Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stat 202: Hypothesis Testing Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Bao Gan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesThis document provides 5 practice problems for hypothesis testing. Problem 1 asks the reader to calculate the power of a test where the null hypothesis is that a population mean is greater than or equal to 80, the alternative is that the mean is less than 80, and a sample of size 20 from a normal distribution with standard deviation 15 has a mean of 72. Problem 2 asks the reader to test if a new SAT prep program is more effective than a traditional program using sample data and a significance level of 0.05. Problem 3 asks the reader to test for a difference in failure pressures of two designs for an air tank using sample data and a significance level of 0.1. Problem 4 asks the reader to test if a new golf ball
Original Description:
Original Title
STAT202-lecture5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides 5 practice problems for hypothesis testing. Problem 1 asks the reader to calculate the power of a test where the null hypothesis is that a population mean is greater than or equal to 80, the alternative is that the mean is less than 80, and a sample of size 20 from a normal distribution with standard deviation 15 has a mean of 72. Problem 2 asks the reader to test if a new SAT prep program is more effective than a traditional program using sample data and a significance level of 0.05. Problem 3 asks the reader to test for a difference in failure pressures of two designs for an air tank using sample data and a significance level of 0.1. Problem 4 asks the reader to test if a new golf ball
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views3 pagesStat 202: Hypothesis Testing Practice Problems
Uploaded by
Bao GanThis document provides 5 practice problems for hypothesis testing. Problem 1 asks the reader to calculate the power of a test where the null hypothesis is that a population mean is greater than or equal to 80, the alternative is that the mean is less than 80, and a sample of size 20 from a normal distribution with standard deviation 15 has a mean of 72. Problem 2 asks the reader to test if a new SAT prep program is more effective than a traditional program using sample data and a significance level of 0.05. Problem 3 asks the reader to test for a difference in failure pressures of two designs for an air tank using sample data and a significance level of 0.1. Problem 4 asks the reader to test if a new golf ball
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Stat 202: Hypothesis Testing Practice Problems
1. Consider testing H0: µ ≥ 80 vs. H1: µ < 80 where µ is the
mean of a normally distributed population having standard
deviation σ = 15. The hypothesis will be tested at the α =
0.01 level of significance, using a sample of size n = 20.
If in fact µ is equal to 72, what is the probability that the
test will correctly reject the null hypothesis? In other
words, find the power of the test at µ = 72.
2. (Based on text problem 11.37) A study has been conducted
to examine the effectiveness of a new experimental
program for preparing high school students for the SAT.
Eighty students have been randomly divided into two
groups of forty. One group receives the experimental
program, and when they take the SAT the sample average
score is equal to X = 1041.10 and the standard deviation of
scores is 130.30. The second group receives a traditional
program. They end up with an average score of X =
1012.48 with a standard deviation of 79.51. Does this
result provide evidence that the new program is more
effective than the traditional program? Test at the α = 0.05
level of significance.
3. (Based on text problem 11.69) A compressor manufacturer
is testing two different designs for an air tank. Testing
involves observing how much pressure a tank can
withstand before it bursts. For a sample of four tanks of
Design A, the average pressure to failure is 1400 psi with a
standard deviation of 250 psi. For a sample of six tanks of
Design B, the average pressure to failure is 1620 psi with a
standard deviation of 230 psi.
Test for a difference in mean pressure to failure for the two
designs, at the α = 0.10 level of significance. Assume that
the two populations of interest are normally distributed and
have the same variance.
4. (Based on text problem 11.80) In an experiment comparing
a new long-distance golf ball with the conventional design,
each of 20 golfers hits one drive with each ball. For each
golfer we calculate d = x1 – x2, where x1 is the distance the
new ball is hit and x2 is the distance the old ball is hit. The
average difference is calculated to equal 9.3, the standard
deviation of differences is 10.5.
Assuming that differences are normally distributed, test to
see if the new ball goes further. Use α = 0.01.
5. (Based on text problem 11.86) A maintenance engineer has
been approached by a supplier who promises less downtime
for machines using its new super lubricant.
The engineer is skeptical of the supplier’s claim, but agrees
to test it. Two samples of machines will be tested for a
month (with and without the new lubricant) and for each
sample we will observe the proportion of machines that are
out of service for more than one hour.
(a) State an appropriate null and alternative hypothesis.
120 machines are randomly selected for the first sample
and are maintained with the new lubricant. 20% are out of
service for more than an hour during the month of the test.
For the second control group sample of 100 machines, the
previous lubricant is used and 30% are out of service for
more than one hour.
(b) Perform the test set up in Part (a) at the α = 0.05 level
of significance.
You might also like
- Assignment 6 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 6 - Engineering Statistics - Spring 2019 PDFSohnal RameezNo ratings yet
- Sample Sizes for Clinical, Laboratory and Epidemiology StudiesFrom EverandSample Sizes for Clinical, Laboratory and Epidemiology StudiesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 (2) - Engineering Statistics PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment 4 (2) - Engineering Statistics PDFNamra FatimaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Critical RegionDocument7 pagesCritical RegionmustafaNo ratings yet
- Factorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodFrom EverandFactorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodNo ratings yet
- CE504 - HW2 - Dec 27, 20Document4 pagesCE504 - HW2 - Dec 27, 20Fofo ElorfiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 - Hypothesis TestingDocument12 pagesTutorial 3 - Hypothesis TestingNoorNabila0% (1)
- Final Tut-6Document2 pagesFinal Tut-6nikhilgyl93No ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument3 pagesAssignmentQazi JunaidNo ratings yet
- Prob Stats Chapter 9 ReviewDocument6 pagesProb Stats Chapter 9 ReviewNhàn Nhạt NhẽoNo ratings yet
- P&S Unit-II 2024Document4 pagesP&S Unit-II 2024kartheekmurala19No ratings yet
- Fstats ch3Document22 pagesFstats ch3ROHIT9044782102No ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 2: Statistical Methods, 2015 Second Year, Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet 2: Statistical Methods, 2015 Second Year, Chemical Engineering DepartmentDebasmita KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 10Document2 pagesProblem Set 10KritikaPandeyNo ratings yet
- MA311 Tutorial 3Document2 pagesMA311 Tutorial 3kiruba karanNo ratings yet
- I3 TD4 Test 2 SamplesDocument5 pagesI3 TD4 Test 2 SamplesChhin VisalNo ratings yet
- Z & T Tests, ANOVA, Correlation: Hypothesis Testing ExamplesDocument33 pagesZ & T Tests, ANOVA, Correlation: Hypothesis Testing ExamplesJovenil BacatanNo ratings yet
- Rev 5 Hypothesis Tests STPM T3Document3 pagesRev 5 Hypothesis Tests STPM T3KwongKH50% (2)
- Statps8 2023 SolDocument8 pagesStatps8 2023 SolAleyna KüçükerNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Extra ProblemsDocument3 pagesProbability and Statistics Extra ProblemsAdil Rashid0% (1)
- Stt315 Quiz 7 SolutionsDocument4 pagesStt315 Quiz 7 SolutionsYasir Al-kathiriNo ratings yet
- Stat Fig8Document10 pagesStat Fig8Christine Louis Dulay JandaNo ratings yet
- Test of Hyp Formula & ProbsDocument12 pagesTest of Hyp Formula & ProbsGnanarajNo ratings yet
- Statistics - AssignmentDocument7 pagesStatistics - AssignmentAmlanjyoti Bhattacharjee71% (7)
- Unit-4 - Hypothesis TestingDocument24 pagesUnit-4 - Hypothesis TestingMANTHAN JADHAVNo ratings yet
- Statps8 2023Document6 pagesStatps8 2023Aleyna KüçükerNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Diabetes Drug TrialDocument33 pagesSix Sigma Diabetes Drug TrialPriyaprasad PandaNo ratings yet
- QBM FinalDocument8 pagesQBM Finalsafura aliyevaNo ratings yet
- Binomial DistributionDocument8 pagesBinomial Distributionchandana19926290% (1)
- All DMAIC Paper For B BDocument125 pagesAll DMAIC Paper For B Bdeepu200778No ratings yet
- Tugas 5 Design of ExperimentDocument8 pagesTugas 5 Design of ExperimentRenaldy SaragihNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples Ch10Document8 pagesSolved Examples Ch10aman_nsuNo ratings yet
- IE 423 - HMW 1Document6 pagesIE 423 - HMW 1Yasemin YücebilgenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 (Chap 4)Document12 pagesExercise 4 (Chap 4)peikee100% (1)
- HND 16Document21 pagesHND 16Bright AjibadeNo ratings yet
- Math Test 2Document3 pagesMath Test 2Julian BelayNo ratings yet
- Ve401 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering: Sample Questions For The Final ExamDocument4 pagesVe401 Probabilistic Methods in Engineering: Sample Questions For The Final ExamEnji HuNo ratings yet
- Probability: HypothesisDocument35 pagesProbability: Hypothesisphoenix102No ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing GuideDocument32 pagesHypothesis Testing GuideKyohyunNo ratings yet
- UTM STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 EXERCISESDocument3 pagesUTM STATISTICS CHAPTER 4 EXERCISESAbdullah BelasegakNo ratings yet
- UCLA Statistics Spring 2003 Homework 4Document2 pagesUCLA Statistics Spring 2003 Homework 4rohitrgt4uNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing GDocument28 pagesHypothesis Testing GRenee Jezz LopezNo ratings yet
- 10 Z TestDocument20 pages10 Z TestNecil PaderanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Chap 4Document11 pagesExercise 4 Chap 4Rheann Marie BugtongNo ratings yet
