Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCLEX - Fluids and Electrolytes
Uploaded by
issaiahnicolle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views4 pagesNCLEX - Fluids and Electrolytes
Uploaded by
issaiahnicolleCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
NCLEX: FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES administering the drug, the priority nursing action is to
1. A client with hypoparathyroidism complains of numbness monitor:
and tingling in his fingers and around the mouth. The a. Urine output.
nurse would assess for what electrolyte imbalance? b. Blood pressure.
a. Hyponatremia c. Bowel movements.
b. Hypocalcemia d. ECG for tall, peaked T waves
c. Hyperkalemia Rationale: Kayexalate causes potassium to be exchanged for
d. Hypermagnesemia sodium in the intestines and excreted through bowel
Rationale: Hypoparathyroidism can cause low serum calcium movements. If client does not have stools, the drug cannot
levels. Numbness and tingling in extremities and in the work properly. Blood pressure and urine output are not of
circumoral area around the mouth are the hallmark signs of primary importance. The nurse would already expect changes
hypocalcemia. Normal calcium level is 9 to 11 mg/dl. in T waves with hyperkalemia. Normal serum potassium is 3.5
2. The nurse evaluates which of the following clients to be at to 5.5 mEq/L.
risk for developing hypernatremia? 5. The nurse is caring for a client who has been in good
a. 50-year-old with pneumonia, diaphoresis, and health up to the present and is admitted with cellulitis of
high fevers the hand. The client's serum potassium level was 4.5
b. 62-year-old with congestive heart failure taking mEq/L yesterday. Today the level is 7 mEq/L. Which of
loop diuretics the following is the next appropriate nursing action?
c. 39-year-old with diarrhea and vomiting a. Call the physician and report results
d. 60-year-old with lung cancer and syndrome of b. Question the results and redraw the specimen
inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) c. Encourage the client to increase the intake of
Rationale: Diaphoresis and a high fever can lead to free water bananas
loss through the skin, resulting in hypernatremia. Loop d. Initiate seizure precautions
diuretics are more likely to result in a hypovolemic Rationale: A client who has been in good health up to the
hyponatremia. Diarrhea and vomiting cause both sodium and present is admitted for cellulitis of the hands. When the serum
water losses. Clients with syndrome of inappropriate potassium goes from 4.5 mEq/L to 7.0 mEq/L with no risk
antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) have hyponatremia, due to factors for hyperkalemia, false high results should be
increased water reabsorption in the renal tubules. suspected because of hemolysis of the specimen. The
3. A client is admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis who, with physician would likely question results as well. Bananas are a
treatment, has a normal blood glucose, pH, and serum food high in potassium. Seizures are not a clinical
osmolality. During assessment, the client complains of manifestation of hyperkalemia.
weakness in the legs. Which of the following is a priority 6. A client is receiving an intravenous magnesium infusion to
nursing intervention? correct a serum level of 1.4 mEq/L. Which of the following
a. Request a physical therapy consult from the physician assessments would alert the nurse to immediately stop
b. Ensure the client is safe from falls and check the most the infusion?
recent potassium level a. Absent patellar reflex
c. Allow uninterrupted rest periods throughout the day b. Diarrhea
d. Encourage the client to increase intake of dairy c. Premature ventricular contractions
products and green leafy vegetables. d. Increase in blood pressure
Rationale: In the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis, the blood Rationale: An intravenous magnesium infusion may be used to
sugar is lowered, the pH is corrected, and potassium moves treat a low serum magnesium level. Normal serum magnesium
back into the cells, resulting in low serum potassium. Client is 1.5 to 2.5 mEq/L. Clinical manifestations of
safety and the correction of low potassium levels are a priority. hypermagnesemia are the result of depressed neuromuscular
The weakness in the legs is a clinical manifestation of the transmission. Absent reflexes indicate a magnesium level
hypokalemia. Dairy products and green, leafy vegetables are a around 7 mEq/L. Diarrhea and PVCs are not clinical
source of calcium. manifestations of high magnesium levels. Hypermagnesemia
4. A client with a potassium level of 5.5 mEq/L is to receive causes hypotension.
sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) orally. After 7. A client with chronic renal failure reports a 10 pound
weight loss over 3 months and has had difficulty taking
calcium supplements. The total calcium is 6.9 mg/dl. 10. An older adult client admitted with heart failure and a
Which of the following would be the first nursing action? sodium level of 113 mEq/L is behaving aggressively
a. Assess for depressed deep tendon reflexes toward staff and does not recognize family members.
b. Call the physician to report calcium level When the family expresses concern about the client's
c. Place an intravenous catheter in anticipation of behavior, the nurse would respond most appropriately by
administering calcium gluconate stating
d. Check to see if a serum albumin level is available a. "The client may be suffering from dementia, and the
Rationale: A client with chronic renal failure who reports a 10 hospitalization has worsened the confusion."
pound weight loss over 3 months and has difficulty taking b. "Most older adults get confused in the hospital."
calcium supplements is poorly nourished and likely to have c. "The sodium level is low, and the confusion will
hypoalbuminemia. A drop in serum albumin will result in a false resolve as the levels normalize."
low total calcium level. Placing an IV is not a priority action. d. "The sodium level is high and the behavior is a result
Depressed reflexes are a sign of hypercalcemia. Normal of dehydration."
serum calcium is 9 to 11 mg/dl. Rationale: Normal serum level is 135 to 145 mEq/L.
8. A client with heart failure is complaining of nausea. The Neurological symptoms occur when sodium levels fall
client has received IV furosemide (Lasix), and the urine below 120 mEq/L. The confusion is an acute condition that
output has been 2500 ml over the past 12 hours. The will go away as the sodium levels normalize. Dementia is
client's home drugs include metoprolol (Lopressor), an irreversible condition.
digoxin (Lanoxin), furosemide, and multivitamins. Which of 11. A client with a serum sodium of 115 mEq/L has been
the following are the appropriate nursing actions before receiving 3% NS at 50 ml/hr for 16 hours. This morning
administering the digoxin? Select all that apply. the client feels tired and short of breath. Which of the
a. Administer an antiemetic prior to giving the digoxin following interventions is a priority?
b. Encourage the client to increase fluid intake a. Turn down the infusion
c. Call the physician b. Check the latest sodium level
d. Report the urine output c. Assess for signs of fluid overload
e. Report indications of nausea d. Place a call to the physician
Rationale: Potassium is lost during diuresis with a loop diuretic Rationale: A complication of hypertonic sodium solution
such as furosemide (Lasix). Hypokalemia can cause digitalis administration is fluid overload. While turning down the
toxicity, which often results in nausea. The physician should be infusion, checking the latest sodium level, and notifying the
notified, and digoxin should be held until potassium levels and physician may all be reasonable, the priority intervention is to
digoxin levels are checked. Peaked T waves and widened assess for manifestations of fluid overload. Assessment is
QRS are manifestations of hyperkalemia. always the priority to determine what action to take next.
9. The nurse is caring for a bedridden client admitted with 12. A client with chronic renal failure receiving dialysis
multiple myeloma and a serum calcium level of 13 mg/dl. complains of frequent constipation. When performing
Which of the following is the most appropriate nursing discharge teaching, which over-the-counter products
action? should the nurse instruct the client to avoid at home?
a. Provide passive ROM exercises and encourage fluid a. Bisacodyl (Dulcolax) suppository
intake b. Fiber supplements
b. Teach the client to increase intake of whole grains c. Docusate sodium
and nuts d. Milk of magnesia
c. Place a tracheostomy tray at the bedside Rationale: Milk of magnesia contains magnesium, an
d. Administer calcium gluconate IM as ordered electrolyte that is excreted by kidneys. Clients with renal failure
Rationale: A client who has a serum calcium of 13 mg/dl has are at risk for hypermagnesemia since their bodies cannot
hypercalcemia. Normal serum calcium is 9 to 11 mg/dl. Fluid excrete the excess magnesium. The client should avoid
intake promotes renal excretion of excess calcium. ROM magnesium-containing laxatives.
exercises promote reabsorption of calcium into bone. Placing a 13. A client is receiving intravenous potassium
tracheostomy at the bedside is a nursing intervention for supplementation in addition to maintenance fluids. The
hypocalcemia. Although calcium gluconate may be urine output has been 120 ml every 8 hours for the past
administered in hypocalcemia, it is never administered IM. 16 hours and the next dose is due. Before administering
the next potassium dose, which of the following is the a. Sodium
priority nursing action? b. Phosphorus
a. Encourage the client to increase fluid intake c. Calcium
b. Administer the dose as ordered d. Magnesium
c. Draw a potassium level and administer the dose if the Rationale: Low serum magnesium levels can inhibit potassium
level is low or normal ions from crossing cell membranes, resulting in potassium loss
d. Notify the physician of the urine output and hold the through the urine. Generally, low magnesium levels must be
dose corrected before potassium replacement is effective.
Rationale: Urine output is an indication of renal function. 17. The nurse should include which of the following
Normal urine output is at least 30 ml/hour. Clients with instructions to assist in controlling phosphorus levels for a
impaired renal function are at risk for hyperkalemia. Initiating a client in renal failure?
lab draw requires a physician order. a. Increase intake of dairy products and nuts
14. The nurse should monitor for clinical manifestations of b. Take aluminum-based antacids such as aluminum
hypophosphatemia in which of the following clients? hydroxide (Amphojel) with or after meals
a. A client with osteoporosis taking vitamin D and c. Reduce intake of chocolate, meats, and whole grains
calcium supplements d. Avoid calcium supplements
b. A client who is alcoholic receiving total parenteral Rationale: Aluminum-based antacids are often prescribed in
nutrition the treatment of renal failure to bind with phosphate and
c. A client with chronic renal failure awaiting the first increase elimination through the GI tract. Dairy products and
dialysis run nuts are foods high in phosphorus. Chocolate, meats, and
d. A client with hypoparathyroidism secondary to thyroid whole grains are foods high in magnesium. Clients with renal
surgery failure often require calcium supplements as a result of poor
Rationale: A client with osteoporosis taking vitamin and vitamin D metabolism and in order to prevent
calcium supplements, a client with chronic renal failure hyperphosphatemia.
awaiting dialysis, and a client with hypoparathyroidism 18. A client with pneumonia presents with the following arterial
secondary to thyroid surgery are at risk for blood gases: pH of 7.28, PaCO2 of 74, HCO3 of 28
hyperphosphatemia. Alcoholics and clients receiving TPN are mEq/L, and PO2 of 45, which of the following is the most
at risk for low phosphorus levels, due to poor intestinal appropriate nursing intervention?
absorption and shifting of phosphorus into cells along with a. Administer a sedative
insulin and glucose. b. Place client in left lateral position
15. A client admitted with squamous cell carcinoma of the c. Place client in high-Fowler's position
lung has a serum calcium level of 14 mg/dl. The nurse d. Assist the client to breathe into a paper bag
should instruct the client to avoid which of the following Rationale: The client with a pH of 7.28, PaCO2 of 74, HCO3 of
foods upon discharge? Select all that apply. 28 mEq/L, and PO2 of 45 is in a state of respiratory acidosis.
a. Eggs Placing the client in high-Fowler's position will facilitate the
b. Broccoli expansion of the lungs and help the client blow off the excess
c. Organ meats CO2. Sedatives would impede respirations. The question does
d. Nuts not indicate which is the affected lung, so left lateral position
e. Canned salmon would not be a first choice. Breathing into a paper bag will
Rationale: Fish, eggs, and organ meats are high in cause the PCO2 to rise higher.
phosphorus. Broccoli, nuts, and canned salmon are high in 19. A client with COPD feels short of breath after walking to
calcium. Clients with lung or breast cancer often have elevated the bathroom on 2 liters of oxygen nasal cannula. The
calcium levels due to tumor-induced hyperparathyroidism. morning's ABGs were pH of 7.36, PaCO2 of 62, HCO3 of
16. A client with pancreatitis has been receiving potassium 35 mEq/L, O2 at 88% on 2 liters. Which of the following
supplementation for four days since being admitted with a should be the nurse's first intervention?
serum potassium of 3.0 mEq/L. Today the potassium level a. Call the physician and report the change in client's
is 3.1 mEq/L. Which of the following laboratory values condition
should the nurse check before notifying the physician of b. Turn the client's O2 up to 4 liters nasal cannula
the client's failure to respond to treatment?
c. Encourage the client to sit down and to take deep
breaths
d. Encourage the client to rest and to use pursed-lip
breathing technique
Rationale: Clients with COPD, especially those who are in a
chronic compensated respiratory acidosis, are very sensitive to
changes in O2 flow, because hypoxemia rather than high CO2
levels stimulates respirations. Deep breaths are not helpful,
because clients with COPD have difficulty with air trapping in
alveoli. There is no need to call the physician since this client
is presently most likely at baseline.
20. A client who had a recent surgery has been vomiting and
becomes dizzy while standing up to go to the bathroom.
After assisting the client back to bed, the nurse notes that
the blood pressure is 55/30 and the pulse is 140. The
nurse hangs which of the following IV fluids to correct this
condition?
a. D5.45 NS at 50 ml/hr
b. 0.9 NS at an open rate
c. D5W at 125 ml/hr
d. 0.45 NS at open rate
Rationale: A client who recently had surgery, is vomiting,
becomes dizzy when standing up, has a blood pressure of
55/30, and has a pulse of 140 is hypovolemic and requires
plasma volume expansion. Isotonic fluids such as 0.9 NS will
expand volume. Hypotonic fluids such as 0.45 NS will leave
the intravascular space. D5W will metabolize into free water
and leave the intravascular space. D5.45 NS is a good
maintenance fluid but a rate of 50 ml per hour is not sufficient
to expand the vascular volume quickly.
21. A client with renal failure enters the emergency room after
skipping three dialysis treatments to visit family out of
town. Which set of ABGs would indicate to the nurse that
the client is in a state of metabolic acidosis?
a. PH of 7.43, PCO2 of 36, HCO3 of 26
b. PH of 7.41, PCO2 of 49, HCO3 of 30
c. PH of 7.33, PCO2 of 35, HCO3 of 17
d. PH of 7.25, PCO2 of 56, HCO3 of 28
Rationale: A pH of 7.33, PCO2 of 35, and HCO3 of 17 and a
pH of 7.25, PCO2 of 56, and HCO3 of 28 both indicate
acidosis. The pH of 7.25 is a respiratory acidosis. A pH of 7.41,
PCO2 of 49, and HCO3 of 30 is a compensated metabolic
alkalosis. A pH of 7.43, PCO2 of 36, and HCO3 of 26 is
normal.
22.
You might also like
- Fluid and Electrolytes Study GuideDocument16 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Study GuideDianaNursing96% (28)
- Maternal-Newborn Nursing DeMYSTiFieD: A Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandMaternal-Newborn Nursing DeMYSTiFieD: A Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- Handout Medical-Surgical Nursing Fluid and ElectrolyteDocument13 pagesHandout Medical-Surgical Nursing Fluid and ElectrolytePaul Christian P. Santos, RN100% (10)
- Band Keratopathy ArticleDocument9 pagesBand Keratopathy ArticleDecha Pradea MaulinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid BaseDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid BaseSeverino Valerio100% (2)
- Medical Surgical Nursing BulletsDocument75 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Bulletsmervilyn100% (3)
- Chapter 16: Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionDocument13 pagesChapter 16: Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances Harding: Lewis's Medical-Surgical Nursing, 11th EditionKrishna RamaNo ratings yet
- Medical and Surgical Nursing PointersDocument104 pagesMedical and Surgical Nursing Pointersoh_chamie100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Diseases NCLEX Review Questions Part 2Document17 pagesGastrointestinal Diseases NCLEX Review Questions Part 2Hasan A AsFour100% (1)
- NCLEX Cardiovascular Exam 2020 - Questions and AnswersDocument74 pagesNCLEX Cardiovascular Exam 2020 - Questions and AnswersNeoGellin83% (6)
- Cirrhosis NCLEX QuestionsDocument7 pagesCirrhosis NCLEX QuestionsShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Fluid & ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesFluid & ElectrolyteskauragiousNo ratings yet
- What Is DysarthriaDocument3 pagesWhat Is DysarthriaAsnan Azis Fatoni100% (1)
- University Students' Self-Efficacy in Online Learning Due To COVID-19Document7 pagesUniversity Students' Self-Efficacy in Online Learning Due To COVID-19issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Final Compre Exam Key AnswersDocument14 pagesFinal Compre Exam Key Answersmj CanilangNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical QandADocument63 pagesMedical Surgical QandAAlona Lumidao100% (8)
- Acupuncture For TinnitusDocument4 pagesAcupuncture For Tinnitussrimaauro5123No ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes ExamDocument3 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Exammonmon100% (3)
- Fluids and Electrolytes - ExamDocument6 pagesFluids and Electrolytes - ExamLouie Bello60% (5)
- Pamantasan NG Cabuyao Banay-Banay, Cabuyao City, Laguna Bachelor of Science in Nursing Diagnostic Examination Iii-ADocument19 pagesPamantasan NG Cabuyao Banay-Banay, Cabuyao City, Laguna Bachelor of Science in Nursing Diagnostic Examination Iii-Aissaiahnicolle100% (2)
- Science 6 - Q2 - L4 - Parts and Function of Excretory SystemDocument28 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - L4 - Parts and Function of Excretory SystemSonny Matias100% (1)
- Special - NCLEX - Exam - Jakarta - Students - PDF Filename UTF-8''Special NCLEX Exam - Jakarta StudentsDocument23 pagesSpecial - NCLEX - Exam - Jakarta - Students - PDF Filename UTF-8''Special NCLEX Exam - Jakarta Studentsrizqi100% (1)
- NCLEX QuestionsDocument5 pagesNCLEX QuestionsMeganNo ratings yet
- Endocrine 50 Questions & AnswersDocument28 pagesEndocrine 50 Questions & AnswersBrooke Susac100% (1)
- Respi-Nclex QuestionsDocument160 pagesRespi-Nclex QuestionsSophia Rose Delos Santos100% (3)
- Medical Surgical Exam Part 1Document16 pagesMedical Surgical Exam Part 1api-382250888% (42)
- 50 Item Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillDocument14 pages50 Item Gastrointestinal Health Problems Test DrillFilipino Nurses Central100% (2)
- Respiratory Disorders NCLEXDocument22 pagesRespiratory Disorders NCLEXPotchiee Pfizer50% (2)
- Fluids & Electrolytes ExamDocument13 pagesFluids & Electrolytes ExamJan Macarambon73% (11)
- Sop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCDocument13 pagesSop For Hemoglobin Determination by HPLCUMMID WashimNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing Examination Part IDocument17 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Examination Part Iɹǝʍdןnos97% (64)
- Hematologic MS Nclex QuestionsDocument36 pagesHematologic MS Nclex QuestionsSophia Rose Delos Santos100% (2)
- Med Surg PNLE Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesMed Surg PNLE Exam Questionsdanielle ordoñezNo ratings yet
- NCP AsthmaDocument2 pagesNCP Asthmaissaiahnicolle0% (1)
- QADocument11 pagesQAGladys FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Review Cardiovascular QuizDocument17 pagesNCLEX Review Cardiovascular QuizApple Mesina100% (2)
- Fluids and Electrolytes 3Document8 pagesFluids and Electrolytes 3Potchiee Pfizer100% (1)
- Answer and Rationale MaternityDocument21 pagesAnswer and Rationale MaternityMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Mrs. Hogan AsthmaDocument4 pagesCase Study 1 Mrs. Hogan Asthmaissaiahnicolle100% (2)
- Fluid and Electrolytes QuizDocument13 pagesFluid and Electrolytes QuizCuttie Anne Galang75% (4)
- Medical - Surgical Nursing 3 & 4: Final ExaminationsDocument6 pagesMedical - Surgical Nursing 3 & 4: Final ExaminationsBRYAN JOSEPH TIONGSON100% (1)
- Fluids and Electrolytes - RATIODocument16 pagesFluids and Electrolytes - RATIOLouie Bello100% (3)
- MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesMEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systemvalentine95% (20)
- Med Surg - Endocrine System QuestionsDocument7 pagesMed Surg - Endocrine System QuestionsKrizia R. Pingke100% (8)
- Saunders Comprehensive Review Nclex - Fluids - ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesSaunders Comprehensive Review Nclex - Fluids - Electrolytesissaiahnicolle100% (1)
- Neuro Nursing With RationaleDocument7 pagesNeuro Nursing With Rationalemaestro1020100% (2)
- Hematologic Disorders NCLEXDocument15 pagesHematologic Disorders NCLEXPotchiee PfizerNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review 1Document422 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review 1jeshemaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument28 pagesEndocrine DisordersRhitzle Ann50% (2)
- Computed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in OntarioDocument71 pagesComputed Tomography Radiation Safety Issues in Ontariopebbles18950% (2)
- 50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesDocument9 pages50 Item Psychiatric Exam Answers and RationalesJune DumdumayaNo ratings yet
- Pamantasan NG Cabuyao: College of NursingDocument78 pagesPamantasan NG Cabuyao: College of NursingissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCLEXDocument13 pagesNCLEXJheanAlphonsineT.MeansNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document15 pagesTest 2Ding DialyzerNo ratings yet
- NCLEX Exam Cardiovascular Surgery CareDocument5 pagesNCLEX Exam Cardiovascular Surgery CareHeather ClemonsNo ratings yet
- Ob Pedia CDDocument13 pagesOb Pedia CDNom NomNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions GUDocument10 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Nclex Questions GUdee_day_8100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal Nursing Test BanksDocument2 pagesGastrointestinal Nursing Test BanksNorhana Manas50% (6)
- CD-NTG BupcDocument9 pagesCD-NTG BupcRho Vince Caño MalagueñoNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure Practice QuestionsDocument3 pagesRenal Failure Practice QuestionsJoslyn Gross100% (3)
- Nursing Questions& AnswersDocument42 pagesNursing Questions& AnswersSanjeev Kumar100% (1)
- Practice Exam - HematologyDocument2 pagesPractice Exam - HematologyrlinaoNo ratings yet
- OBDocument7 pagesOBWilmaBongotanPadawilNo ratings yet
- CorrectsDocument46 pagesCorrectsnursing_hallNo ratings yet
- Test Quiz Hypo Kale MiaDocument6 pagesTest Quiz Hypo Kale MiaVivian Montesena BreganzaNo ratings yet
- NCLEX HomeostasisDocument10 pagesNCLEX HomeostasisAngie MandeoyaNo ratings yet
- 20 Board QuestionsDocument6 pages20 Board QuestionsAnne de VeraNo ratings yet
- MS Question With Rationales 2Document12 pagesMS Question With Rationales 2Tsuyoshi BangNo ratings yet
- CECILIA-Act 2Document3 pagesCECILIA-Act 2issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- SalerioDocument28 pagesSalerioRizqaFebrilianyNo ratings yet
- Self Efficacy 4 PDFDocument39 pagesSelf Efficacy 4 PDFCiara Mae PrincesNo ratings yet
- Article5 1Document6 pagesArticle5 1issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- 212-Article Text-385-1-10-20210209Document7 pages212-Article Text-385-1-10-20210209issaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- PrayerDocument1 pagePrayerissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Self-Efficacy and Clinical Competence of Fourth-Year Nursing Students: A Self-Reported StudyDocument7 pagesSelf-Efficacy and Clinical Competence of Fourth-Year Nursing Students: A Self-Reported StudyissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- The Relationship of Self-Efficacy and Clinical Reasoning of UnderDocument98 pagesThe Relationship of Self-Efficacy and Clinical Reasoning of UnderissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Nurse Education in Practice: Melodie Rowbotham, Rachel M. OwenDocument6 pagesNurse Education in Practice: Melodie Rowbotham, Rachel M. OwenissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- PreviewDocument24 pagesPreviewissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Progression of Clinical Self-Efficacy Among Baccalaureate NursingDocument109 pagesProgression of Clinical Self-Efficacy Among Baccalaureate NursingissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- FullDocument1 pageFullissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Google Meet LinksDocument1 pageGoogle Meet LinksissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP - Cellular AberrationDocument1 pageNCP - Cellular Aberrationissaiahnicolle100% (1)
- NCP For AsthmaDocument1 pageNCP For AsthmaissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- SimsDocument1 pageSimsissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument2 pagesNCP FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Patient InformationDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was: Patient InformationissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Senn Retractors (2) : Instrumentation 1. Av Shunt TrayDocument8 pagesSenn Retractors (2) : Instrumentation 1. Av Shunt TrayissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: Nursing Care Plan FormissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument1 pageIneffective Breathing PatternissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Equipment SuppliesDocument5 pagesEquipment SuppliesissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
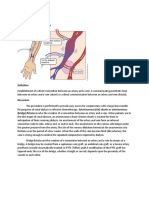
- Arteriovenous Shunt or Arteriovenous (Bridge) FistulaDocument1 pageArteriovenous Shunt or Arteriovenous (Bridge) FistulaissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- CHN Practice Without AnswerDocument19 pagesCHN Practice Without AnswerissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- ETS & CapillaryDocument6 pagesETS & CapillaryRoela Marie AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingNo ratings yet
- A Study of Cisplatin Chemoteraphy and Hearing LossDocument4 pagesA Study of Cisplatin Chemoteraphy and Hearing LossPriska AmeliaNo ratings yet
- GEFITINIBDocument3 pagesGEFITINIBErza GenatrikaNo ratings yet
- Gharama Za Matibabu PKP Kituo Cha AfyaDocument14 pagesGharama Za Matibabu PKP Kituo Cha AfyashaggyzegratNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics and Pathological Principles in Nursing Care Part 4Document2 pagesPharmacodynamics and Pathological Principles in Nursing Care Part 4KBDNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihDocument29 pagesAntibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihPutri Sari SeptirianiNo ratings yet
- Digestive Trans 2Document30 pagesDigestive Trans 2Ericson CandelariaNo ratings yet
- Intake Form: Health Declaration For TravellersDocument1 pageIntake Form: Health Declaration For TravellersJirir vimNo ratings yet
- Restless Leg SyndromeDocument29 pagesRestless Leg SyndromeMarisa FatkiyaNo ratings yet
- CHO Special MCQs #1Document7 pagesCHO Special MCQs #1Praveen LaxkarNo ratings yet
- Sliding Bone Graft JournalDocument3 pagesSliding Bone Graft Journalapi-310305222No ratings yet
- Penn State Hershey Medical Center CitationDocument40 pagesPenn State Hershey Medical Center Citationfox43wpmtNo ratings yet
- MDWF 2060 Skaidre Brown 2Document3 pagesMDWF 2060 Skaidre Brown 2api-354751775No ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Table (GROUP2 BSN IIIB)Document10 pagesCommunicable Disease Table (GROUP2 BSN IIIB)Hershey Cordero BrionesNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFRAHUL RANANo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction: BY: Tharun Balaji Vinay GautamDocument19 pagesGastric Outlet Obstruction: BY: Tharun Balaji Vinay Gautam7hhdfc8vmwNo ratings yet
- Bühler Heim 2018 General Introduction To The Psychotherapy of Pierre JanetDocument18 pagesBühler Heim 2018 General Introduction To The Psychotherapy of Pierre JanetsammyNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFDocument397 pagesOvarian Cancers The National Academies Press PDFnersitiulfahNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Women of Childbearing Age in Yaqshid DistrictDocument82 pagesFactors Associated With Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Women of Childbearing Age in Yaqshid DistrictMohamed Omar HassanNo ratings yet
- BVGH Global Health Primer 10dec07Document72 pagesBVGH Global Health Primer 10dec07hst939No ratings yet
- 2 CSEP-CPT Aerobictheory v2Document20 pages2 CSEP-CPT Aerobictheory v2Nnaemeka NwobodoNo ratings yet
- What Is Mental Health?Document8 pagesWhat Is Mental Health?Sonal SahuNo ratings yet