Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Road Safety Audit of An Existing Road, From Ashram Chowk To Crri
Uploaded by
Suryavenkat RaghavanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Road Safety Audit of An Existing Road, From Ashram Chowk To Crri
Uploaded by
Suryavenkat RaghavanCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Road Safety Audit of an Existing Road, From Ashram Chowk to
CRRI
N. Naveen1,2, Dr. S. Velmurugan3
1(Assistant Professor, K G Reddy College of Engineering and Technology, Hyderabad, India)
2(Research scholar, VELS University, Chennai, India)
3(Sr. Prin. Scientist, Traffic & Safety Division, CRRI, New Delhi, India)
Abstract: “Pedestrian” includes people who walk, sit, stand in public spaces, or use a mobility aid like
walking stick, crutches or wheelchair, be they children, teenagers, adults, elderly persons, persons with
disabilities, workers, residents, shoppers or people-watchers (IRC: 103-2012). Road Safety audit is the formal
procedure for assessing accident potential and safety performance in the provision of new road schemes, the
improvement and rehabilitation of existing road and maintenance of roads. The road selected for this study is
existing road from Ashram Chowk to CRRI, which is at Delhi to Mathura road. The main tool is Road Safety
Audit. This paper explores the defects in the design and other safety features. Thisaudit is a part of CRRI Road
Safety Audit Training Program. In conclusion, we argue that significant measures should be taken on Road
Safety aspects to mitigate the accidents and ensure the safety to pedestrians and vehicular traffic. This paper
mainly highlights the safety in terms of pedestrians and traffic sign post alignment.
Keywords: Accidents, CRRI, Pedestrians, Road Safety Audit, Safety, Sign boards, Vehicular Traffic.
I. INTRODUCTION
Road safety audit assess the operation of a road, focusing on road safety as it affects the users of the
road. These users include pedestrians, cyclists, motorcyclists, truck/ bus drivers, on road public transport users,
etc. Road traffic injuries are the No.1 cause of death among those aged 15–29. Road users are not perfect.The
main cause for the accidents is road users, Confusion in drivers, fatigue, stress, negligence may lead to the
accidents.
RSA is a formal process and not an informal check
Carried out by persons who are independent of the design and the construction
Carried out by persons with appropriate expertise, experience and training
Restricted to road safety issues
The outcome of a road safety audit is the identification of any road safety deficiencies and formulation
of recommendations aimed at removing or reducing those deficiencies.
TABLE1 Percentage wise contribution of various elements in road accidents
ELEMENT PERCENTAGE
Road User 65.0
Road and Surroundings 2.5
Vehicle 2.5
Road User, Road Surroundings 24.0
Road User and Vehicle 4.5
Road User, Road & Surroundings 1.5
and Vehicle
Following considerations should be taken
Level of safety
considering the function of the road
Readability of road
Delineation
Roadside hazards
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 134 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Aspects to be checked are Safety and Operational Implications of alignment and junctions, Any
deviation from standards, Facilities for pedestrians, Cyclists and intermediate transport, Road safety implication
on maintenance, Non-Motorized Road Users, Day and Night Trials checks, Drainage, Climate conditions,
Landscaping, Services, Access, Skid resistance, Fences , Adjacent development, Bridge parapets, Local
Alignment, Visibility, New / existing road surface, Safety Aids on steep hills, Road signs markings, T, X, Y-
junctions, Traffic signals, Adjacent land, Pedestrians, Cyclists, Non-motorized vehicles, Signs and Lighting ,
Lighting, Signs, Variable message signs .
II. SITE SELECTED
The road selected for this study is existing road from Ashram Chowk to CRRI, which is at Delhi to
Mathura road.
Fig 1 The above image showsAshram Chowk to CRRI Road map.
Ashram chowk is a crossways located on the southeastern corner of the Delhi ring road. It is at the
intersection of the ring road and Mathura road from the ITO crossing, the Supreme court, Pragati Maidan,
Purana Quila, Nizamuddin Dargah and Haryana border at Faridabad. The distance between these two points is 4
kilometers. It is a busy area with heavy traffic, even pedestrian traffic is also heavy at this section.
“Pedestrian” includes people who walk, sit, stand in public spaces, or use a mobility aid like walking
stick, crutches or wheelchair, be they children, teenagers, adults, elderly persons, persons with disabilities,
workers, residents, shoppers or people-watchers (IRC: 103-2012).
The key principles of the Safe System approach should be,
i. Recognition of human error in the transport system
ii. Recognition of human physical vulnerability and limits
iii. Promotion of system accountability
iv. Promotion of ethical values in road safety
v. Promotion of societal values
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 135 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
III. INVESTIGATIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Fig 2 Team members of Existing Road Safety Audit with the team head Dr. S Velmurugansir.
This audit is a part of CRRI Road Safety Audit Training Program in July,2017. Some of the checklist
included in this audit are like
i. Is the provision for road signs adequate and in accordance with standards?
ii. Are there any situations where traffic signs themselves are obstructing essential line of sight for drivers
and pedestrians?
iii. General adequacy and visibility of road markings, during day/night time and in wet/ dry weather
conditions
iv. Are the proposed lighting scheme and illumination levels of an appropriate standard, consistent with
the needs of the location, pedestrian and other factors?
v. Are there any poles, columns along the road and comment on whether some or any of them can be
removed, relocated to less hazardous positions etc.
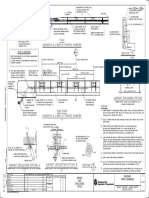
Fig 3The End treatment of Metal Beam Crash Barrier is missing
3.1. Observation
The End treatment of Metal Beam Crash Barrier is missing.
Reason for Concern:
Vehicles plying on the road may hit the protruded MBCB which may result to fatal accident.
Recommendation:
It shall be provided with suitable end treatment with the inclined metal beam mounted to the end post
and fixed into the median.
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 136 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Priority: Highly Essential.
Fig4The sign Boards placed over the footpath and over-head Gantry are place properly
3.2. Observation
The sign Boards placed over the footpath and over-head Gantry are place properly.
Priority: Followed the safety norm completely
Fig5 The slope of ground of the Petrol Pump is towards the carriageway
3.3. Observation
The slope of ground of the Petrol Pump is towards the carriageway
Reason for Concern:
The slope of the ground of petrol pump may discharge the rain water directly to the main carriageway,
resulting in the water-logged situation on the MCW.
Recommendation:
Proper drainage shall be provided to check the water directly discharging to the carriageway.
Priority: Highly Essential
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 137 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Fig6 kerb placed is at a great height
3.4. Observation
Water Logging at the Bus-stop
The floor of the Bus-stop is raised abnormally.
The sign board placed near by the bus stop is obstruction to the pedestrians.
Reason for Concern:
This situation obstructs the pedestrians and the public transport users to enter the bus stop
Recommendation:
The height of the footpath shall be reduced as per the relevant IRC norms, water logging should be
avoided.
Priority: Highly Essential
Fig7 Ganty Post lying on the foot path creating hindrance to the pedestrians.
3.5. Observation
Ganty Post lying on the foot path creating hindrance to the pedestrians & Unnecessary construction on
the footpath
Reason for Concern:
This is creating hindrance to the pedestrians & Causes obstruction on the footpath to the pedestrians
during nights
Recommendation:
It shall be removed immediately & Extra projections should be removed
Priority: Highly Essential
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 138 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Fig8 Trees planted in the median
3.6. Observation
Trees planted in the median.
Reason for Concern:
The branches protruding creates hindrance to the road users obstructs the visibility.
Recommendation:
The Branches shall be trimmed periodically. And the tree plantation shall not be done in the medians.
