Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prenatal Development
Uploaded by
Jea Sheinelle G. DiazCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Prenatal Development
Uploaded by
Jea Sheinelle G. DiazCopyright:
Available Formats
Prenatal Development
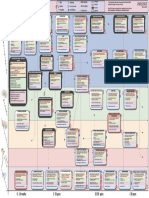
3 Stages of Prenatal Development: [ Week 3:
- These three are different from 3 trimesters of pregnancy. o Binibigyan magdevelop ‘yung brain, heart, blood
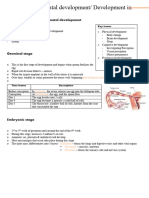
1. Germinal [ 0-2 weeks ] cell, circulatory system, spinal cord, and the
- This is after conception. digestive system.
- The first and shortest stage of the human lifespan.
- This begins with the fallopian tube, when the ovum [ Week 4:
is fertilized by a sperm cell to form a zygote. This o The development of bones, facial structures,
continues as the zygote undergoes several initial cell presence of arms, leg, then nagccontinue na
divisions to form a solid ball of cells called a morula magdevelop and heart, brain, and nervous tissue.
[Consist of 3-4 days]. This continues as morula
undergoes additional changes to become a hollow [ At the end of 4th weeks:
ball of a cell called blastocyst [Consist of 5-7 days]. o Embryo is ¼ inch in length.
When the blastocyst implants in endometrium of the o The heart, digestive system, backbone, and spinal
uterus [Consist of 8-9 days. After implantation cord begin to form.
occurs, the blastocyst is called embryo. The embryo o Placenta (sometimes called “afterbirth”) begins
will soon obtain nutrients from the mother’s blood developing.
via a temporary organ called placenta. o The single fertilized egg is now 10,000 larger than
- The germinal stage of pregnancy starts at the time size at conception.
of conception, when the sperm and the egg combine
to the form of zygote. [ Week 5:
2. Embryonic [ 3-8 weeks/2-8 weeks/5-10 weeks ] o Nabibigyan magdevelop ang eyes, nose, kidney,
- The baby begins a period of dramatic change known lungs, then nagccontinue lang ng formation ang
as the embryonic stage. heart, valves, brain, nervous tissue, and digestive
- During this stage, the baby is called an embryo. track.
- Numerous changes occur during embryonic stage:
● The zygote becomes an embryo. [ Week 6:
● The cell differentiation intensifies. o Nabibigyan magdevelop ang kamay, paa, then
o After the implantation, the cell continues continuation of the development of the brain, heart,
to rapidly divide and clusters of cells begin and circulation system.
to take on different functions which is
called the differentiation. [ Week 7:
o This is the process of gastrulation that o Nabibigyan magdevelop ang hair follicles, nipples,
leads to the formation of 3 distinct layers eyelids, sex organs, first formartion of urine sa
(Germ Layers): kidney, and forst evidence of brain waves.
▪ Ectoderm [Outer layer]
- Formation of skin, nails, hair, [ Week 8:
brains, nervous tissues, cell, o The facial features of the baby are more distinct, then
nose, mouth, and other tissue. the internal organs are well developed too, and also
▪ Mesoderm [Middle Layer] the brain can now send a signal to muscles to move.
- Developing the muscle, bone, The heart development and external sex organ begin
heart, tissue, lungs, reproductive to form.
organs, lymphatic tissue, and
other tissue. [ At the end of 8th weeks:
▪ Endoderm [Inner Layer] o Embryo is 1 ⅛ inches in length.
- Developing the lining of lungs, o Eyes, nose, lips, tongue, ears, and teeth are forming.
bladder, digestive track, tongue, o The embryo is moving, although the mother can not
tonsil, and other organs. feel the movement yet.
o Each layer differentiate to different tissues o Heart is functioning.
and structures.
o The process of differentiation ay nagttake - Starts after the implantation then lasts after 8 weeks after the
place over the period of weeks conception.
simultaneously.
● Life support systems for the embryo develop. ● Organogenesis
● Organ appears. - The process of organ formation during the first
two months of pre-natal period.
- These three layers form [Endoderm, Ectoderm,
Mesoderm], the support system for the embryo
develop rapidly which are: placenta, umbilical o Feeding problems, such as difficulty
cord, amnion. swallowing.
o Hearing loss
- At the end of the embryonic stage, all essential external and o Vision problems
internal organs have been formed. The embryo is now referred ● German Measles
to as a fetus. - The pregnant women who have rubella virus expose their
unborn children as well, which could have severe
Two major direction of growth during embryonic stage: implications.
