Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DNA To PROTEIN (BIOCHEM)
Uploaded by
Gwen Solano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pages1. DNA replication involves several enzymes that work together to copy DNA.
2. DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the leading and lagging strands. Okazaki fragments are created on the lagging strand.
3. DNA ligase binds the Okazaki fragments together. Replication is semi-conservative because the parental DNA strands separate and each daughter molecule contains one old and one new strand.
Original Description:
Original Title
DNA to PROTEIN (BIOCHEM)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. DNA replication involves several enzymes that work together to copy DNA.
2. DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the leading and lagging strands. Okazaki fragments are created on the lagging strand.
3. DNA ligase binds the Okazaki fragments together. Replication is semi-conservative because the parental DNA strands separate and each daughter molecule contains one old and one new strand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views2 pagesDNA To PROTEIN (BIOCHEM)
Uploaded by
Gwen Solano1. DNA replication involves several enzymes that work together to copy DNA.
2. DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix. DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides to the leading and lagging strands. Okazaki fragments are created on the lagging strand.
3. DNA ligase binds the Okazaki fragments together. Replication is semi-conservative because the parental DNA strands separate and each daughter molecule contains one old and one new strand.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
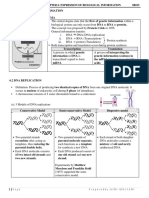
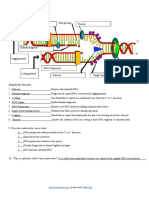
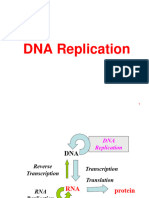
DNA Replication
DNA LIGASE DNA PRIMASE
3’
5’
OKAZAKI FRAGMENT
LAGGING
STRAND
DNA POLYMERASE
LEADING
STRAND DNA HELICASE SINGLE STRAND BINDING PROTEINS
Identify the structure
1. DNA HELICASE Enzyme that unwinds DNA
2. OKAZAKI FRAGMENTS Fragments of copied DNA created on the lagging strand
3. LEADING STRAND The strand that is copied in a continuous way, from the 3’ to 5’ direction
4. DNA LIGASE Binds Okazaki fragments
5. DNA POLYMERASE Builds a new DNA strand by adding complementary bases
6. SINGLE STRAND BINDING PROTEIN Stabilizes the DNA molecule during replication
7. LAGGING STRAND Strand that is copied discontinuously because it is traveling away from helicase
8. DNA PRIMASE Initiates the synthesis DNA by creating a short RNA segment at replication fork
9. Place the events in the correct order:
4 DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in the 5’ to 3’ direction
2 Replication fork is formed
3 DNA polymerase attaches to the primer
5 Okazaki fragments are bound together by ligase
1 DNA helicase unwinds DNA
10. Why is replication called “semi-conservative?”
The procedure of replication is termed as semi-conservative since two copies of the DNA molecule that
originated are made and each copy maintain the data half of the original DNA molecule.
www.biologycorner.com | Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
A A A G T T A G C T G G T T G
U U U C A A U C G A C C A A C
A A A G U U A G C U G G U U G
Phenylalanine Glutamine Serine Threonine Asparagine
www.biologycorner.com | Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
You might also like
- DNA Replication NotesDocument2 pagesDNA Replication NotesMart Tin100% (1)
- Lecture 2 (DNA Replication)Document37 pagesLecture 2 (DNA Replication)M Luqman Hakim100% (1)
- 2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument32 pages2019 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic DNA ReplicationALEXANDRA MARIE BUNQUINNo ratings yet
- 6.2 DNA Replication Full NoteDocument44 pages6.2 DNA Replication Full NotejiaenNo ratings yet
- ReplicationDocument45 pagesReplicationAleena MustafaNo ratings yet
- ObjectivesDocument36 pagesObjectivesMARIAN SABENECIONo ratings yet
- DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument74 pagesDNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisNabilah Rizky Khairunnisa100% (1)
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFDocument32 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFStephy LimboNo ratings yet
- Yacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211Document5 pagesYacomine - Essential Biology 3.4 & 7.2 DNA Replication (HL Only) - 3211joeyacomine100% (1)
- Dna Replication Lecture NotesDocument73 pagesDna Replication Lecture NotesAhmad ShyoukhNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PresentationDocument28 pagesDNA Replication PresentationCelely Nitnit100% (2)
- Genetics, Chapter 3, DNA Replication Lectures (Slides)Document115 pagesGenetics, Chapter 3, DNA Replication Lectures (Slides)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Gene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyFrom EverandGene Editing, Epigenetic, Cloning and TherapyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Kwento Ni Rosario Reflection PaperDocument2 pagesKwento Ni Rosario Reflection PaperGwen SolanoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Identify The StructureDocument3 pagesDNA Replication: Identify The StructureSet FireNo ratings yet
