Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histogram: Image Processing Lec (6) Ahmed AL - Basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
Uploaded by
Glynn HarlowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histogram: Image Processing Lec (6) Ahmed AL - Basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
Uploaded by
Glynn HarlowCopyright:
Available Formats
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.
basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
Histogram
The histogram of an image is a plot of the gray _levels values versus the
number of pixels at that value. A histogram appears as a graph with
"brightness" on the horizontal axis from 0 to 255 (for an 8-bit) intensity
scale) and "number of pixels "on the vertical axis. For each colored image
three histogram are computed, one for each component (RGB, HSL).The
histogram gives us a convenient -easy -to -read representation of the
concentration of pixels versus brightness of an image, using this graph we
able to see immediately:
1 Whether an image is basically dark or light and high or low contrast.
2 Give us our first clues about what contrast enhancement would be
appropriately applied to make the image more subjectively pleasing to an
observer, or easier to interpret by succeeding image analysis operations.
So the shape of histogram provide us with information about nature of the
image or sub image if we considering an object within the image.
For example:
1 Very narrow histogram implies a low-contrast image.
2 Histogram skewed to word the high end implies a bright image.
3 Histogram with two major peaks , called bimodal, implies an object that
is in contrast with the background.
1 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
Examples of the different types of histograms are shown in figure below.
2 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
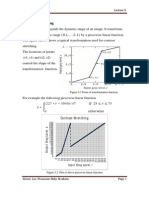
Histogram Modifications
The gray level histogram of an image is the distribution of the gray level
in an image. The histogram can be modified by mapping functions, which
will stretch, shrink (compress), or slide the histogram. Figure below
illustrates a graphical representation of histogram stretch, shrink and
slide.
3 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
Histogram Equalization
Is a popular technique for improving the appearance of a poor image. It's
a function similar to that of a histogram stretch but often provides more
visually pleasing results across a wide range of images.
Histogram equalization is a technique where the histogram of the
resultant image is as flat as possible (with histogram stretching the overall
shape of the histogram remains the same).
The results in a histogram with a mountain grouped closely together to
"spreading or flatting histogram makes the dark pixels appear darker and
the light pixels appear lighter.
The histogram equalization process for digital images consists of four
steps:
1. count the total number of pixels associated with each pixel in intensity
4 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
2.calculate probability of each pixel in intensity in the image matrix
Probability is no. of pixels divided by total no. of pixels(16).
3.calculate cumulative probability
Since we want to change the intensity range to 1- 20 , we multiply cumulative
probability by 20 .
5 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
Image processing Lec(6) Ahmed AL.basha & Saadaldeen AHMED
6 جامعة تكريت \\ علوم الحاسوب
You might also like
- GE fMRIDocument2 pagesGE fMRIPradeep JNANo ratings yet
- CT Basics - Part 1Document27 pagesCT Basics - Part 1bahadirerNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Histogram Equalization Is A Computer Image Processing Technique Used To Improve ContrastDocument12 pagesAdaptive Histogram Equalization Is A Computer Image Processing Technique Used To Improve ContrastViwin SinghNo ratings yet
- Generate VHDL Code From Matlab Code: Bookmark This PageDocument10 pagesGenerate VHDL Code From Matlab Code: Bookmark This PageAnonymous JnvCyu85No ratings yet
- MRI AcronymosDocument7 pagesMRI AcronymosRamirez Suarez Edgardo JoseNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Contrast Image Histogram Contrast Data IntensitiesDocument4 pagesImage Processing Contrast Image Histogram Contrast Data IntensitiesSumit AnchekarNo ratings yet
- Intensity HistogramDocument41 pagesIntensity Histogrambasab_ecens100% (1)
- Comparative Study Histogram Equalization Techniques Brightness Preservation Contrast EnhancementDocument15 pagesComparative Study Histogram Equalization Techniques Brightness Preservation Contrast EnhancementShreekanth ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Histogram Equalization Techniques For Image Enhancement of Grayscale Images of Dawn and DuskDocument5 pagesComparison of Histogram Equalization Techniques For Image Enhancement of Grayscale Images of Dawn and DuskIJMERNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Histogram Adjustments for Image Contrast ControlDocument9 pagesMATLAB Histogram Adjustments for Image Contrast ControlĐỗ Văn TânNo ratings yet
- 6 2022 03 25!05 37 50 PMDocument29 pages6 2022 03 25!05 37 50 PMmustafa arkanNo ratings yet
- Histogram SpecificationDocument6 pagesHistogram SpecificationAbhishek ShaolinNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Techniques for Histogram ModificationDocument71 pagesDigital Image Processing Techniques for Histogram ModificationKALAIVANINo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis Image Ultrasound Liver Using Gray-LevelDocument7 pagesComparative Analysis Image Ultrasound Liver Using Gray-LevelDimona MoldovanuNo ratings yet
- Exp 3.4 - 18bec1060Document12 pagesExp 3.4 - 18bec1060srinivas rajuNo ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument12 pagesDigital Image ProcessingPriyanka DuttaNo ratings yet
- Histogram Using Matlab and ExcelDocument29 pagesHistogram Using Matlab and ExcelOana MironNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Histogram Processing Techniques for EnhancementDocument33 pagesDigital Image Histogram Processing Techniques for EnhancementKarthick VijayanNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancing Techniques Literature SurveyDocument12 pagesImage Enhancing Techniques Literature SurveyAmishi M KapadiaNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of Contrast Enhancement TechniquesDocument5 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Contrast Enhancement TechniquesLidia CorciovaNo ratings yet
- Combined Approach For Image SegmentationDocument4 pagesCombined Approach For Image SegmentationseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- CH 3Document20 pagesCH 3Arebu MarufNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document14 pagesLecture 8محمد ياسر محي الدينNo ratings yet
- Image Processing: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesImage Processing: ObjectiveElsadig OsmanNo ratings yet
- Equalize The Histogram Equalization For Image EnhancementDocument8 pagesEqualize The Histogram Equalization For Image EnhancementGashaw KebedeNo ratings yet
- Image Processing ProjectDocument12 pagesImage Processing ProjectKartik KumarNo ratings yet
- Image Processing: Chapter (3) Part 3:intensity Transformation and Spatial FiltersDocument41 pagesImage Processing: Chapter (3) Part 3:intensity Transformation and Spatial FiltersArSLan CHeEmAaNo ratings yet
- Image Processing With MATLAB: What Is Digital Image Processing? Transforming Digital Information Motivating ProblemsDocument7 pagesImage Processing With MATLAB: What Is Digital Image Processing? Transforming Digital Information Motivating Problemsblack90pearlNo ratings yet
- Local Hist EqualizationDocument8 pagesLocal Hist EqualizationLidia CorciovaNo ratings yet
- Batch 11 (Histogram)Document42 pagesBatch 11 (Histogram)Abhinav KumarNo ratings yet
- Control Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization For Image EnhancementDocument10 pagesControl Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization For Image Enhancementpi194043100% (1)
- Histogram Equalization Image Processing TechniqueDocument5 pagesHistogram Equalization Image Processing TechniqueAshton Paul D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Dip PracticalfileDocument19 pagesDip PracticalfiletusharNo ratings yet
- WAVELETS TheoryDocument8 pagesWAVELETS Theorysohelpasha25No ratings yet
- Medical ImageDocument6 pagesMedical ImagerajasekarNo ratings yet
- Histograms processingDocument4 pagesHistograms processingshivaniNo ratings yet
- Question 1Document37 pagesQuestion 1Khan Raqib MahmudNo ratings yet
- Somaiya Vidyavihar UniversityDocument7 pagesSomaiya Vidyavihar UniversitySonu PradhanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Selection of Contrast Enhancement Techniques in Digital Images Using Fuzzy LogicDocument8 pagesAutomatic Selection of Contrast Enhancement Techniques in Digital Images Using Fuzzy Logicد.مهندس.اسماعيل حميدNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement: Chapter - 5Document21 pagesImage Enhancement: Chapter - 5Manu ManuNo ratings yet
- B7 An Image Enhancement Method For Extracting Multi-License Plate Region Yun 2017Document20 pagesB7 An Image Enhancement Method For Extracting Multi-License Plate Region Yun 2017Ruben CuervoNo ratings yet
- Histogram ToolDocument3 pagesHistogram ToolAhmed El SayedNo ratings yet
- Modified Histogram Based Contrast Enhancement Using Homomorphic Filtering For Medical ImagesDocument5 pagesModified Histogram Based Contrast Enhancement Using Homomorphic Filtering For Medical Imagesmayank tiwariNo ratings yet
- Understanding Image HistogramsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Image HistogramsFaiz ShakhihNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement TechniquesDocument5 pagesImage Enhancement Techniquesمحمد ماجدNo ratings yet
- Image Retrieval Using Both Color and Texture FeaturesDocument6 pagesImage Retrieval Using Both Color and Texture Featuresdivyaa76No ratings yet
- Compusoft, 3 (11), 1276-1281 PDFDocument6 pagesCompusoft, 3 (11), 1276-1281 PDFIjact EditorNo ratings yet
- Image Enhancement TechniquesDocument19 pagesImage Enhancement TechniquesWaqar TanveerNo ratings yet
- DIP - Experiment No.4Document6 pagesDIP - Experiment No.4mayuriNo ratings yet
- Image Processing With MATLAB: Quick ReferenceDocument30 pagesImage Processing With MATLAB: Quick ReferenceEdrian PentadoNo ratings yet
- Image SegmentationDocument7 pagesImage SegmentationAsem YamakNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)Document10 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and Development (IJERD)IJERDNo ratings yet
- 2021 Dip 3Document25 pages2021 Dip 3Abdul KadirNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing: Gray Level EnhancementDocument15 pagesDigital Image Processing: Gray Level EnhancementAsad ullahNo ratings yet
- DIPDocument20 pagesDIPMostafa AdilNo ratings yet
- DeneliwovilopoDocument3 pagesDeneliwovilopoprathamwakde681No ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing QB 2017 - 18Document9 pagesDigital Image Processing QB 2017 - 18PrakherGuptaNo ratings yet
- Alex 2016Document5 pagesAlex 2016Dr.S.NAGARAJANNo ratings yet
- Adaptive HistogramDocument5 pagesAdaptive HistogramMuhammad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Histogram Equalization AlgorithmDocument2 pagesHistogram Equalization Algorithmkedir GemechuNo ratings yet
- AN IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR MIX NOISE AND BLURRING REMOVAL IN DIGITAL IMAGESFrom EverandAN IMPROVED TECHNIQUE FOR MIX NOISE AND BLURRING REMOVAL IN DIGITAL IMAGESNo ratings yet
- Inpainting and Denoising ChallengesFrom EverandInpainting and Denoising ChallengesSergio EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Computational Color Science: Variational Retinex-like MethodsFrom EverandComputational Color Science: Variational Retinex-like MethodsNo ratings yet
- Image Edge Detection Operators ExplainedDocument7 pagesImage Edge Detection Operators ExplainedGlynn HarlowNo ratings yet
- Discussion Chapter#1 Main Points in Ch#1: - Data CommunicationDocument7 pagesDiscussion Chapter#1 Main Points in Ch#1: - Data Communicationambo intangNo ratings yet
- Operating System: DeadlocksDocument12 pagesOperating System: DeadlocksGlynn HarlowNo ratings yet
- Computer Network SecurityDocument177 pagesComputer Network SecurityGlynn HarlowNo ratings yet
- Setting Analog Signal InputDocument7 pagesSetting Analog Signal Inputnmanojkumar_17No ratings yet
- Multirate and Adaptive FiltersDocument55 pagesMultirate and Adaptive FiltersSantanu GhoraiNo ratings yet
- Implementation of DSP algorithms on fixed point DSP processorsDocument13 pagesImplementation of DSP algorithms on fixed point DSP processorsNikhil PanikkarNo ratings yet
- BeGlobe PORTFOLIO ReportDocument6 pagesBeGlobe PORTFOLIO ReportMəhəmməd AğacamalovNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems RoadMapDocument14 pagesEmbedded Systems RoadMapMAHESH VNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Communication Toolbox PrimerDocument344 pagesMATLAB Communication Toolbox PrimerchalimisNo ratings yet
- Advanced Modern Engineering Mathematics 3rd Ed Glyn James Solutions ManualDocument23 pagesAdvanced Modern Engineering Mathematics 3rd Ed Glyn James Solutions ManualIman ArzmanNo ratings yet
- Delhi 2005 document analysisDocument3 pagesDelhi 2005 document analysisAnwesh10000No ratings yet
- 9770M1 3500 25 PDFDocument77 pages9770M1 3500 25 PDFnabil160874No ratings yet
- Reflection Processing Using Matlab PDFDocument99 pagesReflection Processing Using Matlab PDFbagusNo ratings yet
- Onkyo tx-sr308 986Document81 pagesOnkyo tx-sr308 986saom09No ratings yet
- Folded-Frequency Calculator: Aliasing and NyquistDocument5 pagesFolded-Frequency Calculator: Aliasing and NyquistDipanka BorahNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 What Are "Decimation" and "Downsampling"?Document8 pages2.1.1 What Are "Decimation" and "Downsampling"?aatqahNo ratings yet
- Fast Fourier Transform Basics PDFDocument2 pagesFast Fourier Transform Basics PDFVincentNo ratings yet
- DSP MCQ1Document8 pagesDSP MCQ1Bala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers TSD DS Jan-2006 REVDocument2 pagesMicrocontrollers TSD DS Jan-2006 REVAlaa saidNo ratings yet
- Aliasing: Properly Sampled Image of Brick WallDocument7 pagesAliasing: Properly Sampled Image of Brick WallKrutarth PatelNo ratings yet
- Lawrence R. Rabiner, Digital Processing of Speech SignalsDocument527 pagesLawrence R. Rabiner, Digital Processing of Speech Signals서영빈100% (1)
- ICOM IC-7100 BrochureDocument4 pagesICOM IC-7100 Brochuregus289No ratings yet
- NX300Document102 pagesNX300FABIANNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1 SolutionDocument10 pagesTutorial Sheet 1 Solutionsama abd elgelilNo ratings yet
- Proceedings of Spie: Fast Computing of Discrete Cosine and Sine Transforms of Types VI and VIIDocument11 pagesProceedings of Spie: Fast Computing of Discrete Cosine and Sine Transforms of Types VI and VIIhorlandovragasNo ratings yet
- Terez Pitch Detection AlgorithmDocument4 pagesTerez Pitch Detection AlgorithmPeter LeakNo ratings yet
- Assign I P 050209Document2 pagesAssign I P 050209Vinay100% (2)
- Rondeau GR FilteringDocument9 pagesRondeau GR FilteringBruno AlvimNo ratings yet