● Cephalocaudal Development - Infected childbearing can end in miscarriage, or the baby
- The development from head to toe. will be born with abnormalities such as cataracts,
● Proximodistal Development deafness, heart defects, and mental retardation.
- The development from midline outward.
| Arms and legs grow faster than the hands and ● Iodine Deficiency
feet. - The severe iodine deficiency that occurs during pregnancy
is known to cause cretinism and mental impairment.
- Most critical period of baby’s development. - Cretinism and mental retardation are known to be caused
- The embryo’s developmental processes create the foundation by severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy. There is
_________ . During this stage, potentially the emerging currently limited information on the cognitive deficiencies
environmental exposure or genetic flows are likely to have a of children whose mothers experienced iodine deficiency
damage impact on prenatal development. Perhaps they cause during pregnancy.
the embryo’s death or miscarriage. Birth abnormalities are
probably present in embryos if they survive and continue to Types of Cretinism
grow, and develop into fetuses. ○ Neurological Cretinism
| Symptoms are mental retardation, deaf mutism,
- Embryonic stage defects that affect the brain and intellectual squint, spastic diplegia, and disorders of stance and
development: gait.
○ Hypothyroid Cretinism or Myxoedematous
● Alcohol Spectrum Disorder | It is less common and characterised by mental
- Also known as “fetal alcohol syndrome”, brought on retardation (although less severe than in
by a pregnant person’s alcohol intake. neurological cretinism), dwarfism, and
- The most commonly used substance that results in hypothyroidism with associated physical symptoms
birth abnormalities is alcohol. Fetal alcohol spectrum (e.g., coarse and dry skin, husky voice, delayed
disorder results from the embryo being exposed to sexual maturation).
alcohol in the mother's blood. This can lead to
cognitive problems, developmental delays, ● Chromosome Abnormalities
behavioral issues, and unique facial appearance in - Due to the extra copy of chromosomes they are born with
neonates. at birth, people with down syndrome experience altered
cognitive and physical development.
The following issues have been associated with - Due to the extra chromosome that down syndrome
alcohol spectrum disorder: patients are born with, their cognitive and physical
○ Developmental Delay appearance develop abnormally.
○ Irritability
○ Hyperactivity Down syndrome is frequently characterized by learning
○ Poor coordination and behavioral issues like:
○ Abnormalities of facial features. o Delays in speech and language development.
o Attention problems.
● Microcephaly o Sleep difficulties.
- Their head is significantly smaller than normal. o Stubbornness and tantrums.
- It happens when the brain of the baby doesn't develop o Delays in cognition.
accordingly. o Delayed toilet training.
The following issues have been associated with
Microcephaly:
o Seizures 3. Fetal [ 9 weeks - 38 weeks]
o Developmental delay, such as problems with speech - The fetus will continue to develop organs, including
or other developmental milestone (like sitting, the brain and spinal cord.
standing, and walking) - Fetuses will start to develop facial features.
o Intellectual disability (decreased ability to learn and - Fetal heartbeat may now be audible.
function in daily life)
o Problems with movement and balance.
[ Week 9 to 12. o Features such as lips and eyebrows are more distinct, but
o The arm, hand, fingers, finger’s feet, and toes are now the pigment of the color of their eyes is not present yet.
fully formed.
o Nagkakaroon na rin mga movement such as open and [ Week 23
close ng fist and mouth. o Baby’s ears are getting better at picking up sounds. After
o By the end of the 3rd month [end of 1st trimester], mas birth, they might recognize some noises outside the womb
mababa na raw ang possibility ng miscarriages, and all and they are hearing inside now.
the organs and limbs are present and continue to develop
in order to become functional. [ Week 24
o Baby cuts a pretty long and lean figure, but chubbier
[ Week 13 - 16 times are coming. Their skin is still thin and translucent,
o The reproductive organs and genitals are now fully but that will begin to change soon too.
developed.
o Malalaman na sa ultrasound kung male or female ba [ Week 25
‘yung baby. o Baby's wrinkled skin is starting to fill out with baby fat,
making them look more like a newborn. Their hair is
[ Week 16 - 26 beginning to come in, and it has color and texture
o The brain and sensory nerves develop.
o The eyes and ears continue to develop. [ Week 26
o The fetus’s bones have already been developing, but they o Baby is now inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid which
now start to ossify, beginning with the clavicles and help them to develop their lungs. These breathing
bones in the legs. movements are good practice for that first breath of air at
o Alveoli form in the lungs. birth
o Considerable muscle development occurs.
o The intestines develop sufficiently that small amounts of [ Week 27
sugars can be absorbed from the amniotic fluid that is o This is the last week of second trimester. The baby sleeps
swallowed. and wakes on a regular schedule, and their brain is very
active. Their lungs aren't fully formed, but they could
[ Week 16 function outside the womb with medical help.
o The patterning of the baby’s hair has begun but not visible
yet. [ Week 28
o Their legs are more developed. o Baby’s eyesight is developing which may enable them to
o Their hair is more uptight. sense light filtering and front he outside.
o Their ears are close to their final position. o They can blink and their eyelashes are grown in.
[ Week 17 [ Week 27 to 38
o The baby can move their joints and their skeleton. o During weeks 27 to 38 after fertilization, the bones of the
o Soft cartilage is now harding to the bone. fetus complete their development. The fetus also grows
o Umbilical cord is getting stronger and thicker. rapidly during these final weeks, and its body fat
increases substantially. Its formerly wrinkled skin starts
[ Week 18 to plump out as layers of subcutaneous fat are deposited.
o The baby is flexing their hands and legs. ▪ The fetus’s head hair grows thicker
o The pregnant mommy is able to feel those movements. and coarser while the lanugo is shed.
The waxy vernix covering the fetus
[ Week 19 becomes thicker at first, but most of it
o Baby’s senses such as smell, vision, touch, and hearing are will disappear by birth.
developing. ▪ In preparation for breathing after
o The baby is able to hear their mom’s voice. birth, the fetus will repeatedly mimic
breathing by moving the diaphragm.
[ Week 20 By about week 32, the lungs are likely
o The baby can swallow now, and their digestive system is to be fully developed so the fetus can
producing meconium. breathe on its own, should it be born
| Meconium is the baby’s first poop. this early.
▪ The fetus can not only hear and feel
[ Week 21 touch, but its eyes can now detect
o Baby's movements have gone from flutters to full-on light. In fact, the pupils can constrict
kicks and jabs against the walls of womb. and dilate in response to light.
▪ During this phase, the fetus sleeps
[ Week 22 much of the time. Its brain, however,
o The baby now looks almost like a miniature newborn. is continuously active.
You might also like
- DEVPSY - L1 - Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesDEVPSY - L1 - Prenatal DevelopmentJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth AutosavedDocument74 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth AutosavedEuvanie Bualan RusteNo ratings yet
- NMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument49 pagesNMD-4 Prenatal DevelopmentYorgos TheodosiadisNo ratings yet
- Educ 11 Unit 2 ActivityDocument15 pagesEduc 11 Unit 2 ActivityQueen DaguroNo ratings yet
- Embryonic ProcessDocument11 pagesEmbryonic ProcessBobong blyatNo ratings yet
- Fetal Development and Fetal CirculationDocument7 pagesFetal Development and Fetal CirculationLuGeanReb'sNo ratings yet
- Organogenesis: A Brief AccountDocument21 pagesOrganogenesis: A Brief AccountTask BirdNo ratings yet
- Process of FertilisationDocument5 pagesProcess of FertilisationGeorgia SloanNo ratings yet
- E. Activity 3 - Group 6 Pre-Natal PeriodDocument17 pagesE. Activity 3 - Group 6 Pre-Natal PeriodMicole DigmaNo ratings yet
- Embryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)Document30 pagesEmbryogenesis (Week 4-8) & Fetal Period (Week 9-Birth)مالك مناصرةNo ratings yet
- Stages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoDocument3 pagesStages of Fetal (Prenatal) Development Prof. Dymphna CasquejoLynnelljhyen MALUBAYNo ratings yet
- Ed101 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEd101 ReviewerJeff selosaNo ratings yet
- PPT2 Child Development CH1Document81 pagesPPT2 Child Development CH1AarushiNo ratings yet
- Biological BeginningsDocument13 pagesBiological BeginningsAmelinda MarmolNo ratings yet
- Pedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of MortalityDocument3 pagesPedia Normal Fetal Growth Overview of MortalityNeil Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Apbd 1203 Topic 3Document56 pagesApbd 1203 Topic 3Anonymous wsqFdcNo ratings yet
