Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Early Detection and Screening
Uploaded by
Mary Rose Silva GargarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Early Detection and Screening
Uploaded by
Mary Rose Silva GargarCopyright:
Available Formats
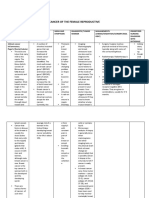
EARLY DETECTION AND SCREENING
1.Breast self- examination 6. Sigmoidoscopy/Colonoscopy
For: are screening tests to look for colorectal cancer.
Monthly The difference between the two tests is the part of
Regular: The best time to do a monthly self-breast the colon they allow the doctor to see. A
exam is about 3 to 5 days after your period starts. sigmoidoscopy is less invasive, because it only looks
Do it at the same time every month. Your breasts at the lower part of your colon.
are not as tender or lumpy at this time in your
monthly cycle. Starting:
Irregular: If you no longer have a period, pick a This test uses a thin, flexible tube with a light and
certain day—such as the first day of each month— camera on one end. Your doctor places this end in
to remind yourself to do BSE. the anus. Then they push it gently up through the
rectum into the lower colon. They can see inside the
Menopause: same day each month. colon through a small scope on the tube or on a
video monitor.
Preparation:
When you arrive for your sigmoidoscopy,
you will change into a hospital gown.
The doctor will ask you to lie on your side
on an exam table.
They will put a sheet over your body so
everything is covered except the test area.
Then, the doctor will gently place the small,
thin tube in your rectum.
They will use the tube to blow some air into
your colon.
The air blows it up a bit so it is easier to see
through the scope.
You might feel bloated or like you need to
go to the bathroom.
Next, the doctor will gently push the tube
up through your rectum into your lower
colon.
Position:
The left lateral (Sims) position
Watch out for:
Continued bleeding after biopsy.
Inflammation of the lining of your belly
(peritonitis)
A perforation (hole) in your intestinal wall,
which is a rare complication.
2.Mammography 7. CT Scan
Yearly Starting: Women ages 40 to 44 should have A computed tomography (CT or CAT) scan
the choice to start annual breast cancer screening allows doctors to see inside your body. It
with mammograms (x-rays of the breast) if they uses a combination of X-rays and a
wish to do so. Women age 45 to 54 should get computer to create pictures of your organs,
mammograms every year. Women 55 and older bones, and other tissues. It shows more
should switch to mammograms every 2 years, or detail than a regular X-ray.
can continue yearly screening They use a narrow X-ray beam that circles
around one part of your body. This
Preparation: provides a series of images from many
Tell your doctor or the technician if you're different angles. A computer uses this
pregnant or think that you could be. information to create a cross-sectional
Eat and take your medication as usual. picture. Like one piece in a loaf of bread,
Don't use body powder, cream, deodorant, this two-dimensional (2D) scan shows a
or lotion on your chest the day of the test. “slice” of the inside of your body.
They may interfere with the X-rays.
You'll need to take off all clothes above
your waist and put on a gown. It's a good
idea to wear a two-piece outfit and to skip
any jewelry.
3. Pap Smear 8. MRI
Sexually Active: All sexually active women are at
risk for contracting HPV and should get a Pap smear Remove:
at least every three years. The test doesn't detect implants or devices
other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It can
occasionally detect cell growth that indicates other remove all metallic objects from pockets
cancers, but it shouldn't be relied on for that and hair, as well as metallic jewelry.
purpose.
Purse, wallet, money clip, credit cards,
Routine: Pap testing every three years for women cards with magnetic strips
ages 21 to 65. Women age 30 and older can
consider Pap testing every five years if the
Electronic devices such as beepers, cell
procedure is combined with testing for HPV.
phones, smartphones and tablets
Hearing aids
Metallic jewelry and watches
Pens, paper clips, keys, coins
Hair barrettes, hairpins, hair clips and some
hair ointments
Shoes, belt buckles, safety pins
Any article of clothing that has metallic
fibers or threads, metallic zippers, buttons,
snaps, hooks, or underwire
If claustrophobic:
Ask questions beforehand. The more
educated and informed you are on the
specifics of the test, the less likely you are
to be surprised by something.
Listen to music. If the exam allows, ask
about listening to music.
Cover your eyes.
Breathe and meditate.
Ask for a blanket.
Stretch beforehand.
Take medication.
Contraindication:
Metallic implants.
Claustrophobia.
Pacemakers, although new protocols allow
imaging in selected cases.
MR-incompatible prosthetic heart valves.
Contrast allergy.
Body weight (MRI tables have specific
weight limitations)
4. Testicular Self- Exam 9. Bone Marrow Exam
During and after a warm shower
1. Stand in front of the mirror Site:
2. Support testicle with 1 hand and feel each The bone marrow fluid (aspirate) and tissue sample
with other hand (biopsy) are usually collected from the top ridge of
Normal: the back of a hipbone (posterior iliac crest).
The testicles should feel smooth, without
any lumps or bumps, and firm but not hard. Preparation:
You may feel a soft tube at the back of each What to eat. You can usually eat or drink
testicle, which is called the epididymis. normally before the test. Ask your health
Abnormal: care team ahead of time to make sure.
A small, hard lump (often about the size of
a pea) is felt on the surface of the testicle, Topics to talk about with your health care
or the testicle is swollen. team. You may not be able to take certain
medications, such as blood thinners, before
your procedure. Tell your health care team
about all medications and supplements you
take. Ask whether you should take them on
your procedure day. You should also bring
up any test concerns you have.
Insurance and cost. Before your
appointment, contact your insurance
provider. Find out how much of the
procedure’s costs it will cover and ask how
much you will have to pay.
Consent. The doctor's office or hospital will
ask you to sign a consent form when you
arrive for the procedure. This form states
that you understand the procedure’s
benefits and risks. The form also states that
you agree to the procedure. If you have
concerns about the procedure, talk with
your doctor before you sign.
Watch out for :
Fever of 101 degrees Fahrenheit/38.3
degrees Celsius or higher
Bleeding that does not stop easily
Unusual discharge or severe pain at the
needle insertion site
Any other signs or symptoms of infection
5. Digital Rectal Examination 10. Oncofetal Antigen
Check: examines a person's lower rectum, pelvis,
and lower belly. This test can help your doctor Normal during: embryogenesis and may increase
check for cancer and other health problems, with certain cancers, making them potentially
including: Prostate cancer in men. An abnormal useful tumor markers
mass in the anus or rectum.
Present in during fetal development but are found
Position: The easiest for the examiner is to have the in adults with certain kinds of cancer.
patient tuck the knees up to the chest, either in the
dorsal lithotomy position or the lateral recumbent Example:
position.
AFP
Sign of Prostate Cancer: alpha-fetoprotein, which is produced by
During the DRE, a doctor inserts a lubricated, hepatocellular carcinoma and some germ cell
gloved finger into the patient's rectum to feel for tumors
lumps, enlargements, or areas of hardness that CEA
might indicate prostate cancer. The procedure lasts carcinoembryonic antigen, which is elevated in
for less than minute and, while uncomfortable, people with colon cancer and other tumors
should cause no pain.
You might also like
- A Sigmoidoscopy Only Examines Up To The Sigmoid. The Most Distal Part of The Colon, While Colonoscopy Examines The Whole Large BowelDocument5 pagesA Sigmoidoscopy Only Examines Up To The Sigmoid. The Most Distal Part of The Colon, While Colonoscopy Examines The Whole Large BowelMa. Ydela MeradoresNo ratings yet
- DX - Thyroid CancerDocument15 pagesDX - Thyroid CancerCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma for Patients and their Supporters: Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeFrom EverandFast Facts: Advanced Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma for Patients and their Supporters: Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeNo ratings yet
- Bone Marrow BiopsyDocument10 pagesBone Marrow BiopsykvnOIfNo ratings yet
- How To Do A Breast SelfDocument7 pagesHow To Do A Breast Selfkassy yeonNo ratings yet
- Cancer Biology AssignmentDocument14 pagesCancer Biology AssignmentAnonymous nQUnkZaANo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests ProcedureDocument18 pagesDiagnostic Tests ProcedureRhodee Kristine DoñaNo ratings yet
- LYMweb0231Scans2017v1 2Document21 pagesLYMweb0231Scans2017v1 2Thenuka AvinashNo ratings yet
