Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vaginitis: Definition: Infectious Disease Affecting The Vagina, Only Rarely Affecting The Vulva
Uploaded by
Suhas Ingale0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesmedical seminar
Original Title
vaginitis
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmedical seminar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesVaginitis: Definition: Infectious Disease Affecting The Vagina, Only Rarely Affecting The Vulva
Uploaded by
Suhas Ingalemedical seminar
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as RTF, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
VAGINITIS
Definition: Infectious disease affecting the vagina,only rarely affecting the vulva.
Causes:
Polymicrobial; Gardenella Vaginalis, Mobiluncus species, Mycoplasma
Hominis, Peptostreptococcus, other various anaerobes , including Prevotella,
Bacteroides ,and
Fusobacterium.
There is shift from a healthy lactobacilli based endogenous flora to
anaerobically based
endogenous flora.
Rectal reservoir of organism leading to autoinfection.
Risk factors: Controversial regarding multiple sexual partners
IUD.
Signs and Symptoms:
Unpleasant vaginal odour,musty or fishy, exacerbated immediately after
intercourse.
Thin gray white vaginal discharge, mildle adherentto vaginal walls.
10-30% with vaginal/vulval irritation.
10% with froathy discharge.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
N.Gonorrhoea.
Chlamydia.
Trichomonas.
E.Coli.
Staphylococci.
Fungal.
Lab Investigation:
Examination of the vaginal discharge by saline wet mouth -
A drop of discharge is collected by pipette is mixed with saline on a warm
glass slide & a cover
slide is placed over it. The wet film is immediately examined under hig
power microscope when
the parasites are recognised by the rotatory movements.
Plenty of pus cells, organisms,
epithelial cells are seen on
Treatment:
Metronidazole 500 mg bid for 7 days
Clindamycin 450 mg tds for 7 days or 2% vaginal cream for 7 days,or
metronidazole
vaginal cream for bacterial vaginosis.
Flagyl is given to husband if there is penile itching.
During treatment period, sex act is suspended.
Metronidazole course is followed by Tab Clotrimazole 100 mg inserted deep
in the vagina daily
at bed time for 6 nights.
For vulval itching Surfaz Cream or Candid V gel is applied on vulva twice
daily for 10 days.
Prevention:
Maintain good hygeine.
Use of condoms for sexual intercourse.
Complications:
Uncommon but include :
adnexal tenderness
PID
Intrauterine infections
You might also like
- Genital Tract Infections Guide: TV, VVC, BV, CervicitisDocument70 pagesGenital Tract Infections Guide: TV, VVC, BV, CervicitisAygulNo ratings yet
- Pruritis Vulvae, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPruritis Vulvae, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Lec.12 Genital Tract Infection (Part 1)Document26 pagesLec.12 Genital Tract Infection (Part 1)شريف محمد حسين شريف يوسفNo ratings yet
- No More Yeast Infection: The Complete Guide on Yeast Infection Symptoms, Causes, Treatments & A Holistic Approach to Cure Yeast Infection, Eliminate Candida, Naturally & PermanentlyFrom EverandNo More Yeast Infection: The Complete Guide on Yeast Infection Symptoms, Causes, Treatments & A Holistic Approach to Cure Yeast Infection, Eliminate Candida, Naturally & PermanentlyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Lower Female Genital Tract InfectionsDocument42 pagesLower Female Genital Tract InfectionsAwal Sher khanNo ratings yet
- Unit-5-4 Benign Conditions of GenitaliaDocument12 pagesUnit-5-4 Benign Conditions of GenitaliaMarkos HabtamuNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhea 1Document26 pagesGonorrhea 1Alessandra Franchesca CortezNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Jasmin P. EgargueDocument33 pagesSexually Transmitted Diseases: Jasmin P. EgargueLiza AingelicaNo ratings yet
- Lower Genital Tract Infections & Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument38 pagesLower Genital Tract Infections & Sexually Transmitted Diseasesraed faisalNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge Causes and TreatmentDocument47 pagesVaginal Discharge Causes and TreatmentGladstone AsadNo ratings yet
- Duh Tubuh Wanita, DR SAYU.,SpKK, WMDocument62 pagesDuh Tubuh Wanita, DR SAYU.,SpKK, WMdickypranataNo ratings yet
- Yayin Ob: 2. Trichomonas VaginalisDocument3 pagesYayin Ob: 2. Trichomonas VaginalisYayin PestañoNo ratings yet
- Pid 180131145647 1Document41 pagesPid 180131145647 1Smriti GroverNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Infections GuideDocument91 pagesGynecologic Infections GuideDegefaw BikoyNo ratings yet
- VaginitisDocument27 pagesVaginitisdrtancerNo ratings yet
- Approach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCDocument16 pagesApproach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCSupekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCDocument16 pagesApproach To Vaginal Discharge: DR Faisal Al Hadad Consultant of Family Medicine & Occupational Health PSMMCSupekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- How STDs SpreadDocument55 pagesHow STDs Spreadjoshy221196No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmmited Diseases: Presenter: Nyangara Rajabu Facilitator: Isaac U. MDocument31 pagesSexually Transmmited Diseases: Presenter: Nyangara Rajabu Facilitator: Isaac U. MnyangaraNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyDocument19 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections and PregnancyBeyins TiuNo ratings yet
