Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ray Optics: Reflection: Single Correct Answer Type
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ray Optics: Reflection: Single Correct Answer Type
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriCopyright:
Available Formats
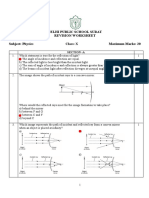
RAY OPTICS: REFLECTION DPP 1
SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE
1 1
1. For a concave mirror, if real image is formed the graph between 𝑢 𝑎𝑛𝑑 is of the form
𝑣
2. In an experiment, the focal length of a concave mirror on a graph is drawn between the magnitudes of u and v. The
graph looks like
3.
The graph shows variation of v with change in u for a mirror. Points plotted above the point
P on the curve are for values of v
a. Smaller than f b. Smaller than 2f
c. Larger than 2f d. Larger than f
4. As the position of an object (u) reflected from a concave mirror is varied, the position of the image (v) also varies.
By letting the u change from 0 to + ∞ the graph between v versus u will be
5. The graph between u and v for a convex mirror is
6. A convergent beam of light is incident on a convex mirror so as to converge to a distance 12 cm from the pole of the
mirror. An inverted image of the same size is formed coincident with the virtual object. What is the focal length of
the mirror?
a. 24 cm b. 12 cm c. 6 cm d. 3 cm
7. A thin rod of 5 cm length is kept along the axis of a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length such that its image is real
and magnified and one end touches the rod. Its magnification will be
a.1 b. 2 c. 3 d. 4
8. A square of side 3 cm is placed at a distance of 25 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. The centre of the
square is at the axis of the mirror and the plane is normal to the axis. The area enclosed by the image of the square is
a. 4cm2 b. 6 cm2 c. 16 cm2 d. 36 cm 2
9. A small piece of wire bent into an L shape with upright and horizontal portions of equal lengths is placed with the
horizontal portion along the axis of the concave mirror whose radius of curvature is 10 cm. If the bend is 20 cm from
the pole of the mirror, then the ratio of the lengths of the images of the upright and horizontal portions of the wire is
ANISH SIR & TEAM 9919495931
a.1 : 2 b. 3 : 1 c. 1 : 3 d. 2 : 1
10. A cube of side 2 m is placed in front of a concave mirror focal length 1 m with its face P at a
distance of 3 m and face Q at a distance of 5 m from the mirror. The distance between the
images of face P and Q and height of images of P and Q and height of images of P and Q are
a.1 m, 0.5 m, 0.25 m b. 0.5 m, 1 m, 0.25 m c. 0.5 m, 0.25 m, 1m d. 0.25 m, 1 m, 0.5 m
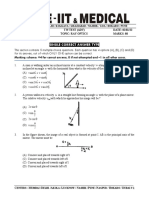
11. AB is an incident beam of light and CD is a reflected beam (the number of reflections for this
may be 1 or more than 1) of light. AB and CD are separated by some distance (may be large).
It is possible by placing what type of mirror on the right side.
a. one plane mirror b. one concave mirror c. one convex mirror d. None of these
12. A point object is moving along principal axis of a concave mirror with uniform velocity towards
pole. Initially the object is at infinite distance from pole on right side of the mirror as shown.
Before the object collides with mirror, the number of times at which the distance between object
and its image is 40 cm is:
a. one time b. two times c. three times d. Data insufficient
MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWERS TYPE
13. A particle is moving towards a fixed convex mirror. The image also moves. If Vi = speed of image and V0 = speed
of the object, then
a. Vi ≤ V0 if |𝑢| < |𝐹| b. Vi > V0 if |𝑢| > |𝐹| c. Vi < V0 if |𝑢| > |𝐹| d. Vi = V0 if |𝑢| = |𝐹|
14. The positions of the object O (real or virtual) and the image 1 (real or virtual) with respect
to the optical axis of a spherical mirror is shown. Then select the possible mirror and its
position to realise it.
a.concave mirror closer to object b. concave mirror closer to image
c. convex mirror closer to object d. convex mirror closer to image
Matching column type
15. Match the options of the Column I Column II
following columns.
A For real extended object, if image formed by a single P Concave
mirror is erect, and if the size of image is smaller
than object, the mirror is
B For real extended object, if the size image is smaller Q Convex
than object, the mirror is
C For real extended object, if image formed by a single R (f, f)
mirror is erect and if the size of image is larger
than object,
D For spherical mirrors, a line u = v will cut the curve S (2f, 2f)
between u and v at a point.
ANSWERS KEY
Single correct answer type 1.a 2.c 3.c 4.a
5. a 6. c 7. b 8.a 9.b 10.d 11. b 12.c
Multiple correct answers type 13. (a, c) 14.(a, c) Matching column type
15. (A) → Q;(B) →P;(D) → S
ANISH SIR & TEAM 9919495931
You might also like
- Spherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesDocument1 pageSpherical Mirror-Vsq1.1-QuesRonit RoyNo ratings yet
- G10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Document10 pagesG10 - Chapter Test 5 Ans - Ch.10 - 06 NOV 23Urmila GNo ratings yet
- 2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S EoDocument6 pages2 Ii We 7 TKB Es 6 CSN G3 S Eony9197171No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Second 2Document3 pagesGrade 10 Second 2Eden Rey ParoanNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsDocument3 pagesPhysics Test Prep: Reflection and MirrorsvaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Arihant Science Class Test-Class-X (MCQ)Document4 pagesArihant Science Class Test-Class-X (MCQ)Hadron ClassesNo ratings yet
- 1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Document11 pages1 - Light Reflection and Refraction (Prashant Kirad)Kshitiz sharmaNo ratings yet
- Light - Padhle TenthiesDocument92 pagesLight - Padhle Tenthiesa9758127118No ratings yet
- Ray Optics Assignment 1Document1 pageRay Optics Assignment 1Kiron StefenNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 10 Science Chapter 10Document28 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 10 Science Chapter 10Nidhi srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- Hapter: Conceptual QuestionsDocument16 pagesHapter: Conceptual QuestionsadelNo ratings yet
- Light+Revision +30 01 2020Document69 pagesLight+Revision +30 01 2020Ramesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 29-Jun-2023Document6 pagesAdobe Scan 29-Jun-2023kpssgaming923No ratings yet
- Physics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesPhysics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoicefgdhNo ratings yet
- 5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFDocument45 pages5+mark+questions +CBSE+X +light +25 12 2019 PDFPiyushNo ratings yet
- O W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791Document89 pagesO W Grukul Science Most Likely CBSE Question Bank For Class 10 Exam-703-791S.P studiesNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument14 pagesLight Reflection and RefractionKalpesh UradeNo ratings yet
- Cbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesCbse Test Paper-02 10 Light Reflection and RefractionAchyut SinghNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument27 pagesOpticsSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Test Optics 1Document4 pagesTest Optics 1Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed SolutionDocument30 pagesRay Optics DC Pandey MCQ With Detailed Solutionvivek100% (1)
- Light-Mirrors and Lens WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight-Mirrors and Lens WorksheetTharunaNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- NCERT ExemplarDocument10 pagesNCERT Exemplarrohitpatra708024No ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNo ratings yet
- Back Exercise Questions NCERT LightDocument9 pagesBack Exercise Questions NCERT LightMinakshi TiwariNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Surat Revision Worksheet Subject: Physics Class: X Maximum Marks: 20Document4 pagesDelhi Public School Surat Revision Worksheet Subject: Physics Class: X Maximum Marks: 20Deb Kumar SarkarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSPramit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Curved Mirrors o LevelDocument14 pagesCurved Mirrors o LevelAZORYNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice TestDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Testchristy angelie mojado67% (3)
- Physics Cl10 Assign3Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign3Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument137 pagesUntitledpranav tomarNo ratings yet
- FAQ PhysicsDocument30 pagesFAQ Physicsamit21oct2005No ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Set 1Document2 pagesReflection of Light Set 1XxxxxxNo ratings yet
- PDF&Rendition 1 13Document5 pagesPDF&Rendition 1 13rishikajn4795No ratings yet
- ScienceDocument4 pagesScienceJay R CristobalNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THDocument5 pagesLight - Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - WARRIOR SERIES CLASS-10THhiranyakshivNo ratings yet
- PHY 121 10 - OpticsDocument38 pagesPHY 121 10 - OpticsChristopher NdamboNo ratings yet
- Physics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesPhysics I Honors: Chapter 13 Practice Test: Multiple ChoicefgdhNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Geometrical OpticsDocument27 pagesExercise On Geometrical OpticssakshamamitagarwalNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1Document6 pagesGrade 10 Physics Chapter 3 Revision Problems - Answer Key: Multiple Choice Questions. Q1NONO0% (1)
- Ray Optics (ADV) Question PaperDocument6 pagesRay Optics (ADV) Question PaperShiv ShettyNo ratings yet
- Light Reflection 1Document22 pagesLight Reflection 1psnarayanan99No ratings yet
- Ntse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Document9 pagesNtse - Assignment 1 - Level 1Anmol SinghNo ratings yet
- LIGHT ASSIGNMENT - JUNOON SCIENCE Light AssignmentDocument3 pagesLIGHT ASSIGNMENT - JUNOON SCIENCE Light AssignmentMack TripathiNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersDocument9 pagesClass X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersAnkur MondalNo ratings yet
