0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 217 views10 pagesElectrochemistry Practice Problems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
AP Chemistry
Ch.17 Electrochemistry: Practice Problems I
1) The half-reaction that occurs at the cathode during the electrolysis of molten sodium bromide is___.
2) 2B1"— Br, +26 € Feqhetion ter. +e
b) Br +26 > 2Br la :
lat + & Na Anodle : Oxjcleton Ss gh |
GNa— Na +e = Br Br
2) What voltage will be produced by this electrochemical cell? = |
a) 42.970 ° [Reduction Potential, E? Cy ca
; Ee ph sae
@us5sv be ‘ca Vee Et bP tae PD io al
c) -L.81V a BOD
) Eete = (-013)- (MOA => ae
a 297V y L =e
athes 7 TH
ae oe > more negative Le 005
3) A galvanic cell is set up using the following helf-reactions: eee SCC i
Zn | Zn’™ (1M) || Ni* (1M) | Ni —
What fhe Aandard Seas A ihe cell? Anodk lord eas? [zn + 2e > Zall E
7 eee
( = (-0.763
a)-0513V —b) -1.013 V ) +1.013 V “Caposisv Gate 2 C0252) (-0-762)
Ecete = tO 513
=—_—
0.763 V|
4) For the reaction shown below, £2 = 0.79 V.
61 (aq) + Cr207 (aq) + 14H” > 3p (aq) + 2Cr** (ag) + TH2O(aq)
Given that the standard reduction potential for Cr207?~ » 2Cr** is 1.33 V, what is E°pa for In(aq)?
3) - ¢
AY +0.54.V Z CA a Lt.
b) -0.54 V coll = Er 9 gui Beri chon 6
tasty Zastte Leth df aoe
. 0292 1/33) — 5° roan le
eae ~ Candle
)-0.18 V
- 254. -Ein sk > Goneb A AS4V
5) According to the information below, what is the standard reduction tential for the half-reaction
M* (aq) + 3. DMG)?
Ms +3 Ag'(ag) > 3 Ags) + M™(aq) ES T2460
b) 0.06 V Ag'(aq)+¢ > Ags) E=+0.80V
0.06 V 5
ae a ne Be (oxiclehion/ Anode)
6)
eeeeee PAG se > Ay (reduc of cect Fock)
Ebete = Etathadle - Emmet) 7
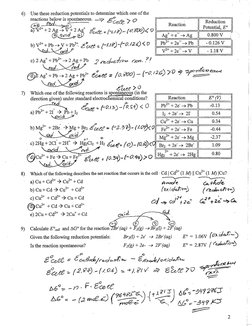
+246 =(t0 #0) - Eprecle Spredle LE"�6) Use these reduction potentials to determine which one of the
reactions below is spontaneous. > £74, > O
: Reduction |
Leman Potential, £° |
3
Ses SV+2 Ag" = (1.19) ~ (250) £01
eae Bete = (118)- (2.509) |
[Lee +263 Pb
Agte >Ag | 0800V ;
L-0i26v_ |
BEEP V EPH Bbcet «(MAC OIZO LO
2Ag+PD 9 pechucHior reer. 7!
\eed. Sted 7
CD Aa + PO Ag+ PE Eeeté = (0.200) — (2/2) 70 9 sprzlemencs
ed. oxi >o
VF+2e>V | -118V_ |
Etzeé
7) Which one of the following reactions is spontangous (in the
direction given) under standard electrochemical conditions? Reaction [| 2) |
Zi * H
2 exeg = F012)-10.S) <0 | Po +26 Pb | -0.13
ore 2 fh (btesow [054 |
if [a +2e> cu | 034 |
D) Me" 42Br. > Me+Br Seeee = (2.37)- (10) 0G 26 Fe | Oa
ee ppsusTe
©) 2g +2Cl 42H" > HECh +h Lice: (0)-l02O
ad {
Br +2e > 2Br |
ORR EIT cheer = 109p-an)70|
Bus
8) Which of the following describes the net reaction that occurs in the cel
a) Cu+Cd* > Cu +d
b) Cut Cd > Cu + Ca
Hy +2¢ > 2Hg |
ll - Cd | Cd®* (1M) || Cu* (1 Mf) [Cu?
ae a
Arode cathele
(oxidation) (ecluchon)
¢) Cut +Cd* > Cut Cd 24 i
Cd» cb 26 GEt2E SG
@eou* +ca> Cut ca
e) 2Cu+Ca* > 20a" + Cd oi ed,
5 oO 2D
9) Calculate Eu and AG? for the reaction ZBr (ag) + Fx(g) > Bro(l) + 2F (aq)
Given the following reduction potentials: Br,(l) + 2¢ >
Is the reaction spontaneous? FQ + 2e- >
E2c0l = Ecctech/raduohine ~ Ennabforicelne
2Br (aq) B= 1.06y (onidati~\)
2F (ag) «B® = 2.879 [ Ceduolio“dy
eb
Eze = (2.98) - (408) Sth PIV D Ele 70 ana
=
Bere -179- F- Ecol
Aes - (nec) (BEES) {*
yey
aan
ey�wand elle be Coast, kD
10) Calculate £%,. and AG? for the following reaction: Cd | Cd”*|| Cu?" | Cu
Is this reaction spontaneous? eridedi~
a o - 64S C\ 49,
ed Gltteze Clafe04ov yee (amebe)/ MHEFC) 10.943
Cats 20° = S Ered 24 OAV . KEP HBKS
Zbatl (1239 -(-040) = 10
11) How many moles of chromium would be electroplated by oe current of 5.2 za through
solution of Cra(SO4)s for 45.0 minutes? Cteduce
5 2 ce ce Ste
60.048 mal) & |
b) 2.9 mol te ( é ct \
Xrm€ Co = x40 “op free Tra Om
6) 0.15 mol i Pe g ve 7 Fesrp)| Smee)
4) 6.9 mol
€) 0.073 mol X = D4 mol Co
——
(reduction)
12) A spoon is made the cath alt inan electroplating apparatus containing a AgNOs solution. How many
grams of Ag will be plated on the spoon ifa current of 2.00 A is passed through the apparatus for 1.90 |
Ge a welt ntl rte
ete ee le
b) 0.150
©) 0.128.g Xgrams he a eae ex Nh
4) 0.0638 g
X20. 2ISF hy
—_—
13) A current of 10.0 amperes flows for 2.00 hours through an electrolytic cell containing a molten salt of
‘metal X. This results in the decomposition of 0.250 mole of metal X at the cathode. The oxidation
state of X in the molten salt is_/3-t (X', x", X", x")
x™ i ee ; '
pat “OA: i
wo eo _ (1902s ee) ate) } Ib nto €
ot ae xX�14) Solutions of Ag’, Cu", Fe and Ti* are electrolyzed with a constant current until 0.10 mol of metal is
deposited. Which will require the. « eetest Jength of time? Te yt
cf
hte Green Gol
15) How many grams of cobalt métal will be deposited when a solution of cobalt (Il) chloride is é
clectrolyzed with a current of 10. amperes for 109 minutes? —s
39
[ingle ae ve ie
Gare X gum « “(8 iy, lori GCE
bP, 7 vee ee
X= Kita 2295 4
—
16) How many minutes will it take to plate out 4.56 g of Ni metal from a solution of Ni* using a
current of 45.5 amps in an electrolytic cell?
8) 0.66 g ee is ze > Cols)
Gr
2.95 Nokes Zo oo
b) 4.55, finesse | Sea
at lms |
aie 48 (tS ese (Ee Nita
Sy 1ss 4.56 - QOIBB4-OE Ab. B2F-52 sec oo S49 9
=
17) Calculate the volume of He gas at 25°C and 1,00 atm that will collect at the cathode when an aqueous
solution of NagSO, is eléctrolyzed for 2.00 hours wit a 10.0-amp current, (ans: 9.121)
cathode (2); 21,0+20 Fh +208
- fia 60, 26003\ bane at th
eee 200s eine ee rol,
Xe 0.373 .
daw, PV= 0 T :
dual Gare 48% ag2i Li [ps12%)
(ote V ts 373 mt 0082 \E
ee
caer�Free Response Question 2000 # 2 nee ieee
: i | Reaction EV) |
a. The standard reduction potential for two half-reactions at 25°C and oe
+ Je Co | -0.28 |
1M concentration are given on the table below.
i. Write the balanced net-ionic equation for the overall reaction. oe [BP + 20 pn | 076 |
ii, Which of the metal ions is reduced in the reaction? Which metal is oxidized?
iii, Calculate the standard potential, E°, and the free-energy, AG", for the overall reaction at 25°C.
(D cafbech) Rechettion: C4 20 Co S%-022V
prade/ Oxiletron «Bh —7 Zit + 2e ne FFOV
phat iene ies alana cere = a4rV (ie)
———
a
[ Co 1s reduced, B08 oxicl zed
° peo 950 \(a4P DT,
HF Ete 6% -(2m 26) (648858 oe)
Gay Ae
AG? = 926 26 Seah wy 93 KTanly
—_
b. Hydrogen peroxide, H;0z, decomposes according to the following equation:
(2) 2Hy0:(aq) > 2H20() + Og) FP=0.55V
The half-reaction below is shown with its standard reduction potential:
(BD) Ong) + 4H (aq) + 4 > 200 FP=123V.