- Genital Tract InfectionDocument96 pagesGenital Tract InfectiondhitaapriliaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory DiseasesDocument83 pagesInflammatory DiseasesIfabiyi OlaniyiNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Fungal InfectionsDocument15 pagesVaginal Fungal InfectionsBalsc Bals BalscNo ratings yet
- Infections of Female Genital TractDocument67 pagesInfections of Female Genital TractSana AftabNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmia neonatorumIIDocument29 pagesOphthalmia neonatorumIIgopscharanNo ratings yet
- Gynecologic Nursing GuideDocument252 pagesGynecologic Nursing GuideQueenete Vallestero CastromeroNo ratings yet
- Lower Genital Tract Infection: Prepared By: Nibal Shawabkeh Supervised By: Dr. Saada JaberDocument63 pagesLower Genital Tract Infection: Prepared By: Nibal Shawabkeh Supervised By: Dr. Saada JaberSupekshya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Lower Genital Tract InfectionDocument51 pagesLower Genital Tract InfectionSarisa SupawimonNo ratings yet
- Vaginal InfectionsDocument24 pagesVaginal InfectionsIvory TranceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 102 Vulvovaginitis: PhysiologyDocument5 pagesChapter 102 Vulvovaginitis: PhysiologyMark LopezNo ratings yet
- CandidiasisDocument3 pagesCandidiasisYanna Habib-MangotaraNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument3 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseaseBrianna ValerioNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis: Etiologic Agent-Candida Albicans. Some Types of Candida Are Resistant To The AntifungalsDocument3 pagesCandidiasis: Etiologic Agent-Candida Albicans. Some Types of Candida Are Resistant To The AntifungalskyawNo ratings yet
- Activity 18 Fungal InfectionsDocument41 pagesActivity 18 Fungal InfectionsLorena Sobrepeña ApiladoNo ratings yet
- 1 Gynecologic Infections 2Document109 pages1 Gynecologic Infections 2Girum SolomonNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology: Gum, Fertility, Contraception, and UrogynaecologyDocument46 pagesGynaecology: Gum, Fertility, Contraception, and UrogynaecologyOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge and Vulvar Disease FinalDocument61 pagesVaginal Discharge and Vulvar Disease FinalrohitNo ratings yet
- Slide 1 STIDocument50 pagesSlide 1 STIMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan Ke-3 REPRODocument29 pagesPertemuan Ke-3 REPROAdi Joyo NegoroNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument132 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesanitacharisNo ratings yet
- Gynaecological InfectionDocument45 pagesGynaecological InfectionEbrahim Adel Ali AhmedNo ratings yet
- Leukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.13032018 PDFDocument128 pagesLeukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.13032018 PDFrujiraNo ratings yet
- Bacterial VaginosisDocument2 pagesBacterial VaginosisMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Gonorrhoea: Signs, Symptoms, Treatment and PreventionDocument16 pagesGonorrhoea: Signs, Symptoms, Treatment and PreventionBerle Joy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Maternal LEC - Week 11 - TransesDocument4 pagesMaternal LEC - Week 11 - TransesEcka- EckaNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted Infections GuideDocument11 pagesSexually Transmitted Infections Guidemark OrpillaNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Discharge + PruritisDocument56 pagesVaginal Discharge + PruritisEkoApriandhiNo ratings yet
- Vulvovaginitis: by James Holencik, DODocument70 pagesVulvovaginitis: by James Holencik, DOSyarifa YuliaNo ratings yet
- Definition-: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Is A Sexually Transmitted Inflammatory Condition of TheDocument7 pagesDefinition-: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Is A Sexually Transmitted Inflammatory Condition of TheanweshaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Sti'S: DR - Aruna Kumari.D. MBBS, DVD, MHA QPCC&C, Ministry of HealthDocument56 pagesOverview of Sti'S: DR - Aruna Kumari.D. MBBS, DVD, MHA QPCC&C, Ministry of HealthDCBNo ratings yet
- Dr. Eka's Guide to Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument67 pagesDr. Eka's Guide to Sexually Transmitted Infectionsuut14No ratings yet
- Ask Epk UuuuDocument14 pagesAsk Epk Uuuuslamet raharjoNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma of The Cervix LDocument29 pagesCarcinoma of The Cervix Lapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Definition:: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (Pid)Document20 pagesDefinition:: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (Pid)Malueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Gram Negative CocciDocument19 pagesLecture - Gram Negative CocciDina MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Synonyms Causative Agents Incubatiob Period Mode of Transmission Signs and Symptoms Period of Communicability Diagnostic Test Medical Management Nursing Management ComplicationsDocument13 pagesSynonyms Causative Agents Incubatiob Period Mode of Transmission Signs and Symptoms Period of Communicability Diagnostic Test Medical Management Nursing Management ComplicationsYnah DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Full RujiraLeukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.02102017 PDFDocument129 pagesFull RujiraLeukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.02102017 PDFrujiraNo ratings yet
- DiphtheriaDocument25 pagesDiphtheriaRohan TejaNo ratings yet
- Pathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionDocument1 pagePathogens of The Vagina-Annie Espinosa - This Is The Revised VersionMicroposterNo ratings yet
- Weil's DiseaseDocument2 pagesWeil's DiseaseSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument2 pagesWhooping CoughSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument2 pagesDefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Wilson'S Disease: DefinitionDocument4 pagesWilson'S Disease: DefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Vulvular Ulcers: 1) Septic Ulcers: Caused byDocument3 pagesVulvular Ulcers: 1) Septic Ulcers: Caused bySuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- FemurDocument8 pagesFemurSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Definition: An Ectopic Pregnancy Is One in Which The Fertilized Ovum IsDocument4 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Definition: An Ectopic Pregnancy Is One in Which The Fertilized Ovum IsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
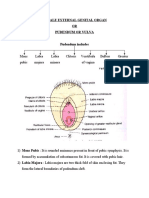
- Female External Genital OrganDocument6 pagesFemale External Genital OrganSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Fibromyoma of UterusDocument5 pagesFibromyoma of UterusSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Depression 1Document5 pagesDepression 1Suhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Femoral Nerve It Is Marked by Joining The Following Two PointsDocument3 pagesFemoral Nerve It Is Marked by Joining The Following Two PointsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Femoral Triangle Anatomy and ContentsDocument4 pagesFemoral Triangle Anatomy and ContentsSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Causticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionDocument6 pagesCausticum: Common Name: - Tinctura Acris Sine Kali First Prover - Dr. Hahnneman IntroductionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Eczema SDocument7 pagesEczema SSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ECLAMPSIADocument2 pagesECLAMPSIASuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis: DefinitionDocument5 pagesDermatitis: DefinitionSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ECZEMA: CAUSES, TYPES & HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENTDocument5 pagesECZEMA: CAUSES, TYPES & HOMEOPATHIC TREATMENTSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Carbo VegetabilisDocument6 pagesCarbo VegetabilisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Chole Lithia SisDocument1 pageChole Lithia SisSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Calcarea CarbinicaDocument6 pagesCalcarea CarbinicaSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Constitution: Constitution: Definition: Human Being Recieves Some Features of Mind & Body From TheDocument4 pagesConstitution: Constitution: Definition: Human Being Recieves Some Features of Mind & Body From TheSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- BoraxDocument4 pagesBoraxSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Conium Maculatum: Common Name: Prover: FamilyDocument4 pagesConium Maculatum: Common Name: Prover: FamilySuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- BELLADONNADocument2 pagesBELLADONNASuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Autoimmune DisordersDocument33 pagesAutoimmune DisordersSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Cadaveric SpasmDocument3 pagesCadaveric SpasmSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The NoseDocument9 pagesAnatomy of The NoseSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction - : Complete Repertory To The Homoeopathic Materia Medica On Disease of The Eyes BerridgeDocument6 pagesIntroduction - : Complete Repertory To The Homoeopathic Materia Medica On Disease of The Eyes BerridgeSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- Aurum MetallicumDocument6 pagesAurum MetallicumSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- ANAEMIASDocument15 pagesANAEMIASSuhas IngaleNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- CBT Strategies: CBT Strategies for Overcoming Panic, Fear, Depression, Anxiety, Worry, and AngerFrom EverandCBT Strategies: CBT Strategies for Overcoming Panic, Fear, Depression, Anxiety, Worry, and AngerNo ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- How To Understand Your Anger For Better Mental Health: How To Control Emotions And Eliminate Stress In Your LifeFrom EverandHow To Understand Your Anger For Better Mental Health: How To Control Emotions And Eliminate Stress In Your LifeNo ratings yet
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Inmersion Into The Shadown Effective Method Of Dark Psychology: How To Use The Best Persuasion Techniques To Achieve Your Best Goals And How To Protect Yourself From Being ManipulatedFrom EverandInmersion Into The Shadown Effective Method Of Dark Psychology: How To Use The Best Persuasion Techniques To Achieve Your Best Goals And How To Protect Yourself From Being ManipulatedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)