Priority: Desirable
Fig9 Electric Pole tilted on the footpath
3.7. Observation
Electric Pole tilted on the footpath.
Reason for Concern:
It is causing hindrance to the pedestrians, it may be fatal in the rainy reason.
Recommendation:
The pole must be removed/replaced.
Priority: Desirable
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 139 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Fig10 Drainage slab are weak and they are destroyed
3.8. Observation
Drainage slab are weak and they are destroyed& Manhole cover is not properly placed
Reason for Concern:
Very dangerous for the pedestrians and may be hazardous during nights and rains& May cause
obstruction to the pedestrians and the cover may gush out due to water during rains
Recommendation:
It should be properly maintained and slabs need to be replaced with good material& Cover need to be
placed properly without causing any projections
Priority: Very Essential
Fig11 Two wheelers using the footpath
3.9. Observation
Two wheelers using the footpath
Reason for concern:
It may cause accidents or uncomfortable to the pedestrians
Recommendation:
Proper maintenance of the footpath should be done and the kerb height should be maintained to avoid
the vehicular movement on the footpath
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 140 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
Priority: Essential
Fig12 Improper access to private properties
3.10. Observation
Improper access to private properties.
Reasons for concern:
Lack of Sight distance, Vehicle entering or leaving private property disrupts traffic on main
carriageway.
Recommendations:
Auxiliary lanes to be provided for safe entry and exit without affecting pedestrians.Adequate warning
signs to be provided. If not possible close or reroute the access.
Priority: High
Fig13 Footpath discontinuous at various sections
3.11. Observation
Footpath discontinuous at various sections.
Reason for concern:
Pedestrian exposure to vehicular traffic as they are forced to walk on the main carriageway.
Recommendation:
Provision for pedestrians to remain on side walk along entire stretch.
Priority: Essential
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 141 | Page
International Journal of Latest Engineering Research and Applications (IJLERA) ISSN: 2455-7137
Volume – 02, Issue – 08, August – 2017, PP – 134-142
IV. CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented a Road Safety Audit that highlighted issues in safety management in clearway
showing the contents like observation, reason for concern, recommendation and priority of the issue. It
examined the defects in the road safety in relation to motorized traffic and pedestrian safety. It suggested the
various recommendations which are easy to do and at low cost. The audit is applied to the risks outside the
framework of standards and codes.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the Organizations/Institutions likeCentral Road
Research Institute, VELS University, K G Reddy College of Engineering and Technology for their contributions
and suggestions for performing this Road Safety Audit.
REFERENCES
[1] Manual on Road Safety by IRC: SP: 88 – 2010
[2] Guidelines for Pedestrian Facilities by IRC: 103 - 2012
[3] Shalini Kanuganti, et al, (2016), Road Safety Analysis Using Multi Criteria Approach: A Case Study in
India, Elsevier
[4] Abdul Rahoof, et al (2017), Road Safety and Road Safety Audit inIndia: A Review, IJTRE
[5] Nicholas N Ferenchak (2014), PedestrainAge and Gender in Relation to Crossing Behavior at
Midblock Crossings inIndia, Science Direct
[6] Humera Banu, et al (2013), Two-Wheeler Riding Patterns, Perceptions and Aggressive Riding
Behavior Among College Youth, IJIRSET
[7] Francis John Gichaga(2016), The Impacts of Road Improvements on Road Safety and Related
