Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GZ - L1 - Animal Taxonomy
Uploaded by
Jea Sheinelle G. DiazOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GZ - L1 - Animal Taxonomy
Uploaded by
Jea Sheinelle G. DiazCopyright:
Available Formats
Animal Taxonomy ● The second word of the name is species.
(Specific identifier/Specific
Epithet)
3 fields of biology: o The species name is usually a latin description of some important
● Taxonomy characteristics of the organisms.
o These are the exclusive na word dun sa species. Example: Sapiens;
- Naming, sorting (based on their characteristics), and classifying
exclusive lang sya for humans.
organisms into groups (based on their similarities/common/shared
characteristics).
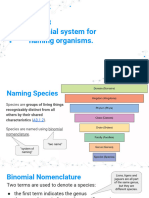
Binomial Nomenclature: Rules for Writing Scientific Names
- Considered as a tool within systematics.
● When we use the Latin name for an organism, we always capitalize
the Genus (First part) but not the species identifier (second part).
[Papangalanan > I-sosort based on their characteristics > I-ggroup na]
● We also print the name in Italics or Underline them.
● Phylogeny For Example:
- History of the evolutionary descent of extant (i.e., presently living) o Acer rubrum (scientific name) - red maple tree (common
or extinct (i.e., no longer living) taxa from ancestral forms. name) or Acer rubrum.
- It’s all about evolutionary history/relationships of different groups ▪ Acer is the Latin name for Maple (genus)
of organisms. ▪ rubrum is the Latin word for Red (species)
o Or the name can be abbreviated as: A. rubrum
● Systematics - Ginagamit lang ang abbreviation kapag ilang beses
- Look into both sorting/identifying organisms and determining their nabanggit o mababangit ang scientific name sa isang papel.
evolutionary relationship. Example: Sa essay, nabanggit mo na yung scientific name sa
- Uses evolutionary relationship as basis for natural taxon. 1st paragraph, sa second and so on paragraph, abbreviation
- The Largest field; Under here are the combination of Taxonomy na lang isususlat mo.
and Phylogeny here. ▪ Paano kapag may dalawang bacteria, magkaiba ang
- Consider as queen of sciences before. kanilang genus, pero nagsisimula sa parehong letter?
- Genetics are now the queen of science and physics is the king of - Hindi na pwedeng mag-apply ng abbreviation.
science.
● Humans are names: Homo sapiens
[ May mga characteristics na exclusive lang for specific organisms at o Homo because of our large brain and upright posture.
mga characteristics na kapareho at mayroon din sa ibang groups kaya o Sapiens because of our intelligence and ability to speak.
mayroon Hierarchy-Seven Levels. ]
Kapag sinulat using a computer: Italicized
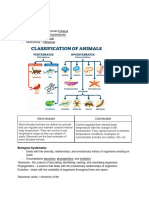
Modern System a Nested Hierarchy-Seven Levels of Organizations Kapag sinulat using the hand: Not italicized but underlined.
Modern System: Magkahiwalay; Example: Homo sapiens
• Each kingdom (plant and animal) was divided into a phylum*
(division for plants) Constructing phylogenies
• Each phylum is divided into smaller groups called class. - Gumagamit ng phylogenetic tree sa pagppresent ng evolutionary
• Each class was divided into orders. history ng mga organisms. Sa pamamagitan nito, bukod sa
• Each order was divided into family (families). evolutionary histroy, naipapakita rin ang relationship nya mula sa
• Each family was divided into genus (plural-genera). iba pang organisms.
• Each genus was divided into a species (scientific name). - Mas bumababa sa Phylogenetic Tree, mas lumalayo ang
relationship.
o Remember: King Phillip Came Over For Grandma’s Soup.
[ In Animal Kingdom, Domain is the most inclusive one. Pinakamataas.
• 3 Domain: Domain Bacteria, Archaea, Eucharia (i.e., humans, rats,
amoeba, etc.)
o After Eucharia, d’yan na papasok ‘yung kingdom. Ang kasama na lang
natin dito since we are under eucarhia ay mga animals o tinatawag na
animalia. Kaya mas inclusive ang domain compare here.
o Phylum: Humans belong to the Phylum Chordata (mga animals na may Bakit kailangan nating malaman ang evolutionary history ng mga
notochord). organisms? Because it is part of the criteria para ma-isama sya sa
o Class: Humans are belong to Class Mammalia (mammals na lang mga tamang grupo nya.
kasama.)
o Order: Humans are under order primates (example: mga baboon,
Homology vs. Homoplasy
orangutan, etc.)
Paano nalalaman ng mga scientist kung magkakamag-anak ba ang
o Family: Humans are under Hominidae (Mga hominid species:
chimpanzee, orangutan) organisms o magkapareho ng ancestors? Using Homology or
o Genus: Humans are under Genus Homo (Homohabilis, Homo erectus, Homoplasy
Homo Sapiens (natitirang genus na lang in the world.), etc)
o Species: Homo sapiens ang ating species.
Binomial Nomenclature [Scientific Name of Human: Homo sapiens] .
● Names were based on Latin or Ancient Greek words - scientists
everywhere understood these languages.
o Latin and Greek words are used because they are considered
dead languages. Meaning, hindi napapalitan o hindi
nagbabago ang kanilang meaning.
● The first word of the scientific name (species name) is the name of
the genus to which the organism belongs.
o The first word is considered as genus. Example: Homo
sapiens; meaning we belong to Genus Homo. Homology: These are the structures that are different in function. That
o The genus name refers to the relatively small group of may be different in function but they came from the same ancestors.
organisms to which a particular type of organisms belongs. Homoplasy/Analogy: Pareho sila ng function pero galing sa
magkaibang ancestors.
You might also like
- Genzoo ReviewerDocument22 pagesGenzoo ReviewerJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology: Species and TaxonomyDocument8 pagesA Level Biology: Species and TaxonomySaeed AbdulhadiNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document3 pagesCH 1Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956No ratings yet
- Bio Short Notes - 240403 - 221805Document169 pagesBio Short Notes - 240403 - 221805munsifmohammed501No ratings yet
- Properties of Living Organisms: 1. Growth MetabolismDocument2 pagesProperties of Living Organisms: 1. Growth MetabolismFida MohamedNo ratings yet
- Biology (Out of Portion)Document51 pagesBiology (Out of Portion)NodiaNo ratings yet
- 1b. Classification 2023 GIVEN3Document10 pages1b. Classification 2023 GIVEN3llekhanya-1No ratings yet
- Biology PDF XiDocument107 pagesBiology PDF XiSania 3003No ratings yet
- 1 The Living World-NotesDocument3 pages1 The Living World-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- Easy To Learn Biology Handbook Bhbz1bDocument169 pagesEasy To Learn Biology Handbook Bhbz1bmohdsarfrazazadNo ratings yet
- Pearson IB Biology HL Sample ChapterDocument28 pagesPearson IB Biology HL Sample Chapterdanijela cetkovicNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Classification of Living ThingsDocument19 pagesLec 3 Classification of Living ThingsEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 - Classification of Living ThingsDocument21 pagesLec-3 - Classification of Living ThingsLamia AkterNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Bio320 PDFDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Bio320 PDFNurul Amirah HossainNo ratings yet
- Animal SystematicsDocument4 pagesAnimal Systematicsmariekatrina.lim06No ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document9 pagesGeneral Biology 2Nicole Margareth SibalNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument11 pagesBiologyMary LeonieNo ratings yet
- Systema Lab Notes 1-2Document4 pagesSystema Lab Notes 1-2jeannegiananNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 and 4 - Classification of Living ThingsDocument19 pagesLec-3 and 4 - Classification of Living ThingsAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- SYSTEMATICSDocument62 pagesSYSTEMATICSkazuhaanemo859No ratings yet
- Species Latin Grammatical FormsDocument4 pagesSpecies Latin Grammatical Formsmaryamehsan100% (1)
- Great English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysDocument10 pagesGreat English - Grammar Rules, Reference Lists and General Knowledge - Isabel UysyoussefNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document7 pagesLecture 4imaniNo ratings yet
- Fish Taxonomy and Systematics: Taxonomic SystemsDocument43 pagesFish Taxonomy and Systematics: Taxonomic Systemssarfaraz.laghari03No ratings yet
- 2 Concept and Use of ClassificationDocument29 pages2 Concept and Use of ClassificationKimberly LinderholmNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Taxonomy: Classification and Naming of Living ThingsChique Ann MaalaNo ratings yet
- Bio 103 Finals Reviewer 1Document13 pagesBio 103 Finals Reviewer 1Lorie Jane De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Binomial System For Naming Organisms (A3.1.3)Document6 pagesBinomial System For Naming Organisms (A3.1.3)gomzj005No ratings yet
- Sci NamesDocument2 pagesSci NamesVincent ValiantNo ratings yet
- Njala University School of Environmental Sciences Department of Biological SciencesDocument28 pagesNjala University School of Environmental Sciences Department of Biological SciencesSheku KallonNo ratings yet
- HowtoDocument2 pagesHowtorheema_ysaisNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - Fa2022 - FinalDocument18 pagesLab 1 - Fa2022 - FinalLiza KleinNo ratings yet
- Pieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusDocument1 pagePieris Homo Lathyrus Sapiens OdoratusjennieNo ratings yet
- Classification Lecture HBDocument18 pagesClassification Lecture HBHarrivcha W.SNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument46 pagesTaxonomyMyra MonicaNo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY BasicsNotes PDFDocument10 pagesZOOLOGY BasicsNotes PDFknarasimhareddyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Taxonomy of InsectDocument6 pagesUnit 5: Taxonomy of InsectAravind SrivasthavNo ratings yet
- Classification of OrganismDocument35 pagesClassification of OrganismJnll JstnNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Gen. Biology II 9th EditionDocument1 pageReviewer Gen. Biology II 9th EditionGARCIA, Denmar Djasthine P.No ratings yet
- Classification PPT - 2Document18 pagesClassification PPT - 2Meilanie Meigie Jacklien KaengNo ratings yet
- Sci KingdomsDocument6 pagesSci KingdomsClaude de alger ObeliaNo ratings yet
- Systematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Document13 pagesSystematics Based On Evolutionary Relationship 1Keith Penaso100% (3)
- Biology Full NotesDocument196 pagesBiology Full NotesNadi Makasaki100% (1)
- Classification of Living OrganismsDocument29 pagesClassification of Living OrganismsOJ ICONICNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 Week-6b 040931Document9 pagesELS Q2 Week-6b 040931nelvinordaniza1No ratings yet
- Intro To ZoologyDocument26 pagesIntro To ZoologyNOELIE IBACARRANo ratings yet
- 08 ClassificationDocument19 pages08 Classificationmilky waysssNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesClassification of Living ThingsBolu AdediranNo ratings yet
- Taxonomyclassification PDFDocument12 pagesTaxonomyclassification PDFsenior highNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Classification LectureDocument1 pageKingdom Classification LectureMadeline Castro PangilinanNo ratings yet
- 2023 Biology HL SampleDocument28 pages2023 Biology HL Sampleasmariaz53No ratings yet
- Taxonomy and KeysDocument8 pagesTaxonomy and KeysJoshua SakalaNo ratings yet
- Biology Module 3Document21 pagesBiology Module 3Joemmel MagnayeNo ratings yet
- ELS Systematics-Week7Document60 pagesELS Systematics-Week7wenshylavador7No ratings yet
- Classificationofanimals 190616135223Document49 pagesClassificationofanimals 190616135223mshahpromoNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-8-Q4-M-4.1 TaxonomyDocument2 pagesSCIENCE-8-Q4-M-4.1 TaxonomyDesiree de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Animal Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Organization: Duration75 Min Grade: 4 CCSS, NgssDocument25 pagesAnimal Taxonomy, Phylogeny and Organization: Duration75 Min Grade: 4 CCSS, Ngssbread genieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuNo ratings yet
- Hsslive - Xi - Biology +1 - The Living WorldDocument1 pageHsslive - Xi - Biology +1 - The Living Worldashlyyyyyy33No ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Edpsy La6Document9 pagesEdpsy La6Jea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- DEVPSY - L1 - Prenatal DevelopmentDocument3 pagesDEVPSY - L1 - Prenatal DevelopmentJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- EDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningDocument3 pagesEDPSY - L2 - Cognitive Views of LearningJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Diaz LA2Document2 pagesDiaz LA2Jea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- InfancyDocument4 pagesInfancyJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Early ChildhoodDocument8 pagesEarly ChildhoodJea Sheinelle G. DiazNo ratings yet
- Robotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0Document119 pagesRobotech Hannibal Digital 114dpi V1.0nonfarb14thNo ratings yet
- HGP Year End Report 2021-2022 NewDocument169 pagesHGP Year End Report 2021-2022 Newangelica sungaNo ratings yet
- Welcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Document4 pagesWelcome Speech For Seminar in College 2Niño Jay C. GastonesNo ratings yet
- Stock Trak AssignmentDocument4 pagesStock Trak AssignmentPat ParisiNo ratings yet
- InflibnetDocument3 pagesInflibnetSuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Getting Things Done BasicsDocument60 pagesGetting Things Done Basicswestelm12100% (10)
- IHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007Document9 pagesIHRM Midterm ASHUVANI 201903040007ashu vaniNo ratings yet
- VtmsDocument2 pagesVtmsLorenz YatcoNo ratings yet
- Nursing ManagementDocument5 pagesNursing Managementheron_bayanin_15No ratings yet
- Site AnalysisDocument4 pagesSite AnalysisS O NALNo ratings yet
- How To Deliver A Good PresentationDocument9 pagesHow To Deliver A Good PresentationGhozi Fawwaz Imtiyaazi LabiibaNo ratings yet
- Beamer Example: Ethan AltDocument13 pagesBeamer Example: Ethan AltManh Hoang VanNo ratings yet
- Study - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFDocument60 pagesStudy - Id23039 - Travel and Tourism in India Statista Dossier PDFaashmeen25No ratings yet
- HDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioDocument2 pagesHDMI To MIPI and LVDS To MIPI Converter Rotator Board Solutions From Q VioSubham KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermo Exam QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermo Exam QuestionssiskieoNo ratings yet
- Getting Started HANADocument86 pagesGetting Started HANAAr RazaNo ratings yet
- 1353apni KakshaDocument43 pages1353apni KakshaArush GautamNo ratings yet
- Consider Typical Robots Consider Typical RobotsDocument16 pagesConsider Typical Robots Consider Typical RobotsOthers ATBP.No ratings yet
- Times Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Document49 pagesTimes Like This Strip-by-Strip (Part 1)Joseph HoukNo ratings yet
- SAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesDocument3 pagesSAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesBharathk Kld0% (1)
- Accessing Biodiversity and Sharing The BenefitsDocument332 pagesAccessing Biodiversity and Sharing The BenefitsNelson MartínezNo ratings yet
- User Guide: Echolife Hg520C Home GatewayDocument25 pagesUser Guide: Echolife Hg520C Home Gatewayluis PavilaNo ratings yet
- TQ Science10 Q3 ST4Document2 pagesTQ Science10 Q3 ST4mae cudal100% (1)
- Service Installation Rules For Connection To Electricity Network (See Chapter 14)Document83 pagesService Installation Rules For Connection To Electricity Network (See Chapter 14)EduardoMorcilloNo ratings yet
- State Magazine, May 2001Document38 pagesState Magazine, May 2001State MagazineNo ratings yet
- Harmonica IntroDocument5 pagesHarmonica Introapi-26593142100% (1)
- Chain Rule 3LNDocument2 pagesChain Rule 3LNsaad khNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet 3 - External Forced Convection - WatermarkUzair KhanNo ratings yet
- Automatic Drive Positioner: SectionDocument207 pagesAutomatic Drive Positioner: SectionHakob AdamyanNo ratings yet
- Lotte Advanced Materials Co., LTD.: ISO 9001:2015, KS Q ISO 9001:2015Document2 pagesLotte Advanced Materials Co., LTD.: ISO 9001:2015, KS Q ISO 9001:2015Tayyab KhanNo ratings yet