Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)
Uploaded by
ChaseOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)
Uploaded by
ChaseCopyright:
Available Formats
!
"
NEW!
Textbook Solutions Expert Q&A Study Pack Practice #
Find solutions for your homework Search
home / study / science / physics / classical physics / classical physics solutions manuals / classical mechanics / 0th edition / chapter 6 / problem 3p
Classical Mechanics (0th Edition)
See this solution in the app
Chapter 6, Problem 3P 13 Bookmarks Show all steps: ON
Post a question
Answers from our experts for your tough
homework questions
Step-by-step solution
Enter question
Step 1 of 10
Use the relation between the speed, distance, and the time to calculate the time taken for the Continue to post
light to traverse the path . 20 questions remaining
The relation between the speed, distance, and the time is given by,
Here, d is the distance travelled by the light, c is the speed of the light, and t is the time taken for Snap a photo from your
phone to post a question
the light.
Comment
My Textbook Solutions
Step 2 of 10
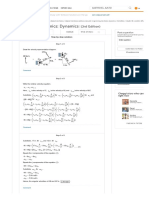
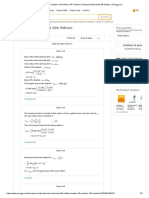
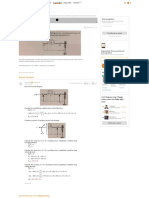
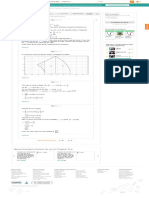
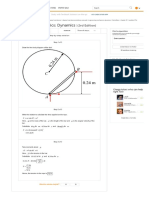
Consider a light is travelling from point to the point . The point lies on the y-axis at
and the point lies on the -plane at . Let Q be the point on the plane Classical Classical Classical
Mechanics Dynamics... Dynamics...
mirror and lies on the -plane at . This situation can be seen in the following figure. 0th Edition 5th Edition 4th Edition
View all solutions
Chegg tutors who can help
right now
S
Rensselaer Polytec… 1433
Josh
Ph.D. in Mathematics 1322
Matthew
University of Color… 996
Find me a tutor
Comment
Step 3 of 10
From the figure, the distance travelled by light from the point to the point Q is,
Similarly, the distance travelled by light from the point Q to the point is,
Thus, the total distance travelled by light from points to is,
Here, d is the total distance travelled by light from points to .
Substitute for , and for in .
Rearrange the equation for t.
The time taken by the light to travel from points to is,
Comment
Step 4 of 10
Substitute for d in .
…… (1)
Comment
Step 5 of 10
Therefore, the time taken by the light to travels the path is
Comment
Step 6 of 10
Differentiate the equation (1) on both sides with respect to z.
From the Fermat’s principle, to find the position of must differentiate with respect to
z and x and the following derivatives are zero. Because the point Q must lie in the same vertical
plane as . So, the necessary condition for a maximum or minimum is given below:
and .
Comment
Step 7 of 10
To prove , we could use the necessary condition for a maximum or minimum that is
The term in the above equation is not equal to zero. This
implies . Therefore, the time taken by the light to travels the path is minimum when
Q has .
Comment
Step 8 of 10
Differentiate the equation (1) on both sides with respect to x.
…… (2)
Substitute for in the equation (2).
To prove that , we could use the necessary condition for a maximum or minimum that is
…… (3)
Comment
Step 9 of 10
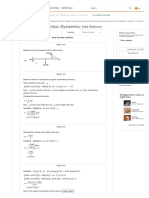
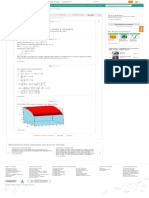
From the figure, we have , and . Rewrite the equation
as follows.
Substitute for .
Comment
Step 10 of 10
We can take the point on the x-axis at .
The distance between the points Q and R is,
From the figure, we have .
Substitute for , and for in .
Substitute for .
Substitute for and for in the equation (3).
In this case, the total angle is . Then the above equation becomes as follows.
Therefore, the Fermat’s principle obeys the law of reflection, that is .
Comments (2)
Was this solution helpful? 16 0
Recommended solutions for you in Chapter 6
Chapter 6, Solution 9P Chapter 6, Solution 15P
The condition for the A car released from point
integral To be stationary 1 on the roller coaster
is …………….... track and it will reach the
point in the shortest
See solution possible time. The...
See solution
ABOUT CHEGG LEGAL & POLICIES CHEGG PRODUCTS AND SERVICES CHEGG NETWORK CUSTOMER
SERVICE
Become a Tutor Advertising Choices Cheap Textbooks Online Tutoring EasyBib
Chegg For Good Cookie Notice Chegg Coupon Sell Textbooks Internships.com Customer Service
College Marketing General Policies Chegg Play Solutions Manual Studyblue Give Us Feedback
Corporate Intellectual Property Chegg Study Help Study 101 Thinkful Help with Chegg
Development Rights Tutors
College Textbooks Test Prep
Investor Relations Terms of Use Help with
eTextbooks Textbook Rental eTextbooks
Jobs Chegg Tutors Terms Chegg Math Solver Used Textbooks
of Service Help to use EasyBib
Join Our Affiliate Mobile Apps Digital Access Plus
Program Global Privacy Codes
Policy UPDATED Manage Chegg
Media Center Study Subscription
Site Map California Privacy Return Your Books
Rights
Textbook Return
Honor Code Policy
© 2003-2020 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)Document1 pageClassical Mechanics: (0th Edition)ChaseNo ratings yet
- Math Tutor: Algebra, Ages 11 - 14: Easy Review for the Struggling StudentFrom EverandMath Tutor: Algebra, Ages 11 - 14: Easy Review for the Struggling StudentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)Document1 pageClassical Mechanics: (0th Edition)ChaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2-001 (Basis) PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 2 2-001 (Basis) PDFJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Classical Mechanics: (0th Edition)Document1 pageClassical Mechanics: (0th Edition)ChaseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2-003 (Basis)Document6 pagesChapter 2 2-003 (Basis)Jamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions Manual, Volume 1 For Serway/Jewett's Physics For Scientists and EngineersDocument5 pagesStudent Solutions Manual, Volume 1 For Serway/Jewett's Physics For Scientists and EngineersMalik AsadNo ratings yet
- Solved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Document1 pageSolved Solve Problem 8.10 Using L. Casagrande's Method.Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument6 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 28P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- 16.8 Parte UnicaDocument20 pages16.8 Parte UnicaAbraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.41. Given q2 3800 LBFT, x1 18 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Question: 5. (A) Write A Pseudocode, Which Runs in O (Nlogn), To Count THDocument4 pagesQuestion: 5. (A) Write A Pseudocode, Which Runs in O (Nlogn), To Count THVinu ShoppingNo ratings yet
- Solved - The function f (x) = tan πx − 6 has a zero at (1 - π) arc...Document19 pagesSolved - The function f (x) = tan πx − 6 has a zero at (1 - π) arc...Malik Ijaz Ali AwanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)bassNo ratings yet
- Consider A Ray of Light Traveling in A Vacuum From...Document2 pagesConsider A Ray of Light Traveling in A Vacuum From...Zahra BatoolNo ratings yet
- Principles of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 208Document1 pagePrinciples of Geotechnical Engineering 7th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg - Com 208Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Calculus: (7th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus: (7th Edition)Abraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.43. A Strip Load of Q 1450 lbft2 ...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Your Question Has Been Answered: Question: 1. (A) Suppose That Each Row of An NX N Array A Consists of L's ADocument3 pagesYour Question Has Been Answered: Question: 1. (A) Suppose That Each Row of An NX N Array A Consists of L's AVinu ShoppingNo ratings yet
- Calculus: (7th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus: (7th Edition)Abraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.46. A Flexible Circular Area of Radi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Calculus: (7th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus: (7th Edition)Abraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Solved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Document1 pageSolved A Permeable Soil Layer Is Underlain by An Impervious La...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionDocument3 pagesSolved - Chapter 10 Problem 14P Solution - Classical Mechanics 0th EditionRyuNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 9.4a. If H1 3 FT, H2 4.5 FT, H 1....Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- The Shaft Is Supported by A Smooth Thrust Bearing .Document2 pagesThe Shaft Is Supported by A Smooth Thrust Bearing .Isk100% (1)
- Calculus: (7th Edition)Document1 pageCalculus: (7th Edition)Abraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and Mathematical Statistics: (2nd Edition)Document3 pagesIntroduction To Probability and Mathematical Statistics: (2nd Edition)J Esa AditiyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)bassNo ratings yet
- Solved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Document1 pageSolved The 5-m High Retaining Wall in Figure 13.40c Is Subject...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Solved - Chapter 3 Problem 69RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionDocument3 pagesSolved - Chapter 3 Problem 69RE Solution - Probability and Statistics For Engineers and Scientists 9th EditionJaleel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Solved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Document1 pageSolved A Pervious Soil Layer Is Sandwiched Between Two Impervi...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- 14 Calculus 7th Edition Textbook SolutionsDocument1 page14 Calculus 7th Edition Textbook SolutionsAbraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Use The Timoshenko Method To Estimate The Critical...Document2 pagesUse The Timoshenko Method To Estimate The Critical...Brighton ToshaNo ratings yet