Characteristics, IATSS Research
[8] YuhaHuvarinen, et al (2017), RoadSafety Audit, Science Direct
[9] Xuchun S Tu (2016), Application of RISC for Road Safety Program Development, Transportation
Research Procedia, Science Direct
[10] Arun S Bagi , et al (2012), Road Safety Audit, IOSRJMCE
[11] Athanasios Galanis, et al (2016), PedestrainRoad Safety in Relation to Urban Road Type and Traffic
Flow, Transportation Research Procedia, Science Direct
[12] ZarulazamEusofe, et al (2016), Assessment of Road Safety Management at Institutional Level
inMalaysia: A Case Study, IATSS Research
[13] Dr Tom V Mathew, IIT Bombay, Accident Studies (2014)
www.ijlera.com 2017 IJLERA – All Right Reserved 142 | Page
You might also like
- AASHTO Roadside Design Guide 4th Ed 2011 PDFDocument316 pagesAASHTO Roadside Design Guide 4th Ed 2011 PDFRenukadevi Rpt85% (34)
- Safety Audit Checklist For RoadworksDocument13 pagesSafety Audit Checklist For RoadworksGovind Shriram ChhawsariaNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Audit of Delhi - Mathura Road: N. Naveen, Dr. T. Ilango, Dr. Abdhesh Kumar SinhaDocument8 pagesRoad Safety Audit of Delhi - Mathura Road: N. Naveen, Dr. T. Ilango, Dr. Abdhesh Kumar SinhaSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Auditof Rural Ghat Roadat Vikarabad DistrictDocument7 pagesRoad Safety Auditof Rural Ghat Roadat Vikarabad Districtaditya gargNo ratings yet
- ROAD SAFETY AUDIT Patherkandi BypassDocument19 pagesROAD SAFETY AUDIT Patherkandi BypassNavarun Vashisth100% (1)
- Road Safety Audit Analysis: A Case Study of National HighwayDocument19 pagesRoad Safety Audit Analysis: A Case Study of National HighwayThasneem K. SNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Audit: Malaysian Practice: Introduction ToDocument64 pagesRoad Safety Audit: Malaysian Practice: Introduction ToChin Thau WuiNo ratings yet
- Rse 2.3Document16 pagesRse 2.3Rudra Sai SandeepNo ratings yet
- Highway & Traffic Engineering: Open-Ended LabDocument11 pagesHighway & Traffic Engineering: Open-Ended LabNor AziraNo ratings yet
- Presentation Arun UpdatedDocument22 pagesPresentation Arun UpdatedArun SethiNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit OF Highways: DR Umakanta PaniDocument47 pagesSafety Audit OF Highways: DR Umakanta PaniUmakanta PaniNo ratings yet
- Review Paper On RSA A Descriptive Approach Towards Road Safety of Dhandhuka To Dholera (Sh-20) in Gujrat StateDocument5 pagesReview Paper On RSA A Descriptive Approach Towards Road Safety of Dhandhuka To Dholera (Sh-20) in Gujrat StateIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Example Proposal TemplateDocument12 pagesExample Proposal TemplateNur HazimahNo ratings yet
- Road ProjectDocument29 pagesRoad ProjectSamson ShineNo ratings yet
- RSSWKL2019 Keynote Speaker 5 Richard Wong Chuen FunDocument49 pagesRSSWKL2019 Keynote Speaker 5 Richard Wong Chuen FunKohNo ratings yet
- Road Accidents and Prevention: April 2017Document8 pagesRoad Accidents and Prevention: April 2017SERGIONo ratings yet
- Sign Boards & IMPDocument10 pagesSign Boards & IMPSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Belagavi: Submitted in Partial Fullfillment For The Award of Bachelor of Engineering in Civil EngineeringDocument30 pagesBelagavi: Submitted in Partial Fullfillment For The Award of Bachelor of Engineering in Civil EngineeringGanesh PugNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal 201884248 (Draft)Document10 pagesResearch Proposal 201884248 (Draft)wedzeNo ratings yet
- A Review On Work Zone Safety During Blackspot Improvement Construction Under Blackspot ManagementDocument7 pagesA Review On Work Zone Safety During Blackspot Improvement Construction Under Blackspot ManagementIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- CAREC Road Safety Engineering Manual 3: Roadside Hazard ManagementFrom EverandCAREC Road Safety Engineering Manual 3: Roadside Hazard ManagementNo ratings yet
- CAREC Road Safety Engineering Manual 2: Safer Road WorksFrom EverandCAREC Road Safety Engineering Manual 2: Safer Road WorksNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study of Providing A Skywalk For Pedestrian at Kalupur Station Road-Ijaerdv04i0294959Document4 pagesFeasibility Study of Providing A Skywalk For Pedestrian at Kalupur Station Road-Ijaerdv04i0294959Editor IJAERDNo ratings yet
- Ieee BeiacDocument6 pagesIeee Beiackairel82No ratings yet
- Traffic Control at Road Works Field GuideDocument34 pagesTraffic Control at Road Works Field GuidePrakash JayappaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument21 pagesProjectNIDHI JARIWALANo ratings yet
- End SemDocument21 pagesEnd SemNIDHI JARIWALANo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Road Safety AuditDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Road Safety Auditqbqkporhf100% (1)
- REAM Guide LineDocument120 pagesREAM Guide Lineshukri83% (6)
- Construction Stage RSA Report - Kanak Gajjar - Team CDocument79 pagesConstruction Stage RSA Report - Kanak Gajjar - Team Ckishy7No ratings yet
- Assessment of Road Infrastructures Pertaining To MDocument7 pagesAssessment of Road Infrastructures Pertaining To MKak NinaNo ratings yet
- Proposal MuqDocument22 pagesProposal Muqamirul hisyamNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Research PaperDocument9 pagesCivil Engineering Research PaperTHE EXPRESSIONISTNo ratings yet
- ROAD SAFETY AUDIT - Roing Hunli 0 To 25Document13 pagesROAD SAFETY AUDIT - Roing Hunli 0 To 25Jayashree HagjerNo ratings yet
- Traffic Planning and Management: Name-Rahul Maji Roll No-10301314080 Civil Engineering Haldia Institute of TechnologyDocument11 pagesTraffic Planning and Management: Name-Rahul Maji Roll No-10301314080 Civil Engineering Haldia Institute of TechnologySaswata PradhanNo ratings yet
- Study of Road Accidents in IndiaDocument51 pagesStudy of Road Accidents in IndiaManish AhujaNo ratings yet
- Cui 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 587 012006Document8 pagesCui 2020 IOP Conf. Ser. - Earth Environ. Sci. 587 012006Rohit BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- Safety Audit Checklist For RoadworksDocument13 pagesSafety Audit Checklist For RoadworksruhanNo ratings yet
- Road SafetyDocument14 pagesRoad SafetyDev Mitra100% (2)
- Jasper 119 2Document13 pagesJasper 119 2Ruttala NaniNo ratings yet
- Farhan 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 404 012045Document7 pagesFarhan 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 404 012045m9870261534No ratings yet
- 2 Road Safety AuditDocument72 pages2 Road Safety AuditEbisa AdamuNo ratings yet
- SafetyBenefitsGuardrail 2017book FinalDocument24 pagesSafetyBenefitsGuardrail 2017book FinalRoger VasquezNo ratings yet
- IIT Support de Cours BEngDocument43 pagesIIT Support de Cours BEngMounawar FaugooNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Audit at Various StagesDocument32 pagesRoad Safety Audit at Various StagesBernard Owusu100% (1)
- Analysis of Road Infrastructural Audits Along Jalan Batu Pahat-Kluang Malaysia: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Road Infrastructural Audits Along Jalan Batu Pahat-Kluang Malaysia: A Case StudyIman AriefNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On The Evaluating Cost-Effective Railway Level Crossing Protection SystemDocument3 pagesA Review Paper On The Evaluating Cost-Effective Railway Level Crossing Protection SystemtmmNo ratings yet
- 01-Road Safety Review Report - Template 234 A - 8 WeekDocument11 pages01-Road Safety Review Report - Template 234 A - 8 WeekcaddNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 802493092HW I-Chap-4 - HandoutDocument34 pagesLecturenote - 802493092HW I-Chap-4 - HandoutHaile GuebreMariamNo ratings yet
