Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PAS 10 Events After The Reporting Period
Uploaded by
panda 1Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PAS 10 Events After The Reporting Period
Uploaded by
panda 1Copyright:
Available Formats
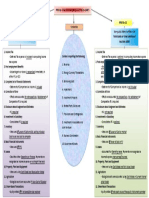
PAS 10 Events after the reporting period
Events after the reporting period are those events, whether favorable o unfavorable, that occurs between the
end of reporting period and the date on which the financial statements are authorized for issue. It also known as
subsequent events. Such events may require either adjustment or disclosure.
Types of events after the reporting period
Adjusting events after the reporting period are those that provide evidence of conditions that exist at the
end of reporting period.
Non-adjusting events after reporting period are those that are indicative of conditions that arise after the
end of reporting period.
Accordingly, an entity must adjust the amounts recognized in the financial statements for adjusting events
that provide evidence of conditions that existed at the end of reporting period.
However, an entity does not recognize events after the reporting period that relate to conditions that only
arose after the reporting period.
The entity is required only to disclosure significant non-adjusting events
Examples:
Adjusting Events Non-adjusting Events
Settlement after the reporting period of a court Business combination after the reporting period
case because it confirms that the entity already Plan to discontinue an operation
had a present obligation at the end of the Major purchase and disposal of asset or
reporting period. expropriation of major asset by government
Bankruptcy of a customer which occurs after Destruction of a major production plant by a fire
the reporting period. after the reporting period
Announcing or commencing the implementation of
Sale of inventories after the reporting period
a major restructuring
may give evidence about the net realizable Abnormally large changes after the reporting
value at reporting date. period in asset prices or foreign exchange rates
The determination after the reporting period of Entering into significant commitments or
the cost of asset purchased or the proceeds contingent liabilities, for example, by issuing
from asset sold before the end of reporting guarantees.
period. Commencing major litigation arising solely from
The determination after the reporting period of events that occurred after the reporting period.
the profit sharing or bonus payment if the Change in tax rate enacted or announced after the
entity has the present obligation at the end of end of reporting period that has a significant effect
reporting period to make such payment. on current and deferred tax asset and liability
The discovery of fraud or errors that show the
financial statements were incorrect.
Financial statements authorized for issue
Financial statements are authorized for issue when the board of directors reviews the financial
statements and authorizes them issue,
In some cases, an entity is required to submit the financial statements to the shareholders for approval
after the financial statements have been issued.
In such cases, the financial statements are authorized for issue on the date of issue by the board of
directors and not on the date when shareholders approve the financial statements.
You might also like
- Collection Agency Removal LetterDocument4 pagesCollection Agency Removal LetterKNOWLEDGE SOURCENo ratings yet
- PAS 16 Property, Plant and EquipmentDocument4 pagesPAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipmentpanda 1No ratings yet
- 1 in The Matter of The IBPDocument3 pages1 in The Matter of The IBPSamantha Ann T. TirthdasNo ratings yet
- ACC2023 - CFAS Note 1 Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsDocument10 pagesACC2023 - CFAS Note 1 Conceptual Framework and Accounting StandardsHailsey WinterNo ratings yet
- IA3 Chapter 2Document7 pagesIA3 Chapter 2Juliana ChengNo ratings yet
- Anti SLAPPDocument19 pagesAnti SLAPPRobert G. Williscroft100% (1)
- PAS 7 Statement of Cash FlowsDocument7 pagesPAS 7 Statement of Cash Flowspanda 1100% (6)
- Chapter 1-Current LiabilitiesDocument15 pagesChapter 1-Current LiabilitiesMonique AlarcaNo ratings yet
- FAR Reviewer - CPAR Test BankDocument31 pagesFAR Reviewer - CPAR Test BankemmanvillafuerteNo ratings yet
