0% found this document useful (0 votes)
746 views2 pagesDNA Replication - Labeling: DNA Primase DNA Ligase
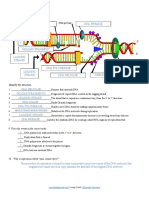
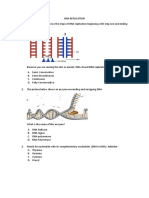
The document provides an overview of DNA replication, including key enzymes and structures involved such as DNA helicase, DNA polymerase, and Okazaki fragments. It outlines the order of events during replication and explains why the process is termed 'semi-conservative.' Additionally, it includes a labeling exercise with a word bank for educational purposes.
Uploaded by
Ederlyn ZateCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
746 views2 pagesDNA Replication - Labeling: DNA Primase DNA Ligase
The document provides an overview of DNA replication, including key enzymes and structures involved such as DNA helicase, DNA polymerase, and Okazaki fragments. It outlines the order of events during replication and explains why the process is termed 'semi-conservative.' Additionally, it includes a labeling exercise with a word bank for educational purposes.
Uploaded by
Ederlyn ZateCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd