Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Child Health Nursing
Uploaded by
Tanmaya SwainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Child Health Nursing
Uploaded by
Tanmaya SwainCopyright:
Available Formats
STAGES OF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
CHILD HEALTH NURSING
1.Prenatal period
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT THEORIES 0-14 days after conception Ovum
1.Psychosocial development – Erikson 14 days to 8 weeks Embryo
2.Psychosexual development- Sigmund Freud 8 weeks to birth Fetus
2.Post natal period
3.Cognitive development – Jean Piaget 0-28 days Neonate
- It defines cognitive acts as ways to adapt to the 1 month- 1 year infant
environment (mental mapping)
1-3 year Toddler
- Schemata- as per this theory ,schemata are categories in
which mind organise and understand the world 3-5 year Pre schooler
6-12 year schooler
NEURON ACADEMY Page 1
13-18 years Adolescent 2 YEARS 4X
3 YEARS 5X
THE PROCESS OF DEVELOPMENT IS IN CEPHALOCAUDAL 5 YEARS 6X
AND PROXIMO-DISTAL DIRECTION
7 YEARS 7X
10YEARS 10X
WEIGHT
AGE WEIGHT
Neonate lose 5-10 % weight in the first 10 days to 2
NORMAL WEIGHT AT BIRTH 2.5 KG – 3.5 KG weeks
AT BIRTH X INFANT LENGTH
6 MONTHS 2X AT BIRTH= 50 CM
1 YEAR 3X 1 YEAR =75 CM
2 YEAR=90 CM
NEURON ACADEMY Page 2
At 1 year chest circumference equals to head
circumference
AFTER THAT
MID UPPER ARM CIRCUMFERENCE
HEIGHT= (AGEX 6)+77CM
At birth= 11-12 cm
At 1 year= 12-16 cm
HEAD CIRCUMFERENCE
AT BIRTH =33-35 CM
MILESTONES
AT 3 MONTH=40 CM
AGE MILESTONE
AT 1 YEAR -45 CM
2 MONTHS SOCIAL SMILE
3 MONTH HOLDING NECK
CHEST CIRCUMFERENCE
8 MONTHS SITTING WITHOUT
AT BIRTH =31 CM
SUPPORT
NEURON ACADEMY Page 3
SUCKING –ENDS AT 3 -4 MONTHS
9 MONTHS STAND WITH SUPPORT
PALMAR GRASP-START AT BIRTH ,ENDS AT 3
12 MONTHS STAND WITHOUT
MONTHS
SUPPORT
PLANTAR GRASP –ENDS AT 8 MONTH
8-9 MONTHS CRAWLS
BABINSKI REFLEX –ENDS BETWEEN 9 -12 MOTHS.
8 – 12 MONTHS PINCER GRASP
WHEN SOLE OF THE FOOT IS STROKED TOES FANS
9 MONTHS SAYS MAMA
OUT
,DADA,WAVES BYE BYE
15 MONTHS WALK ALONE
STARTILE REFLEX-SUDDEN REACTION TO SHARP
NOISE ETC.DISAPPEAR WITHIN 4 MONTHS
REFLEXES MORO REFLEX-SUDDEN MOVEMENT OF THE NECK
OF THE BABY CAUSE RAPID ABDUCTION AND
ROOTING – TOUCH THE CORNER OF THE MOUTH OF
EXTENSION OF HANDS.DIASPPEARS AT 4-5 MONTHS
THE BABY ,THEN BABY TURNS HEAD TOWARDS
STIMULATION.ENDS AT 3-4 MONTHS
NEURON ACADEMY Page 4
TONIC NECK OR FENCING-WHILE TH NEWBORN FALL
2-3 YEAR ONLOOKER
ASLEEP,TURN TO LEFT SIDE ,THE LEFT LEG AND ARM
EXTENDED WHILE RIGHT LEG AND ARM FLEX AND TODDLER (2.5 -4YEARS) PARALLEL
VICEVERSA .DIASAPPEARS AT 3 TO 4 MONTH
PRESCHOOLER(3- 4 YERS) COPERATIVE
VITAL SIGNS – NEW BORN AND INFANT
SCHOOLER (ABOVE 4 COMPETITIVE
TEMPERATURE -97.5 -98 DEGREE F YEARS)
HR- 120-140 BEATS PER MINUTE
RR- 30-60 PER MINUTE
B.P-73/55mmHg
TYPES OF PLAY NEWBORN CARE –some important
points
INFANTS UNOCUPIED
-While suctioning a newborn, suction mouth first
0-2 YEARS SOLITARY
then nostrils with a bulb syringe to prevent
aspiration
NEURON ACADEMY Page 5
-Birth trauma mass -If a baby is exposed to cold ,vasoconstriction may
occur which later result in METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
1.caput succedaneum – edema of the soft tissue
over the bone,subsides within a few days.edema -PHYSIOLOGICAL JAUNDICE (NORMAL)- it appear
crosses the suture line after 24 hours of birh in full term baby and after 48
hours of birth in premature baby.
2.cephalohematoma- swelling due to bleeding into
the area between bone and periosteum. Subsides -PATHOLOGICAL JAUNDICE (ABNORMAL)- jaundice
within 6 weeks.swelling does not cross over the within 24 hours of birth.it indicate early hemolysis
suture line. of red blood cells
-Vitamin k is not synthesized in newborn body so
there is a risk for bleeding disorder.
-Low set ears is related to down syndrom
Vitamin K is administered intramuscularaly,lateral
-Milia – small white sebaceous glands appear on the
aspect of the middle third of the vastus lateralis
forhead ,nose etc
.dose 0.5 to 1 mg .
-First voiding and passing of stool meconium shoul
-During the first week after birth the birth weight
occur within 24 hours after birth
reduced 5 percent to 10 percent.
NEURON ACADEMY Page 6
After 10-14 days the birth weight is regained. 2.Respirotory rate
-While taking input and output chart ,weigh the 3.Muscle tone
diaper and 1 gm of diaper equals 1 ml of urine.
4.Reflex response
-Ortolani’s sign and Barlow’s sign – assessment test
5.Skin color
for developmental dysplasia of the hip.
Total score :10
developmental dysplasia of the hip- head of the
femur is improperly attached to hip socket If the total score is between
c/f – shortening of the affected side limb (Galeazzi’s 8-10 means no depression,no intervention required
sign,Allis’ sign)
4-7 means mild depression,administer oxygen,rub
APGAR SCORE newborn’s back
Dr.Virginia Apgar developed APGAR SCORE . 0-3 means severe depression ,require resucitation.
APGAR score assess five items In apgar scoring if the skin color is pallor or cynosis ,0
is the score given.if the body skin color normal and
1.Heart rate
extremity is blue then 1 point is given.if both the
NEURON ACADEMY Page 7
body and extremity is normal color then 2 point is LARGE FOR GESTATIONAL AGE – newborn who is
given. above 90th percentile on the intrauterine growth
chart.
APGAR SCORE IS ASSESSED AT 1 MINUTE AND AT 5
MINUTE AFTER BIRTH
RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROM
LOW BIRTH WEIGHT ETIOLOGY- HYALINE MEMBRANE DISEASE
(DEFECIENCY OF SURFACTANTS)
-LOW BIRTH WEIGHT – LESS TAN 2500 G
SEESAW RESPIRATION AND EXPIRATORY GRUNTING
-VERY LOW BIRTH WEIGHT –LESS THAN 1500 G
PRESENT
-EXTREMELY LOW BIRTH WIGHT –LESS THAN 100O G
RX- ADMINISTRATION OF SURFACTANTS
SMALL FOR GESTATIONAL AGE- newborn who is
PREVENTION
below 10th percentile on the intrauterine growth
curve ADMINISTRATION OF BETAMETHASON TO MOTHER
48 HOUR BEFORE DELIVERY OF FETUS
NEURON ACADEMY Page 8
Toxoplasmosis
HYPERBILURUBINEMIA’ Other infections- HIV,hepatitis B,syphillis
SERUM BILURUBIN LEVEL MORE THAN 12 MG/DL Rubella
COMPLICATIONS-KERNICTERUS (brain damage due Cytomegalovirus
to deposition of bilurubin in brain cells)
Herpex siplex virus
RX- PHENOBARBITONE
LIVE VACCINE SHOULD NOT BE GIVEN FOR A HIV INFECTED
PHOTOTHERAPY INFANT
COVER EYES/GENITALIA
45 CM DISTANCE BETWEEN BODY AND LIGHT NEONATAL HYPOGLYCEMIA
LESS THAN 40 mg /dL
TORCH SYNDROME OR INFECTIONS ADMIN 10 % IV GLUCOSE AT A RATE OF 2 ML/KG
It includes infections caused by
NEURON ACADEMY Page 9
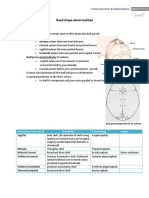
HYDROCEPHALUS Increase in head circumference
-An imbalance in C.S.F production and Macewen’s sign- percussion on head produce
absorption,result in increased ICP cracked pot like sound
