costs of the people needed
companies: Sunlight in the UK and Berendsen on the Continent. to meet production targets or the marketing team must determine
Sunlight is the market leader in the UK. Berendsen is the market costs of promoting services to increase sales. Budgets are also
leader in Norway, Sweden, Denmark and Holland. Sales for the communication tools which allow employees to understand where
combined group in 2008 were worth £954 million. City financial the business is heading.
analysts have forecast that 2009 sales will be at least equivalent to
the 2008 level, if not modestly ahead. This case study shows how the development and use of budgets
contribute to Davis Service Group meeting its objectives.
Sales breakdown by region Sales breakdown by sector
UK & Ireland General Building a budget
facilities
Nordic
Workwear A company’s objectives budget is the overall financial plan
Hotels showing expenditure of the available funds. It is driven by the aims
& restaurants and objectives of the organisation as well as what the organisation
can actually accomplish. Many variables in a business can be
Continental Healthcare
budgeted.
GLOSSARY
Budgets: Planning for the future using Resources: Inputs into a business e.g. Variables: Numbers, amounts or
numbers. These numbers relate to such materials, people, time. situations which can change.
totals as expected costs. The budgeted
figures are related to specific time
periods.
Davis Service Group | Planning a budget
These include:
• sales
• output
• costs – operating and fixed
• profits
• cash flow
• capital investment.
The budget will be based on key assumptions about likely
business conditions for the year ahead. These inform the detailed
operating budgets that plan month-to-month sales, activity Making assumptions
levels and expenditure, for example, staff costs. Managers may A budget needs to make assumptions about how internal and
need to accommodate unexpected changes with flexible budgets. external business conditions will develop and change. Once the
For example, sales may be lower than originally expected, so the effects of these assumptions have been evaluated, managers can
budget may need to reduce marketing expenditure and/or set forecasts for sales turnover and costs to meet profit targets.
operational activities. An increase in orders may require additional Detailed planning can then follow to estimate the plant capacity,
recruitment costs for temporary staffing. Sometimes managers staffing, materials and marketing needed.
use zero budgeting. This means that they must start every year
from zero and justify all planned expenditure, rather than starting Managers use sensitivity analysis to review different scenarios.
from the previous year's figures. This may be appropriate for a They ask questions and consider the impacts of various
specific, self-contained project. In larger firms budgets are alternatives (the ‘what-ifs’). For example:
allocated for defined areas of responsibility such as: The economic outlook What is the overall economic trend for
• cost centres - sub-divisions of an organisation that are a the UK and Europe? For example, increased redundancies
significant source of financial cost, for example, a factory or during a recession would mean less demand for workwear. A
laundry operation sharp rise in the value of the euro against the British pound
• profit centres - units that contribute to the overall profits of the would make earnings from Davis’ European business more
firm, for example, services to hotel groups. valuable to the company.
Budgets often cover one year but may form part of a longer term Competition What is the likely strategy of key competitors?
plan, such as when a business is considering entering a new Is there a risk of any new entrant to the market or an existing
market. Davis Service Group’s budgetary cycle runs from January competitor leaving the market? For example, if a new
competitor appeared in the market, should Davis reduce its
to December:
prices (affecting its profit) or invest in additional marketing
• By July/August, the financial targets for the coming year are
activity? Davis had to react promptly and positively in the UK
agreed.
when two competitors left the market in 2007-8 (one from
• In August/September, the budget is developed; accurate data
bankruptcy and one from a strategic decision to withdraw) to
is collected from the different profit centres from the new set of
take advantage of the opportunity.
assumptions made for the next year.
• In October of each year, these figures and assumptions are Customers How are customer needs likely to change? For
confirmed in formal review meetings. example, some larger clients have been moving from simply
• By December, the full budget has been finalised at country level buying a textile service to wanting a complete solution to
as well as providing the overall Group data. cleanliness and safety needs. Will demand from the hospital
sector grow more than that from hotels and restaurants?
Davis Service Group is careful to set budgets in consultation and
not to impose them on the different parts of the business. In this Staff Is the company recruiting sufficient staff? Are salaries
way, managers at all levels feel involved in the process and are more high enough to keep vital knowledge and experience within the
likely to feel motivated to achieve the targets in their budgets. Group or does Davis need to recruit additional expertise?
GLOSSARY
Assumptions: An assertion about Operating budgets: Budgets that are Zero budgeting: A budgeting system Sensitivity analysis: A model to track
some characteristic of the future that concerned with the short term running which aims to drive down costs by the effect of changes or uncertainty on
may affect the operations or plans of an of the business. initially setting budgets at zero. different variables
organisation. Managers must justify every item of
expenditure.
Davis Service Group | Planning a budget
Suppliers What is happening in supplier markets? For
example, what will be the effect of Far East imports on prices
of workwear? What is the impact of increases or reductions in
utility prices (energy and water)? How will exchange rates
affect costs?
Davis Service Group often constructs two or three possible
scenarios so it can analyse the effects of favourable and less
favourable outcomes on the business. The illustrative data below
highlights the effect on profit of this approach:
Scenario A
£ million JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH
a
Sales revenue 50 55 60
Operating costs 26 29 31
Overheads 20 20 21
Profit 4 6 8
Scenario B (with new competitor)
Variances may be favourable (better than expected) or adverse
£ million JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH (worse than expected). Small variances are inevitable and usually
not significant. A key task of managers is to watch for variances
b
Sales revenue 48 50 45
that are unexpected, either in their size or timing, and take action
Operating costs 24 25 23
accordingly. Managers generally focus their energy on these
Overheads 21 21 21
'exceptions'. For example, the weather can cause an unexpected
Profit 3 4 1 variance for Davis Service Group’s business. June and July 2008
were warm, sunny months in the UK; the hotel and restaurant
* all data is illustrative only
industry was busy and therefore the laundries and their staff were
In Scenario A. Davis increases market share and revenues. busy. This was followed by a wet August. The number of people
The larger volumes and relatively small increase in costs would going on holiday fell and resulted in reduced linen services. The
give increased profits. In Scenario B, a competitor opens a new knock-on effect of reduced traffic in the hotel and restaurant
plant. Sales begin to fall and lower profits would result. Overheads industry was less linen processed at Davis Service Group.
or costs would need to be reduced to meet the gap.
Adverse variances prompt investigation into what has gone
wrong. They may suggest:
• unrealistic budgeting; budget data may need to be revised or
flexed
• a failure with part of the process (e.g. missed targets by sales
Using budgets force); this needs immediate management attention
• a change in the external environment (e.g. a new competitor);
Typical budget statements are given for the Textiles budget/UK this might require a counter-attack with an increased marketing
Midland region of Davis Service Group. The budget for the year budget.
(£81m) is based on the historic year data and the assumptions for
the year. The two forecast outcomes use two different sets of Favourable variances represent good news but should not be
assumptions resulting in lower or higher levels of sales. In the ignored. Instead they may carry an opportunity – perhaps a new
example, sales for the first three months of the year were budgeted market is emerging or a competitor has withdrawn? Either way,
at £19.8m. Actual sales were £20.3m – 2.5% above budget. If this managers are responsible for their budget variances and would need
level of increase were to continue, sales would reach £83m. to report on outcomes and propose action to their own manager.
£m January February March Budget year Historic year Outcome 1 Outcome 2
budget actual budget actual budget actual
Sales 6.4 6.8 6.6 6.4 6.8 7.1 81.0 78.4 78.0 86.5
Davis Service Group | Planning a budget 35
www.dsgplc.co.uk
£m JUNE JULY AUGUST
Budget Actual Variance Budget Actual Variance Budget Actual Variance
% A/F % A/F % A/F
Sales revenue 12.1 13.0 7.4 F 12.9 9.8 24.0 A 11.1 7.6 31.5 A
Operating costs 6.5 6.8 4.6 A 7.0 6.1 12.9 F 5.9 5.4 8.5 F
Gross profit 5.6 6.2 10.7 F 5.9 3.7 37.3 A 5.2 2.2 57.7 A
Budgets use resources so they are closely linked with key At Davis, 750 people are involved with budgeting. The time
performance indicators (KPIs). KPIs help to evaluate the overall these workers give to the budgeting process means they are
performance of the business. Davis Service Group’s KPIs include not available to carry out other responsibilities.
measurement of: • Errors and inaccuracies will always remain since it is impossible to
• organic revenue growth (i.e. sales growth excluding acquisitions) predict the future. Major external events such as rising energy
• operational throughput (e.g. tonnage of linen processed) prices or the global recession may distort the whole process.
