Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GE Case Study
Uploaded by
KAVIN KOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GE Case Study
Uploaded by
KAVIN KCopyright:
Available Formats
GE’s Rotary Compressor Case Solution:
Question 1: What factors in the product development process caused this disaster?
Answer:
Development Phase Factors which caused disaster
Customer Usage difference: GE failed to understand the difference in the
requirements requirements of rotary compressor for air conditioner and refrigerator
Misjudging needs: GE took decision completely on their own without
involving customers, hence misjudged the needs of consumers
Design Ignorance: GE management ignored the fact that rotary motor will run
hotter immediately and hence not suitable for refrigerator
Noise: The new design will be making much noise, this fact was not
considered
No learning from mistakes: They overlooked the recent failure
Implementation Avoided Outsourcing: They didn’t evaluated option of outsourcing
against the option of in house manufacturing
Over Confidence: They avoided the offer of consulting from ex
supervisor
Testing Lack of established testing process: There was no established process
to test the working of the designed rotary compressors
Lack of supervision: Supervisor in place avoided the finding from the
testing process which were showing the fault in rotary compressor
Question 2: Which individuals were responsible for this disaster and why?
Answer:
Individuals who Reason
were responsible
Manufacturing Nothing had been mass-produced with such precision of a tolerance of only 50
Engineers millionths of an inch before, but manufacturing engineers felt sure they could do
it. Which they failed to achieve.
Design Engineers Powdered metal had been tried a decade earlier on air conditioners but did not
work. The design engineers who were new to designing compressors did not
consider the earlier failure important.
Management A consultant suggested that GE should consider a joint venture with a Japanese
company that had a rotary refrigerator compressor already on the market. This
idea was rejected by management. In addition to this the original designer of the
air conditioner rotary compressor, who had left GE, offered his services as a
consultant. GE management also declined this offer.
Supervisors The technician who disassembled and inspected the parts thought they did not
look right. The technician’s supervisors discounted these findings and did not
relay them to upper levels of management.
Testing Staff About 600 compressors were tested in 1983 without a single failure. This
statistics suggests that there must have been a conceptual fault in the testing
precedure
Question 3: How might this disaster have been prevented? What lessons do you think GE learned
from the future?
Answer:
Prevention:
Cost Benefit Analysis:
They should have done cost benefit analysis of both the options available to them to get a deeper
perspective of which one to implement.
Quality System:
There should be quality system in place to check quality of product being designed at every phase i.e.
from product requirements, design to implementation
Design for test market (Product Screening):
They should have designed only few products first to test them against the customer requirements,
working and reliability
Outsourcing:
This was the best option available to them. They were an established player in this product line. They
would have easily prevented this by outsourcing manufacturing of rotary compressors
Lessons from failure:
1. Continuously improve the manufacturing operations according to the customer requirements and
changes in technology and other external environment to compete with competitors
2. Role of management in particular operation’s management is centre to the product success and a
small overlook can cause a great damage
3. Evaluate all the available options thoroughly before implementing
4. Evaluate selected option at every stage of product manufacturing and not in the end only
5. Notice all the small suggestions from the people involved in the operations of product development
Question 4: On what basis was GE attempting to achieve a competitive advantage? How did it fail?
Answer:
GE tried to achieve competitive advantage through product differentiation by improving current
process of manufacturing. They analyzed that their product is not matching on many parameters
provided by their competitors. E.g. making refrigerator compressors required 65 minutes of labor in
comparison to 25 minutes for competitors in Japan and Italy. Moreover, GE’s labor costs were higher.
They planned following improvements in current operations:
to build a new rotary compressor in-house
A rotary compressor weighs less,
One which has one-third fewer parts,
The one which is more energy-efficient than the current reciprocating compressors.
The rotary compressor which also takes up less space, thus providing more room inside the
refrigerator and better meeting customer requirements.
Reason for failure:
They did not evaluate the option of outsourcing against the option of in house manufacturing
correctly.
While considering the option of making is weight less they overlooked the noise made by
current design and the heat generated by current design
They did not learn from their previous mistake and continued with the suggested process and
design
Management overlooked the doubt by consultant regarding the testing results showing zero
failure rates, management also didn’t involve the person who designed rotary processor and
showed overconfidence on its technical staff
You might also like
- MBA FT March/April 2022 Legal Environment of Business ExamDocument2 pagesMBA FT March/April 2022 Legal Environment of Business ExamIndian Lizard King100% (1)
- Western Coalfields - Story of A Buying ProcessDocument6 pagesWestern Coalfields - Story of A Buying ProcessVarsha MoharanaNo ratings yet
- FactoringDocument15 pagesFactoringddakcyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electronic Commerce: What Is E-Commerce Explain The Types of E-Commerce?Document53 pagesUnit 1 Electronic Commerce: What Is E-Commerce Explain The Types of E-Commerce?Mustafa TatiwalaNo ratings yet
- Rameet Kaur, CSRDocument11 pagesRameet Kaur, CSRRameet KaurNo ratings yet
- Financial Manipulation at Pifco-ZenDocument9 pagesFinancial Manipulation at Pifco-ZenAashish KhajuriaNo ratings yet
- Marketing in Indian EconomyDocument15 pagesMarketing in Indian Economyshivakumar NNo ratings yet
- EXIT SEMINAR (Saba Sayyad)Document16 pagesEXIT SEMINAR (Saba Sayyad)saba sayyadNo ratings yet
- Case Study MobDocument1 pageCase Study MobRamamohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument14 pagesBankingAkshay SatoskarNo ratings yet
- Home Solution CaseDocument3 pagesHome Solution CaseshivamNo ratings yet
- A Case Study - JK CementDocument6 pagesA Case Study - JK CementSuzZette TianzonNo ratings yet
- Planning, Design, and Implementation of ERP SystemsDocument39 pagesPlanning, Design, and Implementation of ERP SystemsKLASDJAKLNo ratings yet
- Wipro-12 07 2012Document17 pagesWipro-12 07 2012Himanshu JhaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyRaam Tha BossNo ratings yet
- PRICOL COMPANY OVERVIEW AND STRUGGLEDocument3 pagesPRICOL COMPANY OVERVIEW AND STRUGGLEASK ME ANYTHING SMARTPHONENo ratings yet
- Production and Total Quality ManagementDocument8 pagesProduction and Total Quality ManagementFalguni MathewsNo ratings yet
- Winding up company processDocument9 pagesWinding up company processSarthak SinghNo ratings yet
- Becg Unit-4.Document12 pagesBecg Unit-4.Bhaskaran Balamurali100% (2)
- C3Document33 pagesC3Jatin Modi0% (1)
- Presentation GEDocument22 pagesPresentation GESahil KhoslaNo ratings yet
- The Satyam Computers ScamDocument11 pagesThe Satyam Computers ScamTushar Sahu100% (1)
- Business Skills in E CommerceDocument78 pagesBusiness Skills in E Commerceshaid AhamedNo ratings yet
- Becg Corporate Governance:: Notes Complied by Dr. Dhimen Jani Mba, CBS, Pgdibo, PHD MBA Sem. 1Document32 pagesBecg Corporate Governance:: Notes Complied by Dr. Dhimen Jani Mba, CBS, Pgdibo, PHD MBA Sem. 112Twinkal ModiNo ratings yet
- Cashflow and Fund FlowDocument17 pagesCashflow and Fund FlowHarking Castro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument7 pagesCase StudyDrRitesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument8 pagesCase StudyRohit Rijhwani100% (1)
- A Case Study On Satyam OdysseyDocument5 pagesA Case Study On Satyam OdysseyBushra ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Project Stakeholder ManagementDocument26 pagesProject Stakeholder ManagementTâm ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Causes and Remedies of Industrial SicknessDocument4 pagesCauses and Remedies of Industrial SicknessGurmeet AthwalNo ratings yet
- Satyam Balance Sheet AnalysisDocument3 pagesSatyam Balance Sheet AnalysisHarish100% (12)
- Auditing Liabilities AssertionsDocument7 pagesAuditing Liabilities AssertionsSanjeevParajuliNo ratings yet
- EGMC002 PDF Final PDFDocument9 pagesEGMC002 PDF Final PDFNageshwar SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Problem-Vajra ToolsDocument2 pagesCase Problem-Vajra ToolsSayali Ugale100% (1)
- Major Arguments For and Against Social ResponsibilityDocument10 pagesMajor Arguments For and Against Social ResponsibilityMargielyn UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Project Associate Case StudyDocument5 pagesProject Associate Case StudyBharani KrishnaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS LAW and EthicsDocument2 pagesBUSINESS LAW and EthicsSowjanya TalapakaNo ratings yet
- Government College For Women, Rohtak: "Customer Relationship Managment" AT Kansai Nerolac Paints LTDDocument69 pagesGovernment College For Women, Rohtak: "Customer Relationship Managment" AT Kansai Nerolac Paints LTDMeenu RaniNo ratings yet
- Professional Mis Conduct in AuditingDocument6 pagesProfessional Mis Conduct in Auditingsameerkhan855No ratings yet
- Harshad Mehta and Ketan Parikh ScamDocument6 pagesHarshad Mehta and Ketan Parikh ScamAnkur MadaanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae of Dr. YunusDocument26 pagesCurriculum Vitae of Dr. YunusETTEHAD HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- M & A of Kingfisher and DeccanDocument18 pagesM & A of Kingfisher and DeccanPunit KariaNo ratings yet
- Presentation - On - Companies - Act2013 - K C MehtaDocument116 pagesPresentation - On - Companies - Act2013 - K C MehtasarashviNo ratings yet
- ONICRADocument5 pagesONICRAYatin DhallNo ratings yet
- D.A.Gadgil v. SEBIDocument3 pagesD.A.Gadgil v. SEBIPavithra MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Applied Business Analytics: Starts JUNE 30, 2021 3 Months - OnlineDocument11 pagesApplied Business Analytics: Starts JUNE 30, 2021 3 Months - OnlinekrishnaNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument1 pageProduction and Operations ManagementYash GargNo ratings yet
- (SCD) Chap6-Supply Contracts (Final)Document43 pages(SCD) Chap6-Supply Contracts (Final)Ân LêNo ratings yet
- Becg Unit-3Document13 pagesBecg Unit-3Bhaskaran BalamuraliNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument17 pagesCase Studysubakarthi0% (1)
- Dealers Level of Satisfaction OCL India Cement Internship Project Report 2012-13Document78 pagesDealers Level of Satisfaction OCL India Cement Internship Project Report 2012-13souravkiller4u67% (3)
- Annexure III Curriculum & Detailed Syllabus - Electric Motor Rewinding - 0Document9 pagesAnnexure III Curriculum & Detailed Syllabus - Electric Motor Rewinding - 0Reynaldo PesqueraNo ratings yet
- Choosing Cloud Hosting for Growing Healthcare OrganizationDocument20 pagesChoosing Cloud Hosting for Growing Healthcare OrganizationRomali DasNo ratings yet
- 42407664Document13 pages42407664Ashish KapareNo ratings yet
- Channel FinanceDocument6 pagesChannel FinancePrashant BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Capital Markets in IndiaDocument7 pagesEvolution of Capital Markets in Indiaanon_473668362100% (1)
- Formation of A Public CompanyDocument48 pagesFormation of A Public CompanymmuneebsdaNo ratings yet
- GE Case StudyDocument3 pagesGE Case StudyAnand Manik Ingle100% (1)
- GE's Thermocouple Division Implements JITDocument7 pagesGE's Thermocouple Division Implements JITRajarshi BiswasNo ratings yet
- Mindanao State UniversityDocument7 pagesMindanao State UniversityNap MissionnaireNo ratings yet
- Meeting 7: Team Presentation I: BNP Paribas Fortis: The James' Banking ExperienceDocument3 pagesMeeting 7: Team Presentation I: BNP Paribas Fortis: The James' Banking ExperienceKAVIN K100% (1)
- Simulation Game 19 Feb - 2021Document2 pagesSimulation Game 19 Feb - 2021KAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Undesirable Effects (Ude'S) Cosmetics Company ProblemDocument2 pagesUndesirable Effects (Ude'S) Cosmetics Company ProblemKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- What Is StrategyDocument1 pageWhat Is StrategyKAVIN KNo ratings yet
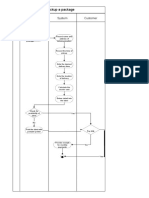
- On The Spot Courier - Pickup A Package: Employee System CustomerDocument1 pageOn The Spot Courier - Pickup A Package: Employee System CustomerKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Building Your Company's VissionDocument2 pagesBuilding Your Company's VissionAkshaya LakshminarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Core Competency Can Be Defined As The Defining Capability That Gives A Competitive AdvantageDocument1 pageCore Competency Can Be Defined As The Defining Capability That Gives A Competitive AdvantageKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Biopportunity Corporation Secures Promising Biofuel TechnologiesDocument2 pagesBiopportunity Corporation Secures Promising Biofuel TechnologiesKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Sales Forecasting and Production PlanningDocument16 pagesSales Forecasting and Production PlanningKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyDocument5 pagesFive Competitive Forces That Shape StrategyKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Scanned Docs CollectionDocument10 pagesCamScanner Scanned Docs CollectionKAVIN K100% (1)
- Explanation of The ProblemDocument48 pagesExplanation of The ProblemKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- GATI OP Case 2 Individual Assignment PDFDocument12 pagesGATI OP Case 2 Individual Assignment PDFKAVIN K100% (7)
- Strategy - An Execution DecisionDocument1 pageStrategy - An Execution DecisionKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- A Case Analysis of Rotary CompressorDocument21 pagesA Case Analysis of Rotary CompressorKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis - Arjun V - 19016Document4 pagesCase Analysis - Arjun V - 19016KAVIN KNo ratings yet
- GATI CASE AnswersDocument4 pagesGATI CASE AnswersKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- MPC QuestionsDocument6 pagesMPC QuestionsKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- A Case Analysis of Rotary CompressorDocument21 pagesA Case Analysis of Rotary CompressorKAVIN KNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma White Belt Certification Training Manual - CSSC 2018-06Document29 pagesSix Sigma White Belt Certification Training Manual - CSSC 2018-06skiprydooNo ratings yet
- Sabp A 033 PDFDocument52 pagesSabp A 033 PDFWalid Megahed100% (2)
- 3 - Engineering Critical Analyses To BS 7910 - in UK Guide On Methods For Assessing The Acceptability of Flaws in Metallic StructurDocument11 pages3 - Engineering Critical Analyses To BS 7910 - in UK Guide On Methods For Assessing The Acceptability of Flaws in Metallic StructurRenato Vargas100% (1)
- Netplan Product Overview: Network Planning and DesignDocument23 pagesNetplan Product Overview: Network Planning and DesignlikameleNo ratings yet
- KSB Etanorm SYA PumpDocument24 pagesKSB Etanorm SYA Pumpsuperdave643100% (2)
- Check List - Product Realisation ProcessDocument4 pagesCheck List - Product Realisation ProcessDisha ShahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument269 pagesUntitledJuan TNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bidirectional Visitor Counter With Automatic Light Control ProjectDocument45 pagesProject Report On Bidirectional Visitor Counter With Automatic Light Control Projectrgf5149No ratings yet
- Contractor Safety Management SystemDocument49 pagesContractor Safety Management Systemchriscivil12No ratings yet
- Designed For Utmost Reliability MM1201Document4 pagesDesigned For Utmost Reliability MM1201smendozaNo ratings yet
- Planning and Commissioning Waste Water Treatment PlantsDocument167 pagesPlanning and Commissioning Waste Water Treatment PlantsChanel67% (3)
- English Basic Training Material Isfs 202010Document133 pagesEnglish Basic Training Material Isfs 202010jamesdouglas20No ratings yet
- Intelligence ProductionDocument30 pagesIntelligence ProductionMitziVasquezNo ratings yet
- Astm D5457Document9 pagesAstm D5457simonNo ratings yet
- Tuesday 11.55 Anthony FaucogneyDocument28 pagesTuesday 11.55 Anthony FaucogneyAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- EPRI - TR - 1009659 - Qualification - Dedication of DigitalDocument98 pagesEPRI - TR - 1009659 - Qualification - Dedication of DigitaldiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practices For Building Quality SoftwareDocument127 pagesEngineering Practices For Building Quality Softwaresurathu naveenNo ratings yet
- The Operation Management Model of Aircraft Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) BusinessDocument8 pagesThe Operation Management Model of Aircraft Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul (MRO) BusinessAbhishek Man ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Development of A Reliability Based Design Framework For Transmission Line Structure FoundationsDocument9 pagesDevelopment of A Reliability Based Design Framework For Transmission Line Structure FoundationsNitesh JainNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Reliability EngineeringDocument15 pagesMaintenance and Reliability EngineeringDivyank AryaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 ReliabilityDocument10 pagesLesson 12 ReliabilityLovesel MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- Power System Architecture NextwindDocument4 pagesPower System Architecture NextwindRain ByarsNo ratings yet
- A Human Error Analysis of Commercial Aviation Accidents Using The Human Factors Analysis and Classification System (HFACS) PDFDocument20 pagesA Human Error Analysis of Commercial Aviation Accidents Using The Human Factors Analysis and Classification System (HFACS) PDFMateus Berbert100% (1)
- Umar Yaqoob ResumeDocument2 pagesUmar Yaqoob ResumeUmar YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Failure Code Hierarchy Is It The Best Design?: John ReeveDocument3 pagesFailure Code Hierarchy Is It The Best Design?: John ReeveElvis DiazNo ratings yet
- Implementing Enterprise Asset Management For DummiesDocument76 pagesImplementing Enterprise Asset Management For DummiesTersoo Apeverga100% (2)
- Review Internal I OME753Document22 pagesReview Internal I OME753priya SNo ratings yet
- 02 2 Software EngineeringDocument23 pages02 2 Software EngineeringOm PhuseNo ratings yet
- Accountancy Bbs 1st Year - Oweisme PDFDocument21 pagesAccountancy Bbs 1st Year - Oweisme PDFPratima Upreti100% (1)
- Developing A Scalable Payment Gateway Using ScalaDocument4 pagesDeveloping A Scalable Payment Gateway Using ScalaTarikaNo ratings yet
- Igbt Note eDocument77 pagesIgbt Note ettarwinNo ratings yet
- Ca$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneFrom EverandCa$hvertising: How to Use More than 100 Secrets of Ad-Agency Psychology to Make Big Money Selling Anything to AnyoneRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (114)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffFrom Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (16)
- $100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoFrom Everand$100M Offers: How to Make Offers So Good People Feel Stupid Saying NoRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- Pre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeFrom EverandPre-Suasion: Channeling Attention for ChangeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (277)
- The Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindFrom EverandThe Catalyst: How to Change Anyone's MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (273)
- Dealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeFrom EverandDealers of Lightning: Xerox PARC and the Dawn of the Computer AgeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (88)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessFrom EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNo ratings yet
- Summary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Traction: Get a Grip on Your Business: by Gino Wickman: Key Takeaways, Summary, and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (10)
- Yes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveFrom EverandYes!: 50 Scientifically Proven Ways to Be PersuasiveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (153)
- Fascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistFrom EverandFascinate: How to Make Your Brand Impossible to ResistRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingFrom EverandHow to Get a Meeting with Anyone: The Untapped Selling Power of Contact MarketingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (28)
- The Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Myth of the Rational Market: A History of Risk, Reward, and Delusion on Wall StreetNo ratings yet
- Scientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"From EverandScientific Advertising: "Master of Effective Advertising"Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (163)
- Obviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItFrom EverandObviously Awesome: How to Nail Product Positioning so Customers Get It, Buy It, Love ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (150)
- How to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorFrom EverandHow to Read People: The Complete Psychology Guide to Analyzing People, Reading Body Language, and Persuading, Manipulating and Understanding How to Influence Human BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (33)
- Summary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: Range: Why Generalists Triumph in a Specialized World by David Epstein: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Lean Product Playbook: How to Innovate with Minimum Viable Products and Rapid Customer FeedbackFrom EverandThe Lean Product Playbook: How to Innovate with Minimum Viable Products and Rapid Customer FeedbackRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (81)
- Launch: An Internet Millionaire's Secret Formula to Sell Almost Anything Online, Build a Business You Love, and Live the Life of Your DreamsFrom EverandLaunch: An Internet Millionaire's Secret Formula to Sell Almost Anything Online, Build a Business You Love, and Live the Life of Your DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (123)
- The Power of Why: Breaking Out In a Competitive MarketplaceFrom EverandThe Power of Why: Breaking Out In a Competitive MarketplaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- How To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!From EverandHow To Win Customers And Keep Them For Life: An Action-Ready Blueprint for Achieving the Winner's Edge!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Brand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleFrom EverandBrand Identity Breakthrough: How to Craft Your Company's Unique Story to Make Your Products IrresistibleRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Jab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldFrom EverandJab, Jab, Jab, Right Hook: How to Tell Your Story in a Noisy Social WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Marketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessFrom EverandMarketing Made Simple: A Step-by-Step StoryBrand Guide for Any BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (203)
- Blue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantFrom EverandBlue Ocean Strategy, Expanded Edition: How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition IrrelevantRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (387)
- Invisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorFrom EverandInvisible Influence: The Hidden Forces that Shape BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (131)
- Building a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will ListenFrom EverandBuilding a StoryBrand: Clarify Your Message So Customers Will ListenRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1248)
- Expert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceFrom EverandExpert Secrets: The Underground Playbook for Creating a Mass Movement of People Who Will Pay for Your AdviceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (364)