Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.4
Uploaded by
Primelift Safety Resources LimitedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.4
Uploaded by
Primelift Safety Resources LimitedCopyright:
Available Formats
LEEA Correspondence Courses
ASSIGNMENT 1.4
Please note: Use the up and down cursor keys to move between fields in this form.
Enter your name and student number in the spaces below.
Name: CORRECTED Student number: 13657
Each question has several answers, only one of which is correct. Select your answer by typing # in
the box.
When complete, save the file using the same name. Then use the upload facility to return it for
marking.
1. The finish of hot rolled steel sections is known as:
Blue
Brown
# Black
Bright
2. Rolling affects the crystal structure of the material by:
Making it coarser
# Refining it and introducing a grain flow
Making the crystals combine together
Flattening the crystals into a sharp pointed needle like form
3. Cracks and laminations in prime steel sections:
# Significantly reduce the strength of the material, affected areas must be totally removed and scrapped
Will run through all of the material from that batch so it must all be scrapped
Will only occur on the surface and so can be easily detected
Have no effect on the strength of the material as they run along the grain and so can be ignored
4. Drop forgings can be readily recognised by:
# The flash line resulting from the removal of excess material forced out of the dies during forging
The bruising resulting from hammering
The fact that they are always circular in cross section
The gall marks caused by heating the steel prior to forging
5. Burning is a fault found on drop forgings, which can be recognised by:
Cracks occurring, particularly on outside bends
Surface laminations, known as gall marks
Cannot be detected by eye
# A glazed appearance due to oxide penetration
6. Gall marks, cracks and similar defects are stress risers which may cause failure:
Due to fatigue
# Due to the notch effect
Due to a change in the materials grain structure
Due to the formation of oxides at the materials surface
© Lifting Equipment Engineers Association 2011 - training\1-4e
1
7. Iron and steel can be cast into the required finished shape, the most common method used is known as:
Pattern casting
Template forming
# Sand casting
Metal pouring
8. A cold shut is a fault that can occur in castings due to:
The mould being left too long before it is opened
Sudden cooling of the casting
The sections of the mould being assembled at low temperature
# Two molten streams of metal coming together at too low a temperature for them to fuse
9. The main fault found in components which have been subject to one of the cold metal cutting processes is:
Cracks and laminations
Porosity
# Dimensional errors
Burning
10. The process of flame cutting steel is based on the fact that:
Steel burns at a lower temperature than a gas and air mixture
# The oxide of steel melts at a lower temperature than steel
Heat is spread over a wide area of the metal surface
Oxygen present in the steel is released by heat
11. Flame cut components should not be used for highly stressed duties unless they are:
Subsequently drop forged
# Machined away for a depth of at least 0.4mm to remove areas affected by carbon migration
Assembled by welding so that the weld covers the cut face for a depth of at least 4mm
Bolted into position
12. The finish of a flame cut edge is dependant on:
# The flame setting and its travel speed
The type of gas used to provide the heat
The carbon content of the steel
The amount of oxygen in the flame
13. Manual arc welding is a process that uses:
Atomic fusion
Solder with a 60% lead content
# Flux coated filler rods
Heat from a gas/air mixture
14. The term MIG welding refers to:
Manually ignited gases
Molten iron gouging
Metal and iron groupings
# Metal inert gas
© Lifting Equipment Engineers Association 2011 - training\1-4e
2
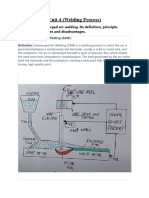
15. The type of weld shown in the illustration is known as:
A butt weld
# A fillet weld
A Tee weld
A double Vee weld
16. The presence of excessive splatter, or splatter which cannot be easily wire brushed off, is a sign that:
# The weld may be porous
That the weld has full penetration
That the wrong filler rod/wire was used
That the parent metal was incorrectly prepared
17. A form of resistance welding used in the manufacture of chain is known as:
Atomic Hydrogen welding
# Flash butt welding
Manual arc welding
Oxy/acetylene welding
18. Heat treatment of steel works on the principle that:
# Temperature affects the chemical and physical composition of the grains
Carbon is released to the atmosphere when steel is heated
Steel has a higher tensile strength when hot
At high temperature an oxide skin is formed which is harder than the parent metal
19. The most common form of heat treatment used in association with the manufacture of lifting gear is known
as:
Annealing
Normalising
Stress relieving
# Hardening and tempering
20. When steel is hardened and tempered, the purpose of tempering is to:
Improve its wear resistance
Increase the hardness even further
Increase its elongation
# Improve its toughness
© Lifting Equipment Engineers Association 2011 - training\1-4e
3
You might also like
- Farm and Workshop Welding, Third Revised Edition: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape MetalFrom EverandFarm and Workshop Welding, Third Revised Edition: Everything You Need to Know to Weld, Cut, and Shape MetalNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument30 pagesWelding DefectsSane ShajanNo ratings yet
- Welding of Cast IronDocument35 pagesWelding of Cast IronincaurcoNo ratings yet
- Guide Cast Iron WeldingDocument8 pagesGuide Cast Iron WeldingAgustine SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Welding 8 - Brazing SolderingDocument19 pagesWelding 8 - Brazing SolderingasitacharyaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing HandbookDocument29 pagesUltrasonic Testing HandbookP A KumarNo ratings yet
- Book Review - Black Skin, White MasksDocument9 pagesBook Review - Black Skin, White MasksKaren A. LloydNo ratings yet
- Welding Lecture1 2Document34 pagesWelding Lecture1 2Dr Abhijeet GangulyNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment: Set-Up and Use of ScaffoldingDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment: Set-Up and Use of ScaffoldingisaacbombayNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument4 pagesWelding Defectsrohini nilajkar0% (1)
- Series 70 Overshots: Instruction Manual 1070Document8 pagesSeries 70 Overshots: Instruction Manual 1070Juan Carlos Perilla MartinNo ratings yet
- Microstructure Study of Welded JointDocument17 pagesMicrostructure Study of Welded JointRatul Islam Antor100% (1)
- Basic Mechanical - Engineering-Soldering Brazing and WeldingDocument10 pagesBasic Mechanical - Engineering-Soldering Brazing and WeldingRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- Welding Interview Questions and Answers PDFDocument11 pagesWelding Interview Questions and Answers PDFMOHANNo ratings yet
- Oil Spill Response Course ContentDocument3 pagesOil Spill Response Course ContentPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Shackles PDFDocument1 pageShackles PDFPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LH 185 DS 0062 6Document6 pagesLH 185 DS 0062 6Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects: Their Causes and PreventionDocument18 pagesWelding Defects: Their Causes and PreventionsanjaykumarmauryaNo ratings yet
- Questions Related To WeldingDocument12 pagesQuestions Related To WeldingpremNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument6 pagesDepartment of EducationJay BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal CrackingDocument9 pagesWelding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal Crackinglakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Nickel and Nickel Alloys: Weldability and Joining of MaterialsDocument4 pagesNickel and Nickel Alloys: Weldability and Joining of MaterialsMehmet SoysalNo ratings yet
- History of Some Special ExplosivesDocument24 pagesHistory of Some Special ExplosivesShazil KhanNo ratings yet
- AE2253 Unit 2Document15 pagesAE2253 Unit 2Jones Jones Jr.No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Welding ProcessDocument57 pagesUnit 5 Welding Processmahammad kamaluddeenNo ratings yet
- Welding Technology Two MarksDocument20 pagesWelding Technology Two Markssai100% (1)
- Neonatal SepsisDocument29 pagesNeonatal SepsisElton Ndhlovu100% (3)
- LEEADocument3 pagesLEEAikponmwonsa100% (1)
- Rigging Gear Store Management RegisterDocument6 pagesRigging Gear Store Management RegisterKhawaja Arslan Ahmed0% (1)
- EpidemiologyDocument26 pagesEpidemiologymohildasadiaNo ratings yet
- Define PatternDocument6 pagesDefine PatternaadhanNo ratings yet
- Advantages of ForgingDocument14 pagesAdvantages of Forgingrehan RNNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 JPDocument16 pagesUnit 3 JPGladiatoR XDNo ratings yet
- Pengelasan (Welding)Document13 pagesPengelasan (Welding)DanilAnshelmusPurbaNo ratings yet
- Soldering, Brazing & WeldingDocument52 pagesSoldering, Brazing & WeldingChandrakantha K100% (1)
- Forging Rolling DefectsDocument16 pagesForging Rolling DefectsAshley JacksonNo ratings yet
- Welding 1Document61 pagesWelding 1عبدالرحمن سيدNo ratings yet
- Welding Upto Gas WeldingDocument26 pagesWelding Upto Gas Weldingrams789No ratings yet
- Werlding MCQDocument12 pagesWerlding MCQapexg3838No ratings yet
- Fabrication (Metal Joining) : Ravishankar M D 17EME14 Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument18 pagesFabrication (Metal Joining) : Ravishankar M D 17EME14 Elements of Mechanical EngineeringSatish HSNo ratings yet
- AL-Si Report PDFDocument6 pagesAL-Si Report PDFAnmol MishraNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY REPORT 3 - Workshop Theory and PracticeDocument11 pagesLABORATORY REPORT 3 - Workshop Theory and Practice22-03844No ratings yet
- AL-Si Report PDFDocument6 pagesAL-Si Report PDFAnmol MishraNo ratings yet
- Braze Welding and Advanced Gas Welding Practice:: Jobs 9-J39-J49Document6 pagesBraze Welding and Advanced Gas Welding Practice:: Jobs 9-J39-J49Willy UioNo ratings yet
- Danial's AssignmentDocument5 pagesDanial's AssignmentRaja Awais LiaqautNo ratings yet
- Fdocuments - in - As Per Api 571 Corrosion Which Occurs Above 204c Per Api 571 Corrosion WhichDocument20 pagesFdocuments - in - As Per Api 571 Corrosion Which Occurs Above 204c Per Api 571 Corrosion Whichsanu patilNo ratings yet
- Assigment WeldingDocument4 pagesAssigment WeldingAnonymous Co9r0PbNo ratings yet
- CPM1 - B2 - CMT AssignmentDocument9 pagesCPM1 - B2 - CMT AssignmentShaikh Nadim AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Ajp Module-2Document75 pagesAjp Module-2Naveen S BasandiNo ratings yet
- Basic Metallurgy For NDT 2Document3 pagesBasic Metallurgy For NDT 2Juan LewisNo ratings yet
- MP Q@aDocument9 pagesMP Q@aAmaresh Movies ASNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding Defects PDFDocument12 pagesTypes of Welding Defects PDFDhiab Mohamed AliNo ratings yet
- Metalurgi WELDINGDocument35 pagesMetalurgi WELDINGFajar SiradzNo ratings yet
- Welding and Types of WeldingDocument9 pagesWelding and Types of WeldingMunem ShahriarNo ratings yet
- Welding AISI 4130 PDFDocument5 pagesWelding AISI 4130 PDFDarioNo ratings yet
- Welding Upto Gas WeldingDocument26 pagesWelding Upto Gas WeldingNabankur RayNo ratings yet
- Preheating N BackWear FacingDocument2 pagesPreheating N BackWear FacingmahendraNo ratings yet
- BME Joining ProcessesDocument11 pagesBME Joining ProcessesalysonmicheaalaNo ratings yet
- Welding Notes (MT - 5th Sem)Document15 pagesWelding Notes (MT - 5th Sem)shivam kumarNo ratings yet
- Building Construction and Material - VDocument20 pagesBuilding Construction and Material - Vkushagra agrawalNo ratings yet
- Defects in Forming ProcessDocument7 pagesDefects in Forming ProcessDhruv BhandariNo ratings yet
- Mep July 23Document24 pagesMep July 23chandramohandass22No ratings yet
- Welding Processes.: Brazing and SolderingDocument12 pagesWelding Processes.: Brazing and SolderingYagnesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing HandbookDocument29 pagesUltrasonic Testing HandbookRafael HernandezNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument19 pagesLearning Objectivesfred gallardoNo ratings yet
- (EW-512-4) - Discontinuities and Defects - Training Workbook-Hobart Institute of Welding Technology (Yasser Tawfik)Document10 pages(EW-512-4) - Discontinuities and Defects - Training Workbook-Hobart Institute of Welding Technology (Yasser Tawfik)Ahmed Shaban KotbNo ratings yet
- Types of WeldingDocument9 pagesTypes of WeldingmerouaneinconuNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Metal FormingDocument7 pages4.1 Metal FormingVinothKumarVinothNo ratings yet
- Welding: Visit For More Learning ResourcesDocument23 pagesWelding: Visit For More Learning Resourcestanu rdNo ratings yet
- Joining of MetalsDocument25 pagesJoining of MetalsSaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Guidelines FieldWeldingandCutting PDFDocument11 pagesGuidelines FieldWeldingandCutting PDFYahirEduardoNavarroKauilNo ratings yet
- Load Securement - Lowbed Truck PDFDocument4 pagesLoad Securement - Lowbed Truck PDFPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- 2022 NCEE Paper 2 Questions SampleDocument4 pages2022 NCEE Paper 2 Questions SamplePrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.9Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.9Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- 2019 NCEE Paper II Questions - (Sample) Pages 1 4Document4 pages2019 NCEE Paper II Questions - (Sample) Pages 1 4Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Office Safety TAMUG 12-2014Document9 pagesOffice Safety TAMUG 12-2014Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Candidate Report SheetDocument1 pageCandidate Report SheetPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- 2022 NCEE Paper 1 Sample Question 2Document4 pages2022 NCEE Paper 1 Sample Question 2Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.7Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.7Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.5Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.5Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.8Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.8Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Maine Farm Safety Program: First Aid For Electrical AccidentsDocument2 pagesMaine Farm Safety Program: First Aid For Electrical AccidentsalfredzNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.6Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.6Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.2Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.2Primelift Safety Resources Limited0% (1)
- LEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.3Document3 pagesLEEA Correspondence Courses: Assignment 1.3Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- 1503 V1 Guidance For Safe Mass Gatherings in Nigeria COVID19Document2 pages1503 V1 Guidance For Safe Mass Gatherings in Nigeria COVID19ZainaAdamuNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Mitigation of COVID-19 at Work: Action ChecklistDocument8 pagesPrevention and Mitigation of COVID-19 at Work: Action ChecklistNarayana swamyNo ratings yet
- 3 112 254 en 20110330 PDFDocument70 pages3 112 254 en 20110330 PDFRauf GebreelNo ratings yet
- Severed Thumb: Health, Safety and EnvironmentDocument1 pageSevered Thumb: Health, Safety and EnvironmentPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Corps Medical & Rescue Services 1Document2 pagesCorps Medical & Rescue Services 1Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Title: Inspection of Tripoli - Libya Beach Wedding Resort: Children's Play AreaDocument3 pagesTitle: Inspection of Tripoli - Libya Beach Wedding Resort: Children's Play AreaPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Outline Plan IGC Week 2Document5 pagesOutline Plan IGC Week 2Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety 0Document53 pagesFire Safety 0Pankaj TuranNo ratings yet
- IGC Risk Assessment FormDocument1 pageIGC Risk Assessment FormPrimelift Safety Resources LimitedNo ratings yet
- Manual Fritadeira PDFDocument136 pagesManual Fritadeira PDFtherasiaNo ratings yet
- The Thermodynamic Principles of Isochoric Cryopreservation.Document18 pagesThe Thermodynamic Principles of Isochoric Cryopreservation.Boris RubinskyNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Topic Covered Are As FollowsDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Topic Covered Are As FollowsBikash SahuNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning in Clinical MedicalDocument7 pagesDistance Learning in Clinical MedicalGeraldine Junchaya CastillaNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitDocument3 pagesLab Manual For Series Parallel Rasonant CircuitManoj PardhanNo ratings yet
- Key MechanicalDocument72 pagesKey MechanicalDasuki FahmiNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 - Toothache Drugs and MedicationsDocument10 pagesPBL 3 - Toothache Drugs and MedicationsAlbert LawNo ratings yet
- Unit of PowerDocument9 pagesUnit of PowerSarathrv RvNo ratings yet
- Project DesertsDocument17 pagesProject Desertssuja_sriniNo ratings yet
- B SC EVS PDFDocument35 pagesB SC EVS PDFAfroz alamNo ratings yet
- Professional DevelopmentDocument1 pageProfessional Developmentapi-488745276No ratings yet
- Paper - Impact of Rapid Urbanization On Agricultural LandsDocument10 pagesPaper - Impact of Rapid Urbanization On Agricultural LandsKosar Jabeen100% (1)
- Zoology Practical 4Document13 pagesZoology Practical 4Asraful IslamNo ratings yet
- GudegDocument15 pagesGudegYenisNo ratings yet
- Rigatoni With Beef and Onion RaguDocument3 pagesRigatoni With Beef and Onion RagumadduxdavidNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment EquipmentDocument8 pagesPhysical Assessment EquipmentHannah TotohNo ratings yet
- Case Study NCP ActualDocument3 pagesCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Assessment of PostureDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - Assessment of Posturehis.thunder122No ratings yet
- Pengertian Recount Text Kls 9Document26 pagesPengertian Recount Text Kls 9MARINDRA RETNONo ratings yet
- Nath Bio-Genes at Inflection Point-2Document9 pagesNath Bio-Genes at Inflection Point-2vinodtiwari808754No ratings yet
- Metrel Mi 3290 Earth AnalyserDocument4 pagesMetrel Mi 3290 Earth AnalyserMarijan MustačNo ratings yet
- RPLB NewDocument22 pagesRPLB NewMeta learnNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Seat Puller KitDocument2 pagesHydraulic Seat Puller KitPurwanto ritzaNo ratings yet
- Aliyani Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Psoriasis A CasecontrolstudyDocument5 pagesAliyani Association Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Psoriasis A CasecontrolstudyAzmi FadhlihNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Review of Electromyography Studies in Normal Shoulders To Inform Postoperative Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff RepairDocument14 pagesA Systematic Review of Electromyography Studies in Normal Shoulders To Inform Postoperative Rehabilitation Following Rotator Cuff Repairshsh ShshsshNo ratings yet