• management retention rate (i.e. keeping experienced staff in • Budgets involve and affect people, they may cause conflict. There
the company) may be difficult choices over where limited funds are spent. Some
• health and safety records (e.g. major incident injury rate) departments with tight budgets could feel constrained. This
• environmental performance (e.g. water and energy consumption). carries the risk of frustrating initiative and enterprise.
As with the budget, action is prompted through variance from the Conclusion
KPI. For example, if a plant's environmental performance has
worsened, does it require additional investment in equipment? If Davis operates across 15 countries and has sales turnover of over
health and safety incidents have increased, do employees need £1 billion. To meet its needs, the company has developed a
more training? robust and detailed budgeting and planning process involving its
managers. Budgeting provides an essential forecasting, control
The benefits and drawbacks of budgeting and feedback system on which effective management depends.
This process translates competitive strategy into reality.
There are many advantages to using budgets. They:
• provide a method of allocating and using resources within the Evidence of the power of managed budgeting was seen as
organisation recession gripped the European economies in 2008. Davis was
• help to monitor and control operations able to assess effects and build new and realistic assumptions
• promote forward thinking into its budgets for the remainder of 2008 and 2009. These have
• show employees an overall picture of the direction of the proved resilient in practice. As an exceptionally challenging year
organisation which can motivate staff ended, the company was on track to fulfil budget expectations.
• help to co-ordinate different departments and align them By identifying and managing risks, Davis Service Group has been
towards shared objectives able to return profits, dividends and cash flow for shareholders in
• provide a framework for delegation. a difficult economic climate. This also allows the business to
invest for growth in 2010 and beyond.
Most importantly, budgets are an early warning system. They
highlight where investigation and appropriate corrective action is
1. Outline the purpose of budgets within organisations.
necessary. For example, Davis recognised as early as 2008 that
2. Explain the relationship between an objectives budget
QUESTIONS
the recession was affecting its UK linen operation. It took action to
and operational budgets.
ensure the impact was managed for the second half of 2008.
3. Analyse the factors that managers might have to take
It then assessed the implications of recession right across the
business – management was put on ‘full alert’. into consideration when preparing budgets.
4. Evaluate how budgeting can contribute to a business
These benefits do not come problem-free: achieving its aims.
• Staff time devoted to budgets carries a real opportunity cost.
GLOSSARY
Key performance indicators: Acquisitions: Where one business Delegation: Authorising someone to do Opportunity cost: The cost of the next
Financial and non-financial measures to takes over another e.g. by purchasing a something in your place. best alternative use that a resource or
monitor performance across a range of majority of shares. capital could be used for.
activities within a function, department
or role.
