Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANZBA Use of Hydrogels Consensus Statement: Background
Uploaded by
wina_rakaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ANZBA Use of Hydrogels Consensus Statement: Background
Uploaded by
wina_rakaCopyright:
Available Formats
ANZBA Use of hydrogels consensus statement
Background
Hydrogel dressings
Hydrogel dressings have been introduced for the acute management of burn injuries.
They are designed to provide cooling of the wound and a dressing function.
Evidence that the cooling function of hydrogel dressing products is as effective as cool running
water for first aid is lacking
First Aid for Burns
The gold standard for burns first aid is 20 minutes of cool running water applied to the burn as soon
as possible (within 1 hour and up to 3 hours) after injury.
This is especially applicable to partial thickness wounds, where cooling may decrease burn wound
progression and improve healing
Dressings
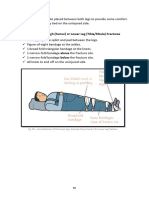
After first aid and wound cleaning, burn wounds should be dressed with appropriate sterile dressings.
Analgesia
Cool moist dressings provide good analgesia for partial thickness burns
Moist dressings rely on exposure to air for their cooling effect via evaporative heat loss
This is helpful for small burns (<10% Total Body Surface Area TBSA) in the first few hours after
injury, but in patients with more extensive injury, may result in hypothermia.
Hypothermia
Prolonged cooling of extensive burn wounds (>20%TBSA in adults and >10 - 15%TBSA in children)
can cause hypothermia - especially in children and the elderly.
Hydrogel or any wet dressing can also be associated with development of hypothermia if exposed
to the air and left in place for prolonged periods
Cooling should be discontinued if hypothermia develops.
The prolonged use of hydrogel dressings in the elderly or children with larger burns may cause
hypothermia, and should be avoided.
Statement
The gold standard for burns first aid is 20 minutes of cool clean running water
If clean running water is not available, immersion in cool water, application of wet towels or
hydrogel or other wet dressings may be useful alternatives for the provision of first aid and
analgesia.
The patient must be kept warm during cooling of the burn wound
After first aid, patients with large burns should be wrapped in dressings that minimize
evaporative heat loss by excluding air from the wound and the outer surface of the dressing.
For transfer to hospital, plastic cling films are suitable if dressings are not available.
May 2012
You might also like
- Optigal’s Q & A for the CLRE: Contact Lens Registry Exam Questions Basic Certification - NCLEFrom EverandOptigal’s Q & A for the CLRE: Contact Lens Registry Exam Questions Basic Certification - NCLENo ratings yet
- GF NOjb 3 GZDXSTD9 I 2 Ol TXAt L03 Z3 X 4 P4 Y2 Q2 Jbi DDocument9 pagesGF NOjb 3 GZDXSTD9 I 2 Ol TXAt L03 Z3 X 4 P4 Y2 Q2 Jbi DsharonchivingeNo ratings yet
- Survival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)From EverandSurvival Skills: How to Survive Anything and Anywhere in the World (A Comprehensive Guide to Preparing for and Overcoming Challenges of Earthquakes)No ratings yet
- First Aid For Minor BurnsDocument2 pagesFirst Aid For Minor BurnsKailyne WatersNo ratings yet
- ABC of Burns First Aid and Treatment of Minor BurnsDocument3 pagesABC of Burns First Aid and Treatment of Minor BurnsDita DitotNo ratings yet
- First Aid on the Farm: Natural and Conventional TreatmentsFrom EverandFirst Aid on the Farm: Natural and Conventional TreatmentsNo ratings yet
- AluminaidDocument5 pagesAluminaidAnonymous Xx82N1tNo ratings yet
- Burns DressingDocument4 pagesBurns DressingBalaMuruganNo ratings yet
- Burns: ABC of Wound HealingDocument4 pagesBurns: ABC of Wound HealingRicardoGamalielNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Appropriate DressingDocument4 pagesHow To Choose The Appropriate DressingDyan TD100% (1)
- BURN Water SafetyDocument24 pagesBURN Water SafetyMary Clair BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument16 pagesBURNSRegina KadenyiNo ratings yet
- SDS - Chlorine Gas - CCMDocument9 pagesSDS - Chlorine Gas - CCMRedleaves Sdn BhdNo ratings yet
- EBSCOhost 3 PDFDocument27 pagesEBSCOhost 3 PDFWawan Febri RamdaniNo ratings yet
- FirstAid InfographicsDocument6 pagesFirstAid InfographicsMihai Ion GhioaldaNo ratings yet
- 350 SDS 22feb2023Document8 pages350 SDS 22feb2023Ying CeNo ratings yet
- Type of Wound Dressing (Qeh2 Workshop)Document22 pagesType of Wound Dressing (Qeh2 Workshop)Eric PaulNo ratings yet
- Sigmadur Semigloss HardenerDocument7 pagesSigmadur Semigloss HardenerSelvakpm06No ratings yet
- (De-Plus D) : Qingdao Doeast Chemical IncDocument1 page(De-Plus D) : Qingdao Doeast Chemical IncHuy ThaiNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1b2 Fj9097.33-160a Msdsnew2Document6 pagesAppendix 1b2 Fj9097.33-160a Msdsnew2RUDDY ALFAN SUBAKTINo ratings yet
- Tds & Msds 100gsx and 100gsxxDocument8 pagesTds & Msds 100gsx and 100gsxxSajid UddinNo ratings yet
- Msds-En-Shell-Tellus-S2-V-22 (00000003)Document9 pagesMsds-En-Shell-Tellus-S2-V-22 (00000003)Ng GaNo ratings yet
- Tekapur 2v1 enDocument2 pagesTekapur 2v1 enEzeval GráficaNo ratings yet
- Initial Management:: First AidDocument6 pagesInitial Management:: First AidxerwaneNo ratings yet
- MSDS MC22Document4 pagesMSDS MC22Fhail MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Gadus S2 A320 2Document8 pagesGadus S2 A320 2Beryl FernandesNo ratings yet
- PWH Info - Antiseptic Solution & Wound DressingDocument16 pagesPWH Info - Antiseptic Solution & Wound Dressingproudofsky100% (1)
- Fabuloso All Purpose Cleaner Liquid Lavender: Section 1. IdentificationDocument9 pagesFabuloso All Purpose Cleaner Liquid Lavender: Section 1. IdentificationElogy HSEQNo ratings yet
- Properties: Chemical Product/ Company NameDocument3 pagesProperties: Chemical Product/ Company NameRishabh PatilNo ratings yet
- Ghs Dowicil 200 MsdsDocument11 pagesGhs Dowicil 200 MsdsEmilia ArceNo ratings yet
- Glutaraldehyde Fact SheetDocument2 pagesGlutaraldehyde Fact SheetLau Karn FongNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesBitumen Safety Data SheetArvandMadan CoNo ratings yet
- 1: 60. MSDS - Diethylene GlycolDocument7 pages1: 60. MSDS - Diethylene GlycolExternal Relations DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Liquid Nitrogen: (Please Ensure That This MSDS Is Received by An Appropriate Person)Document3 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Liquid Nitrogen: (Please Ensure That This MSDS Is Received by An Appropriate Person)SAURABH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Aquatic Hazards and DrowningDocument6 pagesAquatic Hazards and Drowningejelyn100% (2)
- Perawatan LukaDocument49 pagesPerawatan LukaSeptian Wahyu HidayahtullahNo ratings yet
- GeneralDocument23 pagesGeneralGogaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document5 pagesExperiment 4Nitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- MSDS TELLUS S2 M68aDocument5 pagesMSDS TELLUS S2 M68amflorian69No ratings yet
- GHS Format-sds-Gp CleanDocument8 pagesGHS Format-sds-Gp CleanAlan TanNo ratings yet
- MSDS Cement Tiga Roda - Dec 2019Document5 pagesMSDS Cement Tiga Roda - Dec 2019noto.sugiartoNo ratings yet
- MSDS - AcetyleneDocument5 pagesMSDS - AcetyleneNishanthNJNo ratings yet
- Petrothene GA635962Document13 pagesPetrothene GA635962Michelle Kozmik JirakNo ratings yet
- Mask Disinfection Guide For Professional Use North American EnglishDocument6 pagesMask Disinfection Guide For Professional Use North American EnglishRichardNo ratings yet
- 10:59. MSDS - Triethylene GlycolDocument8 pages10:59. MSDS - Triethylene GlycolExternal Relations DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Sds Castrol Grease LM 2 BiDocument4 pagesSds Castrol Grease LM 2 BiengturcompNo ratings yet
- Benzoxe N - Ghs Msds Template Safety Data SheetDocument5 pagesBenzoxe N - Ghs Msds Template Safety Data Sheetelpangjaya jayNo ratings yet
- Desmodur 44 V 20 L: Safety Data Sheet According To GHSDocument14 pagesDesmodur 44 V 20 L: Safety Data Sheet According To GHSKarina MacagnamNo ratings yet
- Therminol® 55 Heat Transfer Fluid: Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesTherminol® 55 Heat Transfer Fluid: Safety Data SheetOmar GRNo ratings yet
- Randolf M Lagundaon: Hazard in RefrigerationDocument2 pagesRandolf M Lagundaon: Hazard in RefrigerationRandolf Igneel LagundaonNo ratings yet
- Bayhydur XP 2655 MSDS PDFDocument10 pagesBayhydur XP 2655 MSDS PDFrogerkid17No ratings yet
- Burn ManagementDocument7 pagesBurn ManagementnrhmhealthNo ratings yet
- "Cryotherapy": Presented ByDocument23 pages"Cryotherapy": Presented Byyaraa6805No ratings yet
- Surgical DressingDocument60 pagesSurgical DressingJeffri syaputraNo ratings yet
- Therminol® 66 Heat Transfer Fluid: Safety Data SheetDocument14 pagesTherminol® 66 Heat Transfer Fluid: Safety Data Sheet266870idNo ratings yet
- SFA Manual Rev 1 2020 - Final 101 126Document26 pagesSFA Manual Rev 1 2020 - Final 101 126Samier MohamedNo ratings yet
- Tekncoat - Technical - Data (1) - 009Document1 pageTekncoat - Technical - Data (1) - 009aboali8686No ratings yet
- Diathermy Scratch Pad From Valley Lab-CovidienDocument4 pagesDiathermy Scratch Pad From Valley Lab-CovidienBob RiouxNo ratings yet
- Drying and Curing Time: Technical Data Sheet Pilot QD PrimerDocument1 pageDrying and Curing Time: Technical Data Sheet Pilot QD PrimerTamerTamerNo ratings yet
- Tourniquet Test - F PDFDocument1 pageTourniquet Test - F PDFArdhiNo ratings yet
- Cataract PDFDocument8 pagesCataract PDFeashelNo ratings yet
- Petechial Hemorrhages in Suicide by Hanging: Riginal RticleDocument7 pagesPetechial Hemorrhages in Suicide by Hanging: Riginal Rticlewina_rakaNo ratings yet
- Petechial Hemorrhages in Suicide by Hanging: Riginal RticleDocument7 pagesPetechial Hemorrhages in Suicide by Hanging: Riginal Rticlewina_rakaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of EarDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of EarAriguna WijayaNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGY OF THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE بحث دكتوره ميDocument22 pagesPHYSIOLOGY OF THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE بحث دكتوره ميSoma Al-otaibyNo ratings yet
- Infodatin Pengelolaan Vaksin Di IndonesiaDocument12 pagesInfodatin Pengelolaan Vaksin Di IndonesiaChristina AgustinNo ratings yet
- Tranexamic AcidDocument13 pagesTranexamic Acidwina_rakaNo ratings yet