Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Informatics Topic No.1
Uploaded by
Hecia Gaga-a0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesThis document discusses nursing informatics, which involves the application of computer science and information technology to manage nursing data and support nursing practice. Specifically:
1. Nursing informatics is concerned with managing nursing information through technologies like electronic health records to support patient care, education, research, and administration.
2. Common challenges nurses face include excessive documentation, long turnaround times for tasks, inaccurate nursing processes, and poor communication. Information technologies can help address these issues by automating documentation, accelerating processes, reducing errors, and improving communication tools.
3. A framework for nursing informatics relies on concepts of collecting and organizing data into information and knowledge to guide decisions and practice. This involves synthesizing information through reporting,
Original Description:
Original Title
Informatics-Topic-No.1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses nursing informatics, which involves the application of computer science and information technology to manage nursing data and support nursing practice. Specifically:
1. Nursing informatics is concerned with managing nursing information through technologies like electronic health records to support patient care, education, research, and administration.
2. Common challenges nurses face include excessive documentation, long turnaround times for tasks, inaccurate nursing processes, and poor communication. Information technologies can help address these issues by automating documentation, accelerating processes, reducing errors, and improving communication tools.
3. A framework for nursing informatics relies on concepts of collecting and organizing data into information and knowledge to guide decisions and practice. This involves synthesizing information through reporting,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views3 pagesInformatics Topic No.1
Uploaded by
Hecia Gaga-aThis document discusses nursing informatics, which involves the application of computer science and information technology to manage nursing data and support nursing practice. Specifically:
1. Nursing informatics is concerned with managing nursing information through technologies like electronic health records to support patient care, education, research, and administration.
2. Common challenges nurses face include excessive documentation, long turnaround times for tasks, inaccurate nursing processes, and poor communication. Information technologies can help address these issues by automating documentation, accelerating processes, reducing errors, and improving communication tools.
3. A framework for nursing informatics relies on concepts of collecting and organizing data into information and knowledge to guide decisions and practice. This involves synthesizing information through reporting,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
What is INFORMATICS o “The development and evaluation of
▪ INFORMATICS applications, tools, processes, and structures
o Used in conjunction with the name of a which assist nurses with the management of
discipline, it denotes an application of data in taking care of patients or supporting
computer science and information science to the practice of nursing.”
the management and processing of data,
information, and knowledge in the named ▪ ORIGIN of Nursing Informatics
discipline. o Increase in knowledge has led to the
o The science of automating information development of many specialties and
interactions subspecialties.
o computer science + information science. o The number of cases increased with increase in
o French word “informatique” = computer population, discovery of more diseases and
science. extension of life expectancy.
HIT – Healthcare Information Technology - refers to o Due to increase workload, lack of time to
the electronic systems health care professionals – channel into useful information or knowledge –
and increasingly, patients – use to store, share, and lead to development of
analyze health information.
Example of HIT: ▪ TOP 4 PROBLEMS OF NURSES IN THE WORKPLACE:
o EHRS – Electronic Health Record System o DOCUMENTATION IS EXCESSIVE
o EHRs allow doctors to better keep track of ▪ writes narratives (patient’s history, progress
your health information and may enable notes, care pans and special reports)
them to see it when you have a problem ▪ fills up forms, records VS in graphing paper
even if their office is closed. EHRs also make and writes in tables input/output
it easier for your doctor to share ▪ Benefit of Information Technology:
information with specialists, so that - Automation relieves nurses on writing
specialists who need your information have on and handling forms thus creating a
it available when it’s needed. paperless environment.
▪ SCOPE OF HIT/EHR - This eliminates ambiguity, redundancy
➢ Provision & documentation of patient care and tedious process of documenting.
➢ Education of healthcare providers - Normally in a paperless clinical area the
➢ Scientific research for advancing healthcare time allotted for documentation should
delivery be 15% of a nurse’s shift.
➢ Administration of healthcare delivery services
➢ Reimbursement for patient care o TURNAROUND TIME IS TOO LONG
➢ Legal and ethical implications ▪ Turnaround time starts from the time a
➢ Safety & quality issues request is made to the time it was fully
accomplished (ex. laboratory tests or
▪ HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS ancillary orders)
o focuses on managing information in all ▪ Turnaround - the process of completing or
healthcare disciplines. the time needed to complete a task,
o uses the capture, retrieval, storage, presenting, especially one involving receiving
sharing and use of biomedical information, data something, processing it, and sending it
and knowledge in providing care, problem out again.
solving and decision making ▪ Benefit of Information Technology:
- Automation helps accelerate the
▪ NURSING INFORMATICS processes of request and facilitate
o According to Scholes & Barbers (1980) – the presentation of current status of result
use of computer technology in all nursing of the request
endeavors: nursing services, education &
research o NURSING PROCESS ARE INACCURATE
o According to Hannah et al. (1994) – any use of ▪ Rushing of nursing process may lead to
information technologies in carrying out nursing commission of errors
functions ▪ ERRORS such as: Medication errors; wrong
o “A combination of computer science, entries, dictation, translation and
information science and nursing science transcription of orders
designed to assist in the management and ▪ Benefit of Information Technology:
processing of nursing data, information and - Automation of these processes mostly
knowledge to support the practice of nursing done beside a patient leads to a great
and the delivery of nursing care.” (Graves, J. R., reduction of errors.
& Corcoran, S., 1989)
o “The use of computers technology to support o COMMUNICATION IS POOR
nursing, including clinical practice, ▪ Communication between healthcare
administration, education, and research.” providers and between departments is
POOR when served with telephone
systems because of its real time nature Provides access to standardized forms,
that requires the presence of both. policies and procedures
▪ Phone lines may be tapped or bugged Access data about client that may be
breaching privacy and confidentiality somewhere in the medical record or
▪ Benefit of Information Technology: elsewhere in health care agency.
- Computers provide different modes of 5. BEDSIDE DATA ENTRY
communications like chat, telephony, - records client assessments, medication
or video-conferencing or e-mail and administration, progress notes, care plan
simple text messaging whatever is updating, client acuity and accrued charges
most convenient and appropriate. 6. COMPUTER BASED CLIENT RECORD EMRs/CPRs
- Provides easy retrieval of specific data such as
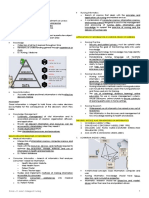
▪ Framework for Nursing Informatics trends in vital signs, immunization records,
o Relies on the central concepts of data, current problems
information and knowledge: - It can be designed to work providers about
o A DATA is defined as discrete entities that are conflicting medications or client parameters
described objectively without interpretation that indicate dangerous conditions
o An INFORMATION as data that is interpreted, 7. ELECTRONIC ACCESS TO CLIENTS
organized or structured ▪ Used extensively in health care to assess and
o A KNOWLEDGE as information that has been monitor client’s conditions
synthesized so that interrelationships are ▪ Data accumulated from various electronic
identified and formalized. devices are stored for research purposes
o Resulting in DECISIONS that guide practice ▪ Can monitor client
▪ Computerized diagnosis
o Synthesizing Information ▪ Telemedicine
▪ 3 Parts:
- reporting information BENEFITS OF COMPUTER AUTOMATION IN THE
- organizing information HEALTH CARE:
- correlation between ideas shared EMR(Electronic Medical Record)
1. Improve access to the medical record
▪ Teaching Nursing Informatics is a must in the 2. Decrease redundancy of data entry
Philippines. 3. Decreased time spent in the documentation
o January 2008 - CHED memorandum order CMO 4. Increased time for client care
NO. 5 series of 2008 to all deans of the colleges 5. Facilitation of data collection for research
of nursing throughout the country. 6. Improve communication and decrease potential for
o CMO NO. 5 series of 2008 error
o It requires the replacement of basic computer 7. Creation of lifetime clinical record
with 3-unit Nursing Informatics in the new
curriculum. NURSING ADMINISTRATION
How it is applied to Nursing Administration:
▪ Application of Nursing Informatics ▪ Automated staff scheduling
o Nursing Informatics can be applied to all areas ▪ E-mail for improved communication
of nursing practice, which include; ▪ Cost analysis and finding trends for budget
▪ clinical practice purposes
▪ administration ▪ Quality assurance and outcomes analysis
▪ education
▪ research PRACTICE MANAGEMENT
Used to order supplies, tests, meals, and services,
NURSING CLINICAL PRACTICE from other departments
How it is applied to Clinical Practice: Allows nursing service to determine the costliest
▪ work list items used by a particular nursing unit.
▪ computer-generated client documentation May provide information or decisions to modify
▪ EMR/CPR budget, provide different staffing, move supplies to
▪ monitoring devices different locations, or make other changes for more
▪ computer-generated NCP efficient and higher quality care
▪ automatic billing
▪ reminders and prompts NURSING EDUCATION
How it is applied to Nursing Education:
COMPUTERS IN NURSING PRACTICE ▪ Computerized record keeping
Functions: ▪ Computerized assisted instruction
1. Records client information ▪ Interactive video technology
2. Provides access to other departments ▪ Distance Learning
3. Used to manage client scheduling ▪ Internet resources
4. Documentation of client’s status & medical records ▪ Presentation software for preparing slides and
keeping handouts
COMPUTERS IN NURSING EDUCATIONS
COMPUTER Assisted Education
PDA (Personal Digital Assistants)
LCD Projectors
Wireless Routers
Desktops
Laptops
Smartphone
VIDEOS/ANIMATIONS
Distance learning
Testing (NCLEX)
Student and course record management
NURSING RESEARCH
How it is applied to Nursing Education:
▪ Computerized literature searching
▪ The adoption of standardized language related to
nursing terms
▪ The ability to find trends in aggregated data
COMPUTERS IN NURSING RESEARCH
1. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
- Useful in locating current literature about the
problem and related concepts. Helps in
searching for existing documents, and e-mail to
colleagues.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Software facilitate searches, contains
thesauruses so that the most appropriate terms
can be selected.
3. RESEARCH DESIGN
- Search literature for instruments that have
already been established or to design and test
instruments that need to be developed for past
study.
4. DATA COLLECTION AND ANALYSIS
- Helps create form for the collection of data
such as informed consent, demographic data,
and recording forms.
Commonly used software for quantitative data
analysis: SPSS (statistical package for social
sciences), SAS (statistical analysis system), Sys
STAT, MYSTAT
5. RESEARCH DISSEMINATION
- computer word processing programs are used
to author the final reports of research and send
research to various readerships.
Help speeds completion or research projects
POINT TO PONDER...
“Computers are incredibly fast, accurate and stupid.
Humans are incredibly slow, inaccurate and brilliant.
Together they are powerful beyond imagination.....”
- Albert Einstein
You might also like
- Nursing Informatics: BSN 2 STUDENTS, SY 2019-2020 Second SemesterDocument34 pagesNursing Informatics: BSN 2 STUDENTS, SY 2019-2020 Second SemesterLevi AckerManNo ratings yet
- NCM210 PrelimDocument10 pagesNCM210 PrelimJasmine Angeli ObilloNo ratings yet
- Informatics L1Document4 pagesInformatics L1RYZELLE SCHWEIN MIRANDANo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument12 pagesNursing InformaticsAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Applications of Nursing Informatics PDFDocument28 pagesApplications of Nursing Informatics PDFKyla Avila TorrevillasNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument14 pagesNursing InformaticsAve Meri Noreen PizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument4 pagesNursing InformaticsRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- NCM 210 - IntroductionDocument44 pagesNCM 210 - Introductionya YaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Week 1Document37 pagesNursing Informatics Week 1Erin Trisha Kristel GaspanNo ratings yet
- Definition of Nursing InformaticsDocument29 pagesDefinition of Nursing InformaticsDon Maur Valete100% (1)
- Nursing Informatics - Part 1Document23 pagesNursing Informatics - Part 1rlinaoNo ratings yet
- PRELIM - Nursing InformaticsDocument20 pagesPRELIM - Nursing InformaticsReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Info LecDocument4 pagesInfo Lecjshaymin8No ratings yet
- 1 - Foundations of Nursing TicsDocument124 pages1 - Foundations of Nursing TicsbunsokoyNo ratings yet
- Final Nursing InformaticsDocument6 pagesFinal Nursing InformaticsJhey-ar Toledo100% (1)
- HIS - Hospital Information SystemDocument8 pagesHIS - Hospital Information SystemAnne Carmel VeranoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Lect - PrelimDocument14 pagesNursing Informatics Lect - PrelimWRONGHEARNo ratings yet
- Phin Prelims Lec 1Document19 pagesPhin Prelims Lec 1ivymapusao07No ratings yet
- Mrs. V. Bhulaxmi M.SC (N) 2 Year Nursing Management Gcon, HydDocument49 pagesMrs. V. Bhulaxmi M.SC (N) 2 Year Nursing Management Gcon, HydBlessy Madhuri100% (1)
- Gathering and Acquiring Nursing Health Care DataDocument17 pagesGathering and Acquiring Nursing Health Care DataMonique LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: de Lara, Denise Dominique M. Quiamco, Precious Diane S. RNDocument113 pagesNursing Informatics: de Lara, Denise Dominique M. Quiamco, Precious Diane S. RNPrecious Diane QuiamcoNo ratings yet
- Technology (Computer) and Nursing WorkDocument6 pagesTechnology (Computer) and Nursing WorkEfjayNo ratings yet
- NIDocument21 pagesNIAlyssa MasacayanNo ratings yet
- Computer Act 7Document5 pagesComputer Act 7josh familarNo ratings yet
- 1 Nursing Informatics: Remember!Document2 pages1 Nursing Informatics: Remember!LAXA FRANCINENo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics 2018Document66 pagesNursing Informatics 2018Undher Ground Maker100% (5)
- NI - Application of Nursing InformaticsDocument4 pagesNI - Application of Nursing InformaticsRose Anne AbivaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Informatics 1Document4 pagesPharmacy Informatics 1barbadillojames419No ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics: P.Vijayalakshmi Clinical InstructorDocument46 pagesNursing Informatics: P.Vijayalakshmi Clinical InstructorGracy CasañaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Health InformaticsDocument2 pagesOverview of Health InformaticsERESTALL SENNDI GRACE OLIVERASNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics PrelimsDocument3 pagesNursing Informatics PrelimsJaaaanNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticesDocument18 pagesNursing InformaticesSakthi DeviNo ratings yet
- First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022: Overview of Health Informatics Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesFirst Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022: Overview of Health Informatics Learning ObjectivesFea Kristine PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 PDFDocument8 pagesUnit 8 PDFratherazhar31No ratings yet
- NCM 110 - Ariola BSN2-5 Finals IpDocument15 pagesNCM 110 - Ariola BSN2-5 Finals IpJenny YenNo ratings yet
- Lecture and Laboratory in Nursing InformaticsDocument6 pagesLecture and Laboratory in Nursing InformaticsNOEL YRIGONNo ratings yet
- Nmi 111 Group EightDocument10 pagesNmi 111 Group EightjabadontagnunNo ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument24 pagesNursing InformaticsOsama ramadanNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Health InformaticsDocument38 pages01 - Introduction To Health InformaticsSaba Ahmed Abu FarhaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Roles, Competencies and SkillsDocument55 pagesNursing Informatics Roles, Competencies and SkillsIrish Jane GalloNo ratings yet
- NSG InfoDocument6 pagesNSG InfoGummy BearsNo ratings yet
- Extinction: Future Model For Nursing DocumentationDocument4 pagesExtinction: Future Model For Nursing DocumentationDwi NopriyantoNo ratings yet
- Telemedicine: Telehealth vs. Telemedicine What Is ? DisavantagesDocument49 pagesTelemedicine: Telehealth vs. Telemedicine What Is ? DisavantagesERIKA ANNE CADAWANNo ratings yet
- NCM 110 Midterm ReviewerDocument3 pagesNCM 110 Midterm ReviewerBrandone Dave ParagosoNo ratings yet
- NCM 104 Community Health Nursing 1: Bachelor of Science in NursingDocument8 pagesNCM 104 Community Health Nursing 1: Bachelor of Science in NursingMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Prelims Nursing InformaticsDocument9 pagesPrelims Nursing InformaticsCrystal Mirana100% (1)
- Dental Informatics IntroductionDocument4 pagesDental Informatics IntroductionDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Ncm110nif Midterm Laboratory NotesDocument12 pagesNcm110nif Midterm Laboratory NotesMicah jay MalvasNo ratings yet
- Online Patients Record Platform Using PHPDocument31 pagesOnline Patients Record Platform Using PHPAmaan B EydreesNo ratings yet
- NCM110 Applications of Nursing Informatics BSN3Document52 pagesNCM110 Applications of Nursing Informatics BSN3bryanmaranan173No ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and SafetyDocument36 pagesEvidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and Safetymagdaashaaban100% (1)
- NCM - 110 Nursing Informatics Modules PDFDocument27 pagesNCM - 110 Nursing Informatics Modules PDFSharmaine DIEGONo ratings yet
- PrelimReviewer NCM110LectDocument18 pagesPrelimReviewer NCM110LectJustine Simeon lagunzadNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 IntroDocument5 pagesTopic 1 Introsammydels98No ratings yet
- Nursing InformaticsDocument7 pagesNursing Informaticsapi-19880840100% (1)
- Nursing InformaticsDocument15 pagesNursing Informaticstehkie04100% (2)
- 2practice Application2Document17 pages2practice Application2YongNo ratings yet
- Critical Care ApplicationsDocument35 pagesCritical Care ApplicationsrdelmoroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics - Computers and NursingDocument5 pagesNursing Informatics - Computers and NursingAllia Rae Diaz GuiaoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Informatics Demystified: A Crash Course for Student NursesFrom EverandNursing Informatics Demystified: A Crash Course for Student NursesNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicineDocument5 pagesHerbal MedicineHecia Gaga-aNo ratings yet
- Imci Rec Form FinalDocument1 pageImci Rec Form FinalHecia Gaga-aNo ratings yet
- A Reading On Gestational DiabetesDocument4 pagesA Reading On Gestational DiabetesHecia Gaga-aNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix (1 & 2)Document9 pagesMarketing Mix (1 & 2)Hecia Gaga-aNo ratings yet
- Kpro March 2006Document6 pagesKpro March 2006Ahmed El-FayoomiNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide: AdviaDocument100 pagesOperator's Guide: Advianguyen minh100% (1)
- 1 ElasticBucklingandSupportConditionsDocument4 pages1 ElasticBucklingandSupportConditionshoangduong260979No ratings yet
- C++ Classes and ObjectsDocument4 pagesC++ Classes and ObjectsAll TvwnzNo ratings yet
- Cat Phan 700 ManualDocument42 pagesCat Phan 700 ManualMarisa ChapelNo ratings yet
- Gsk980Tda Turning Machine CNC System: CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesGsk980Tda Turning Machine CNC System: CharacteristicsPramod YadavNo ratings yet
- Kramer Control BRDocument12 pagesKramer Control BRyogaarsaNo ratings yet
- SDLC ResearchgateDocument10 pagesSDLC ResearchgateAlex PitrodaNo ratings yet
- Hyperion Planning 11.1.2 Implementation Boot Camp Laboratory Manual V10 (11123)Document150 pagesHyperion Planning 11.1.2 Implementation Boot Camp Laboratory Manual V10 (11123)Jitendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Fake News and Message Detection Project Report: September 2021Document13 pagesFake News and Message Detection Project Report: September 2021Kk DataNo ratings yet
- MS VBAProject BinDocument111 pagesMS VBAProject BinMartin LeeNo ratings yet
- Bolting Solutions CatalogDocument74 pagesBolting Solutions Catalogcyrano1091No ratings yet
- Centricity Pacs Quick GuideDocument6 pagesCentricity Pacs Quick GuideEsdras SouzaNo ratings yet
- 6.1.2.12 Lab - Manage Virtual Memory in Windows 7 and Vista-1Document13 pages6.1.2.12 Lab - Manage Virtual Memory in Windows 7 and Vista-1TochiNo ratings yet
- CLX6260FD Service ManualDocument159 pagesCLX6260FD Service ManualAndres Lopez ArandaNo ratings yet
- Error DetailsDocument169 pagesError Detailssuresh_tNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture - Control UnitDocument5 pagesComputer Architecture - Control Unitakoprogram1No ratings yet
- Clinitek Status Plus Operator Manual PDFDocument144 pagesClinitek Status Plus Operator Manual PDFEstie Kiriwenno0% (1)
- EXOSConcepts Bookmap PDFDocument1,670 pagesEXOSConcepts Bookmap PDFbigdrsmithNo ratings yet
- Command Ref AOS v5 10Document322 pagesCommand Ref AOS v5 10SaeedNo ratings yet
- Estimating The Cost-Ship RepairDocument29 pagesEstimating The Cost-Ship RepairMohammad Sholikhan Arif100% (1)
- Process Management in Public AdministrationDocument14 pagesProcess Management in Public AdministrationIllustration WingNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting ReferenceDocument62 pagesTroubleshooting ReferenceMarcio BulhoesNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Detector LogDocument4 pagesPlagiarism Detector LogjackeiNo ratings yet
- SystemVerilog - FAQ - SystemVerilog Faq - PDFDocument8 pagesSystemVerilog - FAQ - SystemVerilog Faq - PDFMadhu Kiran100% (1)
- Cs837: Adv. Operating Systems: Dr. Mian M.HamayunDocument19 pagesCs837: Adv. Operating Systems: Dr. Mian M.HamayunShah ZaibNo ratings yet
- Backup FSX CFGDocument14 pagesBackup FSX CFGMarkus SchützNo ratings yet
- USB Data Logger Temperature: Testo 184 T1 Testo 184 T2 Testo 184 T3Document4 pagesUSB Data Logger Temperature: Testo 184 T1 Testo 184 T2 Testo 184 T3Davi FabregasNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document1 pageUnit 4api-285399009No ratings yet