Davis Service Group | Planning a budget
You might also like
- ACCG200 SolutionCh 09 PDFDocument26 pagesACCG200 SolutionCh 09 PDFlethiphuongdanNo ratings yet
- Perfomance BudjectingDocument72 pagesPerfomance BudjectingAnithaNo ratings yet
- Bic Product Life CycleDocument4 pagesBic Product Life Cycleapi-505775092No ratings yet
- The Outsiders Study GuideDocument24 pagesThe Outsiders Study GuideSal TellezNo ratings yet
- Zaha Hadid Architecture PhilosophiesDocument4 pagesZaha Hadid Architecture PhilosophiesLetu OlanaNo ratings yet
- The Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageDocument5 pagesThe Internal Environment: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive AdvantageHenny ZahranyNo ratings yet
- Adv Budget CaseDocument4 pagesAdv Budget CaseZubala Marium HelalNo ratings yet
- 2.2a Finance - BudgetsDocument22 pages2.2a Finance - BudgetsAni TNo ratings yet
- PDF Budget Control PDFDocument18 pagesPDF Budget Control PDFjoana seixasNo ratings yet
- Budgeting and Budgetary ControlDocument18 pagesBudgeting and Budgetary ControlchandasumaNo ratings yet
- Points To Be Covered in This UnitDocument19 pagesPoints To Be Covered in This UnitVirat JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Budget Deviation AnalysisDocument27 pagesBudget Deviation AnalysisArsenio RojoNo ratings yet
- 5 BudgetingDocument9 pages5 BudgetingXyril MañagoNo ratings yet
- Prof Sunny Sabharwal JgbsDocument28 pagesProf Sunny Sabharwal JgbsVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Iafm Ch11 Fall 2023 NuDocument94 pagesIafm Ch11 Fall 2023 Nugigih satyaNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Budget PreparationDocument26 pagesEthical Issues in Budget PreparationJoseph SimonNo ratings yet
- Kraft BudgetsDocument2 pagesKraft Budgetsapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Simon Chap. 5Document33 pagesSimon Chap. 5harum77No ratings yet
- Budget Classification: Submitted by - AsifDocument14 pagesBudget Classification: Submitted by - AsifAsiFAliNo ratings yet
- Budget PPTDocument15 pagesBudget PPTbushraanwarNo ratings yet
- AE 24 Module 1 BudgetingDocument14 pagesAE 24 Module 1 BudgetingShamae Duma-anNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument18 pagesBudgetOdeneho Kyei Baffour100% (1)
- Lecture 11 BIS ManagerialDocument25 pagesLecture 11 BIS Managerialnada ahmedNo ratings yet
- MA - Budgets and VADocument27 pagesMA - Budgets and VAAyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1.3Document14 pagesLecture 1.3Ratan KalraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Budgeting Budgetary Control - JJDocument26 pagesLecture 9 - Budgeting Budgetary Control - JJTariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Davis Service Group VINEET KUMARDocument19 pagesDavis Service Group VINEET KUMARVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument17 pagesBudgetingdc1901078No ratings yet
- Unit 2: Business BudgetsDocument28 pagesUnit 2: Business BudgetsSHARATH JNo ratings yet
- Financial and Managerial Individual Course WorkDocument12 pagesFinancial and Managerial Individual Course WorkrachkNo ratings yet
- Budget and Budgetory Control System in HeritageDocument5 pagesBudget and Budgetory Control System in HeritagevarunNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument24 pagesBudgetAbhishek ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Business Plans For Agricultural Producers: Risk ManagementDocument5 pagesBusiness Plans For Agricultural Producers: Risk ManagementAdewole OlagokeNo ratings yet
- 1business Plans For Agricultural ProducersDocument5 pages1business Plans For Agricultural ProducersTeshome H/GebrealNo ratings yet
- Budgetary ControlDocument12 pagesBudgetary ControlVipra Bhatia100% (1)
- New IB BM Book (Dragged) 11Document1 pageNew IB BM Book (Dragged) 11celinejaaloukNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii. Master Budget: An Overall Plan: Page 1 of 19Document19 pagesChapter Iii. Master Budget: An Overall Plan: Page 1 of 19Nahum DaichaNo ratings yet