- Perkemb EmbrioDocument32 pagesPerkemb Embriomuhammad hafizNo ratings yet
- 3-Introduction To EmbryologyDocument19 pages3-Introduction To Embryologyuxdan154No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document9 pagesUnit 6Amjad PathanNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pregnancy StagesDocument2 pagesPhysiology of Pregnancy StagesjamiegemNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period: (2 To 8 Weeks After Conception)Document14 pagesEmbryonic Period: (2 To 8 Weeks After Conception)tupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument33 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentDexter Nario0% (1)
- Human DevelopmentDocument15 pagesHuman Developmentapi-3750306No ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument78 pagesGrowth and DevelopmentsukantarautNo ratings yet
- Embryo Development StagesDocument4 pagesEmbryo Development StagesSaranghae momNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Stage of Growth and Development (From Conception To Birth)Document12 pagesPrenatal Stage of Growth and Development (From Conception To Birth)Ohoud ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development: From Single Cell to Full-Term BabyDocument13 pagesPrenatal Development: From Single Cell to Full-Term BabyElisan MarilouNo ratings yet
- DevPsych NewDocument15 pagesDevPsych NewRea Grace YosoresNo ratings yet
- Module #4 Educ Iii Prenatal PeriodDocument10 pagesModule #4 Educ Iii Prenatal PeriodGinaly PicoNo ratings yet
- Pre Natal DevelopmentDocument5 pagesPre Natal DevelopmentJinli BalaticoNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument44 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentMaria ShajiNo ratings yet
- 3prenatal DevelopmentDocument57 pages3prenatal DevelopmentMary Joyce TalamanteNo ratings yet
- Biophysical Aspects of PregnancyDocument34 pagesBiophysical Aspects of PregnancyRucrispi VirayoNo ratings yet
- And Care: Unit Prenatal DevelopmentDocument9 pagesAnd Care: Unit Prenatal DevelopmentPratibha ChNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)Document95 pagesPregnancy and Fetal Development: Shumaila Rani Nursing Instructor (SNC)sadia ahmadNo ratings yet
- Cad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerDocument47 pagesCad Module 11 23 Unit1 Unit5 ReviewerJelmar CastuloNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamDocument12 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth: Prepared by Ms. Sana AslamAmatul MusawarNo ratings yet
- Embryology Notes emDocument32 pagesEmbryology Notes emSavita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Embryonic DevelopmentDocument15 pagesEmbryonic DevelopmentАдия АбуNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - 4Document71 pagesEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.No ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument37 pagesEmbryologySHOWMAN DEEPAKNo ratings yet
- 2 Prenatal Craniofacial Growth 1 2Document151 pages2 Prenatal Craniofacial Growth 1 2Habeeb AL-Absi100% (1)
- MODULE 3 Lesson 1,2,3 Prof LanitDocument16 pagesMODULE 3 Lesson 1,2,3 Prof LanitCRING TVNo ratings yet
- Prenetal - HGDDocument11 pagesPrenetal - HGDJananee RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Fetal DevelopmentDocument31 pagesFetal DevelopmentWelly Surya100% (1)
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Period and Folding of The Embryo PDFDocument54 pagesEmbryonic Period and Folding of The Embryo PDFAdvin BurkeNo ratings yet
- Muralidharan Anantapadmanabhan - 1Document9 pagesMuralidharan Anantapadmanabhan - 1SleepyheadNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Embryology LectureDocument57 pagesYear 2 Embryology LectureIjeoma Doris100% (1)
- Prenatal Development (Child Psychology)Document37 pagesPrenatal Development (Child Psychology)Yel BaldemorNo ratings yet
- Human Embryonic DevelopmentDocument24 pagesHuman Embryonic DevelopmentSri RaamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesLecture 2 Prenatal Developmentmichaelashodeinde35No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Pre Natal DevelopmetDocument22 pagesChapter 2 Pre Natal DevelopmetValshcariegn BalaniNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology: From Fertilization to BirthDocument32 pagesHuman Embryology: From Fertilization to BirthSemere DekeyoNo ratings yet
- Embryology of EARDocument43 pagesEmbryology of EARdharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- PRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT STAGESDocument9 pagesPRE-NATAL DEVELOPMENT STAGESRutchelle Pialago PolesticoNo ratings yet
- Embryology in Weeks SimpleDocument38 pagesEmbryology in Weeks SimpleFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Masa PranatalDocument36 pagesMasa PranatalrennyNo ratings yet
- EmbryoDocument45 pagesEmbryoberhanuNo ratings yet
- Edpsy La6Document9 pagesEdpsy La6Jea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- GZ - L1 - Animal TaxonomyDocument1 pageGZ - L1 - Animal TaxonomyJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- EDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningDocument3 pagesEDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Genzoo ReviewerDocument22 pagesGenzoo ReviewerJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Diaz LA2Document2 pagesDiaz LA2Jea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Early ChildhoodDocument8 pagesEarly ChildhoodJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- InfancyDocument4 pagesInfancyJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document8 pagesWeek 2Kris Adrian MallillinNo ratings yet
- A Framework For Examining How DietDocument11 pagesA Framework For Examining How DietLíbio TapajósNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #19 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document7 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #19 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Medicina 58 01758Document8 pagesMedicina 58 01758charlaayasyafefiNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Retinoblastoma Management and GeneticsDocument12 pagesRecent Advances in Retinoblastoma Management and GeneticsDr Pranesh BalasubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument36 pagesRespiratory SystemLovejoy TiñaNo ratings yet
- Cestodes Worksheet No. 1Document5 pagesCestodes Worksheet No. 1Denika AlmazanNo ratings yet
- PFOonDocument3 pagesPFOonInternational Medical PublisherNo ratings yet
- Pruritus in Keloid Scars Mechanisms and Treatments-1Document20 pagesPruritus in Keloid Scars Mechanisms and Treatments-1widapnNo ratings yet
- Special Senses ActivityDocument8 pagesSpecial Senses ActivityJerene Denzil NacarNo ratings yet
- Hipothalamus & HipofisisDocument42 pagesHipothalamus & HipofisisONe's IwanNo ratings yet
- Name: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicDocument8 pagesName: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicAnoosha FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall Hernias ExplainedDocument53 pagesAbdominal Wall Hernias ExplainedBrother GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Meningoencephalocele of The Temporal Bone-A Case Report: DR.B.V.N Muralidhar Reddy, DR K.V.V.RamjiDocument6 pagesMeningoencephalocele of The Temporal Bone-A Case Report: DR.B.V.N Muralidhar Reddy, DR K.V.V.RamjiNityaNo ratings yet
- Special Examinations & TestsDocument31 pagesSpecial Examinations & TestsyuddNo ratings yet
- Course PlanDocument17 pagesCourse PlanDelphy VargheseNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7Document19 pages2.1 Tutorial Task 6 & 7ENOCH NAPARI ABRAMANNo ratings yet
- Pneumo Tot MergedDocument103 pagesPneumo Tot MergedAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoDocument15 pagesNCM 118 1.5 Shock and Multisystem Disorders Dean Bautista Balmes Barcelon BelarminoNicko Pazon AranasNo ratings yet
- CNS Tumor Map 2020 FullDocument1 pageCNS Tumor Map 2020 FullAlves de MeloNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryameerNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Topic 6 - Human Physiology Revision SheetDocument1 pageIB Biology Topic 6 - Human Physiology Revision SheetFULYA YALDIZNo ratings yet
- My Psychology 1st Edition Pomerantz Test BankDocument8 pagesMy Psychology 1st Edition Pomerantz Test BankRichardHoweycgr100% (45)
- Group 6 Reporting OutlineDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Reporting OutlineDacks WangNo ratings yet
- Class:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and CoordinationDocument16 pagesClass:10 Subject:biology Chapter:control and Coordinationkhushi guptaNo ratings yet
- All CICM Examiner ReportsDocument432 pagesAll CICM Examiner ReportsHani MikhailNo ratings yet
- CHCAGE005 Learner Guide V2.0Document82 pagesCHCAGE005 Learner Guide V2.0rasna kc100% (2)
- Assessing Head, Face and NeckDocument112 pagesAssessing Head, Face and NeckHyacinth Jane Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Infrasound 508Document51 pagesInfrasound 508eltyphysicsNo ratings yet
- PATIENT CASE HPI J.O. Is A 5 Yo Girl Who Is Brought To The PediatricDocument5 pagesPATIENT CASE HPI J.O. Is A 5 Yo Girl Who Is Brought To The PediatricKyla ValenciaNo ratings yet