Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise Chap 4
Uploaded by
Nur MizaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise Chap 4
Uploaded by
Nur MizaCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
INDEPENDENT VARIABLE
The cause is an independent variable. In your analysis, its value is independent of other variables.
2. DEPENDENT VARIABLE
The effect is the dependent variable. Its value depends on changes to the independent variable.
EXAMPLE
RESEARCH QUESTION INDEPENDENT VARIABLE(S) DEPENDENT VARIABLE(S)
How does phone use before The amount of phone use Number of hours of sleep
bedtime affect sleep? before bed Quality of sleep
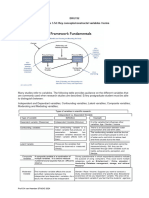
3. MODERATING VARIABLE
is a qualitative (e.g. sex, race, class) or quantitative (e.g. level of reward) variable that affects the
direction and/or strength of the relation between an independent variable and a dependent
variable. Moderating variable has a strong contingent effect on the independent-dependent
variable relationship whereby its presence modifies the original relationship between the
independent-dependent variables. In a schematic diagram, the relationship between these
variables can be represented as follows.
Example
A mediator variable may be something as simple as a psychological response to given events. For example, suppose buying
pizza for a work party leads to positive morale and to the work being done in half the time.
Pizza is the independent variable,
Work speed is the dependent variable,
The mediator, the middle man without which there would be no connection, is positive morale.
4.Intervening Variable (IIV)
Also called the mediator or mediating variable. The presence of this variable strengthens the link
between the independent and dependent variables.
Example
there is an association between being poor and having a shorter life span. Just because someone is poor doesn’t mean that
will lead to an early death, so other hypothetical variables are used to explain the phenomenon. These intervening variables
could include: lack of access to healthcare or poor nutrition.
You might also like
- The Variables in ResearchDocument4 pagesThe Variables in ResearchBryan Jester100% (1)
- VARIABLES and Its TypesDocument6 pagesVARIABLES and Its TypesGenious GeniousNo ratings yet
- Variables in ResearchDocument30 pagesVariables in Researchzorrotran100% (2)
- Applied Human Behavioural Power and Sexual Dynamics - The Book of Social and Sexual Dominance -From EverandApplied Human Behavioural Power and Sexual Dynamics - The Book of Social and Sexual Dominance -No ratings yet
- Types of VariablesDocument4 pagesTypes of VariablesJeffrey Mendoza TamayoNo ratings yet
- What Are Independent and Dependent VariablesDocument13 pagesWhat Are Independent and Dependent VariablesGlendel CayabyabNo ratings yet
- List of VariablesDocument3 pagesList of VariablesKimonye FrancNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 5-Types of VariablesDocument24 pagesCHAPTER - 5-Types of VariablesAbenet YohannesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3. Kinds of Variables and Their UsesDocument3 pagesLesson 3. Kinds of Variables and Their Usesmipan susuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Framework and VariablesDocument21 pagesTheoretical Framework and VariablesFawad LatifNo ratings yet
- Quizz 2 Business Research MethodsDocument2 pagesQuizz 2 Business Research MethodsZunab AzharNo ratings yet
- Variables and Types of VariablesDocument4 pagesVariables and Types of VariablesRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Task 4 The Research Methodology "Research Variable"Document8 pagesTask 4 The Research Methodology "Research Variable"Lara Amanda DwidjoNo ratings yet
- Types of VariablesDocument2 pagesTypes of VariablesCheindy Mae Santos II100% (1)
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledwajeeha tahirNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Concepts and Variables in ResearchDocument19 pagesDifference Between Concepts and Variables in ResearchHabte DebeleNo ratings yet
- VariableDocument3 pagesVariableJaroushie FlynnNo ratings yet
- The Variables: Dr. Godfrey G. Mendoza MaestroDocument13 pagesThe Variables: Dr. Godfrey G. Mendoza MaestroSoleil MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Independent Vrs Dependent VarriablesDocument1 pageIndependent Vrs Dependent Varriablesapi-241105505No ratings yet
- Research Variable 1.1Document3 pagesResearch Variable 1.1Maria Mia FernandezNo ratings yet
- Research Assignment 1Document5 pagesResearch Assignment 1ifatimanaqvi1472No ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Variables: Muhammad Azeem QureshiDocument49 pagesLecture 9: Variables: Muhammad Azeem QureshiNadirNo ratings yet
- Formulating HypothesisDocument17 pagesFormulating HypothesisNian AbalahonNo ratings yet
- Prelim Reviewer KunnoDocument15 pagesPrelim Reviewer KunnoRyza Mae PringNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Business Statistics VariableDocument24 pagesUnit 1 Business Statistics VariableDeepa SelvamNo ratings yet
- Research Assignment 1Document5 pagesResearch Assignment 1ifatimanaqvi1472No ratings yet
- Assignment No:1: Name: Tayyaba Mehmood REG NO: BAF191013 DATE: 3 April 2021 SUBJECT: Business Research and Report WritingDocument5 pagesAssignment No:1: Name: Tayyaba Mehmood REG NO: BAF191013 DATE: 3 April 2021 SUBJECT: Business Research and Report WritingTayyaba MalikNo ratings yet
- Annexure 3.5bDocument4 pagesAnnexure 3.5bNeels van HeerdenNo ratings yet
- Variables in Quantitative ResearchDocument21 pagesVariables in Quantitative Researchjestoni manipol100% (1)
- Variables WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesVariables WPS OfficeSelala MayoNo ratings yet
- Independent and Dependent Variables TutorialDocument2 pagesIndependent and Dependent Variables TutorialDead ShotNo ratings yet
- 1Document6 pages1Clémentine AresNo ratings yet
- Pr. Assignment AnswersDocument3 pagesPr. Assignment AnswersOuiNo ratings yet
- HyDocument31 pagesHyHiba NaseerNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document8 pagesTopic 2Lugalia KelvinNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 GROUP REPORTDocument49 pagesPractical Research 2 GROUP REPORTAnn AloNo ratings yet
- How Are Variables Used in Psychology Research?: The Dependent and Independent VariablesDocument4 pagesHow Are Variables Used in Psychology Research?: The Dependent and Independent Variablescronos hijautuaNo ratings yet
- Business Research Process (Steps 4-5) Slide 22 OnwardDocument21 pagesBusiness Research Process (Steps 4-5) Slide 22 OnwardmarchkotNo ratings yet
- 3.1 - Experimental MethodsDocument39 pages3.1 - Experimental MethodsKhae PadiernosNo ratings yet
- The Variables, Hypothesis and AssumptionsDocument9 pagesThe Variables, Hypothesis and AssumptionsJude BautistaNo ratings yet
- Week 009 Module The Variables, Hypothesis and AssumptionsDocument9 pagesWeek 009 Module The Variables, Hypothesis and AssumptionsMae ChannNo ratings yet
- Paper QRM Group 4Document7 pagesPaper QRM Group 4ShintalrNo ratings yet
- Variables & Concepts: Moazzam AliDocument13 pagesVariables & Concepts: Moazzam AliMuhammad Furqan Aslam AwanNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Identification Directions: Check All Words in The List That Could Operate As Variables in Any ResearchDocument8 pagesActivity 1 Identification Directions: Check All Words in The List That Could Operate As Variables in Any ResearchAlexis CastilloNo ratings yet
- Variables in ResearchDocument5 pagesVariables in Researchhaidermuneeb0004No ratings yet
- Practical Research II 12 Q1 W3Document7 pagesPractical Research II 12 Q1 W3Kielah RequeNo ratings yet
- Variable and Its Kinds: Grade 12 - Practical Research 2Document5 pagesVariable and Its Kinds: Grade 12 - Practical Research 2Jester Guballa de LeonNo ratings yet
- Practical Research VariablesDocument5 pagesPractical Research VariablesAnthony DeeNo ratings yet
- Variable and Operational DefinitionsDocument12 pagesVariable and Operational DefinitionsJACKSON OSUHNo ratings yet
- Science: BiologyDocument22 pagesScience: BiologyMike RollideNo ratings yet
- The Use of VariablesDocument9 pagesThe Use of VariablesyeahboymanNo ratings yet
- Variables Group 5 BSSW-2BDocument2 pagesVariables Group 5 BSSW-2BMary France Paez CarrilloNo ratings yet
- PracRes Additional Notes 3Document9 pagesPracRes Additional Notes 3EllyNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Ii: Self Learning KitDocument5 pagesPractical Research Ii: Self Learning KitMark Ashley LivedNo ratings yet
- Identifikasi Dan Definisi VariableDocument11 pagesIdentifikasi Dan Definisi Variablecronos hijautuaNo ratings yet
- Tel./Fax No. (047) 602 1391 E-Mail Address: Zambales@deped - Gov.ph Website: WWW - Depedzambales.phDocument15 pagesTel./Fax No. (047) 602 1391 E-Mail Address: Zambales@deped - Gov.ph Website: WWW - Depedzambales.phCheska AgrabioNo ratings yet
- RusulDocument4 pagesRusulameer.angle2000No ratings yet
- Kinds of Variables and Their Uses 2Document14 pagesKinds of Variables and Their Uses 2Kurizeru MeiNo ratings yet
- Additional Reference VariableDocument8 pagesAdditional Reference VariablejackblackNo ratings yet
- All About VariablesDocument61 pagesAll About VariablesSasji HasjNo ratings yet