Professional Documents
Culture Documents
For More Information On Bernini's Other Works and Papal Support: Lu Bow, Arthur. "Bernini's Genius". Smithsonian. Vol39 No7 pg76-80, 81-3 (Oct 2008)
Uploaded by
Estela ArusteiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
For More Information On Bernini's Other Works and Papal Support: Lu Bow, Arthur. "Bernini's Genius". Smithsonian. Vol39 No7 pg76-80, 81-3 (Oct 2008)
Uploaded by
Estela ArusteiCopyright:
Available Formats
Gianlorenzo Bernini (1598-1680) is considered one of the most inspiring and influential
sculptors, architects, and draftsmen of the Baroque period. This aesthetic movement
affected all disciplines ranging from painting, sculpture, and architecture to theater and
music. It was a style of magnificence and richness which spread from its origins in Rome
and Paris to the outer reaches of Europe and beyond. The origins of the style can be traced
back to Papal Rome in the early part of the seventeenth century and to the great triad of
Baroque’s pioneers: Bernini, Francesco Borromini, and Pietry da Cortona. Their works
established the principal characteristics of the style. Mainly concerned with performance,
their buildings and works of art became infused with vigor and movement.
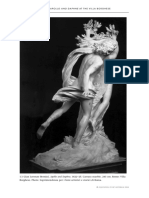
The Baroque combined the arts to engage the viewer through all their senses.
Sculpted figures, such as Bernini’s, seemed to be captured mid-action and in an emotional
appeal to the beholder. Rather than being an observer of a static work of art, the beholder
thus became a participant in a dramatic event. Bernini aptly achieved this sense of theater
in many of his pieces, including the Fountain of the Four Rivers (1651) (Fig.1). Bernini, as a
young child, dazzled his way to his first Papal support with Pope Paul V, who reportedly
declared, "We hope that this youth will become the Michelangelo of his century"1. Over a
long lifetime, Bernini undertook commissions for eight popes, transforming the look of
seventeenth century Rome as Michelangelo had helped shape Florence and Rome a century
1For more information on Bernini’s other works and papal support: Lu Bow, Arthur. “Bernini's
Genius”. Smithsonian. Vol39 no7; pg76-80, 81-3 (Oct 2008).
1
You might also like
- Gian Lorenzo Bernini's Influence On Modern ArtDocument19 pagesGian Lorenzo Bernini's Influence On Modern ArtEmaan FatimaNo ratings yet
- BerniniDocument4 pagesBerniniEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Gian Lorenzo BerniniDocument12 pagesGian Lorenzo BerniniGiulia Galli LavigneNo ratings yet
- BaroquersDocument4 pagesBaroquersApple ManNo ratings yet
- Baroque Music Describes A Style of European Classical Music Approximately Extending From 1600 To 1750Document4 pagesBaroque Music Describes A Style of European Classical Music Approximately Extending From 1600 To 1750Ella AgtotoNo ratings yet
- Puccini: The Illustrated Lives of the Great Composers.From EverandPuccini: The Illustrated Lives of the Great Composers.No ratings yet
- History of Western Arts AssignmentDocument7 pagesHistory of Western Arts AssignmentAsad UllahNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 9 Hand OutDocument7 pagesMapeh 9 Hand Outacmejos0No ratings yet
- Alvar Henrick Aalto: and The Superbly Sited PaimioDocument39 pagesAlvar Henrick Aalto: and The Superbly Sited PaimioNathan JonatNo ratings yet
- Baroque Art ExplanationDocument3 pagesBaroque Art ExplanationLorena LigutanNo ratings yet
- Bernini Apolo Si DaphneDocument30 pagesBernini Apolo Si DaphneAlexandra VranceanuNo ratings yet
- Arts 2nd GradingDocument4 pagesArts 2nd GradingRoen RamonalNo ratings yet
- Mapeh Reviewer - 2ND GradingDocument12 pagesMapeh Reviewer - 2ND Gradinggold rushNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Introduction: The Baroque Style in Western EuropeDocument2 pagesPart 5: Introduction: The Baroque Style in Western Europethot777No ratings yet
- MANNERISMDocument27 pagesMANNERISMVivialyn ContredasNo ratings yet
- Sobre Bernini - ApunteDocument73 pagesSobre Bernini - ApunteDiana GONo ratings yet
- Renaissance & BaroqueDocument4 pagesRenaissance & BaroqueRoxanne BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Baroque PeriodDocument8 pagesBaroque PeriodDarwin Competente LagranNo ratings yet
- BSmith BaroqueRococoDocument9 pagesBSmith BaroqueRococoBiniyam BereketNo ratings yet
- Lippi I Fra CarnevaleDocument17 pagesLippi I Fra CarnevaleMartha GellhornNo ratings yet
- Giotto Di BondoneDocument2 pagesGiotto Di BondoneJoevelyn M. SayongNo ratings yet
- Venetian and Renaissance Period I. The RenaissanceDocument3 pagesVenetian and Renaissance Period I. The RenaissanceJelly SagunNo ratings yet
- Bernini's Cristo VivoDocument12 pagesBernini's Cristo VivoCharles Scribner IIINo ratings yet
- MannerismDocument4 pagesMannerismAdi TriNo ratings yet
- Historical Development of ArtsDocument43 pagesHistorical Development of ArtsEdrian jay TiburcioNo ratings yet
- Gian Lorenzo BerniniDocument9 pagesGian Lorenzo Bernini29antonelgjinaj11No ratings yet
- Cheney LaviniaFontanasNude 2015Document14 pagesCheney LaviniaFontanasNude 2015davidgranadohermosinNo ratings yet
- T - Dziubecki, Space in The Baroque Roman Architecture PDFDocument7 pagesT - Dziubecki, Space in The Baroque Roman Architecture PDFJavi PérezNo ratings yet
- Paganini 2011Document2 pagesPaganini 2011Cristi AntonNo ratings yet
- Beethoven's Symphonies: Nine Approaches to Art and IdeasFrom EverandBeethoven's Symphonies: Nine Approaches to Art and IdeasRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Enacting Perception BA Thesis PDFDocument103 pagesEnacting Perception BA Thesis PDFJelenaNo ratings yet
- Visual Art-Part1Document182 pagesVisual Art-Part1mike gebruNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of MannerismDocument6 pagesOrigin and Development of Mannerismdonna escasinasNo ratings yet
- Baroque ReportDocument32 pagesBaroque ReportMadelaine Soriano PlaniaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6.renaissance and Baroque ArtsDocument60 pagesLesson 6.renaissance and Baroque ArtsmerakilidriellaNo ratings yet
- Gian Lorenzo Bernini - Art ClassDocument41 pagesGian Lorenzo Bernini - Art Classapi-260620287No ratings yet
- Painters: Biographies of Botticelli, Bruegel, Francisco Goya, Giotto, Johannes Vermeer, Leonardo Da Vinci, Raphael, Rembrandt, and WhistlerFrom EverandPainters: Biographies of Botticelli, Bruegel, Francisco Goya, Giotto, Johannes Vermeer, Leonardo Da Vinci, Raphael, Rembrandt, and WhistlerNo ratings yet
- Josephine's Composer: The Life Times and Works of Gaspare Pacifico Luigi Spontini (1774-1851)From EverandJosephine's Composer: The Life Times and Works of Gaspare Pacifico Luigi Spontini (1774-1851)No ratings yet
- Piero Della Francesca in Oxford Art OnlineDocument13 pagesPiero Della Francesca in Oxford Art OnlineceudekarnakNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument21 pagesArtsJean Mae DesquitadoNo ratings yet
- DoniDocument11 pagesDoniTsiliLiNo ratings yet
- BaroqueDocument2 pagesBaroqueEnrico FaiellaNo ratings yet
- Mannerism ArtDocument13 pagesMannerism ArtFrancis SorianoNo ratings yet
- The Venetian and The Northern RenaissanceDocument46 pagesThe Venetian and The Northern RenaissanceJelly SagunNo ratings yet
- Arts VicDocument4 pagesArts Vicjaredviernes0No ratings yet
- 2020 Baroque EraDocument3 pages2020 Baroque EraLungo Protazio MNo ratings yet
- Bernini's Cristo VivoDocument5 pagesBernini's Cristo VivoCharles ScribnerNo ratings yet
- Michelangelo Is Widely Regarded As The Most Famous Artist of The Italian Renaissance. Among HisDocument5 pagesMichelangelo Is Widely Regarded As The Most Famous Artist of The Italian Renaissance. Among HisDhennis Kurt LagoyNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Revised 9Document16 pagesModule 5 Revised 9Edrian EspedillonNo ratings yet
- The Orignis of Legal Revolution History of EcjDocument22 pagesThe Orignis of Legal Revolution History of EcjEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Rose Brown Life Goals List Maker Interactive Instagram StoryDocument1 pageRose Brown Life Goals List Maker Interactive Instagram StoryEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Beige Brown Modern Minimal Yearly PlannerDocument1 pageBeige Brown Modern Minimal Yearly PlannerEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Read Me & LicenseDocument1 pageRead Me & LicenseGracia ImanuellaNo ratings yet
- Pink Grid Playful To Do List PlannerDocument1 pagePink Grid Playful To Do List PlannerEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Pink Grid Playful To Do List PlannerDocument1 pagePink Grid Playful To Do List PlannerEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- The Orignis of Legal Revolution History of EcjDocument22 pagesThe Orignis of Legal Revolution History of EcjEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Law MakingDocument422 pagesThe Mechanics of Law MakingEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- The European Neofunctionalism Content File PDFDocument9 pagesThe European Neofunctionalism Content File PDFEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- The European Neofunctionalism Content File PDFDocument9 pagesThe European Neofunctionalism Content File PDFEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- A Treatise On The Law of AwardsDocument649 pagesA Treatise On The Law of AwardsCristian FlorescuNo ratings yet
- A Treatise On The Law of ObligationsDocument718 pagesA Treatise On The Law of ObligationsEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Communism On SportDocument7 pagesThe Impact of Communism On SportEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- Architecture and Soviet ImaginationDocument21 pagesArchitecture and Soviet ImaginationEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument5 pagesPDFEstela ArusteiNo ratings yet