- CH - 2 For TeacherDocument11 pagesCH - 2 For TeacherEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Budgeting, EnterpreneurshipDocument4 pagesBudgeting, EnterpreneurshipVALENTINE BETTNo ratings yet
- (Project Management Institute) Project Management (B-Ok - Xyz)Document19 pages(Project Management Institute) Project Management (B-Ok - Xyz)Hayelom Tadesse GebreNo ratings yet
- Functional and Activity Based BudgetingDocument5 pagesFunctional and Activity Based BudgetingBrithney ButalidNo ratings yet
- BUDGETINGDocument17 pagesBUDGETINGstannis69420No ratings yet
- Budget Management ThesisDocument5 pagesBudget Management Thesispatricemillertulsa100% (2)
- Budgeting LectureDocument59 pagesBudgeting LectureCristineNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting MasDocument6 pagesCapital Budgeting MasHainiel ReforzadoNo ratings yet
- Unit 14Document25 pagesUnit 14divya kalyaniNo ratings yet
- BudgetDocument6 pagesBudgetKedar SonawaneNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Report BudgetDocument42 pagesManagement Accounting Report BudgetBilly Maravillas Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Types of BudgetsDocument13 pagesTypes of Budgetsucantcmy619No ratings yet
- Budgeting CycleDocument4 pagesBudgeting CycleAhsaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Budget Instrument Management ControlDocument20 pagesBudget Instrument Management ControlabekaforumNo ratings yet
- Ma Ch09 SolutionsDocument27 pagesMa Ch09 SolutionsMin SanNo ratings yet
- Presented by Tonmoy Haldar MBA-2 Year MagnetsDocument22 pagesPresented by Tonmoy Haldar MBA-2 Year MagnetsTonmoy Smriti HaldarNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting IIDocument37 pagesCapital Budgeting IISelahi YılmazNo ratings yet
- MS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingDocument7 pagesMS 3406 Short-Term Budgeting Additional Financing Needed and ForecastingMonica GarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlDocument83 pagesChapter - Three Budgets and Budgetary ControlHace AdisNo ratings yet
- Methodologies: BudgetDocument16 pagesMethodologies: BudgetajithsubramanianNo ratings yet
- Cost ManagmnetDocument5 pagesCost ManagmnetJOYDIP PRODHANNo ratings yet
- The Budgeting Survival GuideDocument11 pagesThe Budgeting Survival GuideSara SyedNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Lecture PresentationsDocument25 pagesBudgeting Lecture PresentationsRight Karl-Maccoy HattohNo ratings yet
- Budgeting GuideDocument5 pagesBudgeting GuideJason KWAGHENo ratings yet
- Master Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1From EverandMaster Budgeting and Forecasting for Hospitality Industry-Teaser: Financial Expertise series for hospitality, #1No ratings yet
- 10 Financial Strategies for Commercial Construction Companies to Maximize Cash Flow and ProfitsFrom Everand10 Financial Strategies for Commercial Construction Companies to Maximize Cash Flow and ProfitsNo ratings yet
- Asw Crisis ManualDocument37 pagesAsw Crisis Manualapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Developing An Effective Organisational StructureDocument6 pagesDeveloping An Effective Organisational Structureapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Disney Emergency PlanDocument32 pagesDisney Emergency Planapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Primark EthicsDocument4 pagesPrimark Ethicsapi-505775092No ratings yet
- SL Bus Man Exemplar 3 Marks and Comments 1Document1 pageSL Bus Man Exemplar 3 Marks and Comments 1api-505775092No ratings yet
- Cadbury EthicsDocument2 pagesCadbury Ethicsapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Caso CimaDocument4 pagesCaso CimastfypradoNo ratings yet
- Amway CSR 2Document4 pagesAmway CSR 2api-505775092100% (1)
