Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Uploaded by
blaze perezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HNC Operations Engineering Noel Jennings Engineering Design AssignmentDocument13 pagesHNC Operations Engineering Noel Jennings Engineering Design AssignmentNoel JenningsNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument55 pagesElectronic ComponentsAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Grant Inspection and Testing Report PDFDocument4 pagesSolar PV Grant Inspection and Testing Report PDFnino causapin50% (2)
- Broadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Document2 pagesBroadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Fer CurtinoNo ratings yet
- 233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCDocument9 pages233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCmuhammad haseebNo ratings yet
- 3.02 Components and Parameters of TransistorsDocument2 pages3.02 Components and Parameters of TransistorsVamsiMadupuNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Replacement TransistorDocument2 pagesChoosing A Replacement TransistorRafael CossNo ratings yet
- Transistors To Transistor SwitchDocument6 pagesTransistors To Transistor SwitchIdrisa EmasoliNo ratings yet
- Transistor Ratings and Packages: Bipolar Junction Transistors (Incomplete)Document2 pagesTransistor Ratings and Packages: Bipolar Junction Transistors (Incomplete)contrasterNo ratings yet
- Difference Between SINGLE-PHASE VERSES THREE-PhaseDocument1 pageDifference Between SINGLE-PHASE VERSES THREE-Phasejay shahNo ratings yet
- Transistor Specifications ExplainedDocument3 pagesTransistor Specifications ExplainedJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- Transistor Specification and Parameter DefinitionsDocument4 pagesTransistor Specification and Parameter Definitionsরায়হান RayhanNo ratings yet
- RF Mosfet BasicsDocument21 pagesRF Mosfet BasicsStephen Dunifer100% (5)
- Transistor Specification ParametersDocument2 pagesTransistor Specification Parametersamanpreet_kaur11No ratings yet
- Phono Cartridge Impedance MatchingDocument5 pagesPhono Cartridge Impedance MatchingSougata DasNo ratings yet
- Oscillator BasicsDocument20 pagesOscillator BasicsRizGust Anunnaki100% (2)
- Bari Ena TheoryDocument4 pagesBari Ena TheoryAbdul BariNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument4 pagesTransistorsapi-3713690No ratings yet
- Important Conclusions and Concepts: BJT SummaryDocument9 pagesImportant Conclusions and Concepts: BJT SummaryTomashita ArenasNo ratings yet
- Gyrator TheoryDocument26 pagesGyrator Theoryramesh krishnaNo ratings yet
- Transistor CasingDocument2 pagesTransistor CasingryinejanNo ratings yet
- Power Supply RepairDocument4 pagesPower Supply RepairterezkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture#03Document17 pagesLecture#03Sarmad AsadNo ratings yet
- Maximum Permissible Flux Density in Transformers at Rated Voltage and FrequencyDocument7 pagesMaximum Permissible Flux Density in Transformers at Rated Voltage and Frequencysalemg82No ratings yet
- Using Transistors As SwitchesDocument1 pageUsing Transistors As SwitchesHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Grounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairDocument8 pagesGrounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairVijai PrasathNo ratings yet
- Driving Nixie With TranzistorsDocument8 pagesDriving Nixie With Tranzistorsfilip_bonacic3908No ratings yet
- DC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsDocument73 pagesDC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsLaurence Camacho AquinoNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument14 pagesTransistorsCarolyne DaleNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Basic Electronics - TransistorDocument66 pagesTopic 6 Basic Electronics - TransistorJENNIFER SERVONo ratings yet
- BITX - A Bidirectional SSB QRP Transceiver For HomebrewersDocument7 pagesBITX - A Bidirectional SSB QRP Transceiver For HomebrewersJuan Manuel Martorell100% (1)
- Introduction To Amplifier DesignDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Amplifier DesignJuanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Transformer DesignDocument18 pagesElectronics Transformer DesignPriyanka Tayal100% (2)
- How To Test A TransistorDocument5 pagesHow To Test A Transistorjuliet coronadoNo ratings yet
- Basics of TransformerDocument22 pagesBasics of Transformert_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Project Report FileDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics Project Report FileweNo ratings yet
- BC547Document3 pagesBC547Rohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Design Grounding TransformersDocument9 pagesDesign Grounding TransformerscalecaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Amplifier DesignDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Amplifier Designdragos62bondar100% (1)
- Using Bipolar Transistors As SwitchesDocument3 pagesUsing Bipolar Transistors As Switchesqqqaaa1No ratings yet
- People Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesPeople Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentshivaNo ratings yet
- 1 General Requirements For TestsDocument7 pages1 General Requirements For TestsmoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - Group 5Document10 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - Group 5Kiel FloresNo ratings yet
- Institutional Training Report EE 3rd SemesterDocument14 pagesInstitutional Training Report EE 3rd Semesterpiyushanand28No ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Transistor)Document6 pagesAppendix 1 Transistor)Achik SniperNo ratings yet
- VLSI Basic Design RulesDocument3 pagesVLSI Basic Design RulesBehnam KhaleghiNo ratings yet
- L3 TransformersDocument62 pagesL3 TransformersORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNo ratings yet
- A Simple Dual Band SSB TransceiverDocument10 pagesA Simple Dual Band SSB Transceiververd leonard100% (1)
- Project FileDocument74 pagesProject Filevinaysnair89No ratings yet
- Techo Notes - Capacitors - Fixed Value: Capacitors Are Usually Referred To by What They Do in A CircuitDocument10 pagesTecho Notes - Capacitors - Fixed Value: Capacitors Are Usually Referred To by What They Do in A Circuitmarciano_meNo ratings yet
- Power Plant ReportDocument17 pagesPower Plant ReportLanz de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document39 pagesElectronics 1Eniola AjaoNo ratings yet
- Grounding TransformersDocument4 pagesGrounding TransformersCharles BenwariNo ratings yet
- Dhiviyansh PunamiyaDocument5 pagesDhiviyansh PunamiyaDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- 300 W Subwoofer Power AmplifierDocument7 pages300 W Subwoofer Power AmplifierHU GO FPNo ratings yet
- Electronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orDocument13 pagesElectronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 111 MergedDocument47 pages111 MergedIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- EE 339 - Solid-State Electronic Devices: Orshansky@mail - Utexas.eduDocument2 pagesEE 339 - Solid-State Electronic Devices: Orshansky@mail - Utexas.eduAshish BansalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Main Difference Between Electrical and ElectronicsDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Main Difference Between Electrical and ElectronicsAmbuj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mechanisms in Petrochemical IndustryDocument11 pagesFailure Mechanisms in Petrochemical IndustryGonzalo GómezNo ratings yet
- Perfusor Space Service ManualDocument134 pagesPerfusor Space Service ManualSkywalker_92100% (1)
- DH100ACDCLWP Watertight Air Duct Smoke Detector With Extended Air Speed RangeDocument8 pagesDH100ACDCLWP Watertight Air Duct Smoke Detector With Extended Air Speed RangeArgile-assholeNo ratings yet
- Hubbell Home SelectDocument62 pagesHubbell Home SelectGabriel Alcantara OrozcoNo ratings yet
- 3x14 AWG 600V Overall Shielded Control Cable - 8BCP103xxxDocument2 pages3x14 AWG 600V Overall Shielded Control Cable - 8BCP103xxxVentas BeorienteNo ratings yet
- What Is Sekhemic Energy? by DR Neb Heru - (Full Nun Tablet - Book)Document258 pagesWhat Is Sekhemic Energy? by DR Neb Heru - (Full Nun Tablet - Book)Neb Heru95% (59)
- Fds181-Sirene AudiovisualDocument3 pagesFds181-Sirene AudiovisualCarlos Frederico Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- 3300xl - 8mm Proximity Transducer System DatasheetDocument36 pages3300xl - 8mm Proximity Transducer System DatasheetPrithwish ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- 02 03 Overcurrent ProtectionDocument136 pages02 03 Overcurrent Protectiondurgakiranyadav100% (3)
