Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
Uploaded by
vicndubOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
Uploaded by
vicndubCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
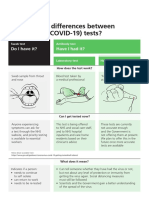
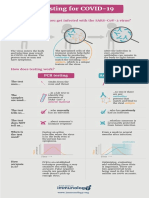
There are three types of tests available for COVID-19: polymerase chain reaction (PCR), antigen, and antibody (serology)
testing. PCR and antigen tests detect whether a person is currently infected, and serology detects whether a person had an
infection in the past. This document is designed to explain the differences between PCR, antigen, and serology testing, and
when one test might be used over another.
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
Why is the PCR tests look for pieces of Antigen tests look for pieces of Serology looks for antibodies 1
test used? SARS-CoV-2, the virus that proteins that make up the SARS- against SARS-CoV-2 in the blood
causes COVID-19, in the nose, CoV-2 virus to determine if the to determine if there was a past
throat, or other areas in the person has an active infection. infection.
respiratory tract to determine if
the person has an active
infection.
How is the In most cases, a nasal or throat In most cases, a nasal or throat In most cases, a blood sample is
test swab is taken by a healthcare swab is taken by a healthcare taken and sent to a lab for
performed? provider and tested. Sometimes provider and tested. Sometimes testing.
the test can be run while you the test can be run while you
wait, and sometimes the swab wait, and sometimes the swab
needs to be sent to a lab for needs to be sent to a lab for
testing. testing.
What does a A positive PCR test means that A positive antigen test means A positive antibody test means
positive test the person being tested has an that the person being tested has that the person being tested was
result active COVID-19 infection. an active COVID-19 infection. infected with COVID-19 in the
mean? past and that their immune
system developed antibodies to
try to fight it off.
1
Antibodies are formed by the body to fight off infections. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the first antibody that is formed against a germ, so it
appears on tests first, usually within 1-2 weeks. The body then forms immunoglobulin G (IgG), which appears on tests about 2 weeks after
the illness starts. IgM usually disappears from the blood within a few months, but IgG can last for years. Some antibody tests test for IgM and
IgG, and some only test for IgG.
Version 2.0 – Released 6/25/2020 Page 1 of 4
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
What does a A negative PCR test means that A negative antigen test means A negative antibody test means
negative person was probably not infected that SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins that the person may not have had
test result at the time their sample was were not detected. However, a COVID-19 in the past. However,
mean? collected. However, it doesn’t negative test does not rule out they could still have a current
mean they won’t get sick – it only COVID-19. If there is still concern infection, and the antibody test
means that they didn’t have that a person has COVID-19 after was collected too soon to give a
COVID-19 at the time of testing. a negative antigen test, then that positive result.
person should be tested again
with a PCR test.
When is it • It can be used to determine • It can be used to quickly • It can identify people who had
helpful? who has an active infection. determine who has an active an infection in the past, even if
• It can help identify people who infection. they had no symptoms of the
are contagious to others. • It can help identify people illness.
who are contagious to others. • In some cases, it could help
• It is a less expensive test determine when COVID-19
than PCR. illness occurred, since we
know that IgM is formed
before IgG and that IgM goes
away before IgG.
• It can help determine who
qualifies to donate
convalescent plasma (a blood
product that contains
antibodies against COVID-19
and can be used as a COVID-
19 treatment).
• If lots of people take the test
in a community, it can help
public health leaders and
researchers know what
percentage of the population
has already had COVID-19.
Version 2.0 – Released 6/25/2020 Page 2 of 4
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
When is it • It does not help determine • It does not accurately rule out • It may be negative if it is used
not as who had an infection in the those who are not infected. too close to the beginning of
helpful? past. • Antigen tests are less sensitive an infection, which is why it
• It also does not help than PCR tests, meaning there should not be used to detect
determine if a person who was may be false negative results. active COVID-19 infection.
exposed to COVID-19 will • Negative tests should be • In areas where there have not
develop active infection during treated as presumptive. If a been many cases of COVID-
the two weeks after exposure. healthcare provider is 19, many of the positive test
In some people, the virus can concerned that the person has results will actually be false
only be found by PCR for a few COVID-19, even after a positives (see Positive
days at the beginning of the negative antigen test, then the Predictive Value 2). Some
infection, so the test might not test result should be confirmed antibody tests have low
find the virus if the swab is with PCR testing. sensitivity 3 and specificity 4
taken more than a few days and thus may not produce
after the illness starts. reliable results.
• In some people, the virus can • Some antibody tests may
be found by PCR in the nose cross-react with other
and throat for several weeks, coronaviruses that are not
even longer than the time that SARS-CoV2, the virus that
they are actually contagious to causes COVID-19, leading to
other people. false test results.
2
Positive predictive value is a measure of how likely it is that a positive test is a true positive rather than a false positive. This is
dependent on how many people in the population being tested have had the disease. When there are very few people in the population that
have had the disease, then there is a higher chance that a positive test is a false positive. When there are many people in a population that
have had the disease, then there is a higher chance that a positive test is a true positive.
3
Sensitivity is sometimes called the “true positive rate.” It measures how frequently the test is positive when the person being tested
actually has the disease. For example, when a test has 80% sensitivity, the test detects 80% of patients with the disease (true positives).
However, 20% of patients with the disease are not detected (false negatives) by the test.
4
Specificity is sometimes called the “true negative rate.” It measures how frequently the test is negative when the person being tested
doesn’t have the disease. For example, when a test has 80% specificity, the test correctly reports 80% of patients without the disease as test
negative (true negatives). However, 20% of patients without the disease are incorrectly identified as testing positive (false positives) by the
test.
Version 2.0 – Released 6/25/2020 Page 3 of 4
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
• This test requires certain kinds • We do not know yet if having
of swabs that may be in short antibodies to the virus that
supply. causes COVID-19 can protect
someone from getting infected
again or, if they do, how long
this protection might last. Until
scientists get more information
about whether antibodies
protect against reinfection with
this virus, everyone should
continue to take steps to
protect themselves and others,
including staying at least 6
feet away from other people
outside of their home (social
distancing), even if they have
had a positive antibody test.
What public • If positive, the health • If positive, the health • If positive, the health
health department will conduct a case department will interview the department will interview the
activities investigation. Contact tracing antigen-positive person about antibody-positive person about
will be will be performed to identify symptoms and if they were symptoms and if they were
conducted? individuals who might have around someone who had around someone who had
been exposed to the PCR- COVID-19. Contact tracing will COVID-19. If the person had
positive person when they be performed. symptoms or was around
could have spread COVID-19. • If negative, no public health someone with COVID-19, the
• If negative, no public health activities will be performed. health department will
activities will be performed. recommend they get a PCR
test. No contact tracing will be
performed.
• If negative, no public health
activities will be performed.
Version 2.0 – Released 6/25/2020 Page 4 of 4
You might also like
- NICE Way to Cure COVID -19From EverandNICE Way to Cure COVID -19Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Management of Common Infections With Antimicrobials Guidance Clinical Practice Guidelines (2019) PDFDocument4 pagesManagement of Common Infections With Antimicrobials Guidance Clinical Practice Guidelines (2019) PDFveerrajuNo ratings yet
- Hiv in Pregnancy FinalDocument73 pagesHiv in Pregnancy Finalapi-3797079No ratings yet
- Full Download Winninghams Critical Thinking Cases in Nursing 5th Edition Harding Solutions ManualDocument28 pagesFull Download Winninghams Critical Thinking Cases in Nursing 5th Edition Harding Solutions Manualnoahmya6100% (26)
- Molecular Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases, 2010, PGDocument207 pagesMolecular Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases, 2010, PGrieza_husein100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedjockoNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedPrincess JanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedJuan PeNo ratings yet
- COVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingDocument5 pagesCOVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingdaam naamNo ratings yet
- AntigenTestingFAQ EnglishDocument2 pagesAntigenTestingFAQ Englishcircuit circuitNo ratings yet
