0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views38 pagesHazard Recognition: Presented at Risk Management Seminar & Workshop Organized by KMI-Banten & AMC/CMA
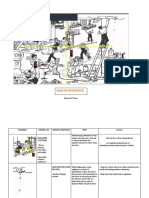
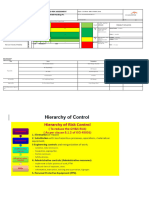
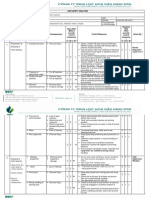
The document discusses hazard recognition and provides examples of common hazards like being caught in, on, or between machinery or equipment, coming into contact with heat, chemicals or electricity, being struck by moving objects, falling, and overexerting oneself. It also discusses methods for preventing injuries from these hazards like using guards, barriers, insulation and following ergonomic practices. The last sections discuss safety inspections and prioritizing hazards based on factors like exposure, frequency and severity of potential injuries.
Uploaded by
Teknik MarinaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views38 pagesHazard Recognition: Presented at Risk Management Seminar & Workshop Organized by KMI-Banten & AMC/CMA
The document discusses hazard recognition and provides examples of common hazards like being caught in, on, or between machinery or equipment, coming into contact with heat, chemicals or electricity, being struck by moving objects, falling, and overexerting oneself. It also discusses methods for preventing injuries from these hazards like using guards, barriers, insulation and following ergonomic practices. The last sections discuss safety inspections and prioritizing hazards based on factors like exposure, frequency and severity of potential injuries.
Uploaded by
Teknik MarinaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd