Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing & Health Sciences Department: Polangui Campus
Uploaded by
Mark Nel NuñezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing & Health Sciences Department: Polangui Campus
Uploaded by
Mark Nel NuñezCopyright:
Available Formats
Bicol University
Polangui Campus
Nursing & Health Sciences Department
Postpartum Psychosis
A rare but serious maternal health illness that occurs in women just after giving birth. A
potentially life-threatening medical emergency, generally requiring rapid intervention,
hospitalization and psychiatric management.
Prevalence in pregnancy and in the first year of postpartum
Postpartum psychosis is the most severe and uncommon form of postnatal affective
illness, with estimated rates of 0.5-1 episodes per 1000 deliveries
The first presenting symptoms are insomnia, mood lability, or occasionally obsessive
concerns regarding to the newborn; elevated or depressed mood, disorganized behavior,
restlessness, irritability, and delusions and hallucinations
Women with postpartum psychosis also show delirium-like features; women can
sometimes show atypical cognitive symptoms, such as disorientation, derealization,
depersonalization, confusion, perplexity, and misrecognition of people.
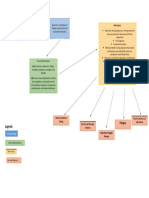
Risk factors Onset Symptoms Consequences Management
Of Untreated
Postpartum
Psychosis
Personal/family Within 4 Manic or -Suicide Hospitalization
history of PP weeks affective Mood Stabilizers
Personal/family -Infanticide Antipsychotics
postpartum Mania
history of BPD Hormones
Genetics Mood lability ECT (Electro
Primiparity Delusions Convulsion Therap
Hormonal changes Hallucinations Antidepressants
Sleep loss Bizarre behavior (with caution)
Higher maternal
age (older than 35) Severe depression
Trauma Confusion
Perplexity
Thought of death
or suicide
References
Understanding Postpartum Psychosis | Rachael Watters
https://youtu.be/8qgV7Yug-xs
Burgerhout-Karin-Marieke.pdf
Prepared by: SODSOD GRESYL R. BSN 2B GROUP B
You might also like
- The Everything Guide to Coping with Panic Disorder: Learn How to Take Control of Your Panic and Live a Healthier, Happier LifeFrom EverandThe Everything Guide to Coping with Panic Disorder: Learn How to Take Control of Your Panic and Live a Healthier, Happier LifeNo ratings yet
- CSB 341Document48 pagesCSB 341TessNo ratings yet
- How to Help Yourself or a Loved One Who Has Bipolar DisorderFrom EverandHow to Help Yourself or a Loved One Who Has Bipolar DisorderNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychosis: Comparing Postpartal Blues, Depression, and PsychosisDocument2 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: Comparing Postpartal Blues, Depression, and PsychosisMay Ann RosalesNo ratings yet
- Women and Mental HealthDocument12 pagesWomen and Mental HealthMugu 123No ratings yet
- Psychiatry ' Psychiatry ' Section Iii: Psychiatry-Pathology Psychiatry-PathologyDocument20 pagesPsychiatry ' Psychiatry ' Section Iii: Psychiatry-Pathology Psychiatry-PathologyLuis Jose VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychosis: Clinical Considerations: Marlene Freeman, M.DDocument9 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: Clinical Considerations: Marlene Freeman, M.DKreshnik IdrizajNo ratings yet
- Post-Partum Psychiatry: AL-Saleh, Yassin, M. College of Medicine, KSUDocument20 pagesPost-Partum Psychiatry: AL-Saleh, Yassin, M. College of Medicine, KSUjpmNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument13 pagesCase Studyapi-599558477No ratings yet
- Depressive-Disorders SheetDocument2 pagesDepressive-Disorders SheetCrystal MarloweNo ratings yet
- Mood-Disorders - Report in PDFDocument32 pagesMood-Disorders - Report in PDFGelynNo ratings yet
- PSYCHOSISDocument12 pagesPSYCHOSISDarwin CauilanNo ratings yet
- PSYCH101 Lecture 10-11 PsychopathologyDocument80 pagesPSYCH101 Lecture 10-11 PsychopathologyLucy YengNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept MapSatanichia McDowell KurumizawaNo ratings yet
- WomenDocument14 pagesWomenMugu 123No ratings yet
- AnxietyDocument4 pagesAnxietyIT’S ME HAYLANo ratings yet
- Educational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Document7 pagesEducational Brochure (Abnormal Psychology)Leonardo YsaiahNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Lecture NotesDocument7 pagesSchizophrenia Lecture NotesHerme BorladoNo ratings yet
- C11 SchizophreniaDocument22 pagesC11 SchizophreniaMaJoy OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Psychiatric Disorders and Recent AdvancesDocument65 pagesPost Partum Psychiatric Disorders and Recent AdvancesAnthonyNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Psychosis-SgdDocument33 pagesPost Partum Psychosis-SgdLyca Mae AurelioNo ratings yet
- Epidemiologia Desenvolvimental Da AnsiedadeDocument22 pagesEpidemiologia Desenvolvimental Da AnsiedadeHortência MariaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Mental Health Comp Case StudyDocument15 pagesPsychiatric Mental Health Comp Case Studyapi-663431559No ratings yet
- 1.3 Mood DisordersDocument7 pages1.3 Mood DisordersDomalaon, Princess Sophia B.No ratings yet
- Careplan 1Document8 pagesCareplan 1api-509642710No ratings yet
- Love Bags For The HomelessDocument1 pageLove Bags For The HomelessTroy CabrillasNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument10 pagesSchizophreniathecountessanna100% (1)
- Psychiatric and Mental Health NursingDocument56 pagesPsychiatric and Mental Health NursingBrielle ShoppNo ratings yet
- Perinatal Psychiatric SyndromesDocument6 pagesPerinatal Psychiatric SyndromesMargarita Valencia MejíaNo ratings yet
- Health Promotion & Screening: Patient Suitability CBT For InsomniaDocument1 pageHealth Promotion & Screening: Patient Suitability CBT For InsomniameilunlyNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case StudyDocument13 pagesPsychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case Studyapi-736973985No ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument11 pagesMood DisordersPrincessXFaithNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Disorders: Dr. Adelene L. YanoDocument56 pagesPsychiatric Disorders: Dr. Adelene L. YanoMarhama MagarangNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi DepresiDocument46 pagesFarmakoterapi DepresiPrinss AntyyNo ratings yet
- Farmakoterapi Sistem Organ II-DepresiDocument73 pagesFarmakoterapi Sistem Organ II-DepresiDISKA YUNIAROHIMNo ratings yet
- Mood Disorders: DR Arghya PalDocument47 pagesMood Disorders: DR Arghya PalRibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aspectos PsiquiatricosDocument52 pagesAspectos PsiquiatricosLu FerjancicNo ratings yet
- Mood DisordersDocument108 pagesMood DisordersAngellene Firmalino50% (2)
- Post Partum DepressionDocument7 pagesPost Partum DepressionDivya ThomasNo ratings yet
- ABPG1103 - Topic 12 - Psychological Disorder - 222Document21 pagesABPG1103 - Topic 12 - Psychological Disorder - 222nureryani bathowiNo ratings yet
- Case Study Mental HealthDocument13 pagesCase Study Mental Healthapi-738695053No ratings yet
- Summary of Mental IllnessDocument6 pagesSummary of Mental IllnessNelsie Duhilag100% (2)
- Anxiety Disorders Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesAnxiety Disorders Lecture NotesHerme BorladoNo ratings yet
- Emergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4Document21 pagesEmergency Psychiatry: Paper B Syllabic Content 7.4CetVital100% (1)
- Psychopathology MSE NotesDocument5 pagesPsychopathology MSE Noteszubair.19cbaNo ratings yet
- Psychedelic Substances: The Little Book ofDocument46 pagesPsychedelic Substances: The Little Book ofpepe100% (2)
- Lect 2 SchizophreniaDocument41 pagesLect 2 SchizophreniaAmier IzzatNo ratings yet
- Depression Lets TalkDocument68 pagesDepression Lets TalkImon PaulNo ratings yet
- Postpartum PsychosisDocument14 pagesPostpartum PsychosisAntony JenNo ratings yet
- Psychosis in WomenDocument7 pagesPsychosis in WomenMarius PaţaNo ratings yet
- Ebook - Mood Swings - Bipolar DisorderDocument28 pagesEbook - Mood Swings - Bipolar DisorderZamar1No ratings yet
- Lithium Therapy in Comorbid Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Cycloid PsychosisDocument3 pagesLithium Therapy in Comorbid Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Cycloid Psychosisyeremias setyawanNo ratings yet
- Neurotic, Stress-Related and Somatoform DisDocument17 pagesNeurotic, Stress-Related and Somatoform Disapi-3703352No ratings yet
- ARM PPT (Trauma and Disociative Disorder)Document9 pagesARM PPT (Trauma and Disociative Disorder)thewarriorprincess02No ratings yet
- Psychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case StudyDocument12 pagesPsychiatric Mental Health Comprehensive Case Studyapi-741551545No ratings yet
- Intro Psychological DisordersDocument39 pagesIntro Psychological DisordersMary Jo LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychosis: DR - Deddy Soestiantoro SPKJ MkesDocument9 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: DR - Deddy Soestiantoro SPKJ MkesiqiqiqiqiqNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RDocument22 pagesLecture 6 - 7oct2022 - RAryaNo ratings yet
- Bahan UTS & UAS Psikiatri FK UNCENDocument3 pagesBahan UTS & UAS Psikiatri FK UNCENBobby R SeptiantoNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psychiatric DisorderDocument30 pagesNeuro Psychiatric DisorderannuNo ratings yet
- Comprehensivem Clinical Case Analysis and Presentation FormatDocument4 pagesComprehensivem Clinical Case Analysis and Presentation FormatMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
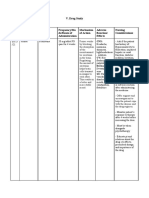
- Drug Study Ver. 2Document2 pagesDrug Study Ver. 2Mark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Iv Cannulation ProcedureDocument5 pagesChecklist For Iv Cannulation ProcedureMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Non Invasive Tests Appreciation of Diagnostic Procedures For Cardiovascular ProblemsDocument9 pagesNon Invasive Tests Appreciation of Diagnostic Procedures For Cardiovascular ProblemsMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Position Description: Associated Students of Umpqua Community College (ASUCC) Student Government Leadership TeamDocument9 pagesPosition Description: Associated Students of Umpqua Community College (ASUCC) Student Government Leadership TeamMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Leaves of Lagerstroemia Speciosa (L) PersDocument2 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Leaves of Lagerstroemia Speciosa (L) PersMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination and Review of SystemsDocument4 pagesPhysical Examination and Review of SystemsMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- A-155 BS Nursing - PCDocument4 pagesA-155 BS Nursing - PCMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Group 8-Case Scenario The Childbearing & Childrearing Family CD Patient Scenario Care Study: The Nagle FamilyDocument5 pagesGroup 8-Case Scenario The Childbearing & Childrearing Family CD Patient Scenario Care Study: The Nagle FamilyMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Pale Appearing Adolescent Female.: Physical Examination and Review of SystemsDocument4 pagesPale Appearing Adolescent Female.: Physical Examination and Review of SystemsMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Best in Liptint Best in Liptint Best in Liptint Best in LiptintDocument34 pagesBest in Liptint Best in Liptint Best in Liptint Best in LiptintMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Anti-Drug Campaign: Oton National High School Oton, IloiloDocument4 pagesAnti-Drug Campaign: Oton National High School Oton, IloiloMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Digestive System - Ingests Food (Takes It In), Digests It (Breaks It Down) Into Nutrient Molecules, Absorbs TheDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Digestive System - Ingests Food (Takes It In), Digests It (Breaks It Down) Into Nutrient Molecules, Absorbs TheMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Labxpress: Hematology Exam Name Result Unit ReferenceDocument2 pagesLabxpress: Hematology Exam Name Result Unit ReferenceMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Full ReportDocument240 pagesFull ReportMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Certification: Polangui Dental & Osseointegration CenterDocument2 pagesCertification: Polangui Dental & Osseointegration CenterMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument12 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
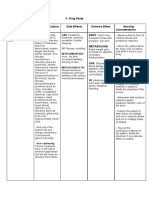
- Drug Study Di Pa FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study Di Pa FinalMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsMark Nel Nuñez100% (1)
- Postpartum Depression and The Baby Blues: Depression in New MothersDocument4 pagesPostpartum Depression and The Baby Blues: Depression in New MothersMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Di Pa FinalDocument3 pagesDrug Study Di Pa FinalMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- CASE #1:: Name of Patient: Lindsay Age: 27 Years Old OB Score: G3P2 Date/Time Admitted: 6:00 AmDocument7 pagesCASE #1:: Name of Patient: Lindsay Age: 27 Years Old OB Score: G3P2 Date/Time Admitted: 6:00 AmMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Assessing COVID-19 Vaccine Literacy: A Preliminary Online SurveyDocument10 pagesAssessing COVID-19 Vaccine Literacy: A Preliminary Online SurveyMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Psychosis: Bicol UniversityDocument4 pagesPostpartum Psychosis: Bicol UniversityMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- The Intrapartal PeriodDocument49 pagesThe Intrapartal PeriodMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- John Karl Bendiola BSN 2B Feb. Postpartum Depression and The Baby BluesDocument5 pagesJohn Karl Bendiola BSN 2B Feb. Postpartum Depression and The Baby BluesMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Cesarean Delivery? Reasons For A Cesarean Delivery IncludeMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Acceptance of COVID-19 Vaccination During The COVID-19 Pandemic in ChinaDocument14 pagesAcceptance of COVID-19 Vaccination During The COVID-19 Pandemic in ChinaMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its SettingDocument11 pagesThe Problem and Its SettingMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Research Design and MethodologyDocument8 pagesResearch Design and MethodologyMark Nel NuñezNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology For Surgical Technologists 2nd Edition Margaret RodriguezDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology For Surgical Technologists 2nd Edition Margaret Rodriguezshriekacericg31u3100% (45)
- Measurements To Guide Your Patient Care: EfficiaDocument16 pagesMeasurements To Guide Your Patient Care: EfficiaXinwen ChenNo ratings yet
- Combat Stress: FM 6-22.5 MCRP 6-11C NTTP 1-15MDocument94 pagesCombat Stress: FM 6-22.5 MCRP 6-11C NTTP 1-15MForum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition by Burtis PDF Full ChapterDocument35 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics 7th Edition by Burtis PDF Full Chapterseesaw.insearchd8k4100% (23)
- Surgical Nutrition PDFDocument8 pagesSurgical Nutrition PDFClever ImaniaNo ratings yet
- Uts Bahasa Inggris Keperawatan Semester 6 Alih Jenjang BBDocument6 pagesUts Bahasa Inggris Keperawatan Semester 6 Alih Jenjang BBNgumpulin ilmuNo ratings yet
- Bioderma FinalDocument17 pagesBioderma FinalHậu PhúcNo ratings yet
- Must Know CorrectionsDocument1 pageMust Know CorrectionsJaneNo ratings yet
- Audit Course Report - The Science of HappinessDocument35 pagesAudit Course Report - The Science of HappinessSANKET SHINGOTENo ratings yet
- DR - Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neurophysical Therapy: Organization and Administration of Emergency CareDocument19 pagesDR - Fatima Ejaz PT Ms Neurophysical Therapy: Organization and Administration of Emergency Carekim suhoNo ratings yet
- CBC PDFDocument1 pageCBC PDFEllen AquinoNo ratings yet
- Final Session Plan - Tam-An (TM1) Marwin NavarreteDocument163 pagesFinal Session Plan - Tam-An (TM1) Marwin NavarreteMarwin NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Aiims Dka ProtocolDocument9 pagesAiims Dka Protocolbbboghara100% (1)
- Site Visit ReportDocument7 pagesSite Visit ReportpozzettiholtNo ratings yet
- English RequimentDocument18 pagesEnglish Requimentrafiz akmalNo ratings yet
- Life and Dignity of The Human PersonDocument3 pagesLife and Dignity of The Human Persongabford333No ratings yet
- Fire Suppression System CO2 Carbon Di Oxide Gas Option BDocument1 pageFire Suppression System CO2 Carbon Di Oxide Gas Option BMirza Yasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mapeh EssayDocument1 pageMapeh EssayJairon BariuanNo ratings yet
- N.A.B.H. Parameter Sheet: Network Hospital Grading ProformaDocument7 pagesN.A.B.H. Parameter Sheet: Network Hospital Grading ProformaDhananjay SainiNo ratings yet
- Deed of Undertaking Limited F2F InternshipDocument2 pagesDeed of Undertaking Limited F2F InternshipMarie LlanesNo ratings yet
- Room Temperature Stability of Drug Products Labeled For Refrigerated StorageDocument3 pagesRoom Temperature Stability of Drug Products Labeled For Refrigerated StorageAhmed YousefNo ratings yet
- How To Measure Cervical Length: Karl Oliver Kagan and Jiri SonekDocument14 pagesHow To Measure Cervical Length: Karl Oliver Kagan and Jiri SoneknidoNo ratings yet
- What Is MindfulnessDocument4 pagesWhat Is MindfulnessPongal PunithaNo ratings yet
- COVID Testing Labs 31052021Document176 pagesCOVID Testing Labs 31052021SangiliNo ratings yet
- Standard Setting ProceduresDocument41 pagesStandard Setting ProceduresRizwan Zafar Ansari100% (1)
- Revsed IVDocument123 pagesRevsed IVZhiela Esteban AbivaNo ratings yet
- Hetzel SuitDocument32 pagesHetzel SuitMitchell BlackNo ratings yet
- Sila Gy 1994Document5 pagesSila Gy 1994Arbey Aponte PuertoNo ratings yet
- Indian Company ListDocument1,230 pagesIndian Company ListSanjukta Nandi74% (70)
- Test Bank For Social Problems 14e 14th Edition William Kornblum Joseph JulianDocument17 pagesTest Bank For Social Problems 14e 14th Edition William Kornblum Joseph JulianMohammad Brazier100% (19)