Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flange Rotation 1602936279
Uploaded by
Neel ShahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flange Rotation 1602936279
Uploaded by
Neel ShahCopyright:
Available Formats
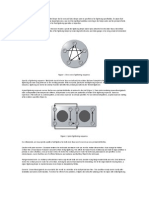
One phenomenon that is encountered in the pressure vessel and piping world is flange rotation.
Rotation
can occur when some form of raised face flange is used, with no contact outside the bolt circle.
As illustrated in the figure to the right, the outer edges of the flange are pulled
toward each other as the bolts are tightened. The inner diameter of the
gasket can be partially unloaded by this process. The effective sealing width
of the gasket is reduced, concentrating the stress on the outer diameter of
the gasket. In addition, thermal expansion and/or contained pressure can
also cause flange rotation.
With thermal expansion and/or contained pressure, the tension in the bolts
decreases as the outer edges of the joint move toward each other. So there
can be a simultaneous increase in stress on (a portion of) the gasket and a
decrease in bolt tension.
In LNG applications, the differential thermal gradients generated result in
differential thermal expansion and contraction in the flanges, which can be detrimental to the sealing
integrity of the joint. Thermal gradients bring about a change in the stiffness of the gasket, which affects the
gasket contact stresses and can result in flange rotation.
Engineers who cope with flange rotation say that it can induce non-
uniformity in gasket contact stresses and significantly increase the
difficulties of sealing a joint and increasing the risk of leakage. Some even
say that rotations as small as 0.10° can make a tight seal almost
impossible.
One way to prevent excess flange rotation is to insert a metal ring between
flange surfaces, outboard of the bolts, as shown in the figure to the left. The
ring must be correctly dimensioned for the flanged joint to work correctly.
However, if it is too thin, the flange may still be able to rotate. If it is too
thick, it may prevent the bolts from properly preloading the gaskets. If it
allows for gasket deflection but prevents rotation, it will provide an outboard
support or fulcrum for the flanges and minimize rotation.
ASME Code recommends that the value of “hG” (radial distance from gasket load reaction to the bolt circle)
should be kept to a minimum to reduce flange rotation at the sealing surface. This results in a very small
clearance between the bolt circle diameter and the gasket, and necessitates a large number of small
diameter bolts rather than a smaller number of large diameter bolts.
You might also like
- Reinforced Masonry Engineering Handbook .6th - Ed.secDocument647 pagesReinforced Masonry Engineering Handbook .6th - Ed.secEc Ef100% (2)
- Piston RingDocument43 pagesPiston RingSudath Kularathna67% (3)
- Flange LeakageDocument29 pagesFlange LeakageSandeep Bhatia100% (2)
- 2019-2-16 Fiber Cut Parts ListDocument50 pages2019-2-16 Fiber Cut Parts ListNguyen Van Hoi100% (3)
- Flange RotationDocument1 pageFlange RotationAnkit LonareNo ratings yet
- GasketsDocument8 pagesGasketsRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Assemble Flanges Correctly for Leak-Free Butterfly ValvesDocument16 pagesAssemble Flanges Correctly for Leak-Free Butterfly ValvesSharon LambertNo ratings yet
- Drill Rod Threads: Tips To Avoid Common Problems and Improve ProductivityDocument9 pagesDrill Rod Threads: Tips To Avoid Common Problems and Improve ProductivityOscarNo ratings yet
- 10 Residual StressDocument21 pages10 Residual StressAlaaNo ratings yet
- WELDING DEFECTS AND REMEDIES GUIDEDocument3 pagesWELDING DEFECTS AND REMEDIES GUIDEebrahem_sahil5188No ratings yet
- Ensure Even Preload with Proper Tightening Tools and SequenceDocument2 pagesEnsure Even Preload with Proper Tightening Tools and SequenceMachineryengNo ratings yet
- How To Control The Warping of Parts in Thin SheetDocument6 pagesHow To Control The Warping of Parts in Thin SheetNeil WayneNo ratings yet
- The Consequence of Bolt FailuresDocument4 pagesThe Consequence of Bolt FailuresasdfgaNo ratings yet
- Hertz Pressure Is The Contact Pressure Between The Roller and The TireDocument2 pagesHertz Pressure Is The Contact Pressure Between The Roller and The TiresufferingpeteNo ratings yet
- Cylinder head bolts with angular tightening techniqueDocument5 pagesCylinder head bolts with angular tightening techniqueAdrianNo ratings yet
- In Torque Technology: Leading The WorldDocument2 pagesIn Torque Technology: Leading The WorldThomas CroweNo ratings yet
- Distortion Prevent and ControlDocument14 pagesDistortion Prevent and ControlTheAnh TranNo ratings yet
- Bearing Operating ConditionsDocument7 pagesBearing Operating ConditionsVolety_Sarma_1703No ratings yet
- Common Causes of Bolted Joint LeakageDocument2 pagesCommon Causes of Bolted Joint LeakageAnonymous avGU1iNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding DesignDocument17 pagesInjection Molding DesignprasathbalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - DistortionDocument22 pagesLesson 5 - DistortionKhepa BabaNo ratings yet
- 1 What Causes Distortion?: Longitudinal ShrinkageDocument21 pages1 What Causes Distortion?: Longitudinal Shrinkage4romi89No ratings yet
- Welding Defects (Copy and Paste Je)Document9 pagesWelding Defects (Copy and Paste Je)Hamimi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Living Hinge DesignDocument9 pagesLiving Hinge Designom.mauryaNo ratings yet
- Torque InstructionsDocument13 pagesTorque Instructionsjfrench_62000No ratings yet
- 5 Basic Weld Joint Configurations ExplainedDocument2 pages5 Basic Weld Joint Configurations Explainedrahul063No ratings yet
- Learn from screw autopsies to prevent catastrophic wearDocument7 pagesLearn from screw autopsies to prevent catastrophic wearShiven KapilNo ratings yet
- A Different Kind of Animal WP April 2020 1Document3 pagesA Different Kind of Animal WP April 2020 1payam.ghafooriNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of BearingDocument21 pagesMaintenance of BearingJakJhonNo ratings yet
- DistortionDocument18 pagesDistortionSteransko100% (1)
- Distortion in Aluminum Welded StructuresDocument3 pagesDistortion in Aluminum Welded StructuresRaron1No ratings yet
- Factor Bolted JointsDocument42 pagesFactor Bolted JointsOliver Kraus100% (1)
- Lapping tapers and seatings to improve fit and finishDocument1 pageLapping tapers and seatings to improve fit and finishsyllavethyjimNo ratings yet
- Phillips Kiln Tires ServicesDocument53 pagesPhillips Kiln Tires ServicesNael100% (14)
- Getting A Good Fit: Selecting The Right Shaft and Housing ToleranceDocument2 pagesGetting A Good Fit: Selecting The Right Shaft and Housing Toleranceeng13No ratings yet
- Design of Flange JointDocument14 pagesDesign of Flange Jointmichal_lysy100% (2)
- Seals and Gaskets: 3.0 Table of ContentsDocument40 pagesSeals and Gaskets: 3.0 Table of Contentsthulasi_krishnaNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engine RepairDocument8 pagesInternal Combustion Engine RepairRyan EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Distortion ControlDocument6 pagesDistortion ControlMOHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- D04 Shaft Deflection Runout Vibration and Axial MotionDocument15 pagesD04 Shaft Deflection Runout Vibration and Axial Motionsuraj dhulannavarNo ratings yet
- Home About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting InfoDocument9 pagesHome About Us Software Services Training Download Pricing Bolting Infopaeg6512No ratings yet
- D15 Integral Journal BearingsDocument9 pagesD15 Integral Journal BearingsSuresh Kumar MittapalliNo ratings yet
- TC ClamsDocument8 pagesTC ClamsSatyam MadameNo ratings yet
- Bidirectional Sealing Ball Valves in Power ApplicationsDocument3 pagesBidirectional Sealing Ball Valves in Power Applicationsxisefengchuang100% (1)
- MEP 1 Shafting SystemDocument19 pagesMEP 1 Shafting SystemYohannes DennisNo ratings yet
- Valve World Nov 2014Document2 pagesValve World Nov 2014windsurferke007No ratings yet
- To Weld or Not To Weld The Face of Kiln RollersDocument3 pagesTo Weld or Not To Weld The Face of Kiln RollerssreeganeshrNo ratings yet
- Chapter D4: Shaft Deflection, Runout, Vibration, and Axial MotionDocument21 pagesChapter D4: Shaft Deflection, Runout, Vibration, and Axial MotionengrasrarNo ratings yet
- Rotary Kiln Shells: 1. Preventive Measures For Longitudinal CracksDocument3 pagesRotary Kiln Shells: 1. Preventive Measures For Longitudinal CracksCarlos Ramón Plazaola LorioNo ratings yet
- Glulam Connection DetailsDocument0 pagesGlulam Connection DetailsMichael SheininNo ratings yet
- Prevent Wrinkling in Deep Drawing With Blank Holder DesignDocument2 pagesPrevent Wrinkling in Deep Drawing With Blank Holder Designa c s reddyNo ratings yet
- Bearing Mounting Basics PDFDocument4 pagesBearing Mounting Basics PDFssoares1989No ratings yet
- Brake Troubleshooting TipsDocument2 pagesBrake Troubleshooting Tips6yk1swyxcNo ratings yet
- A Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesFrom EverandA Book of Helpful Tips on Overhauling a Vintage Engine - Including Car, Motorbike and Lawn Mower EnginesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Rock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesFrom EverandRock Blasting: A Practical Treatise on the Means Employed in Blasting Rocks for Industrial PurposesNo ratings yet
- Popular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoFrom EverandPopular Mechanics: How to Fix Anything: Essential Home Repairs Anyone Can DoRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Bearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsFrom EverandBearings And Bearing Metals: A Treatise Dealing with Various Types of Plain Bearings, the Compositions and Properties of Bearing Metals, Methods of Insuring Proper Lubrication, and Important Factors Governing the Design of Plain BearingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Lotto Ab 2016Document13 pagesLotto Ab 2016Neel ShahNo ratings yet
- Binary Long Term Pairs Laddrer + One Touch + Forex 325 960 120 1790 430 465 180 215 35 1930Document2 pagesBinary Long Term Pairs Laddrer + One Touch + Forex 325 960 120 1790 430 465 180 215 35 1930Neel ShahNo ratings yet
- Brochure WeldersDocument16 pagesBrochure WeldersNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- All Study Programmes in Germany - DAAD - Deutscher Akademischer AustauschdienstDocument2 pagesAll Study Programmes in Germany - DAAD - Deutscher Akademischer AustauschdienstNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel Worksheet PDFDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Excel Worksheet PDFNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Cadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphDocument6 pagesCadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Hum To Tere Ashik Hai Sadiyo PuraneDocument1 pageHum To Tere Ashik Hai Sadiyo PuraneNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Cadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphDocument6 pagesCadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Cadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphDocument6 pagesCadworx & Analysis Solutions: IntergraphNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- IGNOUDocument1 pageIGNOUNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Ashish SinghDocument1 pageAshish SinghNeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Galvanic Cells, The Nernst EquationDocument2 pagesGalvanic Cells, The Nernst Equationanon_86967897No ratings yet
- Intermodal Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in TwoDocument4 pagesIntermodal Stimulated Brillouin Scattering in TwoRamón José Pérez MenéndezNo ratings yet
- Solid State 1 MR DavidDocument188 pagesSolid State 1 MR Davidfrank samndomiNo ratings yet
- 1-PbSO4 Leaching in Citric Acid Sodium Citrate Solution and Subsequent ...Document10 pages1-PbSO4 Leaching in Citric Acid Sodium Citrate Solution and Subsequent ...Gregorio Antonio Valero VerdeNo ratings yet
- Home Assignment 5 PHY 306/604 Statistical MechanicsDocument3 pagesHome Assignment 5 PHY 306/604 Statistical MechanicsSayan KuntiNo ratings yet
- Turbulent Flow Through Pipes: Friction Factor and Velocity DistributionDocument17 pagesTurbulent Flow Through Pipes: Friction Factor and Velocity Distributiondurga345No ratings yet
- Unit 7 Future Home (English For Technology 2)Document2 pagesUnit 7 Future Home (English For Technology 2)Set S. Pirath0% (1)
- CW Spatial ModesDocument5 pagesCW Spatial Modes900pennyNo ratings yet
- De Almeida Et Al., 2015Document11 pagesDe Almeida Et Al., 2015lianyNo ratings yet
- PROTECTIONS & Interlocks Diary 300MWDocument42 pagesPROTECTIONS & Interlocks Diary 300MWkarthick.gNo ratings yet
- Kinematic ViscosityDocument4 pagesKinematic ViscosityAloka KarunarathneNo ratings yet
- Concrete reinforcement ratio calculation and stress analysisDocument36 pagesConcrete reinforcement ratio calculation and stress analysisMifthah Reino AnantaNo ratings yet
- B-144 - Datasheet - PSVDocument6 pagesB-144 - Datasheet - PSVRameez AhmedNo ratings yet
- Martini Absorb 1216Document2 pagesMartini Absorb 1216snailbookNo ratings yet
- Hydro Generators Losses Measurement in Accordance To IEEE-STD-115 and IEC-60034-2Document7 pagesHydro Generators Losses Measurement in Accordance To IEEE-STD-115 and IEC-60034-2saliyarumesh2292No ratings yet
- How smartphone camera specs affect low light performanceDocument2 pagesHow smartphone camera specs affect low light performanceSatyendra KumarNo ratings yet
- MHI Turbine (Main)Document86 pagesMHI Turbine (Main)Service Port100% (2)
- Esas - 1Document37 pagesEsas - 1Rodeth Ann MendozaNo ratings yet
- RAM Frame - Semirigid Diaphragms FAQ - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesDocument8 pagesRAM Frame - Semirigid Diaphragms FAQ - RAM - STAAD Wiki - RAM - STAAD - Bentley CommunitiesPourang EzzatfarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Sheet PDFDocument65 pagesLecture Sheet PDFFaruk abdullahNo ratings yet
- Part 4 - Soft GroundDocument64 pagesPart 4 - Soft GroundsquakeNo ratings yet
- Newtons Third LawDocument20 pagesNewtons Third Lawapi-285179261No ratings yet
- Ambient Vibration Testing of Historical Monuments in OhridDocument11 pagesAmbient Vibration Testing of Historical Monuments in OhridsaulolmNo ratings yet
- CHE3044F Reactor Design Tutorial ProblemsDocument4 pagesCHE3044F Reactor Design Tutorial ProblemsnmhatityeNo ratings yet
- Counterfort Retaining Wall B.C. Punamia 05-Feb-2012Document44 pagesCounterfort Retaining Wall B.C. Punamia 05-Feb-2012Lokesh Sharma40% (5)
- Manuel Des Donnã©es Techniques AQUACIAT LD 150-600 (SEER LT)Document12 pagesManuel Des Donnã©es Techniques AQUACIAT LD 150-600 (SEER LT)umarmirza83No ratings yet
- LensesDocument13 pagesLenseshelmi_tarmiziNo ratings yet
- Experimental Comparison of Single and Multistage Air Compressor EfficienciesDocument11 pagesExperimental Comparison of Single and Multistage Air Compressor EfficienciesJohn barry CorpuzNo ratings yet