Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dea Erator
Uploaded by
呂仲書Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dea Erator
Uploaded by
呂仲書Copyright:
Available Formats
www.powerhx.
com
Designed by Good & Good Design Communicationsㅣ2016. 11.
DEAERATOR
122, Cheoyongsaneop 3-gil, Cheongnyang-myeon, Ulju-gun, Ulsan, 689-892, Korea
TEL : +82-52-237-2213 FAX : + 82-52-237-2235
E-mail : main@powerhx.com Website : http://www.powerhx.com
DEAERATOR
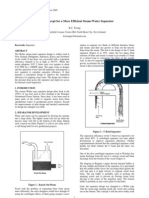
[ Typical Deaerator Connections and Accessories ] [ Large Spray Valve Performance Curve ]
General Principle of deaerating
Inlet Flow
Rate(t/h)
Dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide in the Boiler Feed The removal of dissolved gases from boiler feedwater
Valve flow Velocity(m/sec)
Water of industrial steam generators that are used in is an essential process in a steam system. The presence 150 15 Ex) flow rate 50t/h
Valve lift
flow velocity 8.4m/s
140 14
electricity plants and incineration plants, causes the of dissolved oxygen in feedwater causes rapid localized valve lift 5.9mm
130 13 △P 3.7mAg
corrosion of the Boiler Feed Water Container, which corrosion in boiler tubes. Carbon dioxide will dissolve in 120 12
significantly affects the durability of pipes and all the water, resulting in low pH levels and the production of 110 11
equipment. To eliminate the dissolved oxygen and carbon corrosive carbonic acid. Low pH levels in feedwater cause 100 10
Valve N/Z flow
90 9 Velocity
dioxide, installing a deaerator is essential. This deaerator severe acid attack throughout the boiler system. While 80 8
can also preheat the Boiler Feed Water up to the necessary dissolved gases and low pH levels in the feedwater can be 70 7
Valve lift
temperature as a Feed Water Heater, which helps increase controlled or removed by the addition of chemicals, it is 60 6
Inlet Flow
50 5
the efficiency of the equipment. more economical and thermally efficient to remove these 40 4
Rate(t/h)
gases mechanically. This mechanical process is known 30 3
as deaeration and will increase the life of a steam system 20 2
Ⓐ Water(Condensate) inlet Ⓖ Pressure Gauge Ⓜ Sparger Pipe
10 1
Classification by Shape Ⓑ Spray Valve Ⓗ Level Gauge Ⓝ Deaerator Saddle dramatically. 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Ⓒ Vent Orifice Ⓘ Man Hole Ⓞ Downcomer
Generally, the Deaerator is divided into two parts; the top, Deaeration is based on two scientific principles. The first △P Pressure difference
Ⓓ Vent Nozzle Ⓙ Drain Nozzle Ⓟ Equalizer
deaerating Heater (for degassing) and the bottom, Storage principle can be described by Henry’s Law. Henry’s Law
Ⓔ Relief Valve Ⓚ Tank Saddle Ⓠ OverFlow Nozzle
Section. Due to their different shapes, the deaerating asserts that gas solubility in a solution decreases as the [ O2 concentration in saturated demi-water ]
Ⓕ Tray Box Ⓛ Water Outlet Ⓡ Steam Inlet 14
Heater is classified into Vertical deaerator type, and gas partial pressure above the solution decreases. The
Dissolved Oxygen (in ppm)
12
Horizontal deaerator type. second scientific principle that governs deaeration is the
10
relationship between gas solubility and temperature.
Briefly explained, gas solubility in a solution decreases 8
as the temperature of the solution rises and approaches 6
saturation temperature. A deaerator utilizes both of these 4
natural processes to remove dissolved oxygen, carbon 2
dioxide and other non-condensible gases from boiler
0
feedwater. 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Water Temperature (in Deg C)
The feedwater is sprayed in thin films into a steam
Storage Tank
Storage Tank
atmosphere allowing it to become quickly heated to
saturation. Spraying feedwater in thin films increases [ Power plant process diagram ]
Enclosure wall
the surface area of the liquid in contact with the steam,
>> Vertical deaerator with horizontal storage tank which results in more rapid oxygen removal and lower gas
- Applicable to small and medium capacity(up to 220 ton/hr) concentrations. This process reduces the solubility of all
dissolved gases and removes them from the feedwater.