- Leyland ContinuousDocument4 pagesLeyland Continuousapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Amway CSRDocument4 pagesAmway CSRapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Acca EthicsDocument2 pagesAcca Ethicsapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Bsi QualityDocument4 pagesBsi Qualityapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Portakabin LeanDocument4 pagesPortakabin Leanapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Corus ContinuousDocument4 pagesCorus Continuousapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Nivia SegementationDocument4 pagesNivia Segementationapi-505775092No ratings yet
- Sygenta R D 2Document4 pagesSygenta R D 2api-505775092No ratings yet
- Gillette R DDocument4 pagesGillette R Dapi-505775092No ratings yet
- How Innovation Drives Research and Development: ARM STUDY 29/8/12 11:06 Page 2Document4 pagesHow Innovation Drives Research and Development: ARM STUDY 29/8/12 11:06 Page 2api-505775092No ratings yet
- Kelloggs Edition 13 Full PDFDocument4 pagesKelloggs Edition 13 Full PDFMegz OkadaNo ratings yet
- Daily Time Record Daily Time Record: (Name)Document3 pagesDaily Time Record Daily Time Record: (Name)Jess'ang May Guillermo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Case Law AnalysisDocument8 pagesCase Law Analysisapi-309579746No ratings yet
- Ahsme 1995 PDFDocument7 pagesAhsme 1995 PDFQFDqNo ratings yet
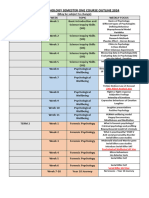
- 2024 Semester Planner - Year 10 PsychologyDocument1 page2024 Semester Planner - Year 10 Psychologyapi-642709499No ratings yet
- CH4 Recommended Problems PDFDocument3 pagesCH4 Recommended Problems PDFnomio12No ratings yet
- Acebedo - Optical - Co. - Inc. - v. - Court - of - AppealsDocument31 pagesAcebedo - Optical - Co. - Inc. - v. - Court - of - AppealsAtheena Marie PalomariaNo ratings yet
- 03 - 1 - Frameworks DrillsDocument12 pages03 - 1 - Frameworks DrillsThanh Phu TranNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Documentsnip3r45No ratings yet
- A To Z Orthodontics Vol 8 CephalometryDocument17 pagesA To Z Orthodontics Vol 8 CephalometryYury Tenorio Cahuana50% (2)
- Competitive Intelligence PDFDocument4 pagesCompetitive Intelligence PDFefsunfreiNo ratings yet
- ch08 Solution Manual Managerial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making PDFDocument54 pagesch08 Solution Manual Managerial Accounting Tools For Business Decision Making PDFMunna Bhattacharjee100% (1)
- A Comparative Approach To Email Classification Using Naive Bayes Classifier and Hidden Markov ModelDocument6 pagesA Comparative Approach To Email Classification Using Naive Bayes Classifier and Hidden Markov ModeleswarlalmechNo ratings yet
- Fere Proposal 1Document30 pagesFere Proposal 1molla fentaye100% (1)
- Grammar Worksheet. VERB TO BE (Simple Past) PDFDocument2 pagesGrammar Worksheet. VERB TO BE (Simple Past) PDFRafael Barcellos0% (1)
- 9th CBSE Maths Test Ch-1Document1 page9th CBSE Maths Test Ch-1Madhav KotechaNo ratings yet
- 1 LiverDocument10 pages1 LiverAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Ischemic Stroke ManagementDocument8 pagesIschemic Stroke ManagementBa LitNo ratings yet
- English 4 - ST3 - Q1Document2 pagesEnglish 4 - ST3 - Q1manuel100% (1)
- 16 31 May21 CVEDocument268 pages16 31 May21 CVEAkshat SinghNo ratings yet
- Business ProposalDocument10 pagesBusiness ProposalThais SallesNo ratings yet
- 50N - Elias's Story - Noli Me Tangere PDFDocument9 pages50N - Elias's Story - Noli Me Tangere PDFvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory AliensDocument9 pagesGame Theory AliensfnirneNo ratings yet
- Genome Browser ExerciseDocument5 pagesGenome Browser ExerciseyukiNo ratings yet
- Espano v. CA, 288 Scra 588Document9 pagesEspano v. CA, 288 Scra 588Christia Sandee SuanNo ratings yet
- Www-Gaia-Com-Article-Am-I-A-Starseed-Types-Characteristics Gaia Starseed StarDocument15 pagesWww-Gaia-Com-Article-Am-I-A-Starseed-Types-Characteristics Gaia Starseed StarJohnNo ratings yet
- ARK-1 / AR-1: Auto Ref / Keratometer / Auto RefractometerDocument6 pagesARK-1 / AR-1: Auto Ref / Keratometer / Auto RefractometerbeniNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Supply Management in Water Flow NetwoDocument15 pagesAn Efficient Supply Management in Water Flow NetwoSARAL JNo ratings yet