Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Visualization and Key Info For Capital Assets and CCA
Uploaded by
Bob BillyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1 Visualization and Key Info For Capital Assets and CCA
Uploaded by
Bob BillyCopyright:
Available Formats
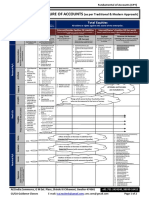
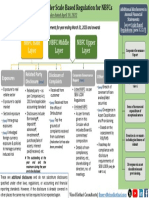
VISUALIZATION TO INTRODUCE MODULE 2 - ADM 4344
CORE CONCEPTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE TAX IMPLICATIONS FROM CASH OUTFLOWS
$$ is spent
Item is not
deductible
Item is a (e.g. personal
capital asset Deduct as Item is added or disallowed
OR current OR to inventory OR
item)
expense (the tax OR
treatement of Item is
inventory is partially
Determine usually the deductible
which CCA same as the (e.g. home
Class accounting office
treatment) expense)
- Rules for year of acquisition vs. rules for years
Determine
subsequent to acquisition
maximum CCA
- Special rules (e.g. CCA cannot create or increase a
per ITA
loss against income from property
For each CCA class, taxpayer can take anywhere
between 0 and maximum CCA allowed per ITA.
Determine
If taxpayer was in low bracket and expected to be
optimal CCA
in higher bracket in subsequent years, it may be
deduction for
good tax planning to take $0 deduction for CCA in
specific
current year
situation
Copyright – Rick Musselman
Not for duplication, reproduction or sharing
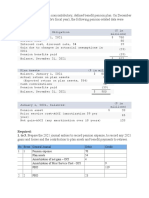
VISUALIZATION TO INTRODUCE MODULE 2 - ADM 4344 (Continued)
CORE CONCEPTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE TAX IMPLICATIONS FROM CASH OUTFLOWS
Typical disposition of asset
Calculation 1: Proceeds of disposition (POD) - AcB = Capital gain (loss)***
depreciable
XXXX assets
*** Important *** Capital loss is denied on disposition of capital
NOTE: AcB = capital cost = adjusted cost base
Calculation 2 (only for dispositions of depreciable capital assets):
UCC - Lesser (POD vs. AcB) = Terminal loss or recapture or reduction of UCC balance with
no immediate effect on taxable income
Other notes
AccII rules allow larger CCA deductions in the year of acquisition for
most capital asset purchases
Record keeping = taxpayer must keep records that have the capital cost of each
individual item in a class
Record keeping = taxpayer must keep records showing individual asset's AcB
for 7 years after disposition
Net additions for the year = additions to the class - reduction of UCC
for dispositions in the class
Dispostions of goodwill have some differences vs. dispositions of other assets
Disposition of certain types of expenditures (called Eligible capital expenditures (ECE) (one
example = goodwill)) is very different if the ECE was purchased prior to 2017. ECE / CEC are
not in scope for the purposes of our course. (CEC was ~ CCA for ECE items)
Copyright – Rick Musselman
Not for duplication, reproduction or sharing
You might also like
- The Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsFrom EverandThe Entrepreneur’S Dictionary of Business and Financial TermsNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains and Losses: Ebook Summary - Chapter 12Document1 pageCapital Gains and Losses: Ebook Summary - Chapter 12arianxxxNo ratings yet
- Project House PropertyDocument35 pagesProject House PropertyishichadhaNo ratings yet
- SM CHDocument53 pagesSM CHInderjeet JeedNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Spec Incl & Exempt IncomeDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Spec Incl & Exempt Incometetelomakgata1No ratings yet
- GROSS INCOME DEDUCTIONS Advance NotesDocument13 pagesGROSS INCOME DEDUCTIONS Advance NotesMary Angeline SalvaneraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Notes - Capital Budgeting DecisionDocument6 pagesChapter 12 Notes - Capital Budgeting DecisionrbarronsolutionsNo ratings yet
- CGT - Slides - Part 1Document26 pagesCGT - Slides - Part 1AceNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Costs SlidesDocument6 pagesBorrowing Costs Slidesgwbadie7No ratings yet
- 36 Nature of Accounts As Per Traditional Modern ApproachDocument2 pages36 Nature of Accounts As Per Traditional Modern ApproachChandresh100% (1)
- Midterm Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMidterm Cheat SheetHelloWorldNowNo ratings yet
- Employee BenefitsDocument3 pagesEmployee BenefitsJAY AUBREY PINEDANo ratings yet
- Afar - Partnership AccountingDocument3 pagesAfar - Partnership Accountingfarah mae raquinioNo ratings yet
- 3 Non-Current Assets TopicDocument43 pages3 Non-Current Assets TopicpesseNo ratings yet
- IAS 12 - Income Taxes - Measuring Deferred Tax - Temporary DifferencesDocument4 pagesIAS 12 - Income Taxes - Measuring Deferred Tax - Temporary DifferencesReenestus DumeniNo ratings yet
- Rules, Required By: Intangible)Document5 pagesRules, Required By: Intangible)Iqra HayatNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument31 pagesCapital BudgetingGUNAWAN WICAKSONO -No ratings yet
- IAS19 Changes: "New Volatility and Extra Complexity"Document1 pageIAS19 Changes: "New Volatility and Extra Complexity"Juan Dela Cruz IIINo ratings yet
- Accounting - AnswerDocument13 pagesAccounting - AnswerINTER SMARTIANSNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains Tax Computation: Exempt AssetsDocument15 pagesCapital Gains Tax Computation: Exempt AssetsGayathri SudheerNo ratings yet
- 2020-09801 2 PDFDocument6 pages2020-09801 2 PDFchristianNo ratings yet
- 4A Special DCDocument1 page4A Special DCJP JimenezNo ratings yet
- Study Unit D - Taxation of CorporatesDocument65 pagesStudy Unit D - Taxation of CorporatesEverjoyNo ratings yet
- 23 Working Capital ManagementDocument98 pages23 Working Capital ManagementMittal Shah100% (1)
- Tangible and Intangible Non Current Assets Lecture NotesDocument20 pagesTangible and Intangible Non Current Assets Lecture NotesDivya NandiniNo ratings yet
- Donell ByrdchenCTP 2023-24 Ch05Document92 pagesDonell ByrdchenCTP 2023-24 Ch05juliapaige2000No ratings yet
- DT A MTP 1 Final May22Document14 pagesDT A MTP 1 Final May22Kanchana SubbaramNo ratings yet
- Ind As 12Document5 pagesInd As 12Akshayaa KarthikaNo ratings yet
- Chương 4Document9 pagesChương 4Hồ Trần Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries - ReviewerDocument2 pagesAdjusting Entries - ReviewerPeter Jonathan ObianoNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains Tax Lecture Summary 2020Document45 pagesCapital Gains Tax Lecture Summary 2020nsnhemachenaNo ratings yet
- LegwailaT 2019 452IncomeVersusCapita TaxLawAnIntroductionDocument2 pagesLegwailaT 2019 452IncomeVersusCapita TaxLawAnIntroductionsnembalindlovuNo ratings yet
- Seminar 2 - Heads of ChargeDocument8 pagesSeminar 2 - Heads of ChargeYong Kwang HanNo ratings yet
- T2 Corporation - Income Tax Guide 2022Document143 pagesT2 Corporation - Income Tax Guide 2022Shakoor AhmadNo ratings yet
- 69769bos280322 P7aDocument14 pages69769bos280322 P7aharitaNo ratings yet
- IND AS 12 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldDocument7 pagesIND AS 12 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldSoham UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- SMEs ALE PDFDocument13 pagesSMEs ALE PDFFranchNo ratings yet
- CA Inter New Syllabus - Subjectwise AnalysisDocument21 pagesCA Inter New Syllabus - Subjectwise AnalysisShubham TiwariNo ratings yet
- SBR FS Disclosures Snippet April 20 2022Document1 pageSBR FS Disclosures Snippet April 20 2022abhishekNo ratings yet
- Ind AS 12 EIRC 10.10.2022Document44 pagesInd AS 12 EIRC 10.10.2022Abhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Will Cost $1.5 Trillion - Committee For A Responsible Federal BudgetDocument2 pagesTax Cuts and Jobs Act Will Cost $1.5 Trillion - Committee For A Responsible Federal BudgetTan SoNo ratings yet