- SPWM Full Bridge Inverter With Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterDocument9 pagesSPWM Full Bridge Inverter With Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterOdnamra AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Philips FWC170Document54 pagesPhilips FWC170Luis Nava CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sadelta Echo Master Plus SCHDocument1 pageSadelta Echo Master Plus SCHSalvi AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Switching SystemDocument6 pagesBasics of Switching SystemSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument21 pagesCase Studyultrasonic81No ratings yet
- Dual/Quad Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifiers OP295/OP495: Features Pin ConfigurationsDocument16 pagesDual/Quad Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifiers OP295/OP495: Features Pin Configurationsabc1000No ratings yet
- 1990 Burr-Brown Integrated Circuits Data Book Supplement 33b PDFDocument657 pages1990 Burr-Brown Integrated Circuits Data Book Supplement 33b PDFpriyaNo ratings yet
- Substation Grounding Grid Design Using ADocument23 pagesSubstation Grounding Grid Design Using ADavid LondoñoNo ratings yet
- YOKOGAWA - WE410 Silica AnalyzerDocument3 pagesYOKOGAWA - WE410 Silica AnalyzerRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design ReportDocument40 pagesVlsi Design ReportUjjwal DhusiaNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own UpsDocument10 pagesBuild Your Own UpssakergayenrNo ratings yet
- Miele C3 Complete ManualDocument36 pagesMiele C3 Complete ManualJoshua BrunnerNo ratings yet
- Sc-Ak780 Manual de Servicio PDFDocument142 pagesSc-Ak780 Manual de Servicio PDFAndres CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Basic Combinatorial CircuitsDocument4 pagesExperiment 8 Basic Combinatorial CircuitsPk KumarNo ratings yet
- Relay Module - PLC-RSC-24DC/21 - 2966171: Key Commercial DataDocument15 pagesRelay Module - PLC-RSC-24DC/21 - 2966171: Key Commercial Datasatheez3251No ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS-II Oct-Nov 2020Document2 pagesELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS-II Oct-Nov 2020Vedula SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesSeries RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisMartNo ratings yet
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Uploaded by
blaze perezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Step by Step Instructions For Transistor
Uploaded by
blaze perezCopyright:
Available Formats
Step by step instructions:
1. Choose a transistor of the same polarity: The first major selection criterion is whether the
transistor is PNP or NPN.
2. Select a replacement transistor of the same material: Most transistors are either silicon or
germanium. As bias voltages and other features are different it is necessary to select a
replacement transistor with the same material.
3. Select the same functional type of transistor: Transistors are normally given an indication of
their application in the datasheets. The replacement should have the same application if
possible.
4. Choose a replacement with the same package: Choosing a replacement transistor with the
same package and pin-out will mean that many of the characteristics including power capability
are the same. Ensuring with pin-out is the same (most but not all transistors have their leads in
order - EBC) will save many problems with fitting.
5. Select a replacement transistor with the same breakdown voltage: Ensure that figures for VCEO
and VCBO etc are at least as high as the original transistor. Voltage at least or higher
6. Check it can take the current: Ensure that the replacement transistor can pass the required
current - it should have an ICmax greater than or equal to the original transistor.
7. Collector Current is Greater than or equal to
8. Select a transistor with a similar Hfe: It is necessary to ensure that the current gain of the
replacement transistor is about the same as the original. Current gain values normally vary
widely even for transistors of the same type so some variation will be acceptable.
9. Similar dc current gain
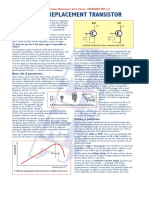
10. Select a replacement transistor with equivalent Ft: It is necessary to ensure that the
replacement transistor will be able to operate at the relevant frequencies, so a similar or slightly
higher Ft is advisable. Don't go for a transistor with a much higher Ft as this may increase the
risk of oscillation.
11. . Don't go for a transistor with a much higher transition frequency
12. Choose a transistor with a similar power dissipation : It is necessary to ensure that the
replacement transistor can handle the power that it will dissipate within the circuit. Choosing a
replacement transistor with a similar can style will often mean that both transistors have a
similar power dissipation.
13. similar power dissipation in collector can be more
14. Check for any special features: While ensuring the features above are selected, there may be
some additional features that need to be considered. These are normally required when
transistors are used in specialist applications.
You might also like
- HNC Operations Engineering Noel Jennings Engineering Design AssignmentDocument13 pagesHNC Operations Engineering Noel Jennings Engineering Design AssignmentNoel JenningsNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument55 pagesElectronic ComponentsAnju GuptaNo ratings yet
- Solar PV Grant Inspection and Testing Report PDFDocument4 pagesSolar PV Grant Inspection and Testing Report PDFnino causapin50% (2)
- Broadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Document2 pagesBroadband Biasing of Amplifiers v00p1112Fer CurtinoNo ratings yet
- 233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCDocument9 pages233 2 V Example 13.23.: C B BC BCmuhammad haseebNo ratings yet
- 3.02 Components and Parameters of TransistorsDocument2 pages3.02 Components and Parameters of TransistorsVamsiMadupuNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Replacement TransistorDocument2 pagesChoosing A Replacement TransistorRafael CossNo ratings yet
- Transistors To Transistor SwitchDocument6 pagesTransistors To Transistor SwitchIdrisa EmasoliNo ratings yet
- Transistor Ratings and Packages: Bipolar Junction Transistors (Incomplete)Document2 pagesTransistor Ratings and Packages: Bipolar Junction Transistors (Incomplete)contrasterNo ratings yet
- Difference Between SINGLE-PHASE VERSES THREE-PhaseDocument1 pageDifference Between SINGLE-PHASE VERSES THREE-Phasejay shahNo ratings yet
- Transistor Specifications ExplainedDocument3 pagesTransistor Specifications ExplainedJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- Transistor Specification and Parameter DefinitionsDocument4 pagesTransistor Specification and Parameter Definitionsরায়হান RayhanNo ratings yet
- RF Mosfet BasicsDocument21 pagesRF Mosfet BasicsStephen Dunifer100% (5)
- Transistor Specification ParametersDocument2 pagesTransistor Specification Parametersamanpreet_kaur11No ratings yet
- Phono Cartridge Impedance MatchingDocument5 pagesPhono Cartridge Impedance MatchingSougata DasNo ratings yet
- Oscillator BasicsDocument20 pagesOscillator BasicsRizGust Anunnaki100% (2)
- Bari Ena TheoryDocument4 pagesBari Ena TheoryAbdul BariNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument4 pagesTransistorsapi-3713690No ratings yet
- Important Conclusions and Concepts: BJT SummaryDocument9 pagesImportant Conclusions and Concepts: BJT SummaryTomashita ArenasNo ratings yet
- Gyrator TheoryDocument26 pagesGyrator Theoryramesh krishnaNo ratings yet
- Transistor CasingDocument2 pagesTransistor CasingryinejanNo ratings yet
- Power Supply RepairDocument4 pagesPower Supply RepairterezkiNo ratings yet
- Lecture#03Document17 pagesLecture#03Sarmad AsadNo ratings yet
- Maximum Permissible Flux Density in Transformers at Rated Voltage and FrequencyDocument7 pagesMaximum Permissible Flux Density in Transformers at Rated Voltage and Frequencysalemg82No ratings yet
- Using Transistors As SwitchesDocument1 pageUsing Transistors As SwitchesHenrique MarquesNo ratings yet
- Grounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairDocument8 pagesGrounding Transformer FAQs - Pacific Crest Transformers - Custom Liquid Filled Transformers & RepairVijai PrasathNo ratings yet
- Driving Nixie With TranzistorsDocument8 pagesDriving Nixie With Tranzistorsfilip_bonacic3908No ratings yet
- DC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsDocument73 pagesDC Power Supply and Voltage RegulatorsLaurence Camacho AquinoNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument14 pagesTransistorsCarolyne DaleNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Basic Electronics - TransistorDocument66 pagesTopic 6 Basic Electronics - TransistorJENNIFER SERVONo ratings yet
- BITX - A Bidirectional SSB QRP Transceiver For HomebrewersDocument7 pagesBITX - A Bidirectional SSB QRP Transceiver For HomebrewersJuan Manuel Martorell100% (1)
- Introduction To Amplifier DesignDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Amplifier DesignJuanNo ratings yet
- Electronics Transformer DesignDocument18 pagesElectronics Transformer DesignPriyanka Tayal100% (2)
- How To Test A TransistorDocument5 pagesHow To Test A Transistorjuliet coronadoNo ratings yet
- Basics of TransformerDocument22 pagesBasics of Transformert_syamprasadNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Project Report FileDocument17 pagesAnalog Electronics Project Report FileweNo ratings yet
- BC547Document3 pagesBC547Rohit VermaNo ratings yet
- Design Grounding TransformersDocument9 pagesDesign Grounding TransformerscalecaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Amplifier DesignDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Amplifier Designdragos62bondar100% (1)
- Using Bipolar Transistors As SwitchesDocument3 pagesUsing Bipolar Transistors As Switchesqqqaaa1No ratings yet
- People Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentDocument28 pagesPeople Oriented Innovation and DevelopmentshivaNo ratings yet
- 1 General Requirements For TestsDocument7 pages1 General Requirements For TestsmoNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor - Group 5Document10 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor - Group 5Kiel FloresNo ratings yet
- Institutional Training Report EE 3rd SemesterDocument14 pagesInstitutional Training Report EE 3rd Semesterpiyushanand28No ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Transistor)Document6 pagesAppendix 1 Transistor)Achik SniperNo ratings yet
- VLSI Basic Design RulesDocument3 pagesVLSI Basic Design RulesBehnam KhaleghiNo ratings yet
- L3 TransformersDocument62 pagesL3 TransformersORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNo ratings yet
- A Simple Dual Band SSB TransceiverDocument10 pagesA Simple Dual Band SSB Transceiververd leonard100% (1)
- Project FileDocument74 pagesProject Filevinaysnair89No ratings yet
- Techo Notes - Capacitors - Fixed Value: Capacitors Are Usually Referred To by What They Do in A CircuitDocument10 pagesTecho Notes - Capacitors - Fixed Value: Capacitors Are Usually Referred To by What They Do in A Circuitmarciano_meNo ratings yet
- Power Plant ReportDocument17 pagesPower Plant ReportLanz de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Electronics 1Document39 pagesElectronics 1Eniola AjaoNo ratings yet
- Grounding TransformersDocument4 pagesGrounding TransformersCharles BenwariNo ratings yet
- Dhiviyansh PunamiyaDocument5 pagesDhiviyansh PunamiyaDhiviyansh Punamiya OT3 - 433No ratings yet
- 300 W Subwoofer Power AmplifierDocument7 pages300 W Subwoofer Power AmplifierHU GO FPNo ratings yet
- Electronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orDocument13 pagesElectronics Repair and Troubleshooting: A Transistor Is A Semiconductor Device Used To Amplify orIra CervoNo ratings yet
- 111 MergedDocument47 pages111 MergedIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Boat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaFrom EverandBoat Maintenance Companions: Electrics & Diesel Companions at SeaNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- EE 339 - Solid-State Electronic Devices: Orshansky@mail - Utexas.eduDocument2 pagesEE 339 - Solid-State Electronic Devices: Orshansky@mail - Utexas.eduAshish BansalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Main Difference Between Electrical and ElectronicsDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Main Difference Between Electrical and ElectronicsAmbuj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Failure Mechanisms in Petrochemical IndustryDocument11 pagesFailure Mechanisms in Petrochemical IndustryGonzalo GómezNo ratings yet
- Perfusor Space Service ManualDocument134 pagesPerfusor Space Service ManualSkywalker_92100% (1)
- DH100ACDCLWP Watertight Air Duct Smoke Detector With Extended Air Speed RangeDocument8 pagesDH100ACDCLWP Watertight Air Duct Smoke Detector With Extended Air Speed RangeArgile-assholeNo ratings yet
- Hubbell Home SelectDocument62 pagesHubbell Home SelectGabriel Alcantara OrozcoNo ratings yet
- 3x14 AWG 600V Overall Shielded Control Cable - 8BCP103xxxDocument2 pages3x14 AWG 600V Overall Shielded Control Cable - 8BCP103xxxVentas BeorienteNo ratings yet
- What Is Sekhemic Energy? by DR Neb Heru - (Full Nun Tablet - Book)Document258 pagesWhat Is Sekhemic Energy? by DR Neb Heru - (Full Nun Tablet - Book)Neb Heru95% (59)
- Fds181-Sirene AudiovisualDocument3 pagesFds181-Sirene AudiovisualCarlos Frederico Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- 3300xl - 8mm Proximity Transducer System DatasheetDocument36 pages3300xl - 8mm Proximity Transducer System DatasheetPrithwish ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- 02 03 Overcurrent ProtectionDocument136 pages02 03 Overcurrent Protectiondurgakiranyadav100% (3)
- SPWM Full Bridge Inverter With Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterDocument9 pagesSPWM Full Bridge Inverter With Transformerless PV Grid Connected InverterOdnamra AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Philips FWC170Document54 pagesPhilips FWC170Luis Nava CastilloNo ratings yet
- Sadelta Echo Master Plus SCHDocument1 pageSadelta Echo Master Plus SCHSalvi AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Basics of Switching SystemDocument6 pagesBasics of Switching SystemSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument21 pagesCase Studyultrasonic81No ratings yet
- Dual/Quad Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifiers OP295/OP495: Features Pin ConfigurationsDocument16 pagesDual/Quad Rail-to-Rail Operational Amplifiers OP295/OP495: Features Pin Configurationsabc1000No ratings yet
- 1990 Burr-Brown Integrated Circuits Data Book Supplement 33b PDFDocument657 pages1990 Burr-Brown Integrated Circuits Data Book Supplement 33b PDFpriyaNo ratings yet
- Substation Grounding Grid Design Using ADocument23 pagesSubstation Grounding Grid Design Using ADavid LondoñoNo ratings yet
- YOKOGAWA - WE410 Silica AnalyzerDocument3 pagesYOKOGAWA - WE410 Silica AnalyzerRangga TaufiqurahmanNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design ReportDocument40 pagesVlsi Design ReportUjjwal DhusiaNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own UpsDocument10 pagesBuild Your Own UpssakergayenrNo ratings yet
- Miele C3 Complete ManualDocument36 pagesMiele C3 Complete ManualJoshua BrunnerNo ratings yet
- Sc-Ak780 Manual de Servicio PDFDocument142 pagesSc-Ak780 Manual de Servicio PDFAndres CaicedoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 8 Basic Combinatorial CircuitsDocument4 pagesExperiment 8 Basic Combinatorial CircuitsPk KumarNo ratings yet
- Relay Module - PLC-RSC-24DC/21 - 2966171: Key Commercial DataDocument15 pagesRelay Module - PLC-RSC-24DC/21 - 2966171: Key Commercial Datasatheez3251No ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS-II Oct-Nov 2020Document2 pagesELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS-II Oct-Nov 2020Vedula SudhakarNo ratings yet
- Series RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisDocument13 pagesSeries RLC Circuit and RLC Series Circuit AnalysisMartNo ratings yet