Professional Documents
Culture Documents
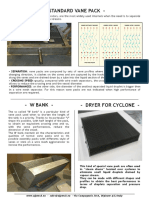
Vane Mist Eliminators: The "VV" Range Is A Plain, No Pocketed
Uploaded by
adrianioantomaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vane Mist Eliminators: The "VV" Range Is A Plain, No Pocketed
Uploaded by
adrianioantomaCopyright:
Available Formats
Vane Mist Eliminators
Vane mist eliminators consist of a series of Both of the above styles can be supplied in
plates or vanes spaced to provide passage for sections for installation through vessel
vapor flow and profiled with angles to manways to be supported on full annular
provide sufficient change of direction for support rings welded to the vessel wall.
liquid droplets to impact, coalesce and drain Alternatively, they can also be supplied as
from the surfaces of the plates. PTC design complete "Vane Packs" where the vanes are
and manufacture a range of vane styles which enclosed in a Frame which is flanged for
provide the following benefits: direct attachment to a "gas box".
• High vapor capacity
• Resistance to fouling
• Low pressure loss
• Effective removal of high liquid loads
The "VV" Range is a plain, no pocketed
style designed for larger droplet removal from
vapor in normal light fouling applications
with either vertical or horizontal gas flow.
“VH-1-F” Droplet Separator
The "VV" Range
The VV is an efficient style of vane mist
eliminator commonly used for removing
entrained liquid from vapor flowing vertically
upwards, and for fouling services. In this
“V-V” Droplet Separator configuration, liquid droplets impinge and
coalesce on the vanes as the vapor flow is
The "VH" Range is designed for droplet elected around the vane profile. The liquid
removal from vapor flowing horizontally. In collected on the vanes drains downwards
this configuration, the vanes are fitted with under gravity so long as the vapor velocity is
hooks (VH11) or pockets (VH-2) to trap and not high enough to cause re-entrainment.
drain the collected liquid. They are generally The graph overleaf shows the relationship
effective at higher vapor velocities at which between vapor rate and the droplet size range
smaller droplet size removal can be achieved. which is effectively removed (typically 99%
removal).
Vane assemblies are fabricated in sections
sized to fit through vessel manways.
Generally, they are supported on an annular
ring welded to the vessel wall with additional
mid-span supports being required where the
vessel diameter exceeds approx 1000mm.
Hold down bars should be fitted to cleats
welded to the vessel wall to secure the pack.
“VH-1” Droplet Separator
Vane Mist Eliminators
The principal applications for this style of through by the vapour. Collection efficiency
droplet separator are the removal of coarse is a function of both vapour velocity and the
entrainment with high liquid load and also difference in density between the vapour and
services of a fouling nature. For severe liquid. The graph below shows the
fouling duty e.g. containing dust, the unit relationship between vapour rate and the
could be installed together with a spray droplet size range which is effectively
system designed to wash out collected solids. removed (typically 99% removal).
PTC offers a hooked (VH-1) design as
standard and a pocketed (VH-2) design for
more arduous applications in clean service.
VH vane packs are fabricated in sections
sized to fit through vessel manways.
Gas & Mist Flow
“VH-1” “VH-2”
The installation arrangement should ensure
that the vane pack is clamped to a ledge and
effectively prevents vapor from bypassing the
vanes. To achieve this, the VH is normally
supplied mounted inside a suitable frame as a
VH-F unit with a drainage channel and
flanged for mounting to a suitable plate or gas
box inside the process vessel.
The "VH” Range
The AlphaMIST VH is a vane pack for
efficient droplet removal and resistance to
fouling suitable for high rate horizontal
vapour flow. Entrained liquid droplets
impinge on the vanes and collect in pockets
that trap the coalesced liquid which then
drains from the unit rather than being blown
Vane Mist Eliminators
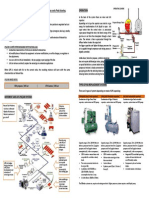
Mist Eliminator Design
The design of vane mist eliminators depends Typically, the pressure drop will be in the
on many factors, but a preliminary sizing can range of 0.2 – 0.8 kPa (approx 20 to 80 mm
be undertaken relatively easily using water gauge).
proprietary K factors in the same way as for
wire mesh demisters.
Face Area
Although it should be treated with caution and
confirmed with PTC before actual use, the
following procedure may be used:
vvme = K . { (ρL – ρV ) / ρV } 0.5
where:
vvme = Max velocity in vanes, m/s
K = K-Factor, see below, m/s
ρL = Density of liquid, kg/m³
ρV = Density of vapour, kg/m³
CFD study of V-V vane design
and:
Avme (m²) = Q (m³/s) / vvme (m/s)
Fine Mist Removal
Removal of very small droplets can be
Vane Style K-Factor
achieved using a two stage mist eliminator by
V-V (vertical gas flow) 0.175
fitting a mesh pad to the upstream face of the
V-V (horizontal gas flow) 0.200
unit to coalesce droplets as small as 4 to 5
VH-1 (horizontal gas flow) 0.225
microns into droplets in the size range which
VH-2 (horizontal gas flow) 0.250
are easily removed by the vane separator?
Pressure Drop
The disadvantage of using the more Add the prefix M to the relevant vane style for
expensive, pocketed designs is that the a two stage mesh / vane mist eliminator.
pressure drop is higher. To estimate the
pressure drop, the following method can be
used:
ρ ρV) . K2
ΔP = C . ( L –
where:
ΔP = Pressure drop, Pa
C = Vane design factor
V-V style, C = 10
VH-1 style, C = 15
VH-2 style, C = 20
You might also like
- Filter Separator English LetterDocument2 pagesFilter Separator English Lettermarcoo8No ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Jngse 2016 01 016Document37 pages10 1016@j Jngse 2016 01 016saiful bahriNo ratings yet
- Bulk Water SeparationDocument1 pageBulk Water SeparationSean MiddletonNo ratings yet
- Losses in Pipe BendsDocument5 pagesLosses in Pipe BendsLove KumarNo ratings yet
- Model 75 Gas Filter Separator LTR PDFDocument4 pagesModel 75 Gas Filter Separator LTR PDFИльяс ГабдуловNo ratings yet
- KIRK KVME Mist EliminatorsDocument2 pagesKIRK KVME Mist EliminatorsSHINo ratings yet
- Vane Pack SeparatorsDocument2 pagesVane Pack SeparatorsIsaac FloresNo ratings yet
- DtEC Mist Eliminators Brochure 140709Document4 pagesDtEC Mist Eliminators Brochure 140709a0aryanNo ratings yet
- Double Pocket Vane DemisterDocument1 pageDouble Pocket Vane DemisterBambang HadinugrohoNo ratings yet
- VGS Vane Separators Are Recommended ForDocument1 pageVGS Vane Separators Are Recommended ForSanthu PeelaNo ratings yet
- 503 Systems - Indirect Fired Heaters - Eng - Apr2010 PDFDocument8 pages503 Systems - Indirect Fired Heaters - Eng - Apr2010 PDFsvnaik14No ratings yet
- Heat duty calculationDocument6 pagesHeat duty calculationwahyuriansyahNo ratings yet
- KIRK Sep-Calc SoftwareDocument4 pagesKIRK Sep-Calc Softwaredhl_tuNo ratings yet
- KIRK KSME Axial Cyclone Swirl Mist Eliminators PDFDocument4 pagesKIRK KSME Axial Cyclone Swirl Mist Eliminators PDFสิทธิไชย อรุณวํฒนชัยNo ratings yet
- Calculos DemisterDocument2 pagesCalculos DemistermoviedohNo ratings yet
- Standard Hook-Up Wires & Cables For ElectronicsDocument124 pagesStandard Hook-Up Wires & Cables For ElectronicsdlstoneNo ratings yet
- LPG Air Mixing 2 A3Document1 pageLPG Air Mixing 2 A3ambientinstal instalNo ratings yet
- Natural Gas Filtration & Separation: To Separate Solid & Liquid Impurities From Natural GasDocument7 pagesNatural Gas Filtration & Separation: To Separate Solid & Liquid Impurities From Natural GasMehdi Hajd KacemNo ratings yet
- Sample Problem StatementDocument2 pagesSample Problem Statementsunildubey02No ratings yet
- 10.0 Troubleshooting Gas Dehydration Operational Problems: F P C C ADocument7 pages10.0 Troubleshooting Gas Dehydration Operational Problems: F P C C AHiep LeNo ratings yet
- Specify Three-Phase SeparatorsDocument12 pagesSpecify Three-Phase SeparatorsRobert MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Mist EliminatorDocument90 pagesMist EliminatordhurjatibhuteshNo ratings yet
- Safety Valve Technical DetailsDocument5 pagesSafety Valve Technical DetailsvineethvskkdNo ratings yet
- Pressurized Glycol Dehy SystemsDocument11 pagesPressurized Glycol Dehy SystemsJagan BoseNo ratings yet
- Vincent PDFDocument4 pagesVincent PDFSarinKorthawornwongNo ratings yet
- Purge Complete Control NarrativeDocument1 pagePurge Complete Control NarrativehadNo ratings yet
- Filtros PecoDocument36 pagesFiltros PecoPedro Luis Choque Mamani100% (1)
- Gas Filter Separators 4Document8 pagesGas Filter Separators 4Anonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet
- Seprasol Plus: Liquid/Gas CoalescersDocument4 pagesSeprasol Plus: Liquid/Gas CoalescersSiavash YarahmadiNo ratings yet
- AX5 Vaporizer Electric Water Bath Type LPG VaporizerDocument2 pagesAX5 Vaporizer Electric Water Bath Type LPG VaporizerRicky DermawanNo ratings yet
- Flare System DesignDocument2 pagesFlare System Designomar alnasserNo ratings yet
- Peerless Separation & Filtration SolutionsDocument2 pagesPeerless Separation & Filtration SolutionsJose Rodrigo Salguero DuranNo ratings yet
- Presentationlu 180126221936 PDFDocument20 pagesPresentationlu 180126221936 PDFhaptoorNo ratings yet
- CMPAPPP Separator Vessel and Filter Design GuideDocument18 pagesCMPAPPP Separator Vessel and Filter Design GuideJWilson73No ratings yet
- Flow and Pressure Drop in Valves and Fittings. Valve Resistance Coefficient and DiameterDocument21 pagesFlow and Pressure Drop in Valves and Fittings. Valve Resistance Coefficient and Diameterjroman33No ratings yet
- Gas Liquid Separation Technology PDFDocument24 pagesGas Liquid Separation Technology PDFr_chulinNo ratings yet
- Three Phase SeparatorDocument9 pagesThree Phase SeparatorboringNo ratings yet
- Sparger Calc MotDocument5 pagesSparger Calc MotRajesh NareNo ratings yet
- 015 VA1 BSWS 00100 GE M3 PID 0040 Legend and SymbolsDocument2 pages015 VA1 BSWS 00100 GE M3 PID 0040 Legend and SymbolsScribd_delNo ratings yet
- Separator PDSDocument7 pagesSeparator PDSprabhuarunkumarNo ratings yet
- Gas Dehydration 090605Document22 pagesGas Dehydration 090605Stiflar SparksNo ratings yet
- Mesh & Vane Mist Eliminator: FiltersDocument16 pagesMesh & Vane Mist Eliminator: Filtersgeorgadam1983No ratings yet
- Inlet Geometry Flow Distribution SeparatorDocument5 pagesInlet Geometry Flow Distribution Separatorchemsac2No ratings yet
- Comparing CoalescersDocument12 pagesComparing Coalescersmohamed_sahnoun_enisNo ratings yet
- DeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesDocument12 pagesDeZURIK KCG Knife Gate ValvesKithkarnonNo ratings yet
- AMISTCO Design ManualDocument16 pagesAMISTCO Design ManualWilliam Novaes100% (1)
- Where To Locate The PSV Inlet NozzleDocument2 pagesWhere To Locate The PSV Inlet NozzleDiego1980bNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Separators ( Separators') - Ascom SeparationDocument5 pages3 Phase Separators ( Separators') - Ascom Separationnaveenbaskaran1989No ratings yet
- HP ScrubberDocument16 pagesHP Scrubbers1308bNo ratings yet
- Coalescer PallDocument16 pagesCoalescer PallJeEJyZaNo ratings yet
- Desalter Salt Balance - 1 PDFDocument1 pageDesalter Salt Balance - 1 PDFengr.shahid041No ratings yet
- 3.0 Systems Division-FiltersDocument8 pages3.0 Systems Division-Filtersmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Cone Design ToolDocument1 pagePressure Vessel Cone Design ToolPramod KumarNo ratings yet
- Acv 12Document2 pagesAcv 12Ali BabasidiNo ratings yet
- CHOKE Valve - Acv12Document2 pagesCHOKE Valve - Acv12limaeronNo ratings yet
- cv-1149 Ctrlvsevduty CopeDocument16 pagescv-1149 Ctrlvsevduty Copegasser ahmedNo ratings yet
- 4428MCR Wavin AS Acoustic Soil PIM SW216 WEB PDFDocument22 pages4428MCR Wavin AS Acoustic Soil PIM SW216 WEB PDFOwen CarrollNo ratings yet
- TRAC Series Annular Control SystemsDocument2 pagesTRAC Series Annular Control SystemsAli Ali100% (1)
- Design Guide - TraysDocument15 pagesDesign Guide - TraysMohamad FaifNo ratings yet
- Sewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionFrom EverandSewage Disposal Works: Their Design and ConstructionNo ratings yet
- FMD Prover Mounting 000 113850 DOC B WDocument3 pagesFMD Prover Mounting 000 113850 DOC B WadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Field Ultrasonic Level SystemDocument12 pagesData Sheet: Field Ultrasonic Level SystemadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Field Intelligent Pump & Level Control SystemDocument8 pagesData Sheet: Field Intelligent Pump & Level Control SystemadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- ODS Metering Systems Services CalibrationsDocument9 pagesODS Metering Systems Services CalibrationsadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter KTEK Products: Measurement Made EasyDocument4 pagesMagnetostrictive Level Transmitter KTEK Products: Measurement Made EasyadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Datum P871: Specification DatafileDocument4 pagesDatum P871: Specification DatafileadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- AT100/AT200 Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter: Module Enhancement & Part Number ChangeDocument2 pagesAT100/AT200 Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter: Module Enhancement & Part Number ChangeadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Sse264gs As 6Document20 pagesSse264gs As 6adrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Field Self-Contained Level Measurement SystemDocument4 pagesData Sheet: Field Self-Contained Level Measurement SystemadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- ABB Instrumentation: Advanced Users GuideDocument32 pagesABB Instrumentation: Advanced Users GuideadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Magnetostrictive Level Transmitter KTEK Products: Measurement Made EasyDocument4 pagesMagnetostrictive Level Transmitter KTEK Products: Measurement Made EasyadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Specialty Level Instrument: AT200VPDocument4 pagesSpecialty Level Instrument: AT200VPadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Applications Sensyflow VT... : Examples: Air, Natural Gas, Gas Mixtures, Pure Gases, ..Document2 pagesApplications Sensyflow VT... : Examples: Air, Natural Gas, Gas Mixtures, Pure Gases, ..adrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- 2600T Series Pressure TransmittersDocument24 pages2600T Series Pressure TransmittersadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Level MagneticLevelGauge Basic Intro Internal-En A 20180618 KM26 F&BsummaryDocument1 pageLevel MagneticLevelGauge Basic Intro Internal-En A 20180618 KM26 F&BsummaryadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- ABB Instrumentation: DATUM P871 and P881 Pressure TransmittersDocument2 pagesABB Instrumentation: DATUM P871 and P881 Pressure TransmittersadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Level MagneticLevelGauge Basic Intro Internal-En A 20180618 KM26 F&BsummaryDocument1 pageLevel MagneticLevelGauge Basic Intro Internal-En A 20180618 KM26 F&BsummaryadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Fluxi 2000/TZ: Turbine Gas MeterDocument8 pagesFluxi 2000/TZ: Turbine Gas MeteradrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- DS 2101110-En Af WebDocument2 pagesDS 2101110-En Af WebadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Fluidic Oscillation MeteringDocument11 pagesFluidic Oscillation MeteringadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Computer MODBUS Interface Description: Operating Manual 42/18-58 ENDocument28 pagesMeasuring Computer MODBUS Interface Description: Operating Manual 42/18-58 ENadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Quantometer MZ: Description ApplicationsDocument6 pagesQuantometer MZ: Description ApplicationsadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- ABB Instrumentation: Installation and Operating InstructionsDocument34 pagesABB Instrumentation: Installation and Operating InstructionsadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Delta ROTARY PDFDocument8 pagesDelta ROTARY PDFSeçkin Doğu TurhalNo ratings yet
- CORUS Energy Meter: Applications DescriptionDocument4 pagesCORUS Energy Meter: Applications DescriptionadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Angus®: Natural Gas Quality AnalyserDocument4 pagesAngus®: Natural Gas Quality AnalyseradrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- D 0 - 2 4 Buf2: 24V/20A DIN Rail Type Buffer ModuleDocument7 pagesD 0 - 2 4 Buf2: 24V/20A DIN Rail Type Buffer ModuleadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Safety Shut-Off Valve Alphard Ca: Applications DescriptionDocument6 pagesSafety Shut-Off Valve Alphard Ca: Applications DescriptionadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Focus GSM: A Smart GSM ModemDocument2 pagesFocus GSM: A Smart GSM ModemadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Jameco Part Number 2094944: Distributed byDocument4 pagesJameco Part Number 2094944: Distributed byadrianioantomaNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document24 pagesSet 1TutorTutorNo ratings yet
- Mumbai: City of DreamsDocument14 pagesMumbai: City of DreamsAnika WahalNo ratings yet
- Faktor OrganisasiDocument9 pagesFaktor OrganisasiNur Fatin NabilahNo ratings yet
- Imeko WC 2012 TC21 O10Document5 pagesImeko WC 2012 TC21 O10mcastillogzNo ratings yet
- Company Introduction PT GEADocument8 pagesCompany Introduction PT GEABegawan Half DoneNo ratings yet
- Resume-Mariam Abdul AzizDocument2 pagesResume-Mariam Abdul Azizmaryam cookNo ratings yet
- Lean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesDocument60 pagesLean Healthy Raw Food Winter RecipesKaio Sol100% (6)
- Strength and Serviceability of Hanger ConnectionsDocument12 pagesStrength and Serviceability of Hanger ConnectionsVitor OlivettiNo ratings yet
- My Personal TimelineDocument4 pagesMy Personal TimelineJerlando M. Pojadas Jr.67% (3)
- Kinetic Study of The Catalytic Reforming of Methane With Carbon Dioxide To Synthesis Gas Over Ni - La2O3 Catalyst PDFDocument8 pagesKinetic Study of The Catalytic Reforming of Methane With Carbon Dioxide To Synthesis Gas Over Ni - La2O3 Catalyst PDFMarcus NguyễnNo ratings yet
- RTR - Nonmetallic Pipng ProcedureDocument16 pagesRTR - Nonmetallic Pipng Proceduremoytabura96100% (1)
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument2 pagesEnthalpy Changesapi-296833859100% (1)
- Types of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesDocument77 pagesTypes of DC Motors Notes Electric DrivesJyothish VijayNo ratings yet
- Way Back To The BibleDocument19 pagesWay Back To The BiblePearlCladelLapidezNo ratings yet
- Choose the Right Low Boy Trailer ModelDocument42 pagesChoose the Right Low Boy Trailer ModelOdlnayer AllebramNo ratings yet
- CXO 7050 Rev 14.3.13 PDFDocument1 pageCXO 7050 Rev 14.3.13 PDFrajaramghoshNo ratings yet
- Piata de Publicitate 2012-2020 - Prezentare RezumativaDocument5 pagesPiata de Publicitate 2012-2020 - Prezentare RezumativamanageranticrizaNo ratings yet
- Maruti Institute of Nursing, Itarsi: Maternal Nursing Child Health Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing FoundationDocument4 pagesMaruti Institute of Nursing, Itarsi: Maternal Nursing Child Health Nursing Medical Surgical Nursing Nursing FoundationHarshaNo ratings yet
- AST Study Centers 2021 Updated Till 25oct2021 GOVT DATADocument33 pagesAST Study Centers 2021 Updated Till 25oct2021 GOVT DATAprasadNo ratings yet
- Biotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainDocument8 pagesBiotensegrity and Myofascial Chains A Global Approach To An Integrated Kinetic ChainMohamed ElMeligieNo ratings yet
- VW Crafter 2f Component Locations EngDocument118 pagesVW Crafter 2f Component Locations EngHugo Emilio Garcia Gonzalez100% (2)
- Intersecting Lines Intersecting Lines Parallel Lines Same LineDocument7 pagesIntersecting Lines Intersecting Lines Parallel Lines Same Lineapi-438357152No ratings yet
- Revised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014Document31 pagesRevised Bsy Elementary Siatonwest 2 and Pio-Macahig - 2014-15 As of June 6 2014api-273918959No ratings yet
- EL FILI CHAPTER 13Document9 pagesEL FILI CHAPTER 13Eduardo Sismundo JrNo ratings yet
- Emd MPC 543Document25 pagesEmd MPC 543jaskaran singhNo ratings yet
- Learn Meanings of 96 Difficult WordsDocument400 pagesLearn Meanings of 96 Difficult WordsVaishali Venkatesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- Letter of Request For Brgy. ProfileDocument2 pagesLetter of Request For Brgy. ProfileRhea Mae MacabodbodNo ratings yet
- Medical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)Document20 pagesMedical Services Recruitment Board (MRB)durai PandiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Marketing Processes and Planning: Assignment BriefDocument4 pagesUnit 2: Marketing Processes and Planning: Assignment BriefGharis SoomroNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Pidilite IndustriesDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Pidilite IndustriesAbhijit DharNo ratings yet