- (L-4) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Jan 19Document52 pages(L-4) - Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Jan 19AyazNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFDocument54 pagesDNA Replication (Prokaryotes) 1 2 PDFItni Si Baat HyNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- DNA Replication FinalDocument85 pagesDNA Replication FinalMahnoor ImranNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationastrogeniusthreeNo ratings yet
- ReplicacionDocument19 pagesReplicacionIvÀnNo ratings yet
- 2.7 7.1DNAReplicationDocument33 pages2.7 7.1DNAReplicationKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Dna Structure Replication and Consensus SequencesDocument125 pagesLecture 3 - Dna Structure Replication and Consensus SequenceskibzwanjikuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)Document36 pagesChapter 1.2 DNA Replication (Autosaved)abdullaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4a - Protein Synthesis - Stu v2Document65 pagesTopic 4a - Protein Synthesis - Stu v2Angel LimNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah Jakarta20.020 Cahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaDocument27 pagesDNA Replication: Dede Renovaldi, M.Sc. (Biomed) Faculty of Medicine & Health Universitas Muhammadiyah JakartaCahya MaharaniNo ratings yet
- 2 - Dna ReplicationDocument25 pages2 - Dna Replicationwonderwolfblood17No ratings yet
- Section 1: General Concepts of DNA ReplicationDocument95 pagesSection 1: General Concepts of DNA ReplicationAqsa YaminNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2B - DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesLesson 2B - DNA ReplicationHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDocument35 pagesDNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudBagus Arya MahartaNo ratings yet
- Edited Part1 CENTRAL DOGMA OF GENETICSDocument16 pagesEdited Part1 CENTRAL DOGMA OF GENETICSSyx CameroNo ratings yet
- Slide 3Document36 pagesSlide 3OdaiNo ratings yet
- Bacterial GeneticsDocument38 pagesBacterial Geneticsfatima zafarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 EM PDFDocument24 pagesLecture 2 EM PDFhuang SteffiNo ratings yet
- CH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFDocument93 pagesCH 12 DNA Genetic Material PDFasaNo ratings yet
- 5 Replikasi Dna 1 - RizkyDocument15 pages5 Replikasi Dna 1 - RizkyNadya TsaneeNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument62 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument25 pagesDNA ReplicationPhilani KheswaNo ratings yet
- 5.molecular Biology Intro Class1Document38 pages5.molecular Biology Intro Class1Chandrachur GhoshNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDocument35 pagesDNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDeni SalmonNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Dr. Muhammad Tahir Assistant Professor COMSATS University Islamabad, Attock CampusDocument16 pagesDNA Replication: Dr. Muhammad Tahir Assistant Professor COMSATS University Islamabad, Attock CampusSaqlain Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- 6.2. DNA Replication PDFDocument75 pages6.2. DNA Replication PDFShania TehNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationDocument12 pagesUnit 8 Biosynthesis of Nucleic Acids - ReplicationMing mingNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA ReplicationLouis HilarioNo ratings yet
- Organization of Bacterial GenomesDocument24 pagesOrganization of Bacterial GenomeshariNo ratings yet
- Bic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonDocument46 pagesBic 159: Biochemistry Week 2 Lecture: Dr. Jody Ann JohnsonJana-Tae KerrNo ratings yet
- 2.7-7.1 Replication-MKDocument19 pages2.7-7.1 Replication-MKadham fadelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationDocument4 pagesLesson 5 CYTO DNA ReplicationTherese TimbalNo ratings yet
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationDocument46 pages2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription and TranslationAcyl HoteitNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Dna Replication1Document44 pages1.3. Dna Replication1sabry tapiaNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument26 pagesDNA ReplicationZainab AshroffNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument59 pagesCentral DogmaFat PatNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument87 pagesDna Replicationspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Signaling Part 2Document27 pagesSignaling Part 2Wissam AlwazaniNo ratings yet
- He - Sample of Informed ConsentDocument2 pagesHe - Sample of Informed ConsentGwen SolanoNo ratings yet
- Moral Dillema - Good To Read (A)Document3 pagesMoral Dillema - Good To Read (A)Gwen SolanoNo ratings yet
- EnneagramDocument17 pagesEnneagramGwen SolanoNo ratings yet
- Purcom Module 1 AnswersDocument11 pagesPurcom Module 1 AnswersGwen SolanoNo ratings yet