Professional Documents
Culture Documents
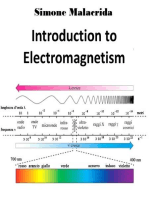
History of Electronics
Uploaded by
Rianna RamosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
History of Electronics
Uploaded by
Rianna RamosCopyright:
Available Formats
History of Electronics 1901 using the Marconi
Antenna.
Great People who Contributed in the
- received the nobel prize
Development of Electronics:
for Physics in 1908.
Thales – discovered that there is an Ambroise Fleming and Lee De Forest –
attraction between straw and dust to invented the vacuum tube (diode,
fossilized tree sap called amber. transistor, etc.) in 1902.
“Amber” – greek word for electron. Lee De Forest – developed the
Charles Coulomb – discovered the force vacuum tube amplifier in 1906.
bet. Electrically charged objects. Vacuum Tube – act like a diode and
Coulomb – unit of electric charge. amplifier, will properly work if its
“Q” – symbol for charge. temperature rise.
C – symbol for coulomb. Nick Holonyak Jr. – invented the first
Allesandro Volta – electricity is produced visible spectrum LED in 1962.
when two different metals are in contact - start of semi-conductor
with moistened cloth. devices – fast response.
Volt – unit of potential difference,
voltage, electromotive force.
Hans Oersted – magnetic field is present
when the current flows in a wire.
Oersted – one unit of magnetism.
George Ohm – relationship between
current and voltage in an electric circuit.
(Ohm’s Law)
Ohm – unit of resistance.
J. J. Thompson – discovered the electron.
- won the nobel prize for
Physics in 1906.
Electronics – study of the flow of
electrons and its uses.
Thomas Alva Edison – invented the
incandescent lamp, phonograph and
early film projector; patented 1093
inventions.
Samuel Morse – invented the telegraph
and the code that bears his name (Morse
Code).
- sent the first telegraph
message in 1844.
Guglielmo Marconi – developed the first
practical inventions in radio telegraphy
over long distances.
- received the first trans-
atlantic radio signal in
You might also like
- History of ElectronicsDocument63 pagesHistory of ElectronicsReinrick MejicoNo ratings yet
- The History of Electronics PioneersDocument32 pagesThe History of Electronics PioneersbigbangNo ratings yet
- History of Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageHistory of Electromagnetic WavesAbegail Faye Lerin PenaruyaNo ratings yet
- Informative SpeechDocument3 pagesInformative SpeechGlenn LagarasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics - PPT - Lesson 1Document24 pagesBasic Electronics - PPT - Lesson 1Myrna CabreraNo ratings yet
- Amber's Static ChargeDocument34 pagesAmber's Static ChargeZaigham SultanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 05 - Thermodynamics - Rianna Joyce R. RamosDocument3 pagesLesson 05 - Thermodynamics - Rianna Joyce R. RamosRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Ancient and Classical History: Static ElectricityDocument15 pagesAncient and Classical History: Static ElectricityCarlos FightNo ratings yet
- Antennas Since Hertz and Marconi PDFDocument7 pagesAntennas Since Hertz and Marconi PDFSatyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kr8800 ManualDocument88 pagesKr8800 ManualAnonymous ugRnnzs9100% (1)
- ComparatorsDocument54 pagesComparatorsbasanna_rvce60% (5)
- Low Frequency Currents 1st BPT ChiragDocument221 pagesLow Frequency Currents 1st BPT ChiragchiragNo ratings yet
- LP - Science Demo Teaching - Bago Oshiro NHSDocument9 pagesLP - Science Demo Teaching - Bago Oshiro NHSLayla Trace100% (1)
- EE 424 Module 1 Part 1Document62 pagesEE 424 Module 1 Part 1Johnjoseph Vera100% (2)
- Experiment 2: Calorimetry Calorimetry Is A Method of Measuring The Heat Transfer Within A Chemical Reaction or OtherDocument7 pagesExperiment 2: Calorimetry Calorimetry Is A Method of Measuring The Heat Transfer Within A Chemical Reaction or OtherRianna Ramos67% (3)
- 1.discovery of Electricity PresentationDocument12 pages1.discovery of Electricity PresentationangelitoNo ratings yet
- Sts ScientistDocument4 pagesSts ScientistNean PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics: Lesson 1: IntroductionDocument24 pagesBasic Electronics: Lesson 1: Introductioni KordiNo ratings yet
- Famous Scientists and Inventors Who Shaped Electronics EngineeringDocument6 pagesFamous Scientists and Inventors Who Shaped Electronics EngineeringDekzie Flores Mimay100% (1)
- History of Electronics RushDocument36 pagesHistory of Electronics RushJiminah Yah100% (1)
- Static Electricity: Module 1: History of ElectricityDocument7 pagesStatic Electricity: Module 1: History of ElectricityCivil EngineeringNo ratings yet
- L2 History SemiconductorDevicesDocument22 pagesL2 History SemiconductorDevicesGautam BafnaNo ratings yet
- 1.what Is ElectricityDocument46 pages1.what Is ElectricityKATE ARBIE LACDO-ONo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 2Document9 pagesBuilding Utilities 2Sheena Mae PugaNo ratings yet
- History of Wireless Communications1 - 2015-07-22Document4 pagesHistory of Wireless Communications1 - 2015-07-22salahberraNo ratings yet
- Abstraction: How Electronics Devices Begin?Document11 pagesAbstraction: How Electronics Devices Begin?Shane Patrick PanilagNo ratings yet
- Electricity History: Benjamin FranklinDocument13 pagesElectricity History: Benjamin FranklinRupesh ShahNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Electricity and MagnetismDocument30 pagesTimeline of Electricity and Magnetismschlemielz75% (4)
- History of Electronics: TransistorDocument18 pagesHistory of Electronics: TransistorAngelo Zaldy FranciaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Topic 1 - ElectricalDocument8 pages01 - Topic 1 - ElectricalAmaranthine FrazierNo ratings yet
- History of ElectronicsDocument19 pagesHistory of ElectronicsElmarie RecorbaNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument6 pagesAssignmentLawrence Emmanuel FerrerasNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Medan - Listrik StatisDocument66 pagesKuliah Medan - Listrik StatisCakralc Wong NgawamNo ratings yet
- Famous Scientists and Inventors-Merged-CompressedDocument299 pagesFamous Scientists and Inventors-Merged-CompressedMaldives CanadaNo ratings yet
- Famous Scientists and InventorsDocument10 pagesFamous Scientists and InventorsRafael AclanNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Electronic: From Vacuum Tube To Solid StateDocument12 pagesA Brief History of Electronic: From Vacuum Tube To Solid StateHarkishen SinghNo ratings yet
- History of Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesHistory of Electricity and MagnetismAngelNo ratings yet
- History of Electronics & SemiconductorsDocument3 pagesHistory of Electronics & SemiconductorsBill Joseph SuguitanNo ratings yet
- Antennas Since Hertz and MarconiDocument7 pagesAntennas Since Hertz and MarconiTaiwo Ayodeji100% (1)
- Term Paper On Radio Submitted ToDocument24 pagesTerm Paper On Radio Submitted ToHabibur Rahman HridoyNo ratings yet
- Circuits MidtermDocument208 pagesCircuits MidtermJohnjoseph Vera100% (1)
- History of ElectricityDocument21 pagesHistory of ElectricityAnbu Kaviraj SubramanianNo ratings yet
- 2201 Chapter 1Document4 pages2201 Chapter 1Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Final Tharani PROJECTDocument67 pagesFinal Tharani PROJECTMohamed BarvishNo ratings yet
- History of Electronics - DumaopDocument11 pagesHistory of Electronics - DumaopAngelo DumaopNo ratings yet
- C8 History Tech IEC 2022Document22 pagesC8 History Tech IEC 2022Laveidem LNNo ratings yet
- EE 424 Module 1 Part 1Document62 pagesEE 424 Module 1 Part 1Leslie MercadoNo ratings yet
- History of Electronics PDFDocument5 pagesHistory of Electronics PDFEj Mar ManabatNo ratings yet
- Scientists in ElectronicsDocument17 pagesScientists in Electronicsgame arenaNo ratings yet
- BEE-Module-1lesson 1Document102 pagesBEE-Module-1lesson 1MARK JOHN AL RODAVIANo ratings yet
- Living in The I.T. EraDocument16 pagesLiving in The I.T. EraAira Mae CrespoNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument3 pagesElectronicsSherlyn MeranNo ratings yet
- History of Electricity and Electronics DevelopmentDocument4 pagesHistory of Electricity and Electronics DevelopmentKorrene ReyesNo ratings yet
- 0 Compile-ECE05Document166 pages0 Compile-ECE05Canteen StirlingNo ratings yet
- Brief History of Electronics and Its ApplicationsDocument1 pageBrief History of Electronics and Its ApplicationsRexi AbonNo ratings yet
- Ece1: Electronics Devices and Circuits: HistoryDocument10 pagesEce1: Electronics Devices and Circuits: HistoryAdriel JohnNo ratings yet
- Atomos: Not To Be CutDocument34 pagesAtomos: Not To Be Cutemo mHAYNo ratings yet
- Electronics History: From Early Discoveries to Modern DevicesDocument75 pagesElectronics History: From Early Discoveries to Modern DevicesYi Yi HlaingNo ratings yet
- Foreign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiDocument3 pagesForeign Famous Scientist: Galileo GalileiCherelyn De LunaNo ratings yet
- History of Elctronics by Ivy Dilla Btled 3bDocument11 pagesHistory of Elctronics by Ivy Dilla Btled 3bIvy DillaNo ratings yet
- History of ElctronicsDocument11 pagesHistory of ElctronicsIvy DillaNo ratings yet
- History and Timeline of ElectricityDocument13 pagesHistory and Timeline of Electricityfelda encinaNo ratings yet
- Unit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS LabelingDocument2 pagesUnit02 - Hazard Comm. GHS LabelingRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- CP and IntroDocument3 pagesCP and IntroRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 Understanding The World of ThermodynamicsDocument1 pageUnit 01 Understanding The World of ThermodynamicsRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Rainwater As An Alternative Source of ElectricityDocument3 pagesRainwater As An Alternative Source of ElectricityRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- NothingDocument12 pagesNothingRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Understanding The SelfDocument11 pagesUnderstanding The SelfRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- STATSDocument4 pagesSTATSRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- 2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and TsunamiDocument3 pages2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake and TsunamiRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Power Generation For A Water Treatment System and Method of Supplying Electricity Using A Flow of LiquidDocument8 pagesHydro-Power Generation For A Water Treatment System and Method of Supplying Electricity Using A Flow of LiquidRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Effects of Online Games, Addiction to Dramas & Social MediaDocument3 pagesEffects of Online Games, Addiction to Dramas & Social MediaRianna RamosNo ratings yet
- Heaven's Electrical GuideDocument36 pagesHeaven's Electrical GuideShofol BiswasNo ratings yet
- Verification Test Report For Radiated EMIDocument16 pagesVerification Test Report For Radiated EMIratheesh vidyadharanNo ratings yet
- What Is 'Gauge' in Physics in Layman's Terms - QuoraDocument3 pagesWhat Is 'Gauge' in Physics in Layman's Terms - QuoraS SpikeNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Devices and ApplicationsDocument52 pagesPower Electronics Devices and Applicationsmanoj kumarNo ratings yet
- Doppler Effect and Redshift QuestionsDocument10 pagesDoppler Effect and Redshift Questionsamy liu :3No ratings yet
- Casio Edifice Qw5122Document7 pagesCasio Edifice Qw5122ataktidisNo ratings yet
- AC Traction Motor, Serial# RH-2232171-1, Asset#2224419-3Document7 pagesAC Traction Motor, Serial# RH-2232171-1, Asset#2224419-3Dragan GigiNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument20 pagesPreviewDominique RamosNo ratings yet
- Rydberg Atoms (Cambridge Monographs On Atomic, Molecular and Chemical Physics) (Thomas F. Gallagher) (Z-Library)Document509 pagesRydberg Atoms (Cambridge Monographs On Atomic, Molecular and Chemical Physics) (Thomas F. Gallagher) (Z-Library)123456subbuNo ratings yet
- Contact and Non Contact ForcesDocument3 pagesContact and Non Contact ForcesFaizan Ahmed100% (1)
- Fets Fwa-2017Document14 pagesFets Fwa-2017Shashe gNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Bank Protection GuideDocument48 pagesCapacitor Bank Protection Guideboedak korporatNo ratings yet
- Overvoltages in Low Voltage Systems Due To Normal Medium Voltage SwitchingDocument4 pagesOvervoltages in Low Voltage Systems Due To Normal Medium Voltage SwitchingAlejandro Solis GomezNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Intensity CalculationsDocument61 pagesElectric Field Intensity CalculationsDarsh PadaliaNo ratings yet
- Torque Motor Rotary TablesDocument35 pagesTorque Motor Rotary TablesAlex Frank RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous MachineDocument15 pagesAsynchronous MachineboumedienNo ratings yet
- Test Report For MC330Document15 pagesTest Report For MC330Felipeandres Lizana BastiasNo ratings yet
- Square Shaded-Pole Motors: Multi-Function DesignDocument5 pagesSquare Shaded-Pole Motors: Multi-Function DesignJimmy Arias (JimmyStron)No ratings yet
- Path Profile Analysis of A LOS System Using 3-D Digital MapDocument11 pagesPath Profile Analysis of A LOS System Using 3-D Digital MapJawad HussineNo ratings yet
- Direct Reading CompassDocument4 pagesDirect Reading Compasshenry okilaNo ratings yet
- Optical Materials: E.R. Brand Ao, M.S. Vasconcelos, E.L. Albuquerque, U.L. FulcoDocument5 pagesOptical Materials: E.R. Brand Ao, M.S. Vasconcelos, E.L. Albuquerque, U.L. FulcoedirozemberghNo ratings yet
- Detuned, Series Filter Reactor: For Power Factor Correction CapacitorDocument4 pagesDetuned, Series Filter Reactor: For Power Factor Correction Capacitorctxd758n100% (1)
- PA Footwear GA Tank AssemblyDocument1 pagePA Footwear GA Tank AssemblyMahidhar TalapaneniNo ratings yet
- A Generalized Approach For The Study of The Non Linear Behaviour PDFDocument5 pagesA Generalized Approach For The Study of The Non Linear Behaviour PDFrenzomcuevaNo ratings yet
- PHY71-Topic 9-Electromagnetic Induction-AK Removed QuestionsDocument20 pagesPHY71-Topic 9-Electromagnetic Induction-AK Removed QuestionsnadalmzrNo ratings yet
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No2, Afs Kalaikunda Class 12A Physics Worksheet 1 (Chapter 1)Document2 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya No2, Afs Kalaikunda Class 12A Physics Worksheet 1 (Chapter 1)D I N E S H K U M A R S A H UNo ratings yet