Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas and tables for AP Statistics
Uploaded by
Bao GanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas and tables for AP Statistics
Uploaded by
Bao GanCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas and Tables for AP Statistics
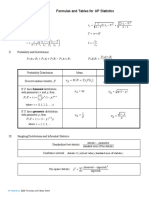
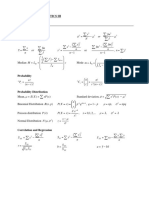
I. Descriptive Statistics
1 ∑ xi 1 2 ∑ ( xi − x )2
x = ∑ xi = s=
x ∑ ( xi − x )=
n n n −1 n −1
ŷ= a + bx y= a + bx
1 x − x yi − y sy
=r ∑ i b=r
n − 1 s x s y sx
II. Probability and Distributions
P ( A ∩ B)
P ( A ∪ B )= P ( A ) + P ( B ) − P ( A ∩ B ) P ( A | B) =
P ( B)
Probability Distribution Mean Standard Deviation
µ X = E ( X ) = ∑ xi P ( xi ) 2
Discrete random variable, X σ X = ∑ ( xi − µ X ) P ( xi )
If 𝑋𝑋 has a binomial distribution
with parameters n and p, then:
µ X = np σX
= np (1 − p )
n
P( X= x= ) p x (1 − p )n − x
x
where x = 0, 1, 2, 3, , n
If 𝑋𝑋 has a geometric distribution
1 1− p
with parameter p, then: µX = σX =
p p
P ( X= x= ) (1 − p ) x −1 p
where x = 1, 2, 3,
III. Sampling Distributions and Inferential Statistics
statistic − parameter
Standardized test statistic:
standard error of the statistic
Confidence interval: statistic ± ( critical value )( standard error of statistic )
( observed − expected )2
Chi-square statistic: χ 2 = ∑ expected
AP Statistics 2020 Formulas and Tables Sheet
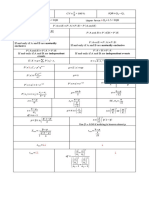
III. Sampling Distributions and Inferential Statistics (continued)
Sampling distributions for proportions:
Random Parameters of Standard Error*
Variable Sampling Distribution of Sample Statistic
For one
population: µ p̂ = p p (1 − p ) p̂ (1 − p̂ )
σ p̂ = s p̂ =
p̂ n n
For two p̂1 (1 − pˆ1 ) pˆ 2 (1 − p̂2 )
populations:
µ pˆ − pˆ= p1 − p2
σ pˆ − pˆ
= +
) s pˆ1 − pˆ 2
p1 (1 − p1 ) p2 (1 − p2= n1
+
n2
pˆ1 − pˆ 2 1 2
n1 n2
1 2
When p1 = p2 is assumed:
1 1
s pˆ ˆ = pˆ c (1 − pˆ c ) +
1 − p2 n
1 n2
X1 + X 2
where p̂c =
n1 + n2
Sampling distributions for means:
Random Standard Error*
Parameters of Sampling Distribution
Variable of Sample Statistic
For one
µX = µ σ s
population: σX = sX =
n n
X
For two
populations: µX = µ1 − µ2 σ12 σ 22 s12 s22
1− X2 σX = + s X −= +
X1 − X 2 1 −X 2 n1 n2 1 X 2 n1 n2
Sampling distributions for simple linear regression:
Random Standard Error*
Parameters of Sampling Distribution
Variable of Sample Statistic
s
sb = ,
µ =β σ sx n − 1
For slope: σb = ,
b
σx n 2
b ∑ ( yi − yˆi )
2 where s =
∑ ( xi − x ) n−2
where σ x = 2
n ∑ ( xi − x )
and s x =
n −1
*Standard deviation is a measurement of variability from the theoretical population. Standard error is the estimate of the standard deviation. If the
standard deviation of the statistic is assumed to be known, then the standard deviation should be used instead of the standard error.
AP Statistics 2020 Formulas and Tables Sheet
You might also like
- Applied Statistics Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesApplied Statistics Cheat Sheetkaungwaiphyo89No ratings yet
- Formulas and tables for AP StatisticsDocument6 pagesFormulas and tables for AP Statisticsbella lubbockNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument11 pagesFormulae Sheetthyanh.vuNo ratings yet
- Midterm Formula SheetDocument3 pagesMidterm Formula SheetShahd AlhamaydaNo ratings yet
- Formulas Statistics II: ∫ = E (X) = ∫ = E (X) = ∫ ∫ Γ (p + 1) =Document1 pageFormulas Statistics II: ∫ = E (X) = ∫ = E (X) = ∫ ∫ Γ (p + 1) =pablo.sazhuangNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Answer Key Chapter 8 16 PDFDocument102 pagesCost Accounting Answer Key Chapter 8 16 PDFByul Productions71% (7)
- Project - Time Series Forecasting - Rajendra M BhatDocument33 pagesProject - Time Series Forecasting - Rajendra M BhatRajendra Bhat80% (10)
- STAT155 Midterm FormulaDocument3 pagesSTAT155 Midterm Formulatariqueshams66No ratings yet
- 978-1260004755 1260004759 Managerial EconomicsDocument17 pages978-1260004755 1260004759 Managerial EconomicsReccebacaNo ratings yet
- Formula sheet for descriptive statistics, probability, and distributionsDocument2 pagesFormula sheet for descriptive statistics, probability, and distributionsJane Chun100% (1)
- Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesStatistics FormulasJayson S. Verdeflor100% (1)
- Granny Flores de PrimaveraDocument10 pagesGranny Flores de PrimaveraYessica Chamorro100% (1)
- Dewa QuestionDocument16 pagesDewa Questionjayapal100% (2)
- Aa290523030002u RC11052023Document3 pagesAa290523030002u RC11052023DEVRAJU S0% (1)
- Ch.23. Measuring A Nation's IncomeDocument24 pagesCh.23. Measuring A Nation's IncomeNa MỹNo ratings yet
- Summary MAS291Document9 pagesSummary MAS291Hiếu PhạmNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics - Formulas and TablesDocument6 pagesAP Statistics - Formulas and TablesJinhui ZhengNo ratings yet
- Hombres y BestiasDocument223 pagesHombres y BestiasPaul GuillenNo ratings yet
- Formulas and tables for AP StatisticsDocument6 pagesFormulas and tables for AP StatisticsHafizNo ratings yet
- AP Stat Free Response QuestionsDocument22 pagesAP Stat Free Response QuestionsLOUELLA JADE SUAREZNo ratings yet
- Ap23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16Document25 pagesAp23 FRQ Statistics - Pdf#page 16malvin.fedyanoNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SDocument2 pagesLinear Transformations If Y Ax + B, Then y A X+B and SmichaelNo ratings yet
- North South University Mat361 Total Marks-30 (Time - 70 Min + 10min)Document8 pagesNorth South University Mat361 Total Marks-30 (Time - 70 Min + 10min)Dipta Kumar Nath 1612720642No ratings yet
- OPMT 1120 Formulae Sheet for Final ExamDocument3 pagesOPMT 1120 Formulae Sheet for Final Examneha.gandhaNo ratings yet
- Materials SB: N) K X XDocument11 pagesMaterials SB: N) K X XNgô Hoàng Bích KhaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetSwarnabha RayNo ratings yet
- Fórmulas Examen (1) 2Document1 pageFórmulas Examen (1) 2acatataacatataNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet: (I) Descriptive Statistics (II) ProbabilityKent BrouwerNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics Formula Sheet - Probability and Statistics FormulasDocument2 pagesAP Statistics Formula Sheet - Probability and Statistics FormulasRocket FireNo ratings yet
- Probability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Document4 pagesProbability Equations: P (A B) P (A) +P (B)Mike SerafinoNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics OverviewDocument3 pagesDescriptive Statistics OverviewSergio Reinoso FuertesNo ratings yet
- mcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02Document19 pagesmcd1110 Sample Test 2b 2012 02dharma alexanderNo ratings yet
- Tong Hop Cong Thuc Mt2013 Lop Thay DungclcDocument9 pagesTong Hop Cong Thuc Mt2013 Lop Thay Dungclcaccphugr3No ratings yet
- σ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Document2 pagesσ p q ≤ n k x a n k p q np (1−p) : ĐÀO QUỐC THÁI - SE1508 - HE150059Quốc Thái ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Summary of Probability 2 1Document3 pagesSummary of Probability 2 1PeArL PiNkNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetSimthembileNo ratings yet
- Formulario Certamen 1Document2 pagesFormulario Certamen 1Ignacia OlivaresNo ratings yet
- P (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXDocument2 pagesP (B !A) P (B) P (A!B) P (B) P (A!B) : 1 F (X) (X) DXFrancisco Javier Colli PintoNo ratings yet
- List of Formulae and Normal TableDocument3 pagesList of Formulae and Normal Table梦魇spiritNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics FormulasDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics FormulasmichaelNo ratings yet
- 1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariableDocument8 pages1 Statistical Project: 2.1 1 Qualitative VariablehelinNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet STAT 2066Document4 pagesFormula Sheet STAT 2066Shane TeddyNo ratings yet
- احصاء د.رياض بابل (1) 1Document128 pagesاحصاء د.رياض بابل (1) 1brhmNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument5 pagesEquation SheetArisha BasheerNo ratings yet
- List of FormulasDocument7 pagesList of Formulastimeijkhout92No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument3 pagesSummaryKHÁNH NGÔ ĐÌNH BẢONo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Math236Document2 pagesFormula Sheet Math236Arvin MoNo ratings yet
- S1 T01 Tabla DistribucionesDocument2 pagesS1 T01 Tabla DistribucionesPruebasNo ratings yet
- Formulas Statistics (2021)Document4 pagesFormulas Statistics (2021)BojackyNo ratings yet
- Mdm4u Fianl Exam Formula PDFDocument1 pageMdm4u Fianl Exam Formula PDFEliz SawNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution 2Document14 pagesPoisson Distribution 2KashafNo ratings yet
- FORMULAS Eng 2020FDocument1 pageFORMULAS Eng 2020FAkash TomNo ratings yet
- Summary MAS291Document10 pagesSummary MAS291Anh TrầnNo ratings yet
- Est Bloque IIDocument2 pagesEst Bloque IIm4nu.k1r0No ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument3 pagesFormula SheetgogogogoNo ratings yet
- IMOmath - Some Sums of Legendre's SymbolsDocument4 pagesIMOmath - Some Sums of Legendre's SymbolsThang ThangNo ratings yet
- CSU Formula SheetDocument1 pageCSU Formula SheetAustin EllisNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Mar 2019 MemoDocument13 pagesMathematics Mar 2019 MemoMatthew MatiyengaNo ratings yet
- Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesCheat SheetChristos StiapisNo ratings yet
- Formulas Stat QM3 - 1617Document3 pagesFormulas Stat QM3 - 1617Wayne DorsonNo ratings yet
- Practice 2 Spring 2020 BISDocument3 pagesPractice 2 Spring 2020 BISAyoub OumousNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tables and Charts 1Document26 pagesStatistical Tables and Charts 1Hoàng Anh KhoaNo ratings yet
- Statistical Tables and Charts PDFDocument26 pagesStatistical Tables and Charts PDFMinh TríNo ratings yet
- AP 2015 Statistics (1)Document65 pagesAP 2015 Statistics (1)sam sunNo ratings yet
- handbook_statDocument2 pageshandbook_statmytu261105No ratings yet
- STA360/601 Midterm SolutionsDocument6 pagesSTA360/601 Midterm SolutionsTanjil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Generalized Linear Models: FX Axb C DX Axb C DXDocument11 pagesGeneralized Linear Models: FX Axb C DX Axb C DXAishat OmotolaNo ratings yet
- Tables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of The Legendre Functions P—½+it(x): Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Regression: Statistics 203: Introduction To Regression and Analysis of VarianceDocument2 pagesNonlinear Regression: Statistics 203: Introduction To Regression and Analysis of VarianceBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT 203: Statistical MethodsDocument5 pagesSTAT 203: Statistical MethodsJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Regression Models: We Have Usually Assumed Regression Is of The FormDocument2 pagesNonlinear Regression Models: We Have Usually Assumed Regression Is of The FormBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-homework1 Homework8Document1 pageSTAT202-homework1 Homework8Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesDocument1 pageSTAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesBao GanNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise #45: Repeat The Previous Exercise Using All 60 ColumnsDocument4 pagesIn Class Exercise #45: Repeat The Previous Exercise Using All 60 ColumnsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Habits for Success in Stat 202Document2 pagesWeekly Habits for Success in Stat 202Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear regression modelsDocument2 pagesNonlinear regression modelsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Computer Labs: Purpose of LabDocument2 pagesComputer Labs: Purpose of LabBao GanNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis (DA) Projects: Exam CoverageDocument2 pagesData Analysis (DA) Projects: Exam CoverageBao GanNo ratings yet
- What To Do?: in Some Cases, It Is Possible To Linearize To Get The Original Model. SupposeDocument2 pagesWhat To Do?: in Some Cases, It Is Possible To Linearize To Get The Original Model. SupposeBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project5Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project5Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project6Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project6Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Iteration & Distribution: Want To Choose As Follows ArgminDocument2 pagesIteration & Distribution: Want To Choose As Follows ArgminBao GanNo ratings yet
- Lab Day and TimeDocument2 pagesLab Day and TimeBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument47 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument4 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus STA 36-202 - Statistics & Data Science Methods Spring 2018Document15 pagesSyllabus STA 36-202 - Statistics & Data Science Methods Spring 2018Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument47 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
- Stat 201 Project 1 AnalysisDocument9 pagesStat 201 Project 1 AnalysisBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesDocument1 pageSTAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesBao GanNo ratings yet
- Euclidean Distance: Q P DistDocument4 pagesEuclidean Distance: Q P DistBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-homework1 Homework2Document2 pagesSTAT202-homework1 Homework2Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Data Mining: Based in Part On Slides From Textbook, Slides of Susan HolmesDocument21 pagesStatistics 202: Data Mining: Based in Part On Slides From Textbook, Slides of Susan HolmesBao GanNo ratings yet
- Sections 1 and 6: Li Li Section 2: NaichenDocument4 pagesSections 1 and 6: Li Li Section 2: NaichenBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project12Document3 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project12Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project7Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project7Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project6Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project6Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Stat 202: Hypothesis Testing Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesStat 202: Hypothesis Testing Practice ProblemsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Cost Total Opportunity Cost Balance Resources Specialization Exchange Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice A 18 6 B 20 5Document2 pagesCost Total Opportunity Cost Balance Resources Specialization Exchange Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice Car Rice A 18 6 B 20 5Tonny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Camarilla EquationDocument4 pagesCamarilla Equationmarcosfa81No ratings yet
- ExpleoDocument13 pagesExpleog_sivakumarNo ratings yet
- M10 Laying MasonryDocument187 pagesM10 Laying Masonrymustied mohammedNo ratings yet
- Inbound 8143484023258758048Document1 pageInbound 8143484023258758048mgilangfreeNo ratings yet
- Var Korea2012Document128 pagesVar Korea2012SERGIO REQUENANo ratings yet
- Data Support RBMDocument1 pageData Support RBMLuthfi shinoNo ratings yet
- Procedures in Recording Business Transaction in A 2-ColumnDocument12 pagesProcedures in Recording Business Transaction in A 2-ColumnPauline Pearl FranciaNo ratings yet
- Statistics at A Glance Contract: NLT / Efrp Open InterestDocument32 pagesStatistics at A Glance Contract: NLT / Efrp Open InterestWilson KuyahNo ratings yet
- Var LaborDocument2 pagesVar LaborFarizal RiestaNo ratings yet
- Risk Analysis, Real Options and Capital Budgeting PDFDocument62 pagesRisk Analysis, Real Options and Capital Budgeting PDFAMIT SINHA MA ECO DEL 2022-24No ratings yet
- Accounting & Marketing Students ListDocument9 pagesAccounting & Marketing Students ListJustine Brylle DomantayNo ratings yet
- Gold Value Framework: Your Gateway To Understanding Gold PerformanceDocument11 pagesGold Value Framework: Your Gateway To Understanding Gold PerformanceHamlet GalvezNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - Measuring Absolute Poverty PDFDocument13 pages6.2 - Measuring Absolute Poverty PDFalabwalaNo ratings yet
- How To Fill Up Product Replacement FormDocument7 pagesHow To Fill Up Product Replacement FormDoraaina100% (1)
- Government Intervention in Economies: Benefits and CriticismsDocument2 pagesGovernment Intervention in Economies: Benefits and CriticismsDominique KristelleNo ratings yet
- Phillips Customer Application - EncryptedDocument2 pagesPhillips Customer Application - EncryptedAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Option Pricing Models: The Binomial ModelDocument10 pagesChapter 4: Option Pricing Models: The Binomial ModelTami DoanNo ratings yet
- Discussion Acctng For MaterialsDocument3 pagesDiscussion Acctng For MaterialsKim Arvin DalisayNo ratings yet
- EMB Capitol Interior Fit Out (Phase 2)Document2 pagesEMB Capitol Interior Fit Out (Phase 2)Jet ArcaNo ratings yet
- IndiGo - WikipediaDocument4 pagesIndiGo - Wikipediashraddha kumariNo ratings yet
- Using The Balanced Scorecard As A Strategic Management SystemDocument19 pagesUsing The Balanced Scorecard As A Strategic Management Systemkaran jainNo ratings yet