0% found this document useful (0 votes)
677 views9 pagesThree Phase Power Calculation
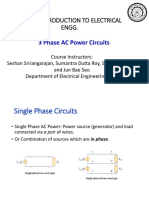
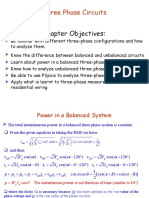
The document discusses power calculations for three-phase systems. It explains that instantaneous power in a balanced three-phase system is non-pulsating and smoother than a single-phase system. It also describes how to calculate active power, reactive power, apparent power, and power factor. Finally, it outlines the two-wattmeter method for measuring total power in a three-phase system using only two wattmeters.
Uploaded by
Gabriel Carl AlpuertoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
677 views9 pagesThree Phase Power Calculation
The document discusses power calculations for three-phase systems. It explains that instantaneous power in a balanced three-phase system is non-pulsating and smoother than a single-phase system. It also describes how to calculate active power, reactive power, apparent power, and power factor. Finally, it outlines the two-wattmeter method for measuring total power in a three-phase system using only two wattmeters.
Uploaded by
Gabriel Carl AlpuertoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd