Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS Labeling
Uploaded by
Rianna Ramos0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesChemistry Lecture
Original Title
Unit02- Hazard Comm. GHS Labeling
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentChemistry Lecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views2 pagesUnit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS Labeling
Uploaded by
Rianna RamosChemistry Lecture
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Lesson 01: CHEMICAL SAFETY 1.
Product Name or Identifier: name of the substance
contained inside the labeled container.
Unit 02: Hazard Communication – GHS Labeling
2. Signal Word: can either be “Warning” or “Danger”,
Hazardous Substances – cause harmful or adverse used to indicate the relative severity of the product
effects to those that they are exposed to. wherein “Danger” indicates more severe hazards and
The GHS Labels “Warning” for less severe hazards.
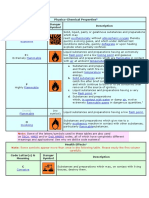
GHS or Globally Harmonized System of Classification 3. Precautionary Symbols or Pictograms:
and Labelling of Chemicals representation of the classification of the chemical hazard
the product has to expose to its user.
- Administered by the United Nations
4. Physical, Health and Environmental Hazard
- Requires manufacturers, importers and
Statements: standardized and assigned phrases that
downstream users and distributors of chemical
describers the hazard based on its classification.
substances and mixtures.
- Objective of unifying the communication on 6. Supplier Identification: gives the name, address, and
hazardous products and of replacing the specific contact details of the manufacturer.
regulations in countries around the world.
7. Supplemental Information: includes additional
GHS Label Template information that the customer requests to include.
The GHS Pictograms and their Representations
Oxidizers – can be solids, liquids, or gases;
materials that are not necessarily combustible
but may generally yield oxygen which may
contribute to or cause combustion reactions.
Flammable Solids – can either be readily
combustible or may cause or contribute to fire
through friction; can be in the form of granules,
powder and pastry which is easily ignited when
come into contact with an ignition source.
Flammable Liquids – with flash points of not
more than 93℃.
Flammable Gases – flammable range in air at
20℃ and at standard pressure of 101.3kPa.
Flammable Aerosols – any gas that (1) was but are fully reversible twenty-one days after
compressed, liquified or dissolved under application.
pressure with a non-refillable container that Serious Eye Damage – production of eye
was made up of metal, glass or plastic and tissue damage or serious physical decay of
(2) contains any component classifies as vision that is not reversible twenty-one days
flammable solid, liquid or gas. after the application.
Emits Flammable Gas – can either be solids Dermal Sensitization – caused by substances
or liquids that are liable to become that induce allergic reaction following
spontaneously flammable or to give off contact to the skin.
flammable gases when get in contact in Acute Toxicity – substances assigned to the
water. Five Toxicity Categories on the basis of LD50
Pyrophorics – substances which can either (oral and dermal) and LC50 (inhalation).
be solids or liquids that are liable to ignite Carcinogens – chemical substances that induce
within five minutes after having been in cancer or increase its incidence.
contact with air even at very small
quantities.
Self – Heating Substances – solids or liquids
that are not classified as pyrophorics but is
liable to self-heat when comes in contact
with air even in the absence of energy.
Self – Reactive Substances - either (1)
thermally unstable liquids or (2) solids that
may undergo strong exothermal
decomposition even in the absence of the
participation of oxygen but (3) are not
classified as corrosives, explosive or organic
peroxides under the GHS.
Organic Peroxides – solid or liquid substance Respiratory Sensitizers – chemical substances
that contains bivalent O – O structure; these that cause the airways to be hypersensitive after
may be liable to explosive decomposition, inhalation of the substance.
burn rapidly, be sensitive to impact or Reproductive Toxicity – may cause infertility,
friction or react dangerously to other adverse effects on sexual functions and/or
substances. developmental toxicity on the offspring.
Corrosive to Metals – materially damaged Target Organ Systemic Toxicity – may cause
metals through chemical reaction. reversible or irreversible damages on specific
Explosives – substances or mixtures of body organs which affects their functions.
substances that can either be solids or Germ Cell Mutagenicity – may cause gene
liquids which in their selves are capable to mutations of organisms to occur.
produce gas, by a chemical reaction, at such Aspiration Toxicity – severe acute effects of
speed as to cause damage to the varying degrees of pulmonary injury or death
surroundings. following aspiration.
Gases Under Pressure – gases that are Acute Aquatic Toxicity – causes injury to
contained inside a receptacle with a pressure aquatic organisms after a short-term exposure to
of not less than 280 Pascal to 20℃. the substances.
Substances Labeled with Skin Corrosion – Chronic Aquatic Toxicity – causes adverse
substances that cause irreversible skin effects to aquatic organisms during exposures
damage following an application of a test based on the organisms life cycle.
substance for four hours.
Skin Irritation – considered when the
substance causes a reversible damage to skin
following an application of a test substance
for four hours.
Substance that causes Eye Irritation – causes
changes in the eye after an application of a
test substance to the front surface of the eye,
You might also like
- HILTI Anchor FasteningDocument91 pagesHILTI Anchor FasteningkstayroskNo ratings yet
- IRC 58 (Plain Jointed Rigid Pavements Design Highways)Document61 pagesIRC 58 (Plain Jointed Rigid Pavements Design Highways)herculesbhai73% (11)
- Box Culvert - ISDocument14 pagesBox Culvert - ISShyamontika Choudhury ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 05 - Thermodynamics - Rianna Joyce R. RamosDocument3 pagesLesson 05 - Thermodynamics - Rianna Joyce R. RamosRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Spec SCAPSA Metallic Material Selected StdsDocument107 pagesSpec SCAPSA Metallic Material Selected StdsSwath M MuraliNo ratings yet
- Hazcom & ChemsafDocument66 pagesHazcom & ChemsafJohn Brix BalisterosNo ratings yet
- How To Segregate Dangerous GoodsDocument15 pagesHow To Segregate Dangerous GoodsSurya DharmaNo ratings yet
- BRE 462 Steel Structures Supporting Composite Floor Slabs FireDocument12 pagesBRE 462 Steel Structures Supporting Composite Floor Slabs FireUmmar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 IMDG CodeDocument32 pagesLesson 1 IMDG CodeBernard Mamora100% (2)
- Hazard Communication: Objective of HAZCOM As Per OSHADocument4 pagesHazard Communication: Objective of HAZCOM As Per OSHAMewnEProwtNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Calorimetry Calorimetry Is A Method of Measuring The Heat Transfer Within A Chemical Reaction or OtherDocument7 pagesExperiment 2: Calorimetry Calorimetry Is A Method of Measuring The Heat Transfer Within A Chemical Reaction or OtherRianna Ramos67% (3)
- Workplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsFrom EverandWorkplace Vocabulary for Esl Students: With Exercises and TestsNo ratings yet
- GS AFES 3 Pond-ChimneyDocument52 pagesGS AFES 3 Pond-ChimneyHabibz ZarnuJi100% (1)
- ChemicAL SAFETY & HAZARD COMMUNICATIONDocument67 pagesChemicAL SAFETY & HAZARD COMMUNICATIONBosh Cosh TrainingsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quiz 1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesChemistry Quiz 1 ReviewerHanzly AurellanoNo ratings yet
- w2 - 02 - Chem Safety - GHS LabelsDocument6 pagesw2 - 02 - Chem Safety - GHS LabelsJohn Rave Manuel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Class 1: Explosives: Items in HouseholdDocument8 pagesClass 1: Explosives: Items in HouseholdKenneth SibonghanoyNo ratings yet
- 1.2 TerminologiesDocument7 pages1.2 TerminologiesPearl DelayNo ratings yet
- Health HazardDocument2 pagesHealth HazardSeptia suciNo ratings yet
- Lecture Hazards and LabelsDocument8 pagesLecture Hazards and LabelsMenna KamelNo ratings yet
- Safety Training For Police MaintenanceDocument8 pagesSafety Training For Police MaintenanceGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Lectures Chemical Hygeine Plan 1Document11 pagesLectures Chemical Hygeine Plan 1Menna KamelNo ratings yet
- MSDS MARINE FUEL VLSFO - DSJDocument10 pagesMSDS MARINE FUEL VLSFO - DSJdsjscribd100% (3)
- Chemical SafetyDocument47 pagesChemical SafetyFlorence JoieNo ratings yet
- Chemical SafetyDocument58 pagesChemical SafetyHanzly AurellanoNo ratings yet
- Classification of Dangerous Goods: Class 1:explosivesDocument5 pagesClassification of Dangerous Goods: Class 1:explosivesSherwin Delfin CincoNo ratings yet
- Dangerous GoodsDocument5 pagesDangerous GoodsFrancis Charles AriolaNo ratings yet
- Cluster 3Document10 pagesCluster 3Anselm Ted MajanilNo ratings yet
- MSDS NX-VG2Document4 pagesMSDS NX-VG2Rohit Soni100% (1)
- Dangerous GoodsDocument26 pagesDangerous GoodsAngelo AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Un Classification Codes For Dangerous GoodsDocument2 pagesUn Classification Codes For Dangerous GoodsOgala OscarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sherif Kandel: Under SupervisorDocument10 pagesDr. Sherif Kandel: Under Supervisormzmameen11No ratings yet
- AromaticConcentrateGrade1 SDS AMER USENDocument16 pagesAromaticConcentrateGrade1 SDS AMER USENsainath iyerNo ratings yet
- WHMIS 2015 Handout3Document18 pagesWHMIS 2015 Handout3Prophet Yves Oscar EliasNo ratings yet
- PictogramDocument15 pagesPictogramCasili EjNo ratings yet
- Chemical ManagementDocument9 pagesChemical Managementeleejohn059No ratings yet
- Chemical Safety SignsDocument2 pagesChemical Safety SignsPaolo CabatoNo ratings yet
- Format - MSDSDocument4 pagesFormat - MSDSAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Bopp Material Safety Data SheetDocument4 pagesBopp Material Safety Data SheetAK ZaiNo ratings yet
- Classes of Hazardous Chemicals - 8.09Document14 pagesClasses of Hazardous Chemicals - 8.09Christian MakandeNo ratings yet
- Abs Irpc Polimaxx SP100 MSDSDocument4 pagesAbs Irpc Polimaxx SP100 MSDScountzeroaslNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Good Worksheet 2 A - Kelompok 4 - D4LB2ADocument6 pagesDangerous Good Worksheet 2 A - Kelompok 4 - D4LB2AFara DilaNo ratings yet
- Element 8 Control of Waste and Land UseDocument33 pagesElement 8 Control of Waste and Land Usezaigham naqviNo ratings yet
- MSDS - Curran SelulosaDocument7 pagesMSDS - Curran SelulosaRivaldi Ahmad HaedirNo ratings yet
- TBT Chemical SafetyDocument2 pagesTBT Chemical SafetySaddiqNo ratings yet
- Unit 2ADocument4 pagesUnit 2ANella NellaNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Goods Classifications - 112Document7 pagesDangerous Goods Classifications - 112Mauro CunhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical SafetyDocument28 pagesChemical SafetyYves CaraangNo ratings yet
- MSDSS1Document4 pagesMSDSS1PeterWayNo ratings yet
- H2O2 50% GHS SDS Rev 6 PDFDocument9 pagesH2O2 50% GHS SDS Rev 6 PDFBayu MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Mexican Regulation SCTDocument43 pagesMexican Regulation SCTJemalNo ratings yet
- History: o o o o o o o oDocument4 pagesHistory: o o o o o o o oChristian ConsignaNo ratings yet
- Assessments Lesson 1 Unit 1Document4 pagesAssessments Lesson 1 Unit 1Thana EsmerayNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet Formic AcidDocument9 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet Formic AcidMuhammad Aasim HassanNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheets, Labels, and Hazardous Chemical EmergenciesDocument1 pageSafety Data Sheets, Labels, and Hazardous Chemical EmergenciesGhost_suolNo ratings yet
- DG Storage - Handling Rev2Document84 pagesDG Storage - Handling Rev2Chuck AnsphilNo ratings yet
- Hazard Assessment Before Lab WorkDocument22 pagesHazard Assessment Before Lab WorkVikas NigamNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Chemical Safety PDFDocument13 pagesModule 5 Chemical Safety PDFMR YOSONo ratings yet
- Chemistry Safety - MANAOGDocument3 pagesChemistry Safety - MANAOGCassiel Iris CaceresNo ratings yet
- Glenn Hazardous ClassesDocument5 pagesGlenn Hazardous ClassesGlenn Russel PinedaNo ratings yet
- Physico-Chemical Properties Code Letter(s) & Meaning Danger Symbol DescriptionDocument2 pagesPhysico-Chemical Properties Code Letter(s) & Meaning Danger Symbol DescriptionAydin ManafovNo ratings yet
- Envi Sci 1Document1 pageEnvi Sci 1TRISHAANN RUTAQUIONo ratings yet
- Working With Security: Practice # 1 Degree of Danger of Chemical CompoundsDocument4 pagesWorking With Security: Practice # 1 Degree of Danger of Chemical CompoundsCod9811No ratings yet
- Safety in The LaboratoryDocument16 pagesSafety in The LaboratoryChristian EduardoNo ratings yet
- DOT LabelsDocument1 pageDOT LabelsCoronavilleNo ratings yet
- LB-10 SDS (English) - 20160630Document5 pagesLB-10 SDS (English) - 20160630agustya alifia el hakim0% (1)
- Laboratory 2 Materials and ProcessesDocument5 pagesLaboratory 2 Materials and ProcessesUnknown MeNo ratings yet
- History of ElectronicsDocument1 pageHistory of ElectronicsRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- CP and IntroDocument3 pagesCP and IntroRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Rainwater As An Alternative Source of ElectricityDocument3 pagesRainwater As An Alternative Source of ElectricityRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Understanding The World of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageUnit 01 Understanding The World of ThermodynamicsRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument12 pagesNothingRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- STATSDocument4 pagesSTATSRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument11 pagesUnderstanding The SelfRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Power Generation For A Water Treatment System and Method of Supplying Electricity Using A Flow of LiquidDocument8 pagesHydro-Power Generation For A Water Treatment System and Method of Supplying Electricity Using A Flow of LiquidRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- RRL Online GamesDocument3 pagesRRL Online GamesRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and TsunamiDocument3 pages2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and TsunamiRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- An Approach For Quick Estimation of Maximum Height of Capillary RiseDocument5 pagesAn Approach For Quick Estimation of Maximum Height of Capillary RiseMaha KaryaNo ratings yet
- Adb Acp 1000Document2 pagesAdb Acp 1000vietpuntocomNo ratings yet
- SCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityDocument39 pagesSCCS1624 Eng PH Salinity SodicityMenzi CekwaneNo ratings yet
- Mineral and Power Resources of Chhota Nagpur RegionDocument10 pagesMineral and Power Resources of Chhota Nagpur RegionJasvinder Singh0% (1)
- Amberlite™ Hpr2800 H Ion Exchange Resin: Product Data SheetDocument4 pagesAmberlite™ Hpr2800 H Ion Exchange Resin: Product Data SheetsamarthNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Eot Crane Hook For Various Cross SectionsDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Eot Crane Hook For Various Cross SectionsFiroz PawaskarNo ratings yet
- Is 5082 1998 PDFDocument11 pagesIs 5082 1998 PDFRa Hul0% (1)
- Bk91 1310 CPF Ved 016 Qac h13 0001 - B - Positive Material Identification Procedure For Basket FiltersDocument8 pagesBk91 1310 CPF Ved 016 Qac h13 0001 - B - Positive Material Identification Procedure For Basket FiltersPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- VLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 CMOS TechnologyDocument25 pagesVLSI Technology Dr. Nandita Dasgupta Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 CMOS TechnologysrividyabadavathNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6. Sewage Disposal SystemDocument7 pagesMODULE 6. Sewage Disposal SystemMatt ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Ug-116 - RT4Document3 pagesUg-116 - RT4miteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Batangas State University College of Engineering, Architecture & Fine ArtsDocument4 pagesBatangas State University College of Engineering, Architecture & Fine ArtsJohn Kevin de CastroNo ratings yet
- Quiz Rce 309Document4 pagesQuiz Rce 309abhiNo ratings yet
- Metamaterial Absorber by VO2Document7 pagesMetamaterial Absorber by VO2Omar FarukNo ratings yet
- Plastic Raw Material MIS: Date 18-Apr-2022Document3 pagesPlastic Raw Material MIS: Date 18-Apr-2022Office atozNo ratings yet
- Nano DeBeeDocument2 pagesNano DeBeeCarmen RaveNo ratings yet
- Expansion Joints For Power Stations Kompaflex BrochureDocument8 pagesExpansion Joints For Power Stations Kompaflex Brochuremdt3eNo ratings yet
- Demoulding of Concrete Cubes From Plastic MDocument4 pagesDemoulding of Concrete Cubes From Plastic MangelinemiuNo ratings yet
- Composite Materials Used For UAVDocument3 pagesComposite Materials Used For UAVAkashNo ratings yet
- Bihar Cement Plant Environment Compliance April Sep 2020Document26 pagesBihar Cement Plant Environment Compliance April Sep 2020Kumar Saurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 3 MonoDocument2 pagesCE Board Nov 2020 - RCD - Set 3 MonoDale MalazzabNo ratings yet
- Deionized Water: Application BulletinDocument2 pagesDeionized Water: Application BulletinpinutaNo ratings yet
- FIP Water Treatment Solutions 2017 LRDocument28 pagesFIP Water Treatment Solutions 2017 LRSomaia Al-AkrasNo ratings yet