- Lrta Vs Natividad DigestDocument2 pagesLrta Vs Natividad DigestAwe SomontinaNo ratings yet
- PAS 10 Events After Reporting PeriodDocument1 pagePAS 10 Events After Reporting PeriodAcissej100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument10 pagesChapter 12 - Events After The Reporting PeriodMarriel Fate CullanoNo ratings yet
- Biological AssetsDocument5 pagesBiological Assetspanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Qualitative CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesCF Qualitative Characteristicspanda 1No ratings yet
- Pas 12Document27 pagesPas 12Princess Jullyn ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Partnership and Corporation Accounting ReviewerDocument9 pagesPartnership and Corporation Accounting ReviewerMarielle ViolandaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Statement of Financial Position PDFDocument22 pagesModule 3 - Statement of Financial Position PDFSandyNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PARTNERSHIP LiquidationFEB 2021Document53 pagesModule 4 PARTNERSHIP LiquidationFEB 2021Grace RoqueNo ratings yet
- Should Always: Exercise 1-1. True or FalseDocument7 pagesShould Always: Exercise 1-1. True or FalseDeanmark RondinaNo ratings yet
- PAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument2 pagesPAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodJennicaBailonNo ratings yet
- Pas 33Document4 pagesPas 33Kimberly Anne ZasonNo ratings yet
- Business Combination-Lesson 1 Business Combination-Lesson 1Document11 pagesBusiness Combination-Lesson 1 Business Combination-Lesson 1heyheyNo ratings yet
- PAS 1 Financial Statement: Income Statement and Comprehensive IncomeDocument21 pagesPAS 1 Financial Statement: Income Statement and Comprehensive Incomepanda 1100% (2)
- Vallix QuestionnairesDocument14 pagesVallix QuestionnairesKathleen LucasNo ratings yet
- PAS 2 InventoriesDocument11 pagesPAS 2 Inventoriespanda 1100% (6)
- Case Digest - Siga-An Vs VillanuevaDocument2 pagesCase Digest - Siga-An Vs Villanuevadanica100% (1)
- PFRS 5Document28 pagesPFRS 5Erica AbegoniaNo ratings yet
- Partnership Liquidation Process and AccountingDocument10 pagesPartnership Liquidation Process and AccountingIan RanilopaNo ratings yet
- PAS 20 Government Grant GuideDocument3 pagesPAS 20 Government Grant Guidepanda 1100% (1)
- PAS 19 Employee Benefits: Short-Term Employee Benefits Are Employee Benefits (Other Than Termination BenDocument5 pagesPAS 19 Employee Benefits: Short-Term Employee Benefits Are Employee Benefits (Other Than Termination BenKaila Clarisse CortezNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Accounting 1B Chapter 19 Borrowing CostsDocument17 pagesIntermediate Accounting 1B Chapter 19 Borrowing CostsjuennaguecoNo ratings yet
- PFRS 7Document22 pagesPFRS 7Princess Jullyn ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial ReportingDocument8 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial ReportingsmlingwaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Policies, Estimates and ErrorsDocument3 pagesAccounting Policies, Estimates and Errorspanda 1No ratings yet
- 2 Matute v. Court of AppealsDocument31 pages2 Matute v. Court of AppealsMary Licel RegalaNo ratings yet
- Sol Man Chapter 4 Accounts Receivable Ia Part 1a 2020 EditionDocument21 pagesSol Man Chapter 4 Accounts Receivable Ia Part 1a 2020 EditionAngela RuedasNo ratings yet
- PAS 1 Presentation of FSDocument18 pagesPAS 1 Presentation of FSpanda 1No ratings yet
- PAS 1 Presentation of FSDocument18 pagesPAS 1 Presentation of FSpanda 1No ratings yet
- PBTC Vs Dahican Lumber Co - Case DigestDocument2 pagesPBTC Vs Dahican Lumber Co - Case DigestsescuzarNo ratings yet
- ANDRADA VS. CERA DigestedDocument2 pagesANDRADA VS. CERA DigestedSam MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Module 6 CFAS PAS 23 - BORROWING COSTDocument6 pagesModule 6 CFAS PAS 23 - BORROWING COSTJan JanNo ratings yet
- Civil Law: Sales and LeaseDocument31 pagesCivil Law: Sales and LeaseJezen Esther Pati100% (1)
- Defenses For Lgu ExpropriationDocument8 pagesDefenses For Lgu ExpropriationJero TakeshiNo ratings yet
- C12 - PAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument3 pagesC12 - PAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodAllaine Elfa100% (1)
- 150.events After The Reporting PeriodDocument6 pages150.events After The Reporting PeriodMelanie SamsonaNo ratings yet