Using the information above in addition to the equation for the decomposition of #702, determine the
value of the standard reduction potential, E°, for the half-reaction below.
O2(g) + 2H (ag) + 2e” D HyOxaq)
—IxXG@)- > 2th0 + Or > 24,0, és -AS5Y
D> 4 4Nts 4e > 2H,0 B= ue3y
Paar 7 v
6» 20, + 4h ae > 2H,9, E%* 042
z
O 42+ 26 yo, (62 DePv)�Free Response Question 2001 #7
Answer the following questions that refer to the galvanic cell ie
shown in the diagram. The two reduction half-reactions that (2.77
occurs in the cell are shown below.
[Reaction _|
Ni +2e7>Ni_|| +
es Z
a, Identify the anode and the cathode of the cell and the direction of electron flow between the electrodes.
. Write the net ionic equation for the overall reaction that occurs as the cell operates and calculate the
value of the standard cell potential, Hn.
c. Determine the value of the standard free-energy, AG*.cn, for the cell.
Indicate how the value of Faex would be affected if the concentration of Ni(VO+)2(ag) was changed
from 1.0 to 0.10M and the concentration of Zn(NOs)2(aq) remained at 1.0M. Justify your answer.
(DB Cathede: Nix 20 7 Ni E57228Y
Proce i tn > BRT age -E%-(27OY
a
a
(D NGreee = - 17 F Eipep
: x
AG cece = -(2rmte)( ate) (Ale)
= F Souk.
Acveet =~ /02 274 Tou, y - 1002 fe
2) eal Decreases far 1.0 & O10~
[ant]: Combect 2 YOM. :
Recusiny coment reared (We) 4 RP
v : 2 etter 3s diver
nectreshien af prockact (BF), Cea oe
1 het (tls, racket), 2edy dachoebers re,
ey Ecoee_fecreaseel Eceek < Eeeee!?30),�Free Response Question 2003B # 6 : i
a Seat er
a. Different electrochemical cells can be constructed using the bg = ll
solutions and electrodes shown below. i I i
‘The standard reduction potential for the chemical species are
given on the table. Eas) | a
Chose the most suitable pair of half-cells and write the balanced
net-ionic equation for the spontaneous reaction that ocours in the
cell that would have the greatest positive value of B°..n
Cat hocle/s
trade] Onidahon: it > A's 86° (x8) Fee
\a2* 2Ae =r Gu + 2ACTT
FAINO)y _ LOMCINGS, —_LOARONO3
b. Caleulate the standard cell poiential, Ey forthe reaction written in question (a).
. ° °
Eccee = Ecad fede - Epnote
ae Voets
Evect = (t284)-(-466) Eze = 2.000
c. A cell is constructed based on the reaction defined in question (a).
i, Label the correct metal strips used for the anode and cathode
electrodes on the cell shown in the diagram below.
Anode: Abayrain wr Cathode:_ Co gper
ii, On the diagram above, show the direction of electron flow between
the electrodes of the cell.
d. Another galvanic electrochemical cell is based on the following reaction: Zn-+ Pb’* > Zn? + Pb
i. Ifthe concentration of Zn™ is decreased from 1.0M to 0.25M, what effect does this have on the cell
potential? Would Zam increase or decrease? Justify your answer.
Eczce ureuld ineroase . peed. ho Lehorfelier's Fevmcighe,
Gberrasing the CorcesMreTon op the prokchs ( zn?) adnves
te peacton Putrtely pte prachuct® , jreseasing ite powey
clactrns and imereadn: he Cell polerttial ExeQe+
ii. Ifthe concentration of Pb* is decreased from 1.64/to 0.25M, what effect does this have on the cell
potential? Would Emurincrease or decrease? Justify your answer.
Laxte versed cherie Reedy, te dovhat beds Rivers
pain py concern from of te ceactarts ( phe) hive
ea echacirne the flow SE echelrors
jeactoos Fourrels the renstowks redocorg te f
ard reclucee Extl.�Free Response Question 2002 #2
‘The reaction between silver ioris and solid zine is given by the following
equation:
2 Ag" (ag) + Znls) > Zr" (ag) + 2.Ag(s)
a. A 1.50g sample of Zn is immersed in 250. mL of 0.110M AgNO3.
i. Identify the limiting reactant. Show work to support your answer.
ii, On the basis of the limiting reactant that you identified in part (i), determine the value of [Zn™*]
after the reaction is complete. Assume that volume change is negligible.
b. Determine the value of the standard potential, Hx, end the standard free-energy, AG*.q, for a galvanic
cell based on the reaction between AgNO;(ag) and solid Zn at 25°C.
(22) 50 mal gt = 150g trot. ae AO4SP mot ty”
aa b> Tea) reecke! por reo.
COMM Ae, 2 Rc My 2 BOAT rma gt ar i
0250 Fatty, 60
ce Ke guanfti ty or Agi outaiede ip fect Han pen
oF Ast rreccleel, ty * (Agnl0s) is phe Gort Biting rode
fein) Krme En? “quae nol ag (Liat a | 2.013? mol a*
Seacted puci tlle ' Zire Agt reacted
pare D=00552M
Car]. 20ietont OF Desars
o27sok
(2) cethock |pecludfina: My” s Za Ay B'= 0 B00V >
2. - (OF
frrvcle] Oxiclafiam + Zn we BF" 20 “S27 F
BY
eece2 (SE
Fol?
AGceee = 9027197 Tiss B03 US
—,
DE geen FE Cage - (amb) FV ys�c. Another galvanic cell is based on the reaction between Ag*(aq) and Cu(s).
i, Write the balanced net-ionic equation for the reaction that occurs in.
the galvanic cell,
ii, Determine the standard potential, E°, for the cell at 25°C.
iti,
Determine the value of the standard free-energy, AG®, for the
reaction between 4g" (ag) and Cu(s) at 25°C.
If the concentration of Cu”* is increased from 1.0M to 1.54, what effect does this have on the cell
potential? Would Zeay increase or decrease? Justify your answer.
Cc) Cotbed [te thuas}ion 2g" 4 E—> a] E090
Prede/oxidod om 1 Core Gbt, 26 E% (93)
iv.
liv)
\ 24 Lhe» be PBA t 2G Pal Ege TONEY
(ew) been F Exel
Cott
Ae? = =(2 me (Ss \(°"2)
Nig, = PP FEE Joule Y 81 Keele
GW) Loree wowed decrease. reeds. ds laches ve,
Mrerecaiog tHe emcentrafion FF x = procloct (Ga :
ives [he rocson pousrds the reocfart, reobacing
the plow of ebclons ond reducing the cet€
porertin€ (Eceté).�Free Response Question 2007 #3.
In an electrolysis device, an external direct-current power supply is
connected to two platinum electrodes immersed in a 1.0M CuSO, (aq)
solution at 25°C. As the cell runs, copper metal is deposited onto one
electrode and O2(g) is produced at the other electrode. The two
seduction half-reactions that occur in the cell are shown below.
P
fae
Reduction Half-Reaction EM cathe 504 fe Po.
O2(g) + 4 Haq) +4 > 2,0) 41.23
Ci? * (aq) + 2e 3 Cu (s) 40.34 Cu™ag) + 2+ Cals)
On the diagram above, indicate which elecirode is the cathode, which is the anode and the direction of
electron flow between the electrodes.
‘Write a balanced net ionic equation for the overall electrolysis reaction that occurs in the cell.
Determine the value of cell reduction potential E” and the free energy AG? for the reaction.
What is the minimum voltage that must be applied across the electrodes to drive the reaction?
An electric current of 1.50 amps passes through the cell for 40.0 minutes,
i. Calculate the mass, in grams, of the Cu(s) that is deposited on the electrode. |
i. Calculate the dry volume, in liters measured at 25°C and 1.16 atm, of O2 (g) that is produced.
(x) Cattocle|edluction’ [GE* +227» Ge] (2
Arecl [onidedion : 2H,0 7 0 tne +e
ieee 0 aout |
{2c./* 20-7 2 *
(+428)
40.24) -
© €,00 = lathde - Ernie Sectt+ ( snrst eerie 3)
eee = “AETV (pedox rH, by iteef, fe
: mat ed{ 6" NES. ot 072) Conall < 34a
DeLee =~
(d) v2 axpvetts
= : (62584)
ue ‘1 SOS 400 minx 698 (antl eN fens 2)
19@ Kefaws Gee (# S Tain NH AES M4 nck,
= L179 gees Ce
pal Gy (irre € 2 20. 00706 mt
COLA) x re OL i 19 gu (BEN Fee. dé »
i . Aversa UAV =I 00736) (2.082) (27
Teal Gar hans: PVT i
10