- Loose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)Document5 pagesLoose Leaf For Mechanics of Materials: (7th Edition)TonkaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- 15.6 Todos Os ExercíciosDocument24 pages15.6 Todos Os ExercíciosAbraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis and Design, SI EditionDocument5 pagesPower System Analysis and Design, SI EditionAkimeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Question: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithDocument3 pagesQuestion: Exercise (Test Your Understanding) A Beam of Yellow Light WithMuhammad SatrioNo ratings yet
- Solved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Document1 pageSolved For A Dynamic Compaction Test, The Weight of The Hammer...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- 24 Calculus 7th Edition Chapter 15.3 Problem 1E SolutionDocument1 page24 Calculus 7th Edition Chapter 15.3 Problem 1E SolutionAbraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Defining The Q-Value As (Mi - MF) Ca, Compute The...Document2 pagesDefining The Q-Value As (Mi - MF) Ca, Compute The...Robert ClarkNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- 16 Calculus 7th Edition Textbook Solutions PDFDocument1 page16 Calculus 7th Edition Textbook Solutions PDFAbraao Zuza CostaNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 10.47. A Flexible Rectangular Area Is S...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- In A Frictionless Incompressible Flow The Veloci...Document1 pageIn A Frictionless Incompressible Flow The Veloci...Mergen KhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document3 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Solved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Document1 pageSolved Refer To Figure 7.25. During An Auger Hole Test To Dete...Cristian A. GarridoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)Document2 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Dynamics: (3rd Edition)george guerraNo ratings yet
- Question: 3. The Radius of The Sun Is R 6.96x10 8 M, and The Distance BeDocument2 pagesQuestion: 3. The Radius of The Sun Is R 6.96x10 8 M, and The Distance BeMichael Sean BumanglagNo ratings yet
- 33198Document8 pages33198tatacpsNo ratings yet
- Biology 20 Unit A Exam OutlineDocument1 pageBiology 20 Unit A Exam OutlineTayson PreteNo ratings yet
- Class NotesDocument610 pagesClass NotesNiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Miele G 666Document72 pagesMiele G 666tszabi26No ratings yet
- ITS US Special Edition 2017-18 - Volume 14 Issue 10Document15 pagesITS US Special Edition 2017-18 - Volume 14 Issue 10Leo Club of University of MoratuwaNo ratings yet
- 01 Fir TheoryDocument2 pages01 Fir TheoryTrịnh Minh KhoaNo ratings yet
- RSLogix 5000 Report(s) 120511Document74 pagesRSLogix 5000 Report(s) 120511Renji JacobNo ratings yet
- Display VFD48-1202FN Analog Style - Arduino Project HubDocument27 pagesDisplay VFD48-1202FN Analog Style - Arduino Project HubPhops FrealNo ratings yet
- Prasna Marga Part I, NotesDocument8 pagesPrasna Marga Part I, NotesSaurav ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ampd Data Sheet Vacuum Casting Resin 8263Document2 pagesAmpd Data Sheet Vacuum Casting Resin 8263Lorenzo Guida0% (1)
- Ramana Cell: +91 7780263601 ABAP Consultant Email Id: Professional SummaryDocument4 pagesRamana Cell: +91 7780263601 ABAP Consultant Email Id: Professional SummaryraamanNo ratings yet
- Gereatric Depression ScaleDocument8 pagesGereatric Depression ScaleKheista Prima NurmalaNo ratings yet
- The Art of DifferentiatingDocument348 pagesThe Art of DifferentiatingIvánPortillaNo ratings yet
- Attach Request: RRC Connection Setup Complete RRC Connection Setup CompleteDocument8 pagesAttach Request: RRC Connection Setup Complete RRC Connection Setup CompleteVusal SuleymanovNo ratings yet
- Route TrainingDocument14 pagesRoute Trainingjohn100% (1)
- Improving Orientation With Yoked PrismDocument2 pagesImproving Orientation With Yoked PrismAlexsandro HelenoNo ratings yet
- Contoh Implementasi QMSDocument8 pagesContoh Implementasi QMSIINNo ratings yet
- Format of Actual BatchDocument16 pagesFormat of Actual Batchaljhon dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Pugh ChartDocument1 pagePugh Chartapi-92134725No ratings yet
- Opposite Integers1Document2 pagesOpposite Integers1Hapsari C. Hanandya NannaNo ratings yet
- CMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) ProcessDocument26 pagesCMMI DAR Effectively Apply The Decision Analysis and Resolution (DAR) Processjgonzalezsanz8914100% (1)
- Chapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyDocument28 pagesChapter 5 - Adlerian TherapyRhalf100% (1)
- Lucas - Econometric Policy Evaluation, A CritiqueDocument28 pagesLucas - Econometric Policy Evaluation, A CritiqueFederico Perez CusseNo ratings yet
- Samgroup: Unli Vocab Now LearningDocument20 pagesSamgroup: Unli Vocab Now LearningBrixter MangalindanNo ratings yet
- Middle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Document56 pagesMiddle East Product Booklet 5078 NOV18Mohamed987No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document5 pagesAssignment 4SnehaNo ratings yet
- Sports Tournament Management SystemDocument6 pagesSports Tournament Management SystemPusparajan PapusNo ratings yet
- Uplift With Moment CalculationDocument4 pagesUplift With Moment CalculationdennykvgNo ratings yet
- Rough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookDocument119 pagesRough Translation of Emil Stejnar's Schutzengel BookJustA Dummy100% (1)
- ADMModule - STEM - GP12EU Ia 7Document27 pagesADMModule - STEM - GP12EU Ia 7Jel SuarezNo ratings yet