The liberated gases are then vented from the deaerator.
This system reduces dissolved oxygen concentration to less
than 0.005 cc/liter (7 ppb) and completely eliminates the
carbon dioxide concentration.
Storage Tank
Storage Tank
A thermal power station is a power plant in which
heat energy is converted to electric power. The turbine
>> Horizontal deaerator with horizontal storage tank is steam-driven. Water is heated, turns into steam
- Applicable to large capacity (over 220 ton/hr) and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical
generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam
is condensed in a condenser and recycled to where it was
heated; The greatest variation in the design of thermal
power stations is due to the different heat sources, fossil
fuel dominates here, although nuclear heat energy and
solar heat energy are also used. Some prefer to use the
term energy center because such facilities convert forms
of heat energy into electrical energy. Certain thermal
power plants also are designed to produce heat energy
[ Structure of spray nozzle, collecting (water) and Undeaerated Water Steam for industrial purposes of district heating, or desalination
distributing tub and tray ] Non-Condensibles(Vented) Deaerated Water of water, in addition to generating electrical power.
You might also like
- Choosing A Selective Hydrogenation SystemDocument9 pagesChoosing A Selective Hydrogenation Systemghasem_726990287No ratings yet
- Stator Water System ChemistryDocument33 pagesStator Water System ChemistrySudhanshu Sekhar Dash100% (1)
- Mitigation of Caustic Stress Corrosion C PDFDocument9 pagesMitigation of Caustic Stress Corrosion C PDFJean YureNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Trading Name of STL Power & Process Controls LTDDocument4 pagesPurpose: Trading Name of STL Power & Process Controls LTDFaraj AlferjaniNo ratings yet
- Piping System RevDocument32 pagesPiping System Revapi-25999517100% (9)
- Pipe Sizing Basic PrinciplesDocument2 pagesPipe Sizing Basic PrinciplesLeonard ChanNo ratings yet
- Optimising Digestion Flash Tank Design For The Alumina IndustryDocument5 pagesOptimising Digestion Flash Tank Design For The Alumina IndustryJuan Manuel ChavarríaNo ratings yet
- Kubota Ductile Iron Pipe: KUBOTA Corporation KUBOTA Membrane USA CorporationDocument10 pagesKubota Ductile Iron Pipe: KUBOTA Corporation KUBOTA Membrane USA CorporationTimNo ratings yet
- 02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-3Document5 pages02.understanding Process Equipment For Operators & Engineers-3Aatish ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Improve The Reliability of High Flux Reboilers PDFDocument7 pagesImprove The Reliability of High Flux Reboilers PDFAbhik BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SPE 56705 Chemical Defoamer Reduction With New Internals in The Mars TLP SeparatorsDocument5 pagesSPE 56705 Chemical Defoamer Reduction With New Internals in The Mars TLP SeparatorsRégis OngolloNo ratings yet
- Tap Flow RateDocument2 pagesTap Flow RateMeng SunNo ratings yet
- Ijett V4i5p58 PDFDocument4 pagesIjett V4i5p58 PDFAndirazakNo ratings yet
- Pipe Sizing For Hot and Cold Water: Part 1 - Basic PrinciplesDocument2 pagesPipe Sizing For Hot and Cold Water: Part 1 - Basic PrinciplesdosandosanNo ratings yet
- 104SE-Combining New and Old Technologies - Inlet Diffuser and Random Packing Dramatically Improve Reactor PerformanceDocument10 pages104SE-Combining New and Old Technologies - Inlet Diffuser and Random Packing Dramatically Improve Reactor PerformanceSHINo ratings yet
- Hydrazine DosingDocument2 pagesHydrazine DosingAnonymous 3HTgMDO100% (1)
- Experimental Efficiency Analysis For Pelton TurbinesDocument5 pagesExperimental Efficiency Analysis For Pelton TurbinesJuan MendozaNo ratings yet
- Vent Away Condensate Pump Frustrations in A FlashDocument6 pagesVent Away Condensate Pump Frustrations in A FlashBramJanssen76No ratings yet
- Stock PumpingDocument12 pagesStock PumpingBapu612345No ratings yet
- Feed Saturator PaperDocument21 pagesFeed Saturator PaperaliNo ratings yet
- Normal.: Boiler and Feedwater LimitsDocument6 pagesNormal.: Boiler and Feedwater LimitsChristian AganoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power Plant Information: Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)Document18 pagesNuclear Power Plant Information: Boiling Water Reactor (BWR)cagertonNo ratings yet
- Deaerator Degradation - Managing Remaining Life and Component ReplacementDocument11 pagesDeaerator Degradation - Managing Remaining Life and Component ReplacementAsh BuzNo ratings yet
- DeaeratorDocument6 pagesDeaeratorSyaeful SyariefNo ratings yet
- Turbine Bypass Valve Technology and ApplicationsDocument25 pagesTurbine Bypass Valve Technology and Applicationsoksa0% (1)
- WatsonDocument6 pagesWatsonLanang Delonix Regia SugiartoNo ratings yet
- Design Concept For A More Efficient Steam-Water SeparatorDocument7 pagesDesign Concept For A More Efficient Steam-Water SeparatorArini RizalNo ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Liquid-Phase Methanol Synthesis in An Impinging Stream ReactorDocument5 pagesThe Characteristics of Liquid-Phase Methanol Synthesis in An Impinging Stream ReactorDenny Muchammad AnwarNo ratings yet
- TB 59 10 - 07 Centec Paulaner1Document3 pagesTB 59 10 - 07 Centec Paulaner1dagNo ratings yet
- New Deaerator For Boiler FeedwaterDocument6 pagesNew Deaerator For Boiler Feedwaterarjmandquest100% (1)
- Boiler FailureDocument6 pagesBoiler FailureMahmoud RefaatNo ratings yet
- Ejector 40 KGDocument2 pagesEjector 40 KGkapilNo ratings yet
- High Water Cut in Stabiler TowerDocument3 pagesHigh Water Cut in Stabiler TowerAnonymous ei87sJPNo ratings yet
- Conducting Water Chemistry of The Secondary Coolant Circuit of Vverbased Nuclear Power Plant Units Constructed Without Using Copper Containing AlloysDocument5 pagesConducting Water Chemistry of The Secondary Coolant Circuit of Vverbased Nuclear Power Plant Units Constructed Without Using Copper Containing AlloysMarcus BaltesNo ratings yet
- Bi-Phase SeparatorDocument19 pagesBi-Phase Separator1mmahoneyNo ratings yet
- Schoepentoeter SEPARADORDocument4 pagesSchoepentoeter SEPARADOREsau EstebanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet HCL Medium SystemsDocument4 pagesDatasheet HCL Medium SystemsLalit VashistaNo ratings yet
- Well Test Facility Specifications 40 X 40 LECMDocument10 pagesWell Test Facility Specifications 40 X 40 LECMDEDI ARDIANSYAH LUBISNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Selective Hydrogenation SystemDocument9 pagesChoosing A Selective Hydrogenation SystemrizaherNo ratings yet
- Httpsdacemirror - Sci Hub - Sejournal Articlabarmaki2009.Pdfdownload TrueDocument12 pagesHttpsdacemirror - Sci Hub - Sejournal Articlabarmaki2009.Pdfdownload TrueNur SyarafanaNo ratings yet
- Desuperheater PDFDocument7 pagesDesuperheater PDFbagastcNo ratings yet
- Midrex Process Water DegasserDocument2 pagesMidrex Process Water DegasserMorteza RafieiNo ratings yet
- Steam Mains and Drainage: Piping LayoutDocument11 pagesSteam Mains and Drainage: Piping Layouthej hejNo ratings yet
- Cu ElectrowinningDocument17 pagesCu ElectrowinningJose Eduardo Osuna AraizaNo ratings yet
- Manual-Boiler-Feed-IND (1) - 15-18 PDFDocument4 pagesManual-Boiler-Feed-IND (1) - 15-18 PDFHicham IdrisiNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Rekayasa ProsesDocument9 pagesJurnal Rekayasa ProsesAmin DarwisNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Steam EjectorsDocument6 pagesTroubleshooting Steam EjectorsGabriel Eduardo Contreras PerozoNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Supply For PlumbingDocument4 pagesDesign of Water Supply For PlumbingLouie MirandaNo ratings yet
- Hazen Williams Coeff For SludgeDocument3 pagesHazen Williams Coeff For Sludgemailmaverick8167No ratings yet
- Brochure Power Industry EN WebDocument32 pagesBrochure Power Industry EN Websudheer kumarNo ratings yet
- High Rate Solids Contact Clarifier HRSCCDocument4 pagesHigh Rate Solids Contact Clarifier HRSCCshambhurajesurywanshi1No ratings yet
- Master Plumber Exam Flash CardsDocument6 pagesMaster Plumber Exam Flash CardsNomer AzanaNo ratings yet
- Oil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesFrom EverandOil and Gas Artificial Fluid Lifting TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshFrom EverandPneumatic and Hydrautic Conveying of Both Fly Ash and Bottom AshNo ratings yet
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisFrom EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A Guide to Ship Repair Estimates in Man-hoursFrom EverandA Guide to Ship Repair Estimates in Man-hoursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Computer-Aided Design of Fluid Mixing Equipment: A Guide and Tool for Practicing EngineersFrom EverandComputer-Aided Design of Fluid Mixing Equipment: A Guide and Tool for Practicing EngineersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Publication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Atlas Steels - "L", "H" and STANDARD GRADES of STAINLESS STEELS Technical NoteDocument4 pagesPublication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Atlas Steels - "L", "H" and STANDARD GRADES of STAINLESS STEELS Technical Notezinha_alNo ratings yet
- Publication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Aremco Inc - High Temperature Materials - Coatings and AdhesivesDocument56 pagesPublication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Aremco Inc - High Temperature Materials - Coatings and Adhesiveszinha_alNo ratings yet
- Publication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Alfsen Og Gunderson - Dehumidifiers For The Oil and Gas ApplicationsDocument4 pagesPublication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Alfsen Og Gunderson - Dehumidifiers For The Oil and Gas Applicationszinha_alNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Preserving Bridge Suspension Span Cables Using DehumidifcationDocument34 pagesPresentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Preserving Bridge Suspension Span Cables Using Dehumidifcationzinha_alNo ratings yet
- Publication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - AkzoNobel - International Paints - Mining and Minerals ApplicationsDocument44 pagesPublication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - AkzoNobel - International Paints - Mining and Minerals Applicationszinha_alNo ratings yet
- Publication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Pickling and Passivating 2015Document7 pagesPublication - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Pickling and Passivating 2015zinha_alNo ratings yet
- Avesta - Crevice Corrosion of Stainless Steels in SeawaterDocument8 pagesAvesta - Crevice Corrosion of Stainless Steels in Seawaterzinha_alNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Beca - Cathodic ProtectionDocument56 pagesPresentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Beca - Cathodic Protectionzinha_al100% (1)
- Presentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - en Engineering - Internal and External Corrosion and Cathodic ProtectionDocument34 pagesPresentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - en Engineering - Internal and External Corrosion and Cathodic Protectionzinha_alNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Beca - Cathodic Protection - MiniDocument16 pagesPresentation - Painting, Coating & Corrosion Protection - Beca - Cathodic Protection - Minizinha_alNo ratings yet
- BRANZ - Study SR325 Update of New Zealand's Atmospheric Corrosivity Map - Part 2Document38 pagesBRANZ - Study SR325 Update of New Zealand's Atmospheric Corrosivity Map - Part 2zinha_alNo ratings yet
- NZTA - Protective Coatings For Steel BridgesDocument63 pagesNZTA - Protective Coatings For Steel Bridgeszinha_alNo ratings yet
- Avesta - Some Factors Affecting Stainless Steel Corrosion in SeawaterDocument8 pagesAvesta - Some Factors Affecting Stainless Steel Corrosion in Seawaterzinha_alNo ratings yet
- BHP - Table of Contents - List of Coatings For Structures, Piping and EquipmentDocument7 pagesBHP - Table of Contents - List of Coatings For Structures, Piping and Equipmentzinha_alNo ratings yet
- Cuisine For The Cure' Now in Its Fifth Year: and They're Off!Document8 pagesCuisine For The Cure' Now in Its Fifth Year: and They're Off!BS Central, Inc. "The Buzz"No ratings yet
- Parle G Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesParle G Literature Reviewaiqbzprif100% (2)
- Condom Size by John GerofiDocument27 pagesCondom Size by John GerofiCondomSize100% (1)
- Scurve Stone Quarry LTDDocument2 pagesScurve Stone Quarry LTDShyam Prasad ThiraviamNo ratings yet
- Araneta vs. de Joya 57 SCRA 59, May 24, 1974Document7 pagesAraneta vs. de Joya 57 SCRA 59, May 24, 1974JohnNo ratings yet
- LQS ManualDocument38 pagesLQS ManualVindyanchal Kumar100% (1)
- DIAC CHECKLIST Migration-PartnerFamilyDocument4 pagesDIAC CHECKLIST Migration-PartnerFamilyHemanth Vinay KumarNo ratings yet
- MIT Open Course Ware - Toy Product DesignDocument3 pagesMIT Open Course Ware - Toy Product Designbatros1No ratings yet
- Lip PlateDocument4 pagesLip PlateNaimi AzizNo ratings yet
- Proud MaryDocument3 pagesProud Maryeomo_usohNo ratings yet
- Mithun Project Tata MotorsDocument69 pagesMithun Project Tata MotorstmithunnsNo ratings yet
- Measurement Lab Manual RADocument20 pagesMeasurement Lab Manual RAVinayak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: BOLD PurevDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: BOLD PurevАмармөнх ПүрэвNo ratings yet
- Operationalising The Qualitative Characteristics of Financial ReportingDocument8 pagesOperationalising The Qualitative Characteristics of Financial Reportingbakhtawar soniaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Abbasid Empire and Community Needs in The Development of Ḥadīth Literature and Islamic ProphetologyDocument9 pagesThe Influence of Abbasid Empire and Community Needs in The Development of Ḥadīth Literature and Islamic ProphetologylmdwdwdqkNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Workdays SchemeDocument2 pagesReduction of Workdays SchemeAndrew GallardoNo ratings yet
- Starbuck - Case Discussion (Back Up)Document14 pagesStarbuck - Case Discussion (Back Up)Nizlan MohamedNo ratings yet
- Choose The Correct Answer:: Fill in With An Indefinite PronounDocument2 pagesChoose The Correct Answer:: Fill in With An Indefinite Pronounsaul enrique silva moncadaNo ratings yet
- 10 Differences Between UK & US EnglishDocument6 pages10 Differences Between UK & US Englishsetu sriNo ratings yet
- Promote Equality, Diversity and Inclusion in The Workplace: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesPromote Equality, Diversity and Inclusion in The Workplace: Multiple Choice QuestionsEsha ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- The Post Humanist ApproachDocument17 pagesThe Post Humanist ApproachfajarsusantoNo ratings yet
- 2023 9 2 1 ColonescuDocument14 pages2023 9 2 1 ColonescuSome445GuyNo ratings yet
- Step-By-Step Install Guide Enterprise Application Servers With Proxmox VE ClusterDocument19 pagesStep-By-Step Install Guide Enterprise Application Servers With Proxmox VE ClusterKefa Rabah100% (1)
- Scholarship BrackettDocument1 pageScholarship Bracketttineyintharvoice100% (1)
- Final Draft Remarkable Race Essay WeeblyDocument4 pagesFinal Draft Remarkable Race Essay Weeblyapi-608440469No ratings yet
- NotanDocument5 pagesNotanapi-247455001No ratings yet
- Tropical Helicopter Underwater Escape Training (T-HUET) Product SpecDocument14 pagesTropical Helicopter Underwater Escape Training (T-HUET) Product SpecKhidir SanusiNo ratings yet
- No FamilyDocument46 pagesNo FamilyWindsurfingFinnNo ratings yet
- DC20 Adventure - The HuntedDocument12 pagesDC20 Adventure - The HuntedFelix JaegerNo ratings yet
- Lime Project ProposalDocument39 pagesLime Project ProposalChalachew ZewdieNo ratings yet