Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of Mortality
Uploaded by
Neil Vincent De AsisCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of Mortality
Uploaded by
Neil Vincent De AsisCopyright:
Available Formats
PEDIATRICS: Normal Fetal Growth and Development;
Overview of Infant Mortality and Morbidity
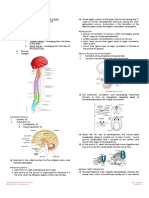
NORMAL FETAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT NEUROLOGIC DEVELOPMENT
Somatic Development 3rd week
Neurologic Development - Neural plate appears on the ECTODERMAL surface of the
Behavioral Development trilaminar embryo
Threat to Fetal Development - Neural tube – CNS
- Neural crest – PNS
SOMATIC DEVELOPMENT
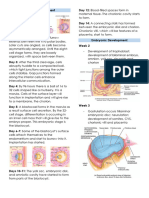
EMBRYONIC PERIOD Neuroectodermal cells Mesoderm
6th day - Neurons - microglial cells
- Implantation begins - Astrocytes
- Embryo will have a blastocyst - Oligodendrocytes
- Ependymal cells
2nd week
- Implantation is complete 5th week
- Uteroplacental circulation has begun - Forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain are evident
- 2 distinct layers - Dorsal and ventral horns of the spinal cord have begun to
o Endoderm form, along with peripheral motor and sensory nerves
o Ectoderm
- Start forming amnion MYELINIZATION
- Begins MIDGESTATION and continues for YEARS
3rd week
- Gastrulation = 3rd layer, the mesoderm End of 8th week
- Neural tube and blood vessels - Gross structure of the nervous system has been established
- Paired heart tubes begin to pump - Cellular level
o Neurons migrate outward to form the 6 cortical
4th-8th week layers
- Lateral folding of embryonic plate o Migration is complete by 6 th month but
- Growth at cranial and caudal ends differentiation continues
- budding of arms and legs = human-like shape
- precursors of skeletal muscles and vertebrae appear Axons and dendrites form synaptic connections at a rapid pace, making
(SOMITES) the central nervous system vulnerable to teratogenic or hypoxic
- lens placode appear (future eyes) influences throughout gestation.
- Brain grows rapidly
- DNA – marker of cell number
End of 8th week - Cholesterol – marker of myelination
- Embryonic period closes - Peals
- Rudiments of all major organ systems have developed o Prenatal – represent growth of neurons
- Crown-rump length = 3 cm o Postnatal – represent rapid growth of glia
FETAL PERIOD - Glial cells
9th week onwards o Important in shaping the brain and in neuronal circuits
- Rapid body growth o For the formation of axonal myelin sheath
- Differentiation of tissues, organs, organ systems o Maintenance of neural pathways
o Removal of waste because the brain has no lymphoid
10th week system for this task
- Face looks human
- Midgut returns to the abdomen from the umbilical cord, - By the time of birth
rotating counterclockwise to bring the stomach, small o Structure of brain is complete
intestine, and large intestine into their normal position o Many cells undergo APOPTOSIS
12th week - Functional Connectivity of the Brain
- Gender of external genitals clearly distinguishable o Disruptions – psychiatric and behavioral disorders
- Lung development proceeds o Begin in fetal life
20th-24th week
- Primitive alveoli formed
- Surfactant production has begun
Third trimester
- Weight triples and length doubles
- Protein, fat, iron, calcium stores increase
YEAR LEVEL 2 NOTES 1
PEDIATRICS: Normal Fetal Growth and Development;
Overview of Infant Mortality and Morbidity
BEHAVIORAL DEVELOPMENT SOMATIC DEVELOPMENT
First neural function seen at 3 rd month Infant Mortality
Major Causes of Infant Death
13-14 weeks – breathing and swallowing Infant Mortality Reduction
17 weeks – grasp reflex, well developed at 27 weeks INFANT MORTALITY
26-28 weeks – eyes opening Infant mortality – number of infant deaths per 1000 live births
MIDGESTATION – full range of neonatal movements can be observed
Live birth
THIRD TRIMESTER - Based on the complete expulsion of the production of
- Fetuses respond to external stimuli with HEART RATE conception from the uterus and 1 of 3 criteria
ELEVATIONS and BODY MOVEMENTS (observed by o Detection of cardiac activity – by auscultation or
ultrasound) palpitation of the umbilical cord stump
o Definite movement generated by voluntary muscle
Behavioral states: contraction
- Quiet sleep o Any respiratory efforts
- Active sleep
- Awake Perinatal period – 28th week of pregnancy through the 7 th postpartum
day
Habituation
- A basic form of learning in which repeated stimulation results Neonatal period – first 28 days of life of a newborn
in a response decrement - Early – 1-7 days
- Late – 8-28 days
PSYCHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN PARENTS
Quickening Primary cause of mortality: Preterm birth and Congenital
- Tangible evidence that a fetus exists as a separate being malformations
- 16-20 weeks - Whereas unsafe sleep practices accounts for the majority of
- Often heightens a woman’s feelings deaths during the remainder of infancy
TERATOGENIC EFFECTS MAJOR CAUSE OF INFANT DEATH
- Decrease growth and cognitive or behavioral deficits US and Europe
- Majority: Preterm birth, congenital malformation, sleep-
SMOKING related
Cigarettes contain NICOTONE - Infections, trauma, birth asphyxia, injuries
- Vasoconstrictor
- Disrupt dopaminergic and serotonergic pathways Developing world
- Low birthweight, stunting, and smaller head circumference - Infection and asphyxia
- Increased risk for learning problems, attention and behavioral
disorders, and long-term health effects In the era of modern neonatal intensive care, most preterm birth
deaths occur among earliest gestational ages (<28 wk), and
ALCOHOL within the 1st few days of life, because of profound respiratory
- Affecting physical development immaturity and insufficiency.
- Affects cognition
- Affects behavior Leading cause of infant death after premature birth
1. Congenital Malformations
COCAINE a. Congenital Heart Disease
- Alterations in placental blood flow and in direct toxic effects 2. Sleep-related deaths
to the developing brain a. SUID b. SIDS
- Exposed adolescents
o Show small but significant effects in behavior and Congenital Malformations
functioning but may not show cognitive impairment - 2nd leading cause of infant death after premature birth
- Prevention
From the book o Folic acid supplementation
- 50% of all pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion, majority o Rubella vaccine
occur in 1st trimester SUID and SIDS
o Chromosomal or other abnormalities SUID (Sudden Unexpected Infant Death)
- Sudden and unexpected
- During infancy
- Suffocation caused by soft objects or excessive bleeding
SIDS (Sudden Infant Death Syndrome)
- Subcategory of SUID
- Sleep-related deaths
Unsafe infant sleep practices – leading cause of death beyond neonatal
period
YEAR LEVEL 2 NOTES 2
PEDIATRICS: Normal Fetal Growth and Development;
Overview of Infant Mortality and Morbidity
Infant Mortality Reduction MODERATE AND EARLY PRETERM NEONATE
- Improving our understanding of the biologic factors that Major morbidities
control gestational duration and initiation of labor and - Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
delivery is key - Intraventricular hemorrhage
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Intramuscular progesterone treatment during pregnancy - Patent ductus arteriosus
- Improving understanding of social determinants of health
and health behavior Intraventricular Hemorrhage
- Smoking during pregnancy - Ruptured capillaries of periventricular white matter and
- Folate supplementation choroid plexus
- Accumulate blood in the lateral ventricles
Folate supplementation - Obstruction of CSF circulation
- Reduced enzyme activity of the folate methylation pathway, - Hydrocephalus
particularly the formation of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, may be
responsible for NTDs or other birth defects Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia
- Reactive airway disease
Recommended Folate Supplementation - Alveolar insufficiency
- No prior history of NTD - Pulmonary hypertension
o 400 micrograms/day; reproductive years - Death
- Mothers with positive history of NTD in previous child/1st - Most common morbidity among NICU survivors
degree relative with NTD - O2 exposure + pressure treatment increase the risk of
o 4 mg/day at least 1 month before conception developing BPD at gestational age
- Women taking Valproate, CBZ - Indicator: Gestational age
o 1-5 mg/day, preconception period o Decreased GA = higher risk of BPD
Necrotizing Enterocolitis
PRETERM BIRTH - Inflammatory in lower GIT most often at distal ilium and
Live birth occurring before 37 th week of gestation ascending colon
- Butod ni sila
Late preterm – 35-36 weeks - 40% of patients – surgical exploration and resection of
Moderate preterm – 32-34 weeks necrotic bowel
Early preterm - <32 weeks
Extreme preterm - <28 weeks Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Common before 28 weeks
Three approaches used - Normally, ductus arteriosus closes minutes after parturition,
1. Last menstrual period (LMP) but will not close if there is no sufficient O2 that will contract
2. Obstetric estimate (OE) the muscles of ductus
3. Combined estimate - Persists: pulmonary overcirculation, complicating respiratory
disease
Genetic variables
- Pregnancy length variants Low Birth Weight – any live birth <2,500 grams
o EBF1 Very Low Birth Weight - <1,500 grams
o EEFSEC
o AGTR2 Intrauterine Growth Restrictions (IUGR)
o WNT4 - Deficiency of fetal growth and abnormal growth trajectory
o ADCY5
o RAP2C Small for Gestational Age (SGA)
- Preterm birth variants - Constitutionally normal, no known genetic abnormalities or
o EBF1 pathologic conditions
o EEFSEC
o AGTR2
LATE PRETERM
- Apneic disorders
- Disorders of thermoregulation
- Hypoglycemia
- Respiratory distress
- Feeding difficulties
- Dehydration
- Suspected sepsis
- Require NICU admission
- Higher risk of longer-term neurologic problems
o ADHD and Learning disorders
- Result from complication of pregnancy or maternal
conditions
YEAR LEVEL 2 NOTES 3
You might also like
- Updated NMAT Study Guide by Astro Dok PDFDocument36 pagesUpdated NMAT Study Guide by Astro Dok PDFJeremy Calderon100% (1)
- Central Nervous System OVL ANA 2103Document76 pagesCentral Nervous System OVL ANA 2103Baguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- Fetal Neurophysiology According To Gestational Age Aida Salihagic Kadic, Maja PredojevicDocument5 pagesFetal Neurophysiology According To Gestational Age Aida Salihagic Kadic, Maja PredojevicDaniela Isidora San Martin CanalesNo ratings yet
- Cell Travel Brochure 2011-2012Document4 pagesCell Travel Brochure 2011-2012Frederick LoganNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Principles of Biochemistry 4th Edition HortonDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Biochemistry 4th Edition HortonSandra Hornyak100% (8)
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument78 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentsukantarautNo ratings yet
- Educ 11 Unit 2 ActivityDocument15 pagesEduc 11 Unit 2 ActivityQueen DaguroNo ratings yet
- 3..0 Lesson NS Development and The NeuronDocument51 pages3..0 Lesson NS Development and The NeuronSuman MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Development of The Central Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesDevelopment of The Central Nervous Systemkutticute_877110165No ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Process of FertilisationDocument5 pagesProcess of FertilisationGeorgia SloanNo ratings yet
- 06 Stages of Brain DevelopmentDocument14 pages06 Stages of Brain DevelopmentGeminiah Eve RockerNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy StagesDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy StagesjamiegemNo ratings yet
- Embryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)Document30 pagesEmbryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)مالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Embryology, Central Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesEmbryology, Central Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfleandro.silvaNo ratings yet
- Development of The Central Nervous SystemDocument39 pagesDevelopment of The Central Nervous SystemRyan SaganNo ratings yet
- Early Development and Refinement of the Central Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesEarly Development and Refinement of the Central Nervous SystemAroojNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous SystemChaGonzalesNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous SystemDocument71 pagesDevelopment of Nervous SystemAbdimalik AliNo ratings yet
- German Measles Infection During Pregnancy Can Damage Fetal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesGerman Measles Infection During Pregnancy Can Damage Fetal DevelopmentJacobNo ratings yet
- Article EmbriologyDocument6 pagesArticle Embriologycestrada10No ratings yet
- PPT2 Child Development CH1Document81 pagesPPT2 Child Development CH1AarushiNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamDocument12 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamAmatul MusawarNo ratings yet
- Pre Natal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPre Natal DevelopmentJinli BalaticoNo ratings yet
- 2008 Advances in Fetal Neurophysiology Jaypee JournalDocument14 pages2008 Advances in Fetal Neurophysiology Jaypee JournalDamara GardelNo ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument4 pagesNs1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyMark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Further ADDED SLIDES L4 PlasticityDocument50 pagesFurther ADDED SLIDES L4 Plasticityjoel.obaid124No ratings yet
- 2011fetal Brain Function Jaypee Journal-AnnotatedDocument7 pages2011fetal Brain Function Jaypee Journal-AnnotatedDamara Gardel100% (1)
- Neuroscience Basics A Guide To The Brain's Involve... - (1.3 Brain Development Steps)Document4 pagesNeuroscience Basics A Guide To The Brain's Involve... - (1.3 Brain Development Steps)yair Enrique Romero OspinoNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)Document95 pagesPregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)sadia ahmadNo ratings yet
- P108.module 5.brain Plasticity-1Document16 pagesP108.module 5.brain Plasticity-1Miles Rommel G. RitosNo ratings yet
- Embryo Edited 2ed LectureDocument17 pagesEmbryo Edited 2ed Lectureapi-249972919No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument296 pagesNervous SystemDr. Serin KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Profed Transes 2Document6 pagesProfed Transes 2paule.miaNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous System - NewkeynoteDocument49 pagesDevelopment of Nervous System - Newkeynotejesse716No ratings yet
- PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT STAGESDocument9 pagesPRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT STAGESRutchelle Pialago PolesticoNo ratings yet
- Neuronal Pathways of Communication: June Levitt, PH.D., LDT, CCC-SLPDocument76 pagesNeuronal Pathways of Communication: June Levitt, PH.D., LDT, CCC-SLPMichael MerlinNo ratings yet
- Embryo For Real CycleDocument31 pagesEmbryo For Real Cyclelovelyc95No ratings yet
- Embryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementDocument38 pagesEmbryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementDasha Vee100% (1)
- 02 - CNS DevelopmentDocument3 pages02 - CNS DevelopmentCemre KuzeyNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - 4Document71 pagesEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.No ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth AutosavedDocument74 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth AutosavedEuvanie Bualan RusteNo ratings yet
- Development of Nervous System: Pakiza M.Sc. PsychologyDocument26 pagesDevelopment of Nervous System: Pakiza M.Sc. PsychologyZain AslamNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer Week 7 To 9 1Document18 pagesMidterm Reviewer Week 7 To 9 1Jay Rome TropiaNo ratings yet
- Embryology: Power Point Presentation by Dr. Nandini DhargalkarDocument57 pagesEmbryology: Power Point Presentation by Dr. Nandini DhargalkarSukanta Sameer SardesaiNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Neurobehavioral ScienceDocument6 pagesAssignment of Neurobehavioral ScienceAnza NoorNo ratings yet
- Tema 2. Morfogénesis Del SNCDocument74 pagesTema 2. Morfogénesis Del SNCflga.franciaasenjoNo ratings yet
- Embryology Type WrittenDocument74 pagesEmbryology Type WrittenAnonymous QqyLDoW1No ratings yet
- Science Rev2 3rdqtrDocument8 pagesScience Rev2 3rdqtrEiric RamosNo ratings yet
- 1-CNS Embryo and AnomalyDocument88 pages1-CNS Embryo and AnomalyRizqi Husni MudzakkirNo ratings yet
- Development of The Optic Nerve of The Rat: Toichiro KuwabaraDocument14 pagesDevelopment of The Optic Nerve of The Rat: Toichiro KuwabaraHari Hara PrabuNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoDocument3 pagesStages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- A. Anatomy of The Developing Embryo: Lecture 18: Chapter 23 - (Development I)Document4 pagesA. Anatomy of The Developing Embryo: Lecture 18: Chapter 23 - (Development I)docnasNo ratings yet
- Laporan Nbss ...Document88 pagesLaporan Nbss ...Nita AndriyaniNo ratings yet
- Physical Development in Early ChildhoodDocument65 pagesPhysical Development in Early Childhoodpaklah_comeyNo ratings yet
- Ch. 3Document13 pagesCh. 3AnnetteNo ratings yet
- Human DEVDocument3 pagesHuman DEVGerald Angelo DeguinioNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-Scientific-Self (1)Document15 pagesChapter-2-Scientific-Self (1)bulcasejohn21No ratings yet
- revkeDocument11 pagesrevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Education Unit 2: Elements and Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesEducation Unit 2: Elements and Stages of Prenatal DevelopmentjamieNo ratings yet
- Case Compilation 2 (Spina Bifida) by Navera, Aleksa Mikael EDocument10 pagesCase Compilation 2 (Spina Bifida) by Navera, Aleksa Mikael Ebtfd2ky4hhNo ratings yet
- 8 EL Husseinys Essentials of Reproductive System @eduwaves360Document195 pages8 EL Husseinys Essentials of Reproductive System @eduwaves360ahmed_abu_alrobNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: Major Fluid CompartmentDocument9 pagesOsmosis: Major Fluid CompartmentMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Download ebook Neuroanatomy Text And Atlas Pdf full chapter pdfDocument67 pagesDownload ebook Neuroanatomy Text And Atlas Pdf full chapter pdfsue.zuniga537100% (19)
- The Respiratory System of OxDocument14 pagesThe Respiratory System of OxHemant JoshiNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Advanced BiologyDocument11 pagesDepartment of Education: Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Advanced BiologysydleorNo ratings yet
- Words of Listening Level 5 U3Document15 pagesWords of Listening Level 5 U3Obaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress The Molecular CoDocument17 pagesInflammation and Oxidative Stress The Molecular CoSerque777No ratings yet
- Exercise 3 RBC CountDocument6 pagesExercise 3 RBC CountJohn Paul DianNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Substance Abuse DisordersDocument14 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Substance Abuse DisordersDee DeeNo ratings yet
- Science WorksheetDocument3 pagesScience WorksheetvienergresourcesNo ratings yet
- UNIT VI Neurobiology of BehaviourDocument18 pagesUNIT VI Neurobiology of BehaviourShatakshi MishraNo ratings yet
- Visualization Peaceful MeadowDocument2 pagesVisualization Peaceful MeadowSagaya AmithaNo ratings yet
- Final Reviewer-Science (151-180)Document3 pagesFinal Reviewer-Science (151-180)KAREN BUENAVISTANo ratings yet
- Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument95 pagesPhysiology of Digestive SystemEsha KumavatNo ratings yet
- RM Ranker NeetDocument40 pagesRM Ranker NeetK. VAMSHI KRISHNANo ratings yet
- Isa P. Tamba - GB 1 - A1 - APA Citation - Individual Worksheet.Document1 pageIsa P. Tamba - GB 1 - A1 - APA Citation - Individual Worksheet.TessaNo ratings yet
- (1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) Testosterone and Cognitive Function - Current Clinical Evidence of A RelationshipDocument9 pages(1479683X - European Journal of Endocrinology) Testosterone and Cognitive Function - Current Clinical Evidence of A RelationshipAlan LuiNo ratings yet
- Basic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6Th Edition Estridge Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument60 pagesBasic Clinical Laboratory Techniques 6Th Edition Estridge Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFflorenceronaldoxo0100% (10)
- Icu Masterclass - Inotropes and Vasopressors: Christopher R. Tainter, MDDocument78 pagesIcu Masterclass - Inotropes and Vasopressors: Christopher R. Tainter, MDHhaNo ratings yet
- English Assignment: Course Name: Assignment No: 01 Assignment Name: News SourceDocument3 pagesEnglish Assignment: Course Name: Assignment No: 01 Assignment Name: News SourceZAMAN SHEIKHNo ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To:, For Other Uses, SeeDocument19 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Jump To:, For Other Uses, Seenassamerg23No ratings yet
- 1st MBBS From 2007 To 2018Document40 pages1st MBBS From 2007 To 2018Govindha Prem PutraNo ratings yet
- 10-Week Hatha Yoga Increases Right Hippocampal Density Compared To Active and Passive Control Groups: A Controlled Structural cMRI StudyDocument11 pages10-Week Hatha Yoga Increases Right Hippocampal Density Compared To Active and Passive Control Groups: A Controlled Structural cMRI StudySupriya KhadeNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximetry ExplainedDocument32 pagesPulse Oximetry Explainedابتسـامه العنزي100% (1)
- Walker - Argulus: Ecology of A Fish PestDocument192 pagesWalker - Argulus: Ecology of A Fish Pestsadida anindyaNo ratings yet
- Laguna Kosmetik Lutronic Aesthetic Encurve™Document4 pagesLaguna Kosmetik Lutronic Aesthetic Encurve™kberenangNo ratings yet
- Igcse Questions Placenta and Umbilical CordDocument3 pagesIgcse Questions Placenta and Umbilical CordFabriV9No ratings yet
- Activity in General Botany Module 3 Plant Cell Metabolism and Plant TissuesDocument6 pagesActivity in General Botany Module 3 Plant Cell Metabolism and Plant TissuesEj Ferrer100% (1)