- Error Correction MethodsDocument2 pagesError Correction MethodsValentina Tan DuNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsHufana, ShelleyNo ratings yet
- 06 - Notes On Discontinued OperationsDocument3 pages06 - Notes On Discontinued OperationsLalaine ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cfas Pas 10 ReviewerDocument1 pageCfas Pas 10 ReviewerSandraNo ratings yet
- PFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapDocument1 pagePFRS of SME and SE - Concept MapRey OñateNo ratings yet
- Accounting for investments in associatesDocument3 pagesAccounting for investments in associatesLiana LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Corporate Liquidation and Reorganization-PROFE01Document3 pagesChapter 3 Corporate Liquidation and Reorganization-PROFE01Steffany RoqueNo ratings yet
- PAS 24 Related Party Disclosures Key RequirementsDocument13 pagesPAS 24 Related Party Disclosures Key Requirementslatte aeriNo ratings yet
- Pas 37 38 40 41 PFRS 1Document5 pagesPas 37 38 40 41 PFRS 1LALALA LULULUNo ratings yet
- CH 32 - Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleDocument3 pagesCH 32 - Noncurrent Asset Held For SaleJm SevallaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Special TransactionsDocument13 pagesAccounting For Special Transactionsviva nazarenoNo ratings yet
- Process For Cash Flow StatementsDocument33 pagesProcess For Cash Flow StatementsP3 PowersNo ratings yet
- PAS 8, 16 Accounting Policies, PPEDocument7 pagesPAS 8, 16 Accounting Policies, PPEalliahnahNo ratings yet
- Pfrs 5 NotesDocument18 pagesPfrs 5 NotesMartha Nicole MaristelaNo ratings yet
- Quiz Printing - Pas 7 - Statement of Cash FlowsDocument1 pageQuiz Printing - Pas 7 - Statement of Cash FlowshasanahNo ratings yet
- Pas 2 Inventories W RecordingDocument13 pagesPas 2 Inventories W Recordingwendy alcoseba100% (1)
- Chapter 9Document7 pagesChapter 9Coursehero PremiumNo ratings yet
- CFAS Notes Chapter 2 ObjectivesDocument5 pagesCFAS Notes Chapter 2 ObjectivesKhey KheyNo ratings yet
- Accounting Chapter 9Document7 pagesAccounting Chapter 9Angelica Faye DuroNo ratings yet
- Separate and Consolidated Dayag Part 3Document4 pagesSeparate and Consolidated Dayag Part 3Edi wow WowNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentBaekhunnie ByunNo ratings yet
- AE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamDocument3 pagesAE 18 Financial Market Prelim ExamWenjunNo ratings yet
- Understanding accounting closure activitiesDocument6 pagesUnderstanding accounting closure activitiesJamaica DavidNo ratings yet
- Pas 1 CfasDocument10 pagesPas 1 CfasPinero JatheuzelNo ratings yet
- Receivables and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ProblemsDocument3 pagesReceivables and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts ProblemsAdyangNo ratings yet
- Receivable FinancingDocument15 pagesReceivable FinancingshaneNo ratings yet
- True or False. Partnership FormationDocument1 pageTrue or False. Partnership Formation촏교새벼No ratings yet
- Understanding Financial Statements /TITLEDocument26 pagesUnderstanding Financial Statements /TITLEMARC BENNETH BERIÑANo ratings yet
- CFAS ReviewerDocument6 pagesCFAS ReviewerAziNo ratings yet
- Current Liabilities - Exercise (Refinancing)Document3 pagesCurrent Liabilities - Exercise (Refinancing)user anonymousNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Audit Services and Financial Statements AuditDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Audit Services and Financial Statements AuditBryzan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- AIS 01 - Handout - 1Document7 pagesAIS 01 - Handout - 1Melchie RepospoloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document2 pagesChapter 13Vince PeredaNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Events After Reporting Period 4studentsDocument22 pagesTopic 5 Events After Reporting Period 4studentsputerimanggis11No ratings yet
- Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument1 pageEvents After The Reporting PeriodFaye RagosNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem 3Document3 pagesPractice Problem 3panda 1No ratings yet
- Why Is Planning An Audit Important?Document5 pagesWhy Is Planning An Audit Important?panda 1No ratings yet
- Epic of IbalongDocument1 pageEpic of Ibalongpanda 1No ratings yet
- Class Interval Tally FrequencyDocument11 pagesClass Interval Tally Frequencypanda 1No ratings yet
- Problem 3&5Document17 pagesProblem 3&5panda 1No ratings yet
- Practice Problem 1Document4 pagesPractice Problem 1panda 1No ratings yet
- Practice Problem 2Document5 pagesPractice Problem 2panda 1No ratings yet
- Accountancy ProfessionDocument5 pagesAccountancy Professionpanda 1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1: General Overview of Government AccountingDocument1 pageChapter 1: General Overview of Government Accountingpanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Elements, Recognition and Measurement, Capital MaintenanceDocument11 pagesCF Elements, Recognition and Measurement, Capital Maintenancepanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Qualitative CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesCF Qualitative Characteristicspanda 1No ratings yet
- Accountancy ProfessionDocument5 pagesAccountancy Professionpanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Objective of Financial ReportingDocument6 pagesCF Objective of Financial Reportingpanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Elements, Recognition and Measurement, Capital MaintenanceDocument6 pagesCF Elements, Recognition and Measurement, Capital Maintenancepanda 1No ratings yet
- CF FS and Reporting EntityDocument5 pagesCF FS and Reporting Entitypanda 1No ratings yet
- CF Objective of Financial ReportingDocument4 pagesCF Objective of Financial Reportingpanda 1No ratings yet
- CF FS and Reporting EntityDocument2 pagesCF FS and Reporting Entitypanda 1No ratings yet
- PAS 16 Borrowing CostsDocument2 pagesPAS 16 Borrowing Costspanda 1No ratings yet
- PAS 8 Accounting Policies, Estimates and ErrorsDocument2 pagesPAS 8 Accounting Policies, Estimates and Errorspanda 1No ratings yet
- Business Law Course ProjectDocument4 pagesBusiness Law Course ProjectLieka CrumpNo ratings yet
- To's Proposed FOF and COLDocument326 pagesTo's Proposed FOF and COLOSDocs2012No ratings yet
- Wjec LA3 A2 A-Level Law Model AnswerDocument2 pagesWjec LA3 A2 A-Level Law Model Answer2j88No ratings yet
- Seagull Ship Management Vs NLRCDocument4 pagesSeagull Ship Management Vs NLRCPenn Angelo RomboNo ratings yet
- Ronald Hazzard v. Immigration and Naturalization Service, 951 F.2d 435, 1st Cir. (1991)Document7 pagesRonald Hazzard v. Immigration and Naturalization Service, 951 F.2d 435, 1st Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Pacasum CaseDocument9 pagesPacasum CaseAlexander Julio ValeraNo ratings yet
- The Lawyer's Duties To The Legal Profession 10, 11 & 12Document2 pagesThe Lawyer's Duties To The Legal Profession 10, 11 & 12Katrina NicolasNo ratings yet
- Separate Appendix of Exhibits #2 - Case No SC16-2031Document58 pagesSeparate Appendix of Exhibits #2 - Case No SC16-2031Neil GillespieNo ratings yet
- Writ of SummonsDocument5 pagesWrit of SummonsHazim HusnulhadiNo ratings yet
- Datatreasury Corporation v. City National Corporation Et Al - Document No. 13Document27 pagesDatatreasury Corporation v. City National Corporation Et Al - Document No. 13Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Rally For Democracy and Progress and 17 Others Versus ELECTORAL COMMISSION OF NAMIBIA and 8 Others - Parker JDocument38 pagesRally For Democracy and Progress and 17 Others Versus ELECTORAL COMMISSION OF NAMIBIA and 8 Others - Parker JAndré Le RouxNo ratings yet
- Court upholds buyers' right to formal deed despite 22-year delayDocument6 pagesCourt upholds buyers' right to formal deed despite 22-year delayCastle CastellanoNo ratings yet
- Afulugencia Vs Metrobank SubpoenaDocument12 pagesAfulugencia Vs Metrobank SubpoenaEthel Joi Manalac MendozaNo ratings yet
- Relevance and types of judgmentsDocument3 pagesRelevance and types of judgmentsAditya Prakash VermaNo ratings yet
- In Re Abad EthicsDocument1 pageIn Re Abad EthicsJernel JanzNo ratings yet
- Receptor IR TSOP4836Document7 pagesReceptor IR TSOP4836damijoseNo ratings yet
- Jay Morton v. Jack W. Browne, 438 F.2d 1205, 1st Cir. (1971)Document2 pagesJay Morton v. Jack W. Browne, 438 F.2d 1205, 1st Cir. (1971)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Price V HighPointeDocument5 pagesPrice V HighPointedissidentmeNo ratings yet
- COA M2016-010, Deputization of Lawyers (Revised Guidelines)Document3 pagesCOA M2016-010, Deputization of Lawyers (Revised Guidelines)TAU MU OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- Nike Inc. v. Matthew Millward and Ralph Lauren Corp.Document14 pagesNike Inc. v. Matthew Millward and Ralph Lauren Corp.Matthew KishNo ratings yet