- Profit & Gain From Business or Profession: Section 145: Taxability As Per Method of Accounting Followed by AssesseeDocument25 pagesProfit & Gain From Business or Profession: Section 145: Taxability As Per Method of Accounting Followed by AssesseeRajesh NangaliaNo ratings yet
- Tax Formula and Tax Determination An Overview of Property TransactionsDocument23 pagesTax Formula and Tax Determination An Overview of Property TransactionsJames Riley Case100% (1)
- AA203 - Cheat Sheet (SB)Document4 pagesAA203 - Cheat Sheet (SB)thooshengbaoNo ratings yet
- CGT - Fundamentals: Currency: 30 August 2017 (v006.5)Document59 pagesCGT - Fundamentals: Currency: 30 August 2017 (v006.5)Jessica YuNo ratings yet
- Bos 45796 CP 4 U 4Document116 pagesBos 45796 CP 4 U 4shrutichhalaniNo ratings yet
- Explain The Procedure of Reconciliation of Financial and Cost Accounting DataDocument6 pagesExplain The Procedure of Reconciliation of Financial and Cost Accounting DataKritika JainNo ratings yet
- Capital GainsDocument122 pagesCapital GainsVaibhav GawadeNo ratings yet
- Capital Gains Tax Lecture Summary 2020Document40 pagesCapital Gains Tax Lecture Summary 2020Tatenda RamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 TaxationDocument4 pagesChapter 17 TaxationTess LiNo ratings yet
- Temp Differences FlashcardsDocument11 pagesTemp Differences FlashcardsKatrina EustaceNo ratings yet
- Business Combination - Statutory MergerDocument7 pagesBusiness Combination - Statutory Mergerma.soledad san diegoNo ratings yet
- Taxation - F6 Fa 2020 Volume Ii (4706)Document75 pagesTaxation - F6 Fa 2020 Volume Ii (4706)Jemila ChowrimotooNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"Document33 pagesUnit - 4: Capital Gains: Proforma For Computation of Income Under The Head "Capital Gains"GauravNo ratings yet
- De La Salle Lipa: Intermediate Accounting 3 Income and Expense Items Affecting Deferred TaxesDocument4 pagesDe La Salle Lipa: Intermediate Accounting 3 Income and Expense Items Affecting Deferred TaxesJere Mae MarananNo ratings yet
- Ch5-Recordedlecturenotes-Fall2023 14 6022767437356836Document40 pagesCh5-Recordedlecturenotes-Fall2023 14 6022767437356836ronny nyagakaNo ratings yet
- Income TaxesDocument11 pagesIncome TaxesamNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Cost of Investment & Net Returns: Katrine Celine C. Gutierrez, CPADocument4 pagesFinancial Management - Cost of Investment & Net Returns: Katrine Celine C. Gutierrez, CPAJerichoNo ratings yet
- Unit C Gross Income and General Deductions V3Document43 pagesUnit C Gross Income and General Deductions V3lloyd madanhireNo ratings yet
- Airlines: Southwest CorporationDocument3 pagesAirlines: Southwest CorporationBob BillyNo ratings yet
- Vershire: CompanyDocument6 pagesVershire: CompanyBob BillyNo ratings yet
- Pink Et Al. 2001Document20 pagesPink Et Al. 2001Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2A - Strategy and CSRDocument12 pagesLecture 2A - Strategy and CSRBob BillyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Strategy Goals Values and PerformanceDocument34 pagesLecture 2 - Strategy Goals Values and PerformanceBob BillyNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Strategy: Strategic ManagementDocument31 pagesThe Concept of Strategy: Strategic ManagementBob BillyNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of Financial Measures in Ontario Hospitals BSC Parkinson Et Al. 2007Document10 pagesA Critical Review of Financial Measures in Ontario Hospitals BSC Parkinson Et Al. 2007Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- Applying The BSC in Hospitals Inamdar and Kaplan 2002Document17 pagesApplying The BSC in Hospitals Inamdar and Kaplan 2002Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- Kollberg and Elg 2011Document20 pagesKollberg and Elg 2011Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Patient and Employee Satisfaction What Happens When The BSC Does Not Work As Planned Lorden Et Al. 2008Document11 pagesA Case Study of Patient and Employee Satisfaction What Happens When The BSC Does Not Work As Planned Lorden Et Al. 2008Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Leases - Additional Kieso Slides (Part 2)Document18 pages2.1 Leases - Additional Kieso Slides (Part 2)Bob BillyNo ratings yet
- France PestelDocument4 pagesFrance PestelSuraj OVNo ratings yet
- Bridgewater: Daily ObservationsDocument15 pagesBridgewater: Daily Observationsdanielkps2903No ratings yet
- Long-Term (Capital Investment) DecisionsDocument11 pagesLong-Term (Capital Investment) DecisionsKariza ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Site Selection Criteria and FactorsDocument4 pages2.1 Site Selection Criteria and Factorseric swaNo ratings yet
- South African Airways v. CIRDocument1 pageSouth African Airways v. CIRAnn QuebecNo ratings yet
- Ingram Micro Malaysia SDN BHD (175932-M)Document10 pagesIngram Micro Malaysia SDN BHD (175932-M)akoolaNo ratings yet
- Va W4Document4 pagesVa W4Jeannie ArringtonNo ratings yet
- Gains On Disposition of PropertyDocument4 pagesGains On Disposition of PropertyGian Carlo RamonesNo ratings yet
- Bir 2305 FormDocument2 pagesBir 2305 FormHanna May Gutierrez AmbaNo ratings yet
- Klash Private Limited Balance Sheet and Profit Loss AccountDocument2 pagesKlash Private Limited Balance Sheet and Profit Loss AccountAbdullahNo ratings yet
- PM Award Nomination Form AffidavitabolitionDocument7 pagesPM Award Nomination Form AffidavitabolitionInformation Point KapurthalaNo ratings yet
- 100 % Stamp Duty Exemption GRDocument3 pages100 % Stamp Duty Exemption GRRadheShyamNo ratings yet
- Business Plan 1Document42 pagesBusiness Plan 1mark platinoNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 11Document23 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 11Aishwarya100% (1)
- Whistleblower ComplaintDocument7 pagesWhistleblower ComplaintThe FederalistNo ratings yet
- S.6 Economics NotesDocument28 pagesS.6 Economics NotesMarvinNo ratings yet
- Tax 1 - Ass No. 2Document6 pagesTax 1 - Ass No. 2De Guzman E AldrinNo ratings yet
- Tax Statement 2014 CbhsDocument1 pageTax Statement 2014 CbhsChandra BhattNo ratings yet
- Tax Case Digests (Tax 2)Document20 pagesTax Case Digests (Tax 2)John Soap Reznov MacTavishNo ratings yet
- GST Goods and Service TaxDocument6 pagesGST Goods and Service Taxprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- Barque Hotels Private Limited-2927Document1 pageBarque Hotels Private Limited-2927Shimoyal RehmanNo ratings yet
- Od 121259060478440000Document1 pageOd 121259060478440000SureshVishwachitranNo ratings yet
- Under Composite Scheme of VAT Assessment Annexure-I Project/ Contract Details (EPC Contracts)Document2 pagesUnder Composite Scheme of VAT Assessment Annexure-I Project/ Contract Details (EPC Contracts)ghaghra bridgeNo ratings yet
- BBA 4year Termsystem PDFDocument44 pagesBBA 4year Termsystem PDFMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- RBC CP Associates Study Material Important Questions FOR ExamDocument15 pagesRBC CP Associates Study Material Important Questions FOR ExamkhudalNo ratings yet
- 2281 w05 QP 1Document12 pages2281 w05 QP 1mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Estate TaxDocument4 pagesEstate TaxRichel888No ratings yet
- Brokers Accreditation AgreementDocument7 pagesBrokers Accreditation AgreementCharmaine CuynoNo ratings yet
- Analysis: Systems Tool For Urban PlanningDocument8 pagesAnalysis: Systems Tool For Urban PlanninglalecrimNo ratings yet
- DISPOSALDocument29 pagesDISPOSALAnand Dubey100% (1)