- First Revision-15 Aug 2017 - DESIGN GUIDELINES PDFDocument277 pagesFirst Revision-15 Aug 2017 - DESIGN GUIDELINES PDFБ. СайнболдNo ratings yet
- Traffic Management During Construction, RSA - 240608Document104 pagesTraffic Management During Construction, RSA - 240608mrasdan100% (2)
- Cavite State University: Don Severino de Las Alas CampusDocument13 pagesCavite State University: Don Severino de Las Alas CampusMigz EscutinNo ratings yet
- Road SafetyDocument2 pagesRoad SafetyumeshapkNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument20 pagesResearch PaperraicacedenoiiNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Protection of Traffic at Active Work ZonesDocument21 pagesMaintenance and Protection of Traffic at Active Work ZonesManav RamaniNo ratings yet
- Roundabout DesignDocument76 pagesRoundabout DesignHans Hans Sadz100% (2)
- PDFDocument100 pagesPDFaditya kumawatNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Rolling Barrier On Pune - Mumbai HighwayDocument6 pagesCase Study On Rolling Barrier On Pune - Mumbai HighwayIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Checklist For IRC SP 73 - 2018Document5 pagesChecklist For IRC SP 73 - 2018gdrplgudcpmcNo ratings yet
- REAM Guide Line PDFDocument120 pagesREAM Guide Line PDFmohd syafiq amirruddin ShariNo ratings yet
- Raveling in Road Projects Causes and Remedies BY ASSOCIATEDINFODocument8 pagesRaveling in Road Projects Causes and Remedies BY ASSOCIATEDINFOSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Blackspot Identification On NHDocument2 pagesBlackspot Identification On NHSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Sign Boards & IMPDocument10 pagesSign Boards & IMPSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- RSA AnxeureDocument35 pagesRSA AnxeureSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Covid-19-Health-Advisory by ACMADocument33 pagesCovid-19-Health-Advisory by ACMASuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- CMS-2-10-15-01-2020 ConversionDocument58 pagesCMS-2-10-15-01-2020 ConversionSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- 7 Introduction To RSA - DR - VMS PDFDocument84 pages7 Introduction To RSA - DR - VMS PDFNikhilKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Fence - Plant OperationDocument39 pagesFence - Plant OperationSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Highway Safety: Safety Audit & Safety in Work ZonesDocument72 pagesHighway Safety: Safety Audit & Safety in Work ZonesSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Around Schools TaskforceDocument68 pagesRoad Safety Around Schools TaskforceSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Safety and Health On Construction Sites IMPDocument1 pageGuidelines For Safety and Health On Construction Sites IMPSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Workzone - Safety - IMP 1 PDFDocument37 pagesWorkzone - Safety - IMP 1 PDFSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Nyngan Solar Plant EHS OM Manual Incl OEMP Rev 31 PDFDocument121 pagesNyngan Solar Plant EHS OM Manual Incl OEMP Rev 31 PDFSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Construction Safety HandbookDocument201 pagesConstruction Safety HandbookSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Nyngan Solar Plant EHS OM Manual Incl OEMP Rev 31 PDFDocument121 pagesNyngan Solar Plant EHS OM Manual Incl OEMP Rev 31 PDFSuryavenkat RaghavanNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering Drawings 10.2 - A3 - 3Document1 pageBridge Engineering Drawings 10.2 - A3 - 3Adnan NajemNo ratings yet
- Concrete BarrierDocument4 pagesConcrete BarrierSara MaroucheNo ratings yet
