Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Uploaded by
NicoleCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CPR ChecklistDocument2 pagesCPR ChecklistJenny Agustin Fabros75% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Anaesthesia Equipment: Anaesthetics OSCE (Compiled by C Lee Kin) 1Document98 pagesAnaesthesia Equipment: Anaesthetics OSCE (Compiled by C Lee Kin) 1Shen BNo ratings yet
- PeriodizationDocument9 pagesPeriodizationStuar TencioNo ratings yet
- ICH CTD SeminarDocument27 pagesICH CTD SeminarSin Poul100% (1)
- Reference ID: 4613105: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedDocument14 pagesReference ID: 4613105: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedNicoleNo ratings yet
- CDK4/6 Inhibitors Administration Checklist: RibociclibDocument1 pageCDK4/6 Inhibitors Administration Checklist: RibociclibNicoleNo ratings yet
- OCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1Document1,255 pagesOCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1NicoleNo ratings yet
- Lacerations & Abrasions: Wound Home Skills KitDocument41 pagesLacerations & Abrasions: Wound Home Skills KitNicoleNo ratings yet
- DR Stanislaw BURZYNSKIDocument22 pagesDR Stanislaw BURZYNSKIpsamiaoue100% (1)
- Z Track InjectionsDocument2 pagesZ Track InjectionssusanloveperegrinoNo ratings yet
- Changing Intravenous Tubing and FluidsDocument4 pagesChanging Intravenous Tubing and FluidsJergens DagangaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Extended Release Drug Delivery SystemDocument9 pagesA Review On Extended Release Drug Delivery SystemTuyến Đặng ThịNo ratings yet
- Drug Alert For The Month of December 2016Document3 pagesDrug Alert For The Month of December 2016amit545No ratings yet
- Cefoperazone and SulbactumDocument3 pagesCefoperazone and Sulbactumiloveit52252No ratings yet
- Drug of Choices PDFDocument10 pagesDrug of Choices PDFRavi Amin100% (1)
- Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010Document26 pagesNatural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010PsineticNo ratings yet
- Drug GuidelinesDocument203 pagesDrug GuidelinesPreth Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Extubation TestDocument5 pagesExtubation TestMel GriffinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandDocument27 pagesTest Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandCary Green100% (39)
- NCR 2018 Philippine Heart CenterDocument862 pagesNCR 2018 Philippine Heart CenterKyla AcyatanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Med Math Made EasyDocument9 pagesNursing Med Math Made EasyFrancesca LopesNo ratings yet
- Price List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Document1 pagePrice List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- List of Approved Institutes in 2013-14: Pharmacy KeralaDocument9 pagesList of Approved Institutes in 2013-14: Pharmacy KeralanoushadNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Harian Sep 18Document20 pagesAntibiotik Harian Sep 18Dewi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument15 pagesSchizophreniaDr. Hem Sagar GautamNo ratings yet
- 8 ReferencesDocument2 pages8 ReferencesSelvakumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 13Document2 pagesLaboratory Activity 13Shekinah AlcarionNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument14 pagesAntidepressantsTuwaij SarrarNo ratings yet
- Allergy and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - Bashir Mahmud ElliasDocument7 pagesAllergy and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - Bashir Mahmud ElliasBashir Mahmud ElliasNo ratings yet
- 12 - Ocular Pharmacology - 343 - 64Document37 pages12 - Ocular Pharmacology - 343 - 64ณัฐ มีบุญNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument6 pagesPharmacology MCQsWaseem SarwarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Norman Rabago 2019 Proposal 1 PDFDocument2 pagesDr. Norman Rabago 2019 Proposal 1 PDFNorman RabagoNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Opioid Conversion GuideDocument17 pagesHow To Use The Opioid Conversion Guidemun_chloeNo ratings yet
- Practice Question Paper BPPKDocument1 pagePractice Question Paper BPPKAyush SrinivasanNo ratings yet
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Uploaded by
NicoleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Novel Therapies Metastatic Breast Cancer
Uploaded by
NicoleCopyright:
Available Formats
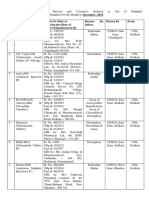
Novel Therapies in
Metastatic Breast Cancer Overview
Abemaciclib Palbociclib Ribociclib
Indication
Abemaciclib is a kinase inhibitor indicated: Palbociclib is a kinase inhibitor indicated for Ribociclib is a kinase inhibitor indicated in
(1) in combination with an aromatase inhibitor the treatment of hormone receptor (HR)- combination with an aromatase inhibitor
as initial endocrine-based therapy for the positive, human epidermal growth factor as initial endocrine-based therapy for the
treatment of postmenopausal women receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced or treatment of postmenopausal women with
with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, metastatic breast cancer in combination with: hormone receptor (HR)-positive, human
human epidermal growth factor receptor (1) an aromatase inhibitor as initial epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-
2 (HER2)-negative advanced or metastatic endocrine based therapy in negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer
breast cancer. postmenopausal women
(2) in combination with fulvestrant for the (2) fulvestrant in women with disease
treatment of women with hormone progression following endocrine
receptor (HR)-positive, human epidermal therapy.
growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative
advanced or metastatic breast cancer with
disease progression following endocrine
therapy.
(3) as monotherapy for the treatment of adult
patients with HR-positive, HER2-negative
advanced or metastatic breast cancer with
disease progression following endocrine
therapy and prior chemotherapy in the
metastatic setting.
Dosing and Administration
Can be taken with or without food; the Capsules are taken orally with food; the Tablets are taken orally with or without
recommended starting dose in combination recommended dose is a 125 mg capsule taken food; in combination with letrozole, the
with fulvestrant is 150 mg twice daily; the orally once daily for 21 consecutive days, recommended starting dose is 600 mg orally
recommended starting dose as monotherapy followed by 7 days off treatment, comprising (three 200 mg tablets) taken once daily for
is 200 mg twice daily. Dosing interruption and/ a complete cycle of 28 days in combination 21 consecutive days, followed by 7 days off
or dose reductions may be required based on with an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant. treatment. Dose interruption, reduction, and/
individual safety and tolerability. Patients should be encouraged to take their or discontinuation may be required, based on
dose at approximately the same time each individual safety and tolerability.
day. If the patient vomits or misses a dose,
an additional dose should not be taken, and
the next prescribed dose should be taken at
the usual time. Dosing interruption and/or
dose reductions are recommended based on
individual safety and tolerability.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions The most common adverse reactions The most common adverse reactions
(incidence of 20% or greater) are diarrhea, (incidence of 10% or greater) are neutropenia, (incidence of 20% or greater) are
neutropenia, nausea, abdominal pain, infection, leukopenia, fatigue, nausea, neutropenia, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea,
infection, fatigue, anemia, leukopenia, stomatitis, anemia, alopecia, diarrhea, leukopenia, alopecia, vomiting, constipation,
decreased appetite, vomiting, headache, thrombocytopenia, rash, vomiting, decreased headache, and back pain. Additional adverse
and thrombocytopenia. Additional adverse appetite, asthenia, and pyrexia. reactions to monitor for include QTc
reactions to monitor for include hepatobiliary prolongations and hepatobiliary toxicity.
toxicity and venous thrombosis.
Updated 6/6/18
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5819)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- CPR ChecklistDocument2 pagesCPR ChecklistJenny Agustin Fabros75% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Anaesthesia Equipment: Anaesthetics OSCE (Compiled by C Lee Kin) 1Document98 pagesAnaesthesia Equipment: Anaesthetics OSCE (Compiled by C Lee Kin) 1Shen BNo ratings yet
- PeriodizationDocument9 pagesPeriodizationStuar TencioNo ratings yet
- ICH CTD SeminarDocument27 pagesICH CTD SeminarSin Poul100% (1)
- Reference ID: 4613105: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedDocument14 pagesReference ID: 4613105: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedNicoleNo ratings yet
- CDK4/6 Inhibitors Administration Checklist: RibociclibDocument1 pageCDK4/6 Inhibitors Administration Checklist: RibociclibNicoleNo ratings yet
- OCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1Document1,255 pagesOCN Exam Flashcard Study System - OCN Test Practice Questions & Review For T-1NicoleNo ratings yet
- Lacerations & Abrasions: Wound Home Skills KitDocument41 pagesLacerations & Abrasions: Wound Home Skills KitNicoleNo ratings yet
- DR Stanislaw BURZYNSKIDocument22 pagesDR Stanislaw BURZYNSKIpsamiaoue100% (1)
- Z Track InjectionsDocument2 pagesZ Track InjectionssusanloveperegrinoNo ratings yet
- Changing Intravenous Tubing and FluidsDocument4 pagesChanging Intravenous Tubing and FluidsJergens DagangaNo ratings yet
- A Review On Extended Release Drug Delivery SystemDocument9 pagesA Review On Extended Release Drug Delivery SystemTuyến Đặng ThịNo ratings yet
- Drug Alert For The Month of December 2016Document3 pagesDrug Alert For The Month of December 2016amit545No ratings yet
- Cefoperazone and SulbactumDocument3 pagesCefoperazone and Sulbactumiloveit52252No ratings yet
- Drug of Choices PDFDocument10 pagesDrug of Choices PDFRavi Amin100% (1)
- Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010Document26 pagesNatural Medicines Comprehensive Database 2010PsineticNo ratings yet
- Drug GuidelinesDocument203 pagesDrug GuidelinesPreth Pal SinghNo ratings yet
- Extubation TestDocument5 pagesExtubation TestMel GriffinNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandDocument27 pagesTest Bank For Daviss Drug Guide For Nurses 16th Edition VallerandCary Green100% (39)
- NCR 2018 Philippine Heart CenterDocument862 pagesNCR 2018 Philippine Heart CenterKyla AcyatanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Med Math Made EasyDocument9 pagesNursing Med Math Made EasyFrancesca LopesNo ratings yet
- Price List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Document1 pagePrice List All Disc SM - DSM 170622Rhesa GuttamaNo ratings yet
- List of Approved Institutes in 2013-14: Pharmacy KeralaDocument9 pagesList of Approved Institutes in 2013-14: Pharmacy KeralanoushadNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Harian Sep 18Document20 pagesAntibiotik Harian Sep 18Dewi PratiwiNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument15 pagesSchizophreniaDr. Hem Sagar GautamNo ratings yet
- 8 ReferencesDocument2 pages8 ReferencesSelvakumar MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 13Document2 pagesLaboratory Activity 13Shekinah AlcarionNo ratings yet
- AntidepressantsDocument14 pagesAntidepressantsTuwaij SarrarNo ratings yet
- Allergy and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - Bashir Mahmud ElliasDocument7 pagesAllergy and Its Permanent Cure With Homeopathic Medicines - Bashir Mahmud ElliasBashir Mahmud ElliasNo ratings yet
- 12 - Ocular Pharmacology - 343 - 64Document37 pages12 - Ocular Pharmacology - 343 - 64ณัฐ มีบุญNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument6 pagesPharmacology MCQsWaseem SarwarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Norman Rabago 2019 Proposal 1 PDFDocument2 pagesDr. Norman Rabago 2019 Proposal 1 PDFNorman RabagoNo ratings yet
- How To Use The Opioid Conversion GuideDocument17 pagesHow To Use The Opioid Conversion Guidemun_chloeNo ratings yet
- Practice Question Paper BPPKDocument1 pagePractice Question Paper BPPKAyush SrinivasanNo ratings yet