-A high shrill cry in an infant can be a sign of Rx
increased ICP
VP shunt –ventriculo peritoneal shunt
Types
AV shunt- ventriculoatrial shunt
-Communicating- no disturbance in C.S.F flow.it
Common sign of shunt malfunctionin toddler-
occurs due to impaired absorption of CSF
headache
-Non communicating- due to obstruction in CSF flow
Common sign of shunt malfunction in older children-
change in level of consciousness
Signs and symtoms
Anterior frontanel bulging CROUP SYNDROME
Sunset eyes INCLUDES
NEURON ACADEMY Page 10
1.ACUTE EPIGLOTTITIS MECONIUM ILEUM IN INFANTS
CHERRY RED SWOLLEN EPIGLOTTITIS
2.LARYNGITIS Kawasaki disease
3.LARYNGOTRACHEOBRONCHITIS Inflamation of the blood vessels throughout the body
BARKING COUGH Signs and symptoms
HAOARSENESS Strawberry tongue
INSPIRATORY STRIDOR High spiking fever
CLEFT LIP AND PALATE
CYSTIC FIBROSIS Cleft lip-failure of fusion of maxiallary and median
nasal process.it is also known as cheiloschisis.
DUE TO GENE MUTATION
Cleft palate is otherwise called as palatoschisis
THICKENED MUCUS GLAND SECRETIONS CAUSE
OBSTRUCTIONS IN PANCREAS AND ALVEOLI Surgical repair of cleft lip-cheiloplasty
NEURON ACADEMY Page 11
Surgical repair of cleft palate-palatoplasty Choking
Surgery usyally performed by age 3-6 months cynosis
ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA AND TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL PYLORIC STENOSIS
FISTULA
Signs and symptoms
-In this condition esophagus terminates before
Pojectile vomiting.
reaches to stomach .Due to this there will be a blind
pouch and fistula forms betwen easophagus and Metabolic alkalosis
trachea
An olive shaped mass in the epigastium
-Excessive drooling of saliva and excessive frothy
Surgical management- pyloromyotomy
saliva in mouth and nose are the main signs
-The 3 C’S of ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA AND
TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL FISTULA CELIAC DISEASE
Coughing
NEURON ACADEMY Page 12
Also known as gluten sensitive enteropathy or celiac MANAGEMENT-AVOID DAIRY PRODUCTS
sprue
Gluten is a protein component found in wheat,oats
HIRSCHPRUNG DISEASE
Patient cannot tolerate gluten in this condition
Hirschprung disease (aganglionic megacolon) is due
It cause steatorrhea,acute diarrhea,severe to absence of ganglionic cells.
malnutrition,anemia etc
Also known as congenital aganglionosis or
Rx-gluten free diet aganglionic megacolon.
LACTOSE INTOLERCANCE It is also associated with down’s syndrome
INABILITY TO DIGEST LACTOSE DUE TO THE ABSENCE It results intestinal obstruction
OF ENZYME LACTASE.CHILD CANT TAKE MILK
Signs
PRODUCTS.
-Ribbon or pellet like stool can be seen in this
COMPLICATION-CALCIUM AND VITAMIN D
DEFICIENCY. -Absence of meconium pass in the first 48 hours
NEURON ACADEMY Page 13
-Bile stained vomiting Hydrostatic redyuction- by using air or fluid pressure.
Rx
Low fiber,high calorie high protein diet OMPHALOCELE
Herniation of the abdominal content through umblical ring
INTUSSUSCEPTION GASTROSCHISIS
Telescoping of one portion of the bowel into another Herniation of abdominal content is lateral to the umblicus
portion causing intestinal obstruction
Signs and symptoms
CRYPTORCHIDISM
-Currant jelly like stools
One or both testes fail to descend into scrotum.
