Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Subject: Experiment #5 PID Controller. Done By: Abdallah Husain Sulieman Daldoom. 31502020130. Eng. Saleem Ghanayem
Uploaded by
Abdallah Daldoom0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views6 pagesOriginal Title
Control Lab3.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views6 pagesSubject: Experiment #5 PID Controller. Done By: Abdallah Husain Sulieman Daldoom. 31502020130. Eng. Saleem Ghanayem
Uploaded by
Abdallah DaldoomCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Control Lab
Subject: Experiment #5 PID controller.
Done by: Abdallah Husain Sulieman Daldoom.
31502020130.
Eng. Saleem Ghanayem.
Objective:
To understand the function and build the derivative
controller and PID controller.
Introduction:
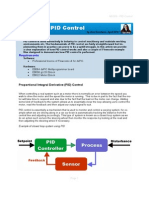
A PID controller is an instrument used in industrial
control applications. PID (proportional integral
derivative) controllers use a control loop feedback
mechanism to control process variables and are the most
accurate and stable controller.
PID control uses closed-loop control feedback to keep
the actual output from a process as close to the target or
setpoint output as possible.
As the name suggests, PID algorithm consists of three
basic coefficients; proportional, integral and derivative
which are varied to get optimal response.
Derivative controller:
A derivative controller called also rate controller because it is
changing the shape of output signal, and do not change the steady
state error, thus why the derivative controller does not work alone.
PID controller:
This type of control is also termed as
three-term control, and is implemented
by a PID Controller. By calculating
and controlling three parameters – the
proportional, integral and derivative of
how much a process variable deviates
from the desired set point value – we
can achieve different control actions
for specific work.
p-controller affect directly to the steady state error, I-controller can make
steady state error equal to zero and D-controller (rate controller) affect the
shape of output signal.
The actuating signal for PID control is:
𝑑𝑒(𝑡)
𝑒𝑎(𝑡) = 𝑘𝑝 ∗ 𝑒(𝑡) + 𝑘𝑑 + 𝐾𝑖 ∫ 𝑒(𝑡). 𝑑𝑡
𝑑𝑡
Simulink:
Circuit diagram for PID controller:
If gain 1 and 2 are equal to zero, then only P-controller will
exist in the system.
If gain 2 is zero, then only PI-controller will exist.
If all gains are not equal to zero, then its PID-controller,
and the error is less and output shape is better as shown
above.
It is possible to remove all the individual controller and
install a PID-controller from Simulink diagram.
All above the red line equal the under. The outputs are not
identical, because the PID controller consist a filter.
If we put Ki= zero, then the controller called PD controller.
The different between two signal is due the difference of
rate time.
Conclusion:
1) The D-controllers is derivative controller that
does not work alone, because no effect will
change in steady state error.
2) D-controller also called rate controller, due its
change only the shape of output.
3) We can change the values of P,I and D
individually using PID controller.
You might also like
- Advanced Techniques and Technology of Computer-Aided Feedback ControlFrom EverandAdvanced Techniques and Technology of Computer-Aided Feedback ControlNo ratings yet
- The Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersDocument15 pagesThe Working Principle of A PID Controller For BeginnersSaber AbdelaalNo ratings yet
- PID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersDocument6 pagesPID Controller Working Principle Explained For BeginnersPramillaNo ratings yet
- PID ControllersDocument6 pagesPID ControllersNguyễn HảiNo ratings yet
- What Is A PID ControllerDocument11 pagesWhat Is A PID ControllerANRG Batch 11No ratings yet
- Digital Pid Controller - 72S173Document15 pagesDigital Pid Controller - 72S173Pandimadevi GanesanNo ratings yet
- PID ControlDocument32 pagesPID ControlSyamil RahmanNo ratings yet
- PID ReportDocument38 pagesPID ReportNishiya Vijayan100% (1)
- Control SystemsDocument18 pagesControl Systemsgayatri jaltareNo ratings yet
- Design and applications of fuzzy logic PID controllerDocument19 pagesDesign and applications of fuzzy logic PID controllerPriya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Tarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Document13 pagesTarea2 Investigacion-Mcca-190090Christian MendezNo ratings yet
- PID CONTROLLER EXPERIMENTDocument13 pagesPID CONTROLLER EXPERIMENTMohd KhairiNo ratings yet
- Name: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeDocument11 pagesName: Roll: Year: Department: Subject: Subject CodeMayukh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Proportional Integral Derivative (PID)Document27 pagesProportional Integral Derivative (PID)GilagidkidNo ratings yet
- PID ControllerDocument5 pagesPID ControllerAbhilash MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- Chap19 SDocument99 pagesChap19 STest GgNo ratings yet
- DA-PID DesignDocument6 pagesDA-PID Designjamal2877No ratings yet
- 21 THDocument32 pages21 THujjwal kumarNo ratings yet
- How Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning MethodsDocument12 pagesHow Does A PID Controller Work - Structure & Tuning Methodsmurugan1984No ratings yet
- Pid Control TheoryDocument8 pagesPid Control TheorySonu SinghNo ratings yet
- MX009 - Proportional Integral Derivative Control PDFDocument5 pagesMX009 - Proportional Integral Derivative Control PDFjorgemdp5No ratings yet
- Chap19 SDocument108 pagesChap19 SRaghad AlnajimNo ratings yet
- PID TIA Portal 5Document110 pagesPID TIA Portal 5Yogi KipiantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Programming The PID AlgorithmDocument103 pagesChapter 19 Programming The PID AlgorithmMr KevinNo ratings yet
- PlssDocument21 pagesPlssKrishi ChhedaNo ratings yet
- PID control of inverted pendulum systemDocument11 pagesPID control of inverted pendulum systemShivankyJaiswalNo ratings yet
- PID Controller Analysis for Smart CarDocument30 pagesPID Controller Analysis for Smart CarGarimaAsthaNo ratings yet
- Chap19 SDocument111 pagesChap19 SIsraelNo ratings yet
- Lab11 - Autotuning PDFDocument26 pagesLab11 - Autotuning PDFEng. Ebrahim A. AlrohmiNo ratings yet
- Lab11 - AutotuningDocument26 pagesLab11 - AutotuningEng. Ebrahim A. AlrohmiNo ratings yet
- Week14pidmay242016pe3032 160530081519Document57 pagesWeek14pidmay242016pe3032 160530081519AztvNo ratings yet
- AVR221 Discrete PID ControllerDocument10 pagesAVR221 Discrete PID ControllerSadık KorkmazNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Background - The Regulation ProblemDocument19 pagesControl Systems Background - The Regulation ProblemHilmy Pramuditya FhansuriNo ratings yet
- Basic Understanding of PID ControllersDocument9 pagesBasic Understanding of PID ControllersNimesh GunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Optimize PID Controller Tuning for Process Control SystemsDocument62 pagesOptimize PID Controller Tuning for Process Control SystemsHuy Nguyen LuongNo ratings yet
- A Design of A PID Self-Tuning Controller Using Labview: Mohammad A. K. Alia, Tariq M. Younes, Shebel A. AlsabbahDocument11 pagesA Design of A PID Self-Tuning Controller Using Labview: Mohammad A. K. Alia, Tariq M. Younes, Shebel A. AlsabbahEdgar Maya PerezNo ratings yet
- Universidad Politécnica Salesiana: Sistema de Control en Tiempo ContinuoDocument6 pagesUniversidad Politécnica Salesiana: Sistema de Control en Tiempo ContinuoAndres LozanoNo ratings yet
- PID Controller Design: Itce470: Control Sysytem Experiment No. 4Document5 pagesPID Controller Design: Itce470: Control Sysytem Experiment No. 4HALIMANo ratings yet
- Over View of PID ControllerDocument2 pagesOver View of PID ControllerJawad SandhuNo ratings yet
- Special Nonlinear PID ControllersDocument25 pagesSpecial Nonlinear PID ControllersawalmeidaNo ratings yet
- Pid ThoryDocument24 pagesPid ThoryPravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 PLC PDFDocument15 pagesUnit 3 PLC PDFMahesh ShendeNo ratings yet
- L-14 (SS) (Iac) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document10 pagesL-14 (SS) (Iac) ( (Ee) Nptel)Marvin BayanayNo ratings yet
- BenchtopPIDController WhPaperDocument26 pagesBenchtopPIDController WhPaperfirosekhanNo ratings yet
- Contro EngineeringDocument29 pagesContro EngineeringNor AshimyNo ratings yet
- PID Controller Ziegler Nichols MethodDocument7 pagesPID Controller Ziegler Nichols MethodMuhammad RedhaNo ratings yet
- Real Time Speed Control of DC Motor With Unknown Transfer Function Through PIDDocument6 pagesReal Time Speed Control of DC Motor With Unknown Transfer Function Through PIDArbab HaiderNo ratings yet
- Guidelines To Pid Controll - LabviewDocument6 pagesGuidelines To Pid Controll - LabviewJimmy Joel ColqueNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: ControllersDocument7 pagesUnit 2: ControllersBhartish AchutaraoNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 3Document25 pagesLecture2 3vrushalibhattNo ratings yet
- Control Lab Project ReportDocument28 pagesControl Lab Project ReportDanyal QamarNo ratings yet
- Priyanka RajputDocument5 pagesPriyanka RajputajieNo ratings yet
- Control Manual Lab 8Document12 pagesControl Manual Lab 8Hussain HadiNo ratings yet
- Control Strategy, Selective Control SystemDocument10 pagesControl Strategy, Selective Control SystemHutama Putra WibawaNo ratings yet
- InTech-Pid Control TheoryDocument17 pagesInTech-Pid Control TheoryAbner BezerraNo ratings yet
- PID ControllerDocument44 pagesPID ControllerDeepthiNo ratings yet
- PID CONTROLLER LECTURE ON AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICSDocument31 pagesPID CONTROLLER LECTURE ON AUTOMATION AND ROBOTICSAndré GomesNo ratings yet
- PID control of mechanical systemDocument12 pagesPID control of mechanical systemanagha joshiNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesDocument11 pagesSampling and Field Testing at Wastewater Treatment FacilitiesSundarapandiyan SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- Fair Directory 02-2016Document44 pagesFair Directory 02-2016Ravichandran SNo ratings yet
- Managed Pressure Drilling MPD BrochureDocument5 pagesManaged Pressure Drilling MPD Brochureswaala4realNo ratings yet
- Hellstorm NotesDocument57 pagesHellstorm NotesDeni ZenNo ratings yet
- Diagrama 4 AMBIENT AIR TEMPER..Document1 pageDiagrama 4 AMBIENT AIR TEMPER..Gustavo PérezNo ratings yet
- Hearing Aid InformationDocument22 pagesHearing Aid InformationDeepakRodeyNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractramyaNo ratings yet
- Recycle ProgramDocument2 pagesRecycle ProgramKaps BlazeNo ratings yet
- Taylors 10 Minute Diagnosis Manual Symptoms and Signs in The Time Limited Encounter PDFDocument656 pagesTaylors 10 Minute Diagnosis Manual Symptoms and Signs in The Time Limited Encounter PDF19marvoloNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in General MathematicsAira Jane Irarum78% (18)
- 5988-4082EN Designers GuidDocument82 pages5988-4082EN Designers GuidAndreaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Pruning Equipment American Arborist Supplies, Tree Care, Climbing EquipmentDocument1 pagePneumatic Pruning Equipment American Arborist Supplies, Tree Care, Climbing EquipmentSalman JoNo ratings yet
- Amco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRDocument24 pagesAmco Veba Marine - Brochure - LRHươngTpuNo ratings yet
- OrlDocument186 pagesOrlMuli MaroshiNo ratings yet
- Thermal Performance of Air-Cooled Condensing Units by CFD SimulationDocument2 pagesThermal Performance of Air-Cooled Condensing Units by CFD SimulationFauziah JeraiNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: Introduction of The StudyDocument21 pagesChapter-1: Introduction of The StudyViswanathanNo ratings yet
- Course Progression Map For 2021 Commencing Students: E3001 Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) Common First YearDocument21 pagesCourse Progression Map For 2021 Commencing Students: E3001 Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) Common First YearNguyễn An KhoaNo ratings yet
- Atlas MothDocument1 pageAtlas Mothlililala92No ratings yet
- Seminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesDocument20 pagesSeminar Application of Nitrous Oxide in AutomobilesSaikat BadyakarNo ratings yet
- Ras Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)Document4 pagesRas Abu Aboud Stadium Daily Report 040 (20190613)tuan50% (2)
- Basics of Scientific Writing, Scientific Research, and Elementary Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesBasics of Scientific Writing, Scientific Research, and Elementary Data Analysisburhan sabirNo ratings yet
- CD 0400 CH 4 X 100 ML: For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Only. LinearityDocument1 pageCD 0400 CH 4 X 100 ML: For in Vitro Diagnostic Use Only. LinearityNguyễn ThơiNo ratings yet
- My Version of Meatlaof Project DraftDocument3 pagesMy Version of Meatlaof Project DraftCloue Faye I. BasalloNo ratings yet
- Full Report-Disinfectant and SanitizerDocument19 pagesFull Report-Disinfectant and Sanitizermohd addinNo ratings yet
- Kapla ResumeDocument35 pagesKapla ResumeAbinashNo ratings yet
- Top 21 Largest EMS Companies in WorldDocument22 pagesTop 21 Largest EMS Companies in WorldjackNo ratings yet
- The Future - G&VDocument6 pagesThe Future - G&VManuelHerreraMontoyaNo ratings yet
- Reverse Phrase Action Camera LightsDocument40 pagesReverse Phrase Action Camera LightsDINDO AzucenaNo ratings yet
- XR5 9 Element 5 Band Yagi 20-17-15-12-10MDocument16 pagesXR5 9 Element 5 Band Yagi 20-17-15-12-10Msboonuy331No ratings yet
- Violet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceDocument16 pagesViolet Flame Clearing of The Heart ServiceMySecret Gardenmdp82% (11)