Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AGO Nist Anta Gonist: Dela Cruz, Kimberly H. BSN Ii - Faye Abdellah Agonist
Uploaded by
Dela cruz Kimberly0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageAgonists activate receptors to produce a biological response, like methadone. They mimic neurotransmitters in the brain and cause muscle contraction. Antagonists block agonists from eliciting responses by binding to receptors instead. Both must be structurally similar to receptors' active sites. Both are important in human body chemistry and pharmacology, and drugs like methadone and naltrexone are used to treat opioid addiction.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pharmacology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAgonists activate receptors to produce a biological response, like methadone. They mimic neurotransmitters in the brain and cause muscle contraction. Antagonists block agonists from eliciting responses by binding to receptors instead. Both must be structurally similar to receptors' active sites. Both are important in human body chemistry and pharmacology, and drugs like methadone and naltrexone are used to treat opioid addiction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views1 pageAGO Nist Anta Gonist: Dela Cruz, Kimberly H. BSN Ii - Faye Abdellah Agonist
Uploaded by
Dela cruz KimberlyAgonists activate receptors to produce a biological response, like methadone. They mimic neurotransmitters in the brain and cause muscle contraction. Antagonists block agonists from eliciting responses by binding to receptors instead. Both must be structurally similar to receptors' active sites. Both are important in human body chemistry and pharmacology, and drugs like methadone and naltrexone are used to treat opioid addiction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
DELA CRUZ, KIMBERLY H.
BSN II – FAYE ABDELLAH
AGO ANTA
NIST GONIST
AGONIST
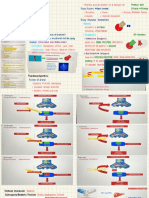
Ligands that activate a receptor to produce a biological response. An agonist is It increases
A drug which imitates the action of neurotransmitters in the brain. something that cellular function
causes a specific
A muscle whose contraction moves a part of the body directly. if they block the
physiological action of a
DRUG: methadone
response in substance that
the cell normally decreases
Both agonists and antagonists have to be structurally similar to the Cellular function
in order to fit into the active site of the receptor
Both receptor sites Those molecules
Are drugs that bind
Both are key players in the chemistry of the human body and in that bind to
to cell receptors
pharmacology. specific receptors
and cause a that prevent the
DRUG: Both used to treat opioid addiction process in agonists from
ANTAGONIST the cell to become eliciting biological
more active. response.
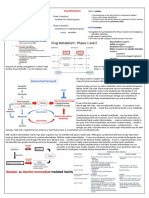
Ligands that block agonist mediated responses
A drug the blocks neurotransmitters.
A muscle whose action counteracts that of agonist.
Examples of Examples are
DRUG: Naltrexone
full agonists are naltrexone and
heroin, oxycodone, naloxone. Naloxone
methadone, is sometimes used
hydrocodone, to reverse a
morphine, opium heroin overdose.
and others.
You might also like
- PharmacologyDocument1 pagePharmacologyNabeel Hamza HamzaNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsDocument26 pagesNCM 106 PHARMACOLOGY - PrelimsKelsey Macaraig100% (3)
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument25 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeSai Sasivardhan GampaNo ratings yet
- Agonists This Means That TheyDocument5 pagesAgonists This Means That TheyMaya Audrey KanekoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Organic MedicinalsDocument7 pagesModule 1 Organic MedicinalsMARIA FREDIJEAN CARIÑONo ratings yet
- CC 2Document4 pagesCC 2Mary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics SCDocument5 pagesPharmacodynamics SCPearl PearlNo ratings yet
- Prescripcion de Antibioticos en OdontologiaDocument6 pagesPrescripcion de Antibioticos en OdontologiaSamuel Vazquez CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument39 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeArya StarkNo ratings yet
- Receptors Used As Drug Target: ReceptorDocument1 pageReceptors Used As Drug Target: ReceptorIqbal Hossain NoyonNo ratings yet
- Introducing Pharma (Drug) Cology..Document17 pagesIntroducing Pharma (Drug) Cology..monoj5859No ratings yet
- Insignis Pharma PharmacodynamicsDocument9 pagesInsignis Pharma PharmacodynamicsMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument51 pagesPharmacologyAndy MirandaNo ratings yet
- General Pharmacodynamic PrinciplesDocument7 pagesGeneral Pharmacodynamic PrinciplesKrizza Camere100% (1)
- Biochem Lec M-3Document13 pagesBiochem Lec M-3GE SalenNo ratings yet
- Pdynamics For PrescrberDocument6 pagesPdynamics For PrescrberpdladvaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Drug ActionDocument41 pagesMechanism of Drug ActionEryanda Dinata100% (1)
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument21 pagesPHARMACOLOGYAllisson BeckersNo ratings yet
- 4) Pharma LectureDocument22 pages4) Pharma LectureKhushboo IkramNo ratings yet
- Nootropics - Smart Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument6 pagesNootropics - Smart Drugs Cheat Sheet: by ViaRajaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 & 2Document14 pagesTopic 1 & 2Julianne Marie LacsentoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PkokineticsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To PkokineticspdladvaNo ratings yet
- Transes PharmacodynamicsDocument36 pagesTranses PharmacodynamicsGwyneth Koleen Lopez100% (1)
- PharmaDocument4 pagesPharmaJake RenNo ratings yet
- Orgmed Act 1 LabDocument3 pagesOrgmed Act 1 LabrlpmanglicmotNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Block 1.3 - PharmacodynamicsDocument12 pagesPharmacology Block 1.3 - Pharmacodynamicsdaleng subNo ratings yet
- Farmakodinamik Dasar Farmakodinamik DasarDocument52 pagesFarmakodinamik Dasar Farmakodinamik DasarRatnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesChapter 1 PharmacologyMaria Luisa VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document94 pagesChapter 1rab yoNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry I 1435h: Drug Structure & Pharmacological ActivityDocument59 pagesMedicinal Chemistry I 1435h: Drug Structure & Pharmacological ActivityAbd ElraHman ElbahraWyNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Behavior: Neuro Hormones. GABA, Glycine Peptides (Opiates)Document35 pagesBiological Bases of Behavior: Neuro Hormones. GABA, Glycine Peptides (Opiates)Adeel AizadNo ratings yet
- PCRO ChasticsDocument6 pagesPCRO ChasticsDaniel ThanapalNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Pharmacodynamics PhaseDocument3 pagesWeek 2 - Pharmacodynamics PhaseTEDDY BEAR PRODUCTIONNo ratings yet
- First Sem Pharma NotesDocument75 pagesFirst Sem Pharma NotesLindsay LunodNo ratings yet
- PHARMACODYNAMICS NOTES Part1Document21 pagesPHARMACODYNAMICS NOTES Part1Subhasish NayakNo ratings yet
- P 3 Drug Receptor Interactions 1 (IV)Document14 pagesP 3 Drug Receptor Interactions 1 (IV)Mai elvi KhairaniNo ratings yet
- 219 Drug Treatments For AddictionDocument5 pages219 Drug Treatments For AddictionJoe HEATHNo ratings yet
- A Brain On Cannabinoids The Role of Dopamine in Reward SeekingDocument14 pagesA Brain On Cannabinoids The Role of Dopamine in Reward SeekingJoão MaiaNo ratings yet
- Drugs and ReceptorsDocument4 pagesDrugs and ReceptorsbenjanunezgNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY Drugs Used For Cholinomimetic EffectsDocument45 pagesSUMMARY Drugs Used For Cholinomimetic EffectsMargaret RNo ratings yet
- Lecture-12: Chapter - 3: Introduction of PharmacodynamicsDocument3 pagesLecture-12: Chapter - 3: Introduction of Pharmacodynamicsবাংলা দেশNo ratings yet
- Intro + Pharmacodynamics 2Document46 pagesIntro + Pharmacodynamics 2Dana E AbuqaudNo ratings yet
- CCHM Lecture QuizzesDocument3 pagesCCHM Lecture QuizzesGrace GasconNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday LifeDocument19 pagesChemistry in Everyday LifeCricket HDNo ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacodynamics: 2.1 General Principles of Drug ActionDocument23 pages2 Pharmacodynamics: 2.1 General Principles of Drug ActionayushiNo ratings yet
- I. The Nature of Drugs: Pharmacodynamic PrinciplesDocument1 pageI. The Nature of Drugs: Pharmacodynamic PrinciplesMuez AlkeblawiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasDocument10 pagesPharmacology Pharmacodynamics: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasSultan Abdul Hamid IINo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Daily Life - Study NotesDocument38 pagesChemistry in Daily Life - Study NotesTamoghna Dey100% (1)
- BP (Protein Binding)Document13 pagesBP (Protein Binding)Babu PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry in Everyday Life: 1. DrugsDocument9 pagesChemistry in Everyday Life: 1. DrugsArya StarkNo ratings yet
- Pharma Trans Le1Document60 pagesPharma Trans Le1Kunal TribhuvanNo ratings yet
- Drugs and Receptors: DG Lambert BSC (Hons) PHDDocument4 pagesDrugs and Receptors: DG Lambert BSC (Hons) PHDantyka kawaNo ratings yet
- Prpm113: Pharmaceutical Biochemistry: Midterms CoverageDocument6 pagesPrpm113: Pharmaceutical Biochemistry: Midterms CoveragehaafizaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action For Psychiatric Drugs - EditedDocument6 pagesMechanism of Action For Psychiatric Drugs - EditedPawel kNo ratings yet
- 18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFDocument17 pages18 - Chemistry in Everyday Life (New) PDFthinkiit60% (10)
- Finals ReviewerDocument5 pagesFinals ReviewerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Ex - Effect of Physostigmine and Atropine On DRCDocument9 pagesEx - Effect of Physostigmine and Atropine On DRCAryan Pisat100% (1)
- AQA Biology GCSE Unit 4.4 Bioenergetics Higher Revision Activity MatDocument6 pagesAQA Biology GCSE Unit 4.4 Bioenergetics Higher Revision Activity MatJessica DaiNo ratings yet
- Endocannabinoid SystemDocument12 pagesEndocannabinoid SystemMaria Luiza BressanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Mechanisms in Pharmacology and TherapeuticsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Mechanisms in Pharmacology and TherapeuticsNo ratings yet
- Classification of Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument16 pagesClassification of Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsSheemaNo ratings yet
- Painkillers 5.9.12Document4 pagesPainkillers 5.9.12Saerom Yoo EnglandNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Drugs Act 1952 (Consolidated To No 23 of 1990) PDFDocument11 pagesDangerous Drugs Act 1952 (Consolidated To No 23 of 1990) PDFdesmond100% (1)
- Sedative and HypnoticsDocument37 pagesSedative and Hypnoticsprajyot khedekarNo ratings yet
- Atypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateDocument16 pagesAtypical Antidepressants - Pharmacology, Administration, and Side Effects - UpToDateMelissandreNo ratings yet
- NO Nama Harga Modal (Hna) Harga Jual (Hna)Document48 pagesNO Nama Harga Modal (Hna) Harga Jual (Hna)ressy oliviaNo ratings yet
- Prescription Drug Abuse in Los Angeles County: Background and Recommendations For ActionDocument20 pagesPrescription Drug Abuse in Los Angeles County: Background and Recommendations For ActionSouthern California Public RadioNo ratings yet
- How To Start The Conversation: Avoid? Ask & Assess Advise & ActDocument4 pagesHow To Start The Conversation: Avoid? Ask & Assess Advise & ActPSmNo ratings yet
- PT - Dayaanugerah Dewatasakti Jl. Taman Jemursari Selatan 1/ 7 Surabaya Nama Produck HNA Hna+Ppn Nama Produck HNA Hna+PpnDocument16 pagesPT - Dayaanugerah Dewatasakti Jl. Taman Jemursari Selatan 1/ 7 Surabaya Nama Produck HNA Hna+Ppn Nama Produck HNA Hna+PpnYuliSetiyantoNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Medications During PregnancyDocument20 pagesPsychotropic Medications During PregnancyMaria Von ShaftNo ratings yet
- Pemba Has AnDocument15 pagesPemba Has AnYuyun PujiartiNo ratings yet
- Anticholinergic & Antispasmodic AgentDocument31 pagesAnticholinergic & Antispasmodic AgentSaha DirllahNo ratings yet
- NarcanDocument1 pageNarcanKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Pre Gabal inDocument1 pagePre Gabal inDian ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Taiwan API Manufacturer ListDocument4 pagesTaiwan API Manufacturer Listkalyani dynamicsNo ratings yet
- Basic PsychoPharma MnemonicsDocument21 pagesBasic PsychoPharma MnemonicsJoseph Rommel Castro CortezNo ratings yet
- Health 9 Q2 M2Document16 pagesHealth 9 Q2 M2Alyssa Isabel De NievaNo ratings yet
- AripiprazoleDocument2 pagesAripiprazoleKrisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- DAMS PSYCHIATRY Extra Notes For Students-1Document31 pagesDAMS PSYCHIATRY Extra Notes For Students-1meetsinhhermaNo ratings yet
- Ceramah Harry PotterDocument94 pagesCeramah Harry PotterNor Ba'yahNo ratings yet
- Daftar Ed DekatDocument1 pageDaftar Ed DekatAbePrasetyaNo ratings yet
- Med Chem IDocument5 pagesMed Chem ISaqline MondalNo ratings yet
- Drugs) : NO Jenis Obat (The Dosis (Dosage) Jumlah (Amount) NO Jenis Obat (The Drugs) Dosis (Dosage) Jumlah (Amount)Document2 pagesDrugs) : NO Jenis Obat (The Dosis (Dosage) Jumlah (Amount) NO Jenis Obat (The Drugs) Dosis (Dosage) Jumlah (Amount)Ria FiNo ratings yet
- 2023.07.25 - Knox County Forensic Center 2022 Reports Released (DRD Report)Document36 pages2023.07.25 - Knox County Forensic Center 2022 Reports Released (DRD Report)WVLT NewsNo ratings yet
- Shreya Thokal - Drug Addiction Biology ProjectDocument15 pagesShreya Thokal - Drug Addiction Biology Project28-Shreya ThokalNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetics, IV Sedation and Pain ManagementDocument70 pagesLocal Anesthetics, IV Sedation and Pain ManagementHosam GomaaNo ratings yet
- Neuroleptic Malignant SyndromeDocument18 pagesNeuroleptic Malignant Syndromedrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs-Good LectureDocument55 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs-Good LecturealijanmarwatNo ratings yet
- Decoding An Epidemic: Getting Beyond Conventional WisdomDocument39 pagesDecoding An Epidemic: Getting Beyond Conventional WisdomNational Press FoundationNo ratings yet
- Drug Education and Vice ControlDocument8 pagesDrug Education and Vice ControlElhen Grace ParchamentoNo ratings yet