-child will takes fetal position
EPISPADIAS- urethral orifice is located on the dorsal
-Fecal vomiting surface (upper) of penis
Rx
NEURON ACADEMY Page 14
HYPOSPADIAS- urethral orifice is located on the ventral
surface( below) of penis
NEURAL TUBE DEFECT
MARFAN SYNDROME
ETIOLOGY
Connective tissue disorder due to fibrillin-1 gene defect
-FOLIC ACID DEFICIENCY
Tall and thin body with visual and cardiac problems
-SODIUM VALPORATE INTAKE IN PREGNANCY
-INCREASED ALPHA FETO PROTIEN
WILMS TUMOR (NEPHROBLASTOMA)
PREVENTION
WILMS TUMOR – common kidney tumor of chilhood
- FOLIC ACID 0.4 MG FOR ANTENATAL WOMEN
MALIGNANT NEOPLASM
NEURAL TUBE DEFECT (TYPES)
MASS IN THE ABDOMEN
ANENCEPHALY-PARTIAL OR COMPLETE ABSCENCE OF
AVOID PALPATION OF ABDOMEN .RUPTURE CAUSES BRAIN
SPREADING OF CANCER CELLS.
NEURON ACADEMY Page 15
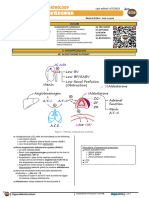
ENCEPHALOCELE- HERNIATION OF BRAIN THROUGH CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE -classification
SKULL
ACYANOTIC CYANOTIC
SPINA BIFIDA -INCOMPLETE CLOING OF SPINE AND
MEMBRANES AROUND THE SPINAL CORD
ASD TETROLOGY OF FALLOT
SPINA BIFIDA –TYPES
VSD TGA(TRANSPOSITION OF GREAT-
1.spina bifida occulta- common ,there will be
covering of skin later PDA ARTERIES)
2.meningocele COARCTATION OF AORTA TRICUSPID ATRESIA
3.myelomeningocele AORTIC STENOSIS
PULMONIC STENOSIS
NEURON ACADEMY Page 16
TETROLOGY OF FALLOT -includes
Pulmonar artery disease
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Ventricular septal defect
Overriding of aorta
NEURON ACADEMY Page 17
You might also like
- REVIEWERDocument14 pagesREVIEWERMaria Lejani TerencioNo ratings yet
- LCC PediaDocument71 pagesLCC PedianucahersheyskatNo ratings yet
- TCC101 Converted 2Document20 pagesTCC101 Converted 2Francis De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Assessing Newborns and Infants RevieweDocument11 pagesAssessing Newborns and Infants RevieweLaurisse April Necesito100% (1)
- 5 - Infancy For StudentsDocument56 pages5 - Infancy For StudentsaplesgjskNo ratings yet
- Concept of Growth and DevelopmentDocument31 pagesConcept of Growth and DevelopmentApRil Anne BalanonNo ratings yet
- Newborn Assessment PDFDocument51 pagesNewborn Assessment PDFMilca DavidNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Booklet by Win Nursing CoachingDocument116 pagesPaediatric Booklet by Win Nursing CoachingAkshya YadavNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Health Promotion of The Infant and FamilyDocument5 pagesChapter 10 Health Promotion of The Infant and FamilyDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- Psy 2 - MDocument9 pagesPsy 2 - MMae Racquel Grace RamosNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Growth and Development in A NutshellDocument25 pagesPediatric Growth and Development in A NutshellJeno Luis J. ACUBNo ratings yet
- The Nursing Care of A Family With A NewbornDocument5 pagesThe Nursing Care of A Family With A NewbornDonell EscalanteNo ratings yet
- W2 PaedsDocument34 pagesW2 Paedssogolhatami02No ratings yet
- Pedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of MortalityDocument3 pagesPedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of MortalityNeil Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument10 pagesPediatricssachinsaaho123No ratings yet
- m102 The NewbornDocument36 pagesm102 The NewbornMA. JYRELL BONITONo ratings yet
- Human Devlopment 1: Level 1Document27 pagesHuman Devlopment 1: Level 1Rahul Kumar DiwakarNo ratings yet
- Lec-Dem Delivery TechniqueDocument54 pagesLec-Dem Delivery TechniqueGraciela Lou Mana-ayNo ratings yet
- Complete Guide To Pediatric NusringDocument135 pagesComplete Guide To Pediatric NusringSANKARNo ratings yet
- Juwak, Jassim - Act 2Document4 pagesJuwak, Jassim - Act 2JASSIM JUWAKNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentChandu RajNo ratings yet
- Physical Development of Infants & Toddlers: "A Baby Is God's Opinion That Life Should Go On, " - Carl SandburgDocument25 pagesPhysical Development of Infants & Toddlers: "A Baby Is God's Opinion That Life Should Go On, " - Carl SandburgshielamaetaljalerasanNo ratings yet
- Pedia AssessmentDocument10 pagesPedia AssessmentPatel PrakrutiNo ratings yet
- 1 Growth and DevelopmentDocument7 pages1 Growth and DevelopmentMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Children Birth To Age 2 Page 89Document16 pagesUnderstanding Children Birth To Age 2 Page 89Kayla TurnerNo ratings yet
- Theories Relevant To Nursing PracticeDocument61 pagesTheories Relevant To Nursing PracticeAngel BarrocaNo ratings yet
- Undrestanding The Focus Pediatric Nursing Common TermsDocument11 pagesUndrestanding The Focus Pediatric Nursing Common Termsyasodha maharajNo ratings yet
- Notes - Week 3 4 - Postnatal DevelopmentDocument68 pagesNotes - Week 3 4 - Postnatal DevelopmentSyuhadaNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion Across Lifespan Intrauterine To NewbornDocument11 pagesHealth Promotion Across Lifespan Intrauterine To Newbornmichaella pizarroNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing, 8th EditionDocument5 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing, 8th EditionErica Marie H FabrigasNo ratings yet
- CP 3Document18 pagesCP 3Rubina MasihNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Growth and Development Are Often Associated With Chronic or Severe Illness or May Be The Only Symptom of Parental Neglect or AbuseDocument12 pagesDisorders of Growth and Development Are Often Associated With Chronic or Severe Illness or May Be The Only Symptom of Parental Neglect or AbuseSari SaryonoNo ratings yet
- Boards Study GuideDocument13 pagesBoards Study GuideSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument60 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument65 pagesImmediate Newborn CareShania CabucosNo ratings yet
- Normal Growth and Development TransDocument2 pagesNormal Growth and Development TransCharlie DyNo ratings yet
- Pediatric DR PDFDocument135 pagesPediatric DR PDFVinu Poojapranavam100% (1)
- Case # 2Document10 pagesCase # 2steffiNo ratings yet
- Psy 1 Notes LectureDocument3 pagesPsy 1 Notes LectureSkrt brrt brtNo ratings yet
- Maternal ReportDocument55 pagesMaternal ReportPattNo ratings yet
- Physical GrowthDocument11 pagesPhysical GrowthAbdulrahman AlsulimaniNo ratings yet
- Child and Adolescent Development PDFDocument118 pagesChild and Adolescent Development PDFArcie CatliNo ratings yet
- THE NEWBORN: Physiologic ResponsesDocument6 pagesTHE NEWBORN: Physiologic Responseslailanie_pabloNo ratings yet
- Theraex 3 Primitive Reflexes LevittDocument26 pagesTheraex 3 Primitive Reflexes LevittEsterGrefielNo ratings yet
- VL Module Newborn Part 2 2023Document17 pagesVL Module Newborn Part 2 2023ilaomaricholmNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - ASSIGNMENT Pedia - Ma'am Zeani: Profile of The NewbornDocument6 pagesNCM 107 - ASSIGNMENT Pedia - Ma'am Zeani: Profile of The NewbornJane BautistaNo ratings yet
- (YUD) Tahap Tumbuh KembangDocument54 pages(YUD) Tahap Tumbuh KembangfitriNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer MCNDocument11 pagesFinals Reviewer MCNKayobi BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 28 Health AssessmentDocument41 pagesChapter 28 Health AssessmentCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Normal Growth and DevelopmentDocument66 pages1.2. Normal Growth and DevelopmentMUSLIHAH MD DESANo ratings yet
- The Development of Performance SkillsDocument54 pagesThe Development of Performance Skillshazell_aseronNo ratings yet
- The Musculoskeletal System: Gert J. Breur, Sean P. Mcdonough, Rory J. TodhunterDocument18 pagesThe Musculoskeletal System: Gert J. Breur, Sean P. Mcdonough, Rory J. TodhunterRizki Nandasari SulbahriNo ratings yet
- Newborn RevDocument14 pagesNewborn RevRuthangela GarciaNo ratings yet
- INFANTDocument11 pagesINFANTjcngonzalesNo ratings yet
- PBL TUMBUH KEMBANG DAN GERIATRI Group 15 Modul 1Document57 pagesPBL TUMBUH KEMBANG DAN GERIATRI Group 15 Modul 1Nurfi Resni Fitra RamdaNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development 3Document46 pagesGrowth and Development 3DR AAMNo ratings yet
- Human DevelopmentDocument62 pagesHuman Developmenttatzicole09No ratings yet
- Infancy: Physical and Cognitive Development: Muha Mad A Riff I BrahimDocument79 pagesInfancy: Physical and Cognitive Development: Muha Mad A Riff I BrahimReentsha EllyNo ratings yet
- Novorodence Ishrana I Poremecaji DR Svetlana RajakDocument170 pagesNovorodence Ishrana I Poremecaji DR Svetlana Rajakni60No ratings yet
- Powerful Potential of Parents: Critical Influences, Ages 0 – 5, Extending into K-12 GradesFrom EverandPowerful Potential of Parents: Critical Influences, Ages 0 – 5, Extending into K-12 GradesNo ratings yet
- Proton TherapyDocument21 pagesProton Therapytrieu leNo ratings yet
- CCU NCP Week 2Document4 pagesCCU NCP Week 2April Kate BanagodosNo ratings yet
- By: Negesse T. (M.SC, N) : Management of Patient With Neurologic DysfunctionDocument53 pagesBy: Negesse T. (M.SC, N) : Management of Patient With Neurologic DysfunctionErsido SamuelNo ratings yet
- PNLE III For Medical Surgical NursingDocument13 pagesPNLE III For Medical Surgical NursingZymer Lee Abasolo100% (1)
- WBI05 01 MSC 20180124Document24 pagesWBI05 01 MSC 20180124Asem BarhoushNo ratings yet
- Sih Ar 2015Document230 pagesSih Ar 2015Ali SaeedNo ratings yet
- Scope of Artificial Intelligence in MedicineDocument4 pagesScope of Artificial Intelligence in MedicineAtul DwivediNo ratings yet
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 pagesETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- Bone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerDocument26 pagesBone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerSarah Nabella PutriNo ratings yet
- Stroke - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument31 pagesStroke - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRhonskiiNo ratings yet
- Head Shape Abnormalities and HydrocephalusDocument7 pagesHead Shape Abnormalities and HydrocephalusZweNo ratings yet
- Libro, Schulze, 2016 Disnomia en Pacientes Con EpilepsiaDocument16 pagesLibro, Schulze, 2016 Disnomia en Pacientes Con EpilepsiaRicardo Jose De LeonNo ratings yet
- Omar THE ADRENAL GLANdDocument4 pagesOmar THE ADRENAL GLANdRenien Khim BahayaNo ratings yet
- Sodium and PotassiumDocument7 pagesSodium and PotassiumLUALHATI VILLASNo ratings yet
- Multiple Sclerosis Medical-Surgical NursingDocument5 pagesMultiple Sclerosis Medical-Surgical NursingNoelyn BaluyanNo ratings yet
- Case 1 FinalDocument70 pagesCase 1 FinalMaria Charis Anne IndananNo ratings yet
- Electroencephalography: Preparation of Patients and Assisting With EEGDocument15 pagesElectroencephalography: Preparation of Patients and Assisting With EEGPaul MNo ratings yet
- Headache Syndromes, Oxford, 2020Document561 pagesHeadache Syndromes, Oxford, 2020luizmiranda108No ratings yet
- General Patho Lab2 2Document93 pagesGeneral Patho Lab2 2عبد الرحمن عصام ابوديابNo ratings yet
- Subgroup 2 Ovarian CystDocument257 pagesSubgroup 2 Ovarian CystCharlie AbagonNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 6th Edition Kenneth SaladinDocument11 pagesHuman Anatomy 6th Edition Kenneth SaladinRosennaseNo ratings yet
- Otvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachDocument551 pagesOtvori Pediatric Surgical Diseases A Radiologic Surgical Case Study ApproachslatkaNo ratings yet
- ESMA BERRA KARAMAN Assignment 4 255161 679572555Document3 pagesESMA BERRA KARAMAN Assignment 4 255161 679572555berra kNo ratings yet
- Emotional Reactions To ConditionDocument4 pagesEmotional Reactions To ConditionsmanitkmNo ratings yet
- Biologija Latin TermsDocument7 pagesBiologija Latin TermsappleNo ratings yet
- Pathological Anatomy IntroDocument27 pagesPathological Anatomy IntroJoiya KhanNo ratings yet
- NEUROPATHOLOGYDocument28 pagesNEUROPATHOLOGYPratama SutardiNo ratings yet
- Physiological Changes in PregnancyDocument40 pagesPhysiological Changes in PregnancyArhum SiddiqiNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii-Biology Project-2023-24Document16 pagesClass-Xii-Biology Project-2023-24soumyaranjanmahakud5No ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet