Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abstract
Uploaded by
Udit kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract
Uploaded by
Udit kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
The presence of natural fractures in the subsurface makes the activity of the oil well extremely difficult.
One of the most critical functions for drilling mud is to maintain the bottom hole pressure in a well to
prevent invasions of undesirable high-pressure influxes (oil / gas / water), which can lead to a significant
mud loss in the formation of a well and thus to an adverse effect on the integrity of pressurized water.
The purpose of this paper is to conduct a thesis on fluid flow through natural fractures through
computer fluid dynamics (CFD), which will provide an integrated understanding of flow in fractured
media. The analysis was conducted using an ANSYS (Fluent) 3-dimensional stable CFD model. The model
describes fracture as an empty space between two circular disks for simplicity and validation purposes.
In addition, single-phase fluid is known to flow through fractures. Correlations for determining the width
and invasion radius of the fractures for special mud-rheological properties were defined by resolving the
flow equations in the model. A similar association can be formed with knowledge of the rheological
properties of drilling fluid before drilling starts and after the loss of circulation, which are of great help
to take immediate action during loss of circulation, i.e. determination of the size of lost circulatory
particles and are also useful at a well developmental stage in the determination of the area affected.
You might also like
- Mathematical Modeling of Gas Volumetric Flow Rate: Akinade AkinwumiDocument5 pagesMathematical Modeling of Gas Volumetric Flow Rate: Akinade AkinwumiUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- 15 KimDocument10 pages15 KimUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment For MID Topic: Basics of BlastingDocument65 pagesAssignment For MID Topic: Basics of BlastingUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- A Phased Approach To Mine Dewatering PDFDocument8 pagesA Phased Approach To Mine Dewatering PDFUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment For MID Topic: Mine Planning & DesignDocument57 pagesAssignment For MID Topic: Mine Planning & DesignUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Name: Udit Kumar Das Roll: 23Document4 pagesName: Udit Kumar Das Roll: 23Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- (2020) SAS Affiliate ResourcesDocument28 pages(2020) SAS Affiliate ResourcesUdit kumar100% (2)
- Ore 10000 Ton/d HMDS, TPH Nos. Operator 40 11 11 65 7 7 105 5 5 150 4 4 210 3 3 270 3 3Document4 pagesOre 10000 Ton/d HMDS, TPH Nos. Operator 40 11 11 65 7 7 105 5 5 150 4 4 210 3 3 270 3 3Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Mining Science and Technology: Martin Brook, Bruce Hebblewhite, Rudrajit MitraDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Mining Science and Technology: Martin Brook, Bruce Hebblewhite, Rudrajit MitraUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- November 2012 - October 2013Document7 pagesNovember 2012 - October 2013Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- Future Prospect Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in Bangladesh: Economic and Technological Case StudiesDocument15 pagesFuture Prospect Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in Bangladesh: Economic and Technological Case StudiesMahmudur RahmanNo ratings yet
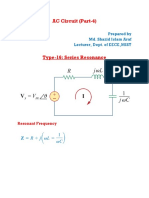
- AC Circuit (Part-4)Document14 pagesAC Circuit (Part-4)Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- HSC Ev Higher Mathematics 1st Paper 3rd Chapter Note PDFDocument19 pagesHSC Ev Higher Mathematics 1st Paper 3rd Chapter Note PDFUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Eece PDFDocument19 pagesEece PDFUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit (Part-2) : Prepared by Md. Shazid Islam Araf Lecturer, Dept. of EECE, MISTDocument21 pagesAC Circuit (Part-2) : Prepared by Md. Shazid Islam Araf Lecturer, Dept. of EECE, MISTUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- HSC Ev Higher Mathematics 1st Paper 3rd Chapter Note PDFDocument19 pagesHSC Ev Higher Mathematics 1st Paper 3rd Chapter Note PDFUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit (Part-1)Document17 pagesAC Circuit (Part-1)Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- Eng Mechanics1Document19 pagesEng Mechanics1Udit kumarNo ratings yet
- Lec-06 Dewatering MethodsDocument23 pagesLec-06 Dewatering MethodsUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- CFD Modeling of WBGT For An Offshore PlatformDocument10 pagesCFD Modeling of WBGT For An Offshore PlatformUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Perforation Geometry Influence On Flow Performance Using CFD PDFDocument17 pagesUnderstanding Perforation Geometry Influence On Flow Performance Using CFD PDFUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Using The Coal Mine Roof Rating (CMRR) To Assess Roof Stability in U.S. Coal MinesDocument8 pagesUsing The Coal Mine Roof Rating (CMRR) To Assess Roof Stability in U.S. Coal MinesUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Hse in Mine VentilationDocument14 pagesHse in Mine VentilationUdit kumarNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)