- Mri ScanDocument8 pagesMri ScanBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- MCU Patient Guide: What You Need to Know About a Micturating Cysto-Urethrogram TestDocument2 pagesMCU Patient Guide: What You Need to Know About a Micturating Cysto-Urethrogram TestBomasNo ratings yet
- Breast BiopsyDocument39 pagesBreast Biopsyiangould12No ratings yet
- Tests For Breast CancerDocument12 pagesTests For Breast CancerBeverly Bautista-OrtezaNo ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixDocument21 pagesCervical Cancer Is A Disease in Which Malignant (Cancer) Cells Form in The Tissues of The CervixnyseaNo ratings yet
- Ogexamination 110401040414 Phpapp02 PDFDocument26 pagesOgexamination 110401040414 Phpapp02 PDFDika RizkiardiNo ratings yet
- Tests and DiagnosisDocument2 pagesTests and DiagnosisAnonymous 8KN8IR1GTWNo ratings yet
- Laser Surgery: DescriptionDocument22 pagesLaser Surgery: DescriptionAnonymous qnE08HcNo ratings yet
- Cervical Punch Biopsy PILDocument2 pagesCervical Punch Biopsy PILAna BicosNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Cancer and Cervical CancerDocument19 pagesDiagnosis of Cancer and Cervical CancerJam Knows RightNo ratings yet
- 1 2 BRDocument25 pages1 2 BRrahmani bagherNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Head and Neck CancerDocument3 pagesDiagnosing Head and Neck CancerRaunakNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck CancerDocument3 pagesHead and Neck CancerRaunakNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis, and StagingDocument9 pagesDiagnosis, and StagingRio Taruna JatiNo ratings yet
- Manual Vacuum AspirationDocument3 pagesManual Vacuum AspirationDredd Alejo SumbadNo ratings yet
- Exploratory LaparotomyDocument1 pageExploratory LaparotomyShannen Madrid TinduganNo ratings yet
- CT Scanning InfoDocument1 pageCT Scanning InfoZahid IbkNo ratings yet
- What Is A Colposcopy?Document4 pagesWhat Is A Colposcopy?Marky Ponce PerezNo ratings yet
- BiopsyDocument22 pagesBiopsysrai60584No ratings yet
- Colposcopy and Cervical BiopsyDocument4 pagesColposcopy and Cervical BiopsyAries Chandra KencanaNo ratings yet
- Cuarteros, Richiel M.: Cervical Examination Definition and PurposeDocument7 pagesCuarteros, Richiel M.: Cervical Examination Definition and Purposejanna mae patriarcaNo ratings yet
- Prepare and Care For Clients Scheduled For Medical ProcedureDocument40 pagesPrepare and Care For Clients Scheduled For Medical ProcedureAbekail BryanNo ratings yet
- CT Scan IntroductionDocument5 pagesCT Scan Introductionankithns102No ratings yet
- CT Scan PatientDocument3 pagesCT Scan PatientMarta KitaNo ratings yet
- Diagnosing Lung CancerDocument6 pagesDiagnosing Lung CancerDenny LukasNo ratings yet
- Scan Tehc.Document23 pagesScan Tehc.senlerselvanNo ratings yet
- Endometrial Biopsy and CervicaDocument2 pagesEndometrial Biopsy and CervicaFahmi NugrahaNo ratings yet
- How Is Ovarian Cancer DiagnosedDocument2 pagesHow Is Ovarian Cancer DiagnosedWiedya kristiantiNo ratings yet
- Antinetal ScreaningDocument19 pagesAntinetal Screaningkololll lllknNo ratings yet
- What Is LymphomaDocument4 pagesWhat Is LymphomaMicaela BonaffiniNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis Procedures For Breast CancerDocument32 pagesDiagnosis Procedures For Breast CancerRhiza PagdangananNo ratings yet
- Tecnologias Preventivaz - ActENF - Clinica - CompressedDocument2 pagesTecnologias Preventivaz - ActENF - Clinica - Compressedadrianjv04No ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Procedure For CancerDocument11 pagesNon-Invasive Procedure For CancerFatma Nor Aljanna Macog100% (1)
- BiospyDocument2 pagesBiospyDenver TanhuanNo ratings yet
- TAH and BSO (TAH-BSO) Is Still Considered The Standard Operative Procedure For Patients With Endometrial CancerDocument3 pagesTAH and BSO (TAH-BSO) Is Still Considered The Standard Operative Procedure For Patients With Endometrial CancerVanessa VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cervical SmearDocument4 pagesCervical SmearSabrina11No ratings yet
- Cervical Cancer ScreeningDocument25 pagesCervical Cancer Screening6ixSideCreate MNo ratings yet
- The Colposcopy Examination: Cervical ScreeningDocument12 pagesThe Colposcopy Examination: Cervical ScreeningDivika ShilvanaNo ratings yet
- Pap SmearDocument8 pagesPap Smearsmv2No ratings yet
- What Is An UltrasoundDocument7 pagesWhat Is An UltrasoundStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Radiology Preps Sniff Test Chest FluorosDocument2 pagesRadiology Preps Sniff Test Chest FluorosRohith S RajuNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGYDocument3 pagesRADIOLOGYwendy carinoNo ratings yet
- Lumbar PunctureDocument5 pagesLumbar Puncturechaudharitrushar007No ratings yet
- Gastroenterologist in Northwest HoustonDocument1 pageGastroenterologist in Northwest HoustonHoward HamatNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedures in Respiratory DiseaseDocument26 pagesDiagnostic Procedures in Respiratory DiseaseChandanaNo ratings yet
- How to Do Breast and Testicular Self-ExamsDocument33 pagesHow to Do Breast and Testicular Self-ExamsMaJo GuanteroNo ratings yet
- VCUG (Voiding Cystourethrogram) What It IsDocument3 pagesVCUG (Voiding Cystourethrogram) What It IsNinaNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Junction AdenocarcinomaDocument17 pagesGastroesophageal Junction AdenocarcinomaAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Breast Self Examination BSEDocument33 pagesBreast Self Examination BSESoma Al-mutairiNo ratings yet
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Johns Hopkins Medicine 2Document1 pageComputed Tomography (CT) Scan Johns Hopkins Medicine 2Sandra EnyonamNo ratings yet
- Activity 2: Timeline of DumpawaDocument1 pageActivity 2: Timeline of DumpawaMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingDocument3 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Ambo, Pilita Gargar, Mary Rose Quiñonez, Anna Marie Rodriguez, Jam MikaDocument26 pagesAmbo, Pilita Gargar, Mary Rose Quiñonez, Anna Marie Rodriguez, Jam MikaMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Health HX&SBARDocument6 pagesHealth HX&SBARMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Common Oncology DrugsDocument2 pagesCommon Oncology DrugsMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementsDocument5 pagesAirway ManagementsMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- J.B.'s Suicidal Ideation and Depression TreatmentDocument6 pagesJ.B.'s Suicidal Ideation and Depression TreatmentMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Cancer of the Female Reproductive: Signs, Diagnosis and Nursing CareDocument9 pagesCancer of the Female Reproductive: Signs, Diagnosis and Nursing CareMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs and Common Nursing ProceduresDocument6 pagesVital Signs and Common Nursing ProceduresMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Treating Borderline Personality DisorderDocument7 pagesTreating Borderline Personality DisorderMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingDocument3 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in Critical CarenursingMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementsDocument5 pagesAirway ManagementsMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Premarital SexDocument2 pagesPremarital SexMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Airway Obstruction and Hemorrhage ManagementDocument17 pagesAirway Obstruction and Hemorrhage ManagementMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Imci Clinicalpaper PneumoniaDocument12 pagesImci Clinicalpaper PneumoniaMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Caring for Clients with Mood DisordersDocument7 pagesCaring for Clients with Mood DisordersMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Caring for Clients with Maladaptive BehaviorsDocument13 pagesCaring for Clients with Maladaptive BehaviorsMary Rose Silva Gargar100% (1)
- Premarital SexDocument2 pagesPremarital SexMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Aids and Substance Use and AbuseDocument2 pagesAids and Substance Use and AbuseMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Premarital SexDocument2 pagesPremarital SexMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer 1Document10 pagesBreast Cancer 1Mary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Analysis About Typhoon HaiyanDocument2 pagesAnalysis About Typhoon HaiyanMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy 1Document7 pagesEctopic Pregnancy 1Mary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Saint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan FormDocument10 pagesSaint Paul University Dumaguete College of Nursing Nursing Care Plan FormMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Dengue FeverDocument76 pagesCase Study On Dengue FeverMary Rose Silva Gargar0% (1)
- Dangers of SMOKINGDocument2 pagesDangers of SMOKINGMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument1 pageAcute Glomerulonephritis Diagnosis & TreatmentMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- MeningitisDocument1 pageMeningitisMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy Clinical PaperDocument30 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Clinical PaperMary Rose Silva GargarNo ratings yet
- Milestone in The Evolution of EndosDocument11 pagesMilestone in The Evolution of EndosGleison Elias SilvaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Colonoscopy Screening On RisksDocument10 pagesEffect of Colonoscopy Screening On RisksAnderson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Asge Primer 2017 Pgs117 125 Single PageDocument9 pagesAsge Primer 2017 Pgs117 125 Single PageMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Running A Colorectal Surgery ServiceDocument21 pagesRunning A Colorectal Surgery ServicebloodsphereNo ratings yet
- New Mock 1-2022Document29 pagesNew Mock 1-2022nemalijyothsna3No ratings yet
- MD Questions 3Document38 pagesMD Questions 3Shell VenkatNo ratings yet
- Colon cancer screening recommendations and barriersDocument7 pagesColon cancer screening recommendations and barriersKen Ancheta LagayadaNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis COLON CANCERDocument4 pagesCase Analysis COLON CANCERBelle A. Basilio50% (2)
- GastrolentrologyDocument38 pagesGastrolentrologyshaik.hossain2No ratings yet
- Colonoscopy For DummiesDocument79 pagesColonoscopy For Dummiesmike.krawulski9224100% (3)
- Surgery of Colon and Rectum for Cancer, Diverticulitis and MoreDocument12 pagesSurgery of Colon and Rectum for Cancer, Diverticulitis and MoreNarita Ekananda Agesta RaswitaNo ratings yet
- LITERATURE REVIEW ON ENDOSCOPY EXAMINATIONDocument29 pagesLITERATURE REVIEW ON ENDOSCOPY EXAMINATIONShenaquitaIvandraNo ratings yet
- Signs and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, IncludesDocument18 pagesSigns and Symptoms: Colorectal Cancer, Also Called Colon Cancer or Large Bowel Cancer, Includesphvega06No ratings yet
- Colon, Rectum & AnusDocument6 pagesColon, Rectum & AnusLeikkaNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument14 pagesColon Cancerrosalinda100% (1)
- Rectal CancerDocument20 pagesRectal CancerSantosh BabuNo ratings yet
- Intestinal DisordersDocument11 pagesIntestinal DisordersJessica0% (1)
- 3 2 1 Code It 5th Edition Green Solutions Manual 1Document31 pages3 2 1 Code It 5th Edition Green Solutions Manual 1elizabeth100% (28)
- New BoleanDocument3 pagesNew BoleanSachi AnandNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Flexible Endoscopy: Basic SkillsDocument5 pagesAn Introduction To Flexible Endoscopy: Basic SkillsDzikri TakariyantiNo ratings yet
- Sigmoidoscopy Preparation Instructions: How Do I Plan For The Procedure?Document5 pagesSigmoidoscopy Preparation Instructions: How Do I Plan For The Procedure?Mani KandanNo ratings yet
- GI Procedures and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesGI Procedures and Nursing ResponsibilitiesShaina DiyaNo ratings yet
- Sigmoidoscopy and Colonoscopy Request FormDocument2 pagesSigmoidoscopy and Colonoscopy Request FormAbdullahi AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assessment of GI SystemDocument40 pagesAssessment of GI SystemJeffRy SinyOe100% (1)
- Ulcerative ColitisDocument7 pagesUlcerative ColitisShaira Anne Fuentes BaroniaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Staging of Colorectal CancerDocument20 pagesClinical Presentation, Diagnosis, and Staging of Colorectal CancerJose Luis Marin CatacoraNo ratings yet
- Handout For PatientsDocument1 pageHandout For Patientsapi-640781324No ratings yet
- Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Staging of Colorectal Cancer UpToDateDocument39 pagesClinical Presentation Diagnosis and Staging of Colorectal Cancer UpToDateSean SialanaNo ratings yet
- Colonoscopi IndicationDocument26 pagesColonoscopi IndicationTony HardianNo ratings yet
- Colorectal Screening AlgorithmDocument12 pagesColorectal Screening Algorithmsavvy_as_98No ratings yet