- BA 578 Live Fin Set2Document17 pagesBA 578 Live Fin Set2Sumana Salauddin100% (1)
- P&S Important QuestionDocument1 pageP&S Important QuestionPartha SarathyNo ratings yet
- Chi-Square Test For Variance or Standard DeviationDocument3 pagesChi-Square Test For Variance or Standard DeviationMarvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- Ae2223-II Exam 150414 FinalDocument14 pagesAe2223-II Exam 150414 FinalAhmed Valentin KassemNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 & Unit 5Document59 pagesUnit 4 & Unit 5Sankeerth Chary0% (1)
- Individual Assignment AnswerDocument4 pagesIndividual Assignment AnswerChee HongNo ratings yet
- UpgradDocument8 pagesUpgradLata SurajNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis Testing For AnalysisDocument8 pagesHypothesis Testing For AnalysisforecellNo ratings yet
- Hw8 and Hw9 - Ms2200Document2 pagesHw8 and Hw9 - Ms2200KoshkaNo ratings yet
- Description 2Document33 pagesDescription 2Meow MeowNo ratings yet
- Statistics: 1.3 The Chi-Squared Test For Two-Way Tables: Rosie Shier. 2004Document4 pagesStatistics: 1.3 The Chi-Squared Test For Two-Way Tables: Rosie Shier. 2004JJwilliamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ProblemsCO1Document34 pagesTutorial ProblemsCO1Haripriya KuchipudiNo ratings yet
- PGP14060 QM S5Document3 pagesPGP14060 QM S5eshika.jain2512No ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document4 pagesAssignment 4sandeep BhanotNo ratings yet
- STAT 203: Statistical MethodsDocument5 pagesSTAT 203: Statistical MethodsJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear regression modelsDocument2 pagesNonlinear regression modelsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Weekly Habits for Success in Stat 202Document2 pagesWeekly Habits for Success in Stat 202Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Regression Models: We Have Usually Assumed Regression Is of The FormDocument2 pagesNonlinear Regression Models: We Have Usually Assumed Regression Is of The FormBao GanNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Regression: Statistics 203: Introduction To Regression and Analysis of VarianceDocument2 pagesNonlinear Regression: Statistics 203: Introduction To Regression and Analysis of VarianceBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesDocument1 pageSTAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesBao GanNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis (DA) Projects: Exam CoverageDocument2 pagesData Analysis (DA) Projects: Exam CoverageBao GanNo ratings yet
- Lab Day and TimeDocument2 pagesLab Day and TimeBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project6Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project6Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Computer Labs: Purpose of LabDocument2 pagesComputer Labs: Purpose of LabBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument4 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
- What To Do?: in Some Cases, It Is Possible To Linearize To Get The Original Model. SupposeDocument2 pagesWhat To Do?: in Some Cases, It Is Possible To Linearize To Get The Original Model. SupposeBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-homework1 Homework8Document1 pageSTAT202-homework1 Homework8Bao GanNo ratings yet
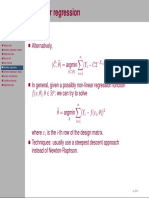
- Iteration & Distribution: Want To Choose As Follows ArgminDocument2 pagesIteration & Distribution: Want To Choose As Follows ArgminBao GanNo ratings yet
- Stat 201 Project 1 AnalysisDocument9 pagesStat 201 Project 1 AnalysisBao GanNo ratings yet
- In Class Exercise #45: Repeat The Previous Exercise Using All 60 ColumnsDocument4 pagesIn Class Exercise #45: Repeat The Previous Exercise Using All 60 ColumnsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Data Mining: Based in Part On Slides From Textbook, Slides of Susan HolmesDocument21 pagesStatistics 202: Data Mining: Based in Part On Slides From Textbook, Slides of Susan HolmesBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument47 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
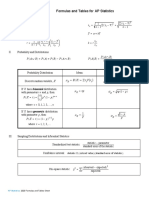
- Formulas and tables for AP StatisticsDocument2 pagesFormulas and tables for AP StatisticsBao GanNo ratings yet
- Statistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelDocument47 pagesStatistics 202: Statistical Aspects of Data Mining Professor Rajan PatelBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-homework1 Homework2Document2 pagesSTAT202-homework1 Homework2Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project5Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project5Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Euclidean Distance: Q P DistDocument4 pagesEuclidean Distance: Q P DistBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesDocument1 pageSTAT 202: Experimental Statistics I, Part 2: Credits: 2 Class Type: Graduate Course PrerequisitesBao GanNo ratings yet
- Sections 1 and 6: Li Li Section 2: NaichenDocument4 pagesSections 1 and 6: Li Li Section 2: NaichenBao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project12Document3 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project12Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus STA 36-202 - Statistics & Data Science Methods Spring 2018Document15 pagesSyllabus STA 36-202 - Statistics & Data Science Methods Spring 2018Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project7Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project7Bao GanNo ratings yet
- STAT202-lecture2 Project6Document4 pagesSTAT202-lecture2 Project6Bao GanNo ratings yet
- Logical FallaciesDocument15 pagesLogical FallaciesLouis Marvil AbalaNo ratings yet
- 2018 January Proficiency Session 2 A VersionDocument2 pages2018 January Proficiency Session 2 A VersionUğur GiderNo ratings yet
- Wa0016.Document7 pagesWa0016.amjad.khan12133122No ratings yet
- Innatek BCST-50 BarCode Scanner Supplementary ManualDocument25 pagesInnatek BCST-50 BarCode Scanner Supplementary ManualBruno MagneNo ratings yet
- Ratio & Proport-WPS OfficeDocument43 pagesRatio & Proport-WPS OfficeRovelyn Sangalang CabreraNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Exam ArtDocument4 pagesYear 7 Exam ArtBarminga KamurenNo ratings yet
- Common Themes in LiteratureDocument2 pagesCommon Themes in LiteratureMoon5627No ratings yet
- Élan VitalDocument3 pagesÉlan Vitalleclub IntelligenteNo ratings yet
- AccessibilityDocument8 pagesAccessibilityHaroon RasheedNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Conducting Condition Assessment of Education FacilitiesDocument200 pagesGuidelines For Conducting Condition Assessment of Education FacilitiesMichael MatshonaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL APPROVAL FORMDocument2 pagesCHEMICAL APPROVAL FORMYosep SasadaNo ratings yet
- PVT Behavior of Fluids: Dr. M. SubramanianDocument58 pagesPVT Behavior of Fluids: Dr. M. SubramanianRama GaurNo ratings yet
- Division Quarterly Unified Test English 6Document21 pagesDivision Quarterly Unified Test English 6rogielynNo ratings yet
- Math (Safal)Document3 pagesMath (Safal)AdowNo ratings yet
- Citizen ShiftDocument36 pagesCitizen ShiftsorogollentoNo ratings yet
- SE-409 Aluminium Enclosure SE-409-0-0-A-0-11284: RevisionDocument1 pageSE-409 Aluminium Enclosure SE-409-0-0-A-0-11284: RevisionAhmet MehmetNo ratings yet
- Vol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteDocument11 pagesVol 5, No 2 November, Pp. 99-111 P-ISSN 2549-4880, E-ISSN 2614-1310 Journal DOI: WebsiteSyarah RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Waterjets: An Experiment to Determine Flow RatesDocument5 pagesCalibrating Waterjets: An Experiment to Determine Flow Ratespacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- SAT Practice Test 1 Combined PDFDocument122 pagesSAT Practice Test 1 Combined PDFRay728No ratings yet
- Final CBoW 2020 (Dilnesaw)Document267 pagesFinal CBoW 2020 (Dilnesaw)dilnesaw teshomeNo ratings yet
- 08 - Marian-Avram Vincze, Horatiu-Stefan GrifDocument4 pages08 - Marian-Avram Vincze, Horatiu-Stefan GrifBudiandra Yusuf MahendraNo ratings yet
- Dosicard-R User's Manual (1) - FixedDocument67 pagesDosicard-R User's Manual (1) - Fixedbogdy0073No ratings yet
- Literacy Day in IndiaDocument10 pagesLiteracy Day in IndiaThe United IndianNo ratings yet
- Avio Et Al., 2016Document10 pagesAvio Et Al., 2016Aditya RahmanNo ratings yet
- Formulating Rules in Finding The NTH TermDocument17 pagesFormulating Rules in Finding The NTH TermMaximino Eduardo SibayanNo ratings yet
- Global Citizenship Courseware SSP032 GCED 1Document24 pagesGlobal Citizenship Courseware SSP032 GCED 1siegaralphNo ratings yet
- I. Trabelsi, K. Yoneyama, Z. Abbes, M. Amri, X. Xie, T. Kisugi, H.I. Kim, M. Kharrat, K. YoneyamaDocument8 pagesI. Trabelsi, K. Yoneyama, Z. Abbes, M. Amri, X. Xie, T. Kisugi, H.I. Kim, M. Kharrat, K. YoneyamaCleaver BrightNo ratings yet
- Quarter 4 - MELC 11: Mathematics Activity SheetDocument9 pagesQuarter 4 - MELC 11: Mathematics Activity SheetSHAIREL GESIMNo ratings yet
- Mathematics F4 Us3Document5 pagesMathematics F4 Us3VERONEJAY MAIKALNo ratings yet
- January 2005 QP - C1 EdexcelDocument20 pagesJanuary 2005 QP - C1 EdexcelAbid KhanNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsFrom EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)