- Light-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024Document5 pagesLight-Reflection & Refraction - Practice Sheet - 10th Board Booster 2.0 2024yashasvisharma sharmaNo ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument50 pages10 LightNaveen Kumar100% (1)
- 10 THDocument3 pages10 THRohitNo ratings yet
- Reflection (Homework) SAS Grade 11Document6 pagesReflection (Homework) SAS Grade 11merry glorNo ratings yet
- Sci Collab TayoDocument22 pagesSci Collab TayoJullie Ann AcuninNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 10 M3ST3Document3 pagesQ2 Science 10 M3ST3Leother Yee SosmenaNo ratings yet
- Light Assign MentDocument32 pagesLight Assign MentAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 pagesLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNo ratings yet
- 10 PhysicsDocument6 pages10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- QUIZ in Reflection and MirrorsDocument18 pagesQUIZ in Reflection and Mirrorssrija vijjapu100% (1)
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDocument40 pages18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Wiriti Led TubeDocument1 pageWiriti Led TubeVenodaren VelusamyNo ratings yet
- Thin Film Solar Cell WikiDocument7 pagesThin Film Solar Cell Wikivishrao1984No ratings yet
- FS003 Module Week03Document8 pagesFS003 Module Week03Joana Francisca VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Curved MirrorsDocument7 pagesCurved MirrorsRhain CongayoNo ratings yet
- Region Province Reference NumberDocument12 pagesRegion Province Reference NumberdrazhellNo ratings yet
- Date Code - Osram - 1994-PresentDocument2 pagesDate Code - Osram - 1994-PresentMuzeul LampilorNo ratings yet
- II PUC Physics 2017 PDFDocument49 pagesII PUC Physics 2017 PDFKumari S75% (4)
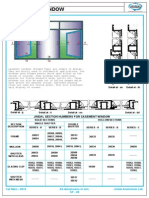
- 20) Casement Window SectionsDocument21 pages20) Casement Window SectionsMinal Agarwal0% (1)
- CA2C Online V4Document57 pagesCA2C Online V4Muhammad FazleyNo ratings yet
- ATW Pricelist 2021Document14 pagesATW Pricelist 2021Erlangga Bayu100% (1)
- Reflection of Light 1-12Document26 pagesReflection of Light 1-12chirayuaggarwal2006No ratings yet
- Posted 7-23-'04 This Next Page Contains Information On This Camera. Creation By-M - B - Utkuq' NJDocument33 pagesPosted 7-23-'04 This Next Page Contains Information On This Camera. Creation By-M - B - Utkuq' NJPaulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNo ratings yet
- Residential Construction Windows & DoorsDocument38 pagesResidential Construction Windows & Doorsdinesh royalNo ratings yet
- Telescope Design 2Document6 pagesTelescope Design 2Jim100% (3)
- Saint-Gobain Sekurit Automotive Glazing Production ProcessesDocument1 pageSaint-Gobain Sekurit Automotive Glazing Production ProcessesAmir BakhshiyanNo ratings yet
- What Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellDocument9 pagesWhat Is Solar Cell Working Mechanism Why We Use Solar Cell P-V System Describe Different Types of Solar Cell Efficiency Uses of Solar CellrishabhNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics - Mirrors and LensesDocument74 pagesGeometric Optics - Mirrors and Lenses11-CG14 Jao, Kathleen Maye E.No ratings yet
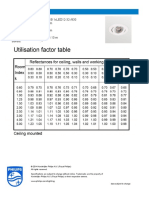
- Uf Table 16wDocument1 pageUf Table 16wCarolina IskandarNo ratings yet
- SolarControl enDocument109 pagesSolarControl enberymoNo ratings yet
- Price List Firefly Lighting November 2019 IssueDocument36 pagesPrice List Firefly Lighting November 2019 IssueMiko F. Rodriguez100% (1)
- Medical Lamps: 2018 CatalogueDocument16 pagesMedical Lamps: 2018 CatalogueAnonymous dGFqrw5vO100% (1)
- Depo ToyotaDocument103 pagesDepo ToyotaGarry McKay100% (1)
- Lab 1Document5 pagesLab 1Nur HanisNo ratings yet
- Light WorksheetDocument11 pagesLight Worksheetkobayashirei602No ratings yet
- Daytime Running Lights,: Wiring DiagramDocument7 pagesDaytime Running Lights,: Wiring DiagramstefanVasNo ratings yet
- Panou Solar FV Trina Solar 475 - 505 - Fisa Tehnica - Site TrinaDocument2 pagesPanou Solar FV Trina Solar 475 - 505 - Fisa Tehnica - Site TrinaBirshopulosNo ratings yet
- Images: All Shopping News Videos Maps BooksDocument1 pageImages: All Shopping News Videos Maps BooksChloe Raine LandinginNo ratings yet
- M.E Ped - R2017 - X86077 (PS5092)Document2 pagesM.E Ped - R2017 - X86077 (PS5092)MR.R. JEBA RAJNo ratings yet
- S3E M2 SolarPV PDFDocument60 pagesS3E M2 SolarPV PDFNofal AghayarliNo ratings yet
- LED T8 Type B Spec SheetDocument5 pagesLED T8 Type B Spec SheetSERGIO ERIC RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Vibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeFrom EverandVibration and Frequency: How to Get What You Want in LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- The 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandThe 60 Minute Quantum Physics Book: Science Made Easy For Beginners Without Math And In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (49)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (78)
- Let There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessFrom EverandLet There Be Light: Physics, Philosophy & the Dimensional Structure of ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- The Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseFrom EverandThe Illustrated Theory of Everything: The Origin and Fate of the UniverseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- AP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeFrom EverandAP Physics 1 Premium, 2024: 4 Practice Tests + Comprehensive Review + Online PracticeNo ratings yet