Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 3 21
Uploaded by
api-5203161580 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views22 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
114 views22 pages3 3 21
Uploaded by
api-520316158Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
Drag the correct
drawing to each box
Atoms & Molecules
MATTER
• Matter is made of tiny particles. These particles are too small
to be seen – even with a microscope!
• These particles are called atoms.
• Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter.
Matter 4 © Stephanie Elkowitz
STATES OF MATTER
• Matter is found in three different forms on Earth. We call
these forms the states of matter.
• Each state of matter is made of particles that are packed
together tightly, loosely or very loosely.
• There three major states of matter are solid, liquid and gas.
Matter 5 © Stephanie Elkowitz
SOLID
• Matter that is composed of atoms
tightly packed together is called solid.
• The atoms are packed so tightly that
they cannot move around. However,
the atoms are able to vibrate.
• A solid has a definite shape and
volume. In other words, a solid holds
its shape and volume on its own.
• Examples:
– Ice
– Pencil
Matter 6 © Stephanie Elkowitz
States of Matter
SOLIDS
A SOLID is matter that has a defined shape and will not lose its shape.
FIXED VOLUME AND FIXED SHAPE
Molecules in a solid are tightly
Examples of solids:
1.Chair
packed and vibrate slightly, but
2.Table do not move around each other.
3.Golf Ball
4.Hockey Puck
5.Glass Jar
LIQUID
• Matter that is composed of atoms
loosely packed together is called
liquid.
• There is some space between the
atoms so the atoms can slightly move
around.
• Liquids have definite volume but do
not have a definite shape. Liquids take
the shape of their container.
• Examples:
– Water
– Alcohol
Matter 8 © Stephanie Elkowitz
States of Matter
LIQUIDS
A LIQUID is matter that will take the shape of any container it is placed in
put has a fixed volume.
Molecules in a liquid are loosely
Examples of LIQUIDS:
1.Water packed and can slide past each
2.Soda other.
3.Milk
4.Juice
5.Tomato Sauce
GAS
• Matter that is composed of atoms
very loosely packed together is called
gas.
• There is a lot of space between the
atoms and they are constantly moving
around.
• Gases do NOT have a definite volume
or shape. Gases take the shape and
volume of their container.
• Examples:
– Water Vapor
– Oxygen
Matter 10 © Stephanie Elkowitz
States of Matter
GASES
A GAS is matter that does NOT have a fixed shape or volume, but will
completely take up all the space in a container.
MOST GASES ARE INVISIBLE!!!!
Molecules in a gas are spread
Examples of GASSES: out and move freely.
1.Oxygen
2.Helium
3.Carbon Dioxide
4.Nitrogen
5.Carbon Monoxide
PLASMA
• Plasma is a 4th state of matter.
• It is the most common state of
matter in the Universe, but it is
not commonly found on Earth.
• Plasma is most like a gas.
• When a gas is heated to a very
high temperature, electrons are
“torn off” the atoms. This results
in a mass of positively charged
atoms and negatively charged
electrons – a plasma.
Matter 12 © Stephanie Elkowitz
PLASMA
• Plasma is found in the space between planets, solar systems
and galaxies.
• Stars, including our sun, are actually spheres of plasma.
Matter 13 © Stephanie Elkowitz
PLASMA
• Plasma is not common on Earth but can be
found both naturally and manmade.
• Lightning forms plasma momentarily.
Lightning is very hot and heats air around it.
The heat from lightning causes the gas
around it to change into plasma. When you
observe the “bright light” of lightning, you
are actually observing plasma.
• Plasma can be man-made using electricity.
With fluorescent lights, electricity is passed
through a tube of neon gas. The electricity
transforms the neon gas into plasma. The
“glowing light” is plasma.
Matter 14 © Stephanie Elkowitz
Video: Fuse School
HEATING & COOLING
• A phase change takes place because thermal energy is
transferred to or from a substance. The transfer of thermal
energy is called heat.
• Adding thermal energy to a substance is called heating.
• Removing thermal energy from a substance is called cooling.
Matter 18 © Stephanie Elkowitz
HEATING & COOLING
• When a substance is heated, it melts or evaporates.
– When heat is added to a solid, it melts to a liquid.
– When heat is added to a liquid, it evaporates to a gas.
Solid Liquid Gas
Matter 19 © Stephanie Elkowitz
HEATING & COOLING
• When a substance is cooled, it freezes or condenses.
– When a gas is cooled, it condenses to a liquid.
– When a liquid is cooled, it freezes to a solid.
Solid Liquid Gas
Matter 20 © Stephanie Elkowitz
PHASE CHANGE
• A substance will change phases at a
specific temperature.
– Freezing Point: The temperature at
which a liquid freezes
– Melting Point: The temperature at
which a solid melts
The melting point of water is 0°C
– Boiling Point: the temperature at
which a liquid evaporates
– Condensation Point: the
temperature at which a gas
condenses
Matter 21 © Stephanie Elkowitz
Click on Link
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Effect of Elements On SteelDocument18 pagesEffect of Elements On SteelMohamed Ahmed MaherNo ratings yet
- 5 13 Geometry and VolumeDocument22 pages5 13 Geometry and Volumeapi-520316158No ratings yet
- SWBAT: Write Numbers From Expanded Form To Standard Form.: ObjectiveDocument33 pagesSWBAT: Write Numbers From Expanded Form To Standard Form.: Objectiveapi-520316158No ratings yet
- 5 12 Plotting PointDocument22 pages5 12 Plotting Pointapi-520316158No ratings yet
- SWBAT: Round To The Nearest Hundredths Place.: ObjectiveDocument34 pagesSWBAT: Round To The Nearest Hundredths Place.: Objectiveapi-520316158No ratings yet
- SWBAT: Write Numbers From Expanded Form To Standard Form.: ObjectiveDocument31 pagesSWBAT: Write Numbers From Expanded Form To Standard Form.: Objectiveapi-520316158No ratings yet
- 4 14 Multiplying or Dividing by 10Document36 pages4 14 Multiplying or Dividing by 10api-520316158No ratings yet
- 04 08 Review Part 1Document28 pages04 08 Review Part 1api-520316158No ratings yet
- 3 3 21Document22 pages3 3 21api-520316158No ratings yet
- 3 22 21Document14 pages3 22 21api-520316158No ratings yet
- 3 25 Iab A B Order of OperationsDocument21 pages3 25 Iab A B Order of Operationsapi-520316158No ratings yet
- M/D A/S: Unit One: Number TheoryDocument1 pageM/D A/S: Unit One: Number Theoryapi-520316158No ratings yet
- Objective: SWBAT Solve Problems by Using The Order of OperationsDocument21 pagesObjective: SWBAT Solve Problems by Using The Order of Operationsapi-520316158No ratings yet
- Review For 2 16Document15 pagesReview For 2 16api-520316158No ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument17 pagesAcid BaseNia LisnaNo ratings yet
- Flavor - Sensory CitrusDocument14 pagesFlavor - Sensory CitrusAgnetha LintangNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document9 pagesChemistry 2arch360No ratings yet
- GATE QuestionsDocument95 pagesGATE QuestionsashoknrNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab (Midterms) : November 2015 Dr. Mark CalbanDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Lab (Midterms) : November 2015 Dr. Mark Calbanrichmarkconag1No ratings yet
- AA7075Document7 pagesAA7075Trial_TNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Analysis: Product Number: C0750 Batch Number: SLBQ5205VDocument1 pageCertificate of Analysis: Product Number: C0750 Batch Number: SLBQ5205VAnonymous pCIauPOGNo ratings yet
- 02 API 570 Points To RecallDocument6 pages02 API 570 Points To RecallMohammedBujairNo ratings yet
- Application of X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Technique in Nano Composite MaterialsDocument36 pagesApplication of X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Technique in Nano Composite MaterialsDuygu Deniz EryaşarNo ratings yet
- Weathering of RocksDocument2 pagesWeathering of Rocksvee propagandaNo ratings yet
- Phosgene Msds E4641ttDocument7 pagesPhosgene Msds E4641ttArif Adi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Sno2 FDocument5 pagesSno2 FLa Viola FiorentinaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument42 pagesNuclear ChemistryneerajNo ratings yet
- Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent For Determination of Reducing SugarDocument7 pagesUse of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent For Determination of Reducing SugarLANANo ratings yet
- Torben RasmussenDocument4 pagesTorben Rasmussenkuruvillaj2217No ratings yet
- Effects of Parameter Changes On The Structure and Properties of Low-Density Polyethylene FoamDocument9 pagesEffects of Parameter Changes On The Structure and Properties of Low-Density Polyethylene FoamZunaida ZakariaNo ratings yet
- LeadCare II User ManualDocument24 pagesLeadCare II User ManualririmonirNo ratings yet
- Resto Sem Report Common ErrorsDocument40 pagesResto Sem Report Common ErrorsGolda-Fiel Tolentino LanguisanNo ratings yet
- (EDQM) 2020 Technical Guide For The Elaboration of MNG - Medicinal Products Containing Chemically Defined Active SubstancesDocument14 pages(EDQM) 2020 Technical Guide For The Elaboration of MNG - Medicinal Products Containing Chemically Defined Active SubstancesAn TaNo ratings yet
- prEN 10149-1 (2011) PDFDocument16 pagesprEN 10149-1 (2011) PDFneiva201950% (2)
- Alstom - Integrated Solutions For Coal-Fired Power PlantsDocument3 pagesAlstom - Integrated Solutions For Coal-Fired Power PlantsAlmario SagunNo ratings yet
- Special Examination (Mid-Final)Document4 pagesSpecial Examination (Mid-Final)waqasrazammmmNo ratings yet
- Petrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21Document72 pagesPetrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21lucianduNo ratings yet
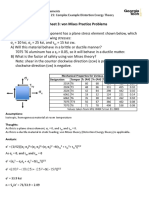
- Worksheet 3: Von Mises Practice Problems: X y XyDocument6 pagesWorksheet 3: Von Mises Practice Problems: X y XyMouad Thf100% (1)
- MF 7009 - Non Destructive Evaluationmay June 2016Document2 pagesMF 7009 - Non Destructive Evaluationmay June 2016kannankrivNo ratings yet
- Artigo Sobre EstribosDocument5 pagesArtigo Sobre EstribosPaulo CotteNo ratings yet
- Practicum Journal of Chemical Separation Principles Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)Document5 pagesPracticum Journal of Chemical Separation Principles Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)Rizki AuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FermentationDocument6 pagesChapter 7 FermentationBRENDAN CHIEW CHANG RONG MoeNo ratings yet
- DT202B THERMAL TOP P 200 RH01 HONEY GLASSINE 65 UPM Raflatac SPADocument2 pagesDT202B THERMAL TOP P 200 RH01 HONEY GLASSINE 65 UPM Raflatac SPArcNo ratings yet