- BMJ m2284 FullDocument2 pagesBMJ m2284 FullSisca PrimaNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Document3 pagesCovid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Amy LawsonNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicDocument1 pageThe Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicChloe WrightNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSTIYOM SANo ratings yet
- Covid19 TestingDocument3 pagesCovid19 TestingNational Content DeskNo ratings yet
- Biozek Medical Reduced2Document21 pagesBiozek Medical Reduced2Adam LNo ratings yet
- John HopkinsDocument38 pagesJohn HopkinskanchitsNo ratings yet
- Why Use Real Time RT-PCR?Document4 pagesWhy Use Real Time RT-PCR?Tanzila SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument2 pagesFlowAlexander FrostNo ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Document4 pagesRapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Febri RirinNo ratings yet
- CMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsDocument1 pageCMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsdineshNo ratings yet
- The Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesDocument1 pageThe Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesqwNo ratings yet
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Document2 pagesPost-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Tati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Coronavirus TestsDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Coronavirus TestsRosano Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Covid-19 TestsDocument3 pagesTwo Types of Covid-19 TestsFhea Fernandez CarinanNo ratings yet
- Self Care Guide Pantai 1Document33 pagesSelf Care Guide Pantai 1puterishaliza272No ratings yet
- تقرير ايوDocument9 pagesتقرير ايوAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Public Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Document6 pagesPublic Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Pablo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Antigen LectureDocument20 pagesCovid19 Antigen LectureUSI- CAMANO, JAY C.No ratings yet
- Lecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVDocument6 pagesLecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- Types of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of HealthDocument3 pagesTypes of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of Healthgolden abidemNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Hiv/Aids: Masroni, S.Kep., NS., M.S. (In Nursing)Document19 pagesHiv/Aids: Masroni, S.Kep., NS., M.S. (In Nursing)Sherly OctaviaNo ratings yet
- Teste PCR Superbio2Document6 pagesTeste PCR Superbio2Guilherme MonteiroNo ratings yet
- IGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishDocument1 pageIGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishAdhimasRadityaNo ratings yet
- Serological Testing of HIVDocument4 pagesSerological Testing of HIVhamody662002No ratings yet
- Caracterizacion NigeriaDocument9 pagesCaracterizacion NigeriaAndrea LunaNo ratings yet
- FAQs Asymptomatic TestingDocument4 pagesFAQs Asymptomatic TestingAnonyNo ratings yet
- ZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1Document10 pagesZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- Understanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalAna CatarinaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMradharani023No ratings yet
- Clinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgADocument9 pagesClinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgAreginabrizolaraNo ratings yet
- Counselling in Hiv/Aids: Qurrot Ulain TaherDocument34 pagesCounselling in Hiv/Aids: Qurrot Ulain TaherBhawna JoshiNo ratings yet
- COVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Document21 pagesCOVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Buku DosaNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV 2 Testing TypesDocument4 pagesSARS CoV 2 Testing TypesFree PeepNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Covid-19 Rapid and PCR TestsDocument2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Covid-19 Rapid and PCR TestsMedilife DigitalNo ratings yet
- Covid-19: Testing TimesDocument2 pagesCovid-19: Testing TimeshgfksqdnhcuiNo ratings yet
- Jama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Document1 pageJama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Tech MitNo ratings yet
- COV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebDocument3 pagesCOV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebmattramjiawanNo ratings yet
- Step 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019Document5 pagesStep 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019yuliaNo ratings yet
- What Is PCR Testing?: Chloe KentDocument1 pageWhat Is PCR Testing?: Chloe KentMacin FlipNo ratings yet
- BSI Resource COVID19 TestingDocument1 pageBSI Resource COVID19 TestingHelenaMarquezCruzadoNo ratings yet
- Types of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XDocument19 pagesTypes of HIV and HIV Testing (2) .PPT.XronojerutomNo ratings yet
- HIV Antibody and HIV Antigen p24 Seminar PaperDocument4 pagesHIV Antibody and HIV Antigen p24 Seminar PaperAna ŠimunovićNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Test For HIVDocument7 pagesLaboratory Test For HIVBayu Eko SaputroNo ratings yet
- Testing For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Document2 pagesTesting For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Mini Review Laboratory Diagnosis For Covid-19: A Mini-ReviewDocument5 pagesMini Review Laboratory Diagnosis For Covid-19: A Mini-ReviewwellaNo ratings yet
- The Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesDocument34 pagesThe Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesEldo TaufilaNo ratings yet
- Who RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Document38 pagesWho RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Đức HòaNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Winninghams Critical Thinking Cases in Nursing 5th Edition Harding Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Winninghams Critical Thinking Cases in Nursing 5th Edition Harding Solutions Manual PDFsophiafostercqcv100% (9)
- Mushtaq Ahmad: Running Head: REFLECTIVE LOG 1Document5 pagesMushtaq Ahmad: Running Head: REFLECTIVE LOG 1Shafiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Health FormDocument2 pagesHealth Formrhea engayNo ratings yet
- Classification of Diabetes Mellitus - Endotext - NCBI BookshelfDocument11 pagesClassification of Diabetes Mellitus - Endotext - NCBI BookshelfSwati ParijaNo ratings yet
- New Application FileDocument147 pagesNew Application FilevicentemariscalNo ratings yet
- TextDocument17 pagesTextnaser zoabiNo ratings yet
- First Aid Kit ContentsDocument8 pagesFirst Aid Kit Contentsalexis mae lavitoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Nematode Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Nematode Study GuideKristine Marie PateñoNo ratings yet
- F Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Document15 pagesF Buski 111003095909 Phpapp01Ashik MajumdarNo ratings yet
- PemphigusDocument1 pagePemphigusiSmayli (smyle-smayl)No ratings yet
- Candida Infection, Integrated Science, 4.3Document13 pagesCandida Infection, Integrated Science, 4.3Anesia Andrews100% (1)
- Deeper Trial - Asco 2021Document26 pagesDeeper Trial - Asco 2021Vuong Dinh Thy HaoNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology of Coronary Heart DiseasesDocument31 pagesEpidemiology of Coronary Heart DiseasesShaimaa EmadNo ratings yet
- Jessica Le - Covid-19Document3 pagesJessica Le - Covid-19api-523306558No ratings yet
- Group 1 8 Concept PaperDocument24 pagesGroup 1 8 Concept PaperEljay Manuel CabactulanNo ratings yet
- Dry Skin Behind Ear, Flaky, Scaly, Cracked, Baby, Red, Itchy, Skin Rash, Causes, PeelingDocument4 pagesDry Skin Behind Ear, Flaky, Scaly, Cracked, Baby, Red, Itchy, Skin Rash, Causes, Peelingsunziv19No ratings yet
- Disorders of The Skeletal SystemDocument7 pagesDisorders of The Skeletal SystemjheaNo ratings yet
- The Biotherapics Influenzinum and Oscilococcinum in The Treatment of Influenza Virus FluDocument1 pageThe Biotherapics Influenzinum and Oscilococcinum in The Treatment of Influenza Virus Fluweb3351No ratings yet
- Dhanusthamba/Dhanurvata/Tetanus: Dr. Mahesh C KundagolDocument19 pagesDhanusthamba/Dhanurvata/Tetanus: Dr. Mahesh C KundagolkundagolNo ratings yet
- Cancer Informative OutlineDocument2 pagesCancer Informative OutlinetuanmalikNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity MuscleDocument3 pagesLab Activity MuscleGeorge IvyNo ratings yet
- WHAT IS PARKINSONsDocument6 pagesWHAT IS PARKINSONsRPNNo ratings yet
- Infection Control in Dental Practice 2009Document3 pagesInfection Control in Dental Practice 2009wildernest1No ratings yet
- LB 1 (Form Data Kesakitan) - September 2020Document10 pagesLB 1 (Form Data Kesakitan) - September 2020Christian RekoNo ratings yet
- History Taking.-ConvulsionDocument2 pagesHistory Taking.-ConvulsionMohammedNo ratings yet
- Lingua - Anatomi Dan Kelainan LidahDocument51 pagesLingua - Anatomi Dan Kelainan LidahKemalLuthfanHindamiNo ratings yet
- How Weight Loss Can Transform Your LifeDocument1 pageHow Weight Loss Can Transform Your Lifeanbrosewakaba2002No ratings yet
- KGMU Pathology (2000-2020)Document10 pagesKGMU Pathology (2000-2020)Prepladder ChyNo ratings yet