- Roadside Design Guide, 4 Edition 2011: AASHTO - Subcommittee On Design June 11, 2012 Portland, MaineDocument31 pagesRoadside Design Guide, 4 Edition 2011: AASHTO - Subcommittee On Design June 11, 2012 Portland, MaineJohnny GaitánNo ratings yet
- Road Safety 2013 BergDocument45 pagesRoad Safety 2013 BergjoebriffaNo ratings yet
- Virginia Department of Transportation: Guardrail Installation Training ManualDocument71 pagesVirginia Department of Transportation: Guardrail Installation Training ManualLarry Wayne Sumpter, JrNo ratings yet
- Standard DetailsDocument168 pagesStandard DetailsMurathan Paksoy100% (1)
- UnitPriceList - Alberta TransportationDocument47 pagesUnitPriceList - Alberta TransportationrimranyNo ratings yet
- Tp14328e - Roadway Safety Benchmarks Over TimeDocument61 pagesTp14328e - Roadway Safety Benchmarks Over Timescimpean1913No ratings yet
- 10 Misc DesignDocument70 pages10 Misc DesignRukwende Ande DiyoNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Safety TrainingDocument25 pagesScaffolding Safety Trainingmt_powers100% (1)
- Highway Construction Specs 2013Document658 pagesHighway Construction Specs 2013Caoimhín JonesNo ratings yet
- Standardcis195!5!11 (Quality Assessment System For Completed Road Works)Document73 pagesStandardcis195!5!11 (Quality Assessment System For Completed Road Works)Ray_Mie_262100% (2)
- Davidson - Beuttel ComplaintDocument23 pagesDavidson - Beuttel ComplaintWSETNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Roadside Hazard ManagementDocument61 pagesChapter 12 Roadside Hazard ManagementPutri RannaNo ratings yet
- Metal Beam Crash Barrier (W Beam & Thrie Beam)Document6 pagesMetal Beam Crash Barrier (W Beam & Thrie Beam)Deevin Seismic SystemsNo ratings yet
- Roadway Design GuidelinesDocument488 pagesRoadway Design GuidelinesxproximaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Hand BookDocument51 pagesBridge Hand BookShreya JhaveriNo ratings yet
- Barrier RailingDocument7 pagesBarrier RailingVincentNo ratings yet
- Road Safety Audit of Balsamand Hisar Bypass Road MDR 107Document8 pagesRoad Safety Audit of Balsamand Hisar Bypass Road MDR 107Editor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Geometric Design of Roadways Is Separated Into Three LevelsDocument21 pagesGeometric Design of Roadways Is Separated Into Three LevelsChris AdaminovicNo ratings yet
- Bridge Barriers in Relation To The Crash Testing Standards: Wasim QADIRDocument8 pagesBridge Barriers in Relation To The Crash Testing Standards: Wasim QADIR정주호No ratings yet
- Warrants and Guidelines For Installation of GuardrailDocument107 pagesWarrants and Guidelines For Installation of GuardrailValentínNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding Method StatementDocument115 pagesScaffolding Method Statementbulzae100% (1)
- Steel Crash Barriers: Current ProvisionDocument9 pagesSteel Crash Barriers: Current ProvisionNIBEDITA DEYNo ratings yet
- Standard Specifications and Code of Practice For Road Bridges Section - 1 General Features of DesignDocument51 pagesStandard Specifications and Code of Practice For Road Bridges Section - 1 General Features of DesignSaurabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- 7-8. Traffic Control Devices and Night Time VisibilityDocument55 pages7-8. Traffic Control Devices and Night Time Visibilityanuj sharmaNo ratings yet
- CRITERIA-GuideRail & Median BarriersDocument15 pagesCRITERIA-GuideRail & Median BarriersMartbenNo ratings yet
- Safence Manual NZ 0718Document20 pagesSafence Manual NZ 0718sattar12345No ratings yet
- Mort&H, MSRDC, Mumbai, Maharashtra Schedules To AgreementDocument6 pagesMort&H, MSRDC, Mumbai, Maharashtra Schedules To AgreementAkshay PendurkarNo ratings yet
- Schedule C PKG 6Document13 pagesSchedule C PKG 6Pavement VasupradaNo ratings yet