Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force Systems and Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Krishna Vivek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views4 pagesOriginal Title
1. Force systems and equilibrium
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
104 views4 pagesForce Systems and Equilibrium
Uploaded by
Krishna VivekCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
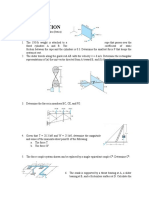
Chapter 1: Force systems and equilibrium
1. Draw free body diagram of horizontal member.
2. When the 0.05-kg body is in the position shown, the linear spring
is stretched 10 mm. Determine the force P required to break
contact at C.
3. The uniform slender bar of length 2r and mass m rests against
the circular surface as shown. Determine the normal force at
the small roller A.
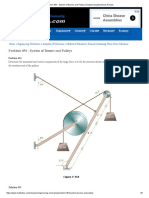
4. The weight W=6 kN hangs from the cable which passes over the
pulley at F. Neglecting the weights of the bars and the pulley,
determine the magnitude of the pin reaction at D.
5. Determine the mass of each of the two cylinders if they cause
a sag of s = 0.5 m when suspended from the rings at A and B.
6. Find the smallest angle θ for which a sufficiently large force P
would cause the uniform log AB of weight W to tip about A.
7. The uniform bar of length L and weight W is kept in the
horizontal position by friction. Determine the smallest possible
coefficient of static friction between the bar and the inclined
surfaces.
8. Determine the range of mass m over which the system is in
static equilibrium. The coefficient of static friction between the
cord and the upper curved surface is 0.20, while that between
the block and the incline is 0.40. Neglect friction at the pivot O.
Answers:
1. NA
2. 5.59 N
3. 0.892mg
4. 4.39 kN
5. 27.94 N
6. 47.1 degrees
7. 0.268
8. 6.16 to 28.3 kg
You might also like
- Engineering Mechanics Question BankDocument15 pagesEngineering Mechanics Question BankSatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- MAE 241 - Final ExamDocument8 pagesMAE 241 - Final ExamDarran CairnsNo ratings yet
- Problem 454 - System of Booms and Pulleys - Engineering Mechanics ReviewDocument6 pagesProblem 454 - System of Booms and Pulleys - Engineering Mechanics ReviewjmezapNo ratings yet
- 2017 Data Center BrochureDocument16 pages2017 Data Center BrochurekennethNo ratings yet
- 3-4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems PDFDocument24 pages3-4 Three-Dimensional Force Systems PDFewineta assefaNo ratings yet
- Resultant Force Systems Statics ProblemsDocument13 pagesResultant Force Systems Statics ProblemsGladwin BuquironNo ratings yet
- Thevenins TheoremDocument37 pagesThevenins TheoremGautam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: Force Systems Chapter 2 SummaryDocument36 pagesEngineering Mechanics: Force Systems Chapter 2 SummaryBesart Kryeziu100% (1)
- ADS 3M Novec 1230 FPF DIOM 06-237256-001 - AA With Addenda - 0421Document312 pagesADS 3M Novec 1230 FPF DIOM 06-237256-001 - AA With Addenda - 0421Natan VillalonNo ratings yet
- 2 Resultants of Force SystemsDocument24 pages2 Resultants of Force SystemsAngelo Luis RosNo ratings yet
- 222Document9 pages222physicsdocs100% (1)
- MCE321 - Friction Lecture NoteDocument6 pagesMCE321 - Friction Lecture NoteBright OvieNo ratings yet
- Friction & Moment of Inertia-Engineering Mechanics-IIT-KanpurDocument51 pagesFriction & Moment of Inertia-Engineering Mechanics-IIT-KanpurNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Problem 8.1: SolutionDocument227 pagesProblem 8.1: SolutionPaul Reyna Rojas0% (1)
- Unit II B QuestionsDocument19 pagesUnit II B QuestionsPiyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Answers Vector Mechanics 10thDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Answers Vector Mechanics 10thstorm7847No ratings yet
- Introduction to Fluid Mechanics FundamentalsDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Fluid Mechanics Fundamentalssandrew784No ratings yet
- Chapter Three Moments and Parallel Coplanar Forces: Aarignon's TheoremDocument11 pagesChapter Three Moments and Parallel Coplanar Forces: Aarignon's TheoremQaria shehzadiNo ratings yet
- Enginnering MechanicsDocument13 pagesEnginnering MechanicsSatheesh SekarNo ratings yet
- Buckling of Struts - MKMDocument8 pagesBuckling of Struts - MKMAbdur Rasheed RasheedNo ratings yet
- Y17 Statics - Force Systems - Problems PDFDocument30 pagesY17 Statics - Force Systems - Problems PDFJerico CruelNo ratings yet
- Chap2 StrainDocument36 pagesChap2 Strainasif kiyaniNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics - Problems and Solutions - Solved Problems in Basic PhysicsDocument12 pagesFluid Statics - Problems and Solutions - Solved Problems in Basic PhysicsEsther oluwatosin AdeyemiNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument62 pagesFrictionchellamvNo ratings yet
- Vibrations and Its Types: Presented By: Er. Sahil Sharma Department of Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesVibrations and Its Types: Presented By: Er. Sahil Sharma Department of Civil EngineeringSaHil ShaRmaNo ratings yet
- Overviews of StaticsDocument70 pagesOverviews of StaticsJacous WcyNo ratings yet
- PFC PosterDocument1 pagePFC PosterAwais Rehman KambohNo ratings yet
- Measuring Beam Bending MomentsDocument1 pageMeasuring Beam Bending MomentsTarique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersDocument10 pagesMechanics of Materials-1 - 2-Mark Question and AnswersSrikant PotluriNo ratings yet
- To Investigate Band Study The Effect of Varying The Current and The Voltage On The Arc Welded SpecimenDocument5 pagesTo Investigate Band Study The Effect of Varying The Current and The Voltage On The Arc Welded SpecimenRao MaazNo ratings yet
- Friction Flat Belts PDFDocument25 pagesFriction Flat Belts PDFMuhammad Amirul Haziq Bin Zawawi100% (1)
- Flight of Elastic Band LAB - Trixie Le - 2nd PeriodDocument5 pagesFlight of Elastic Band LAB - Trixie Le - 2nd PeriodTrixie LeNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System ExperimentDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning System ExperimentBoJassim100% (1)
- Ampere's LawDocument20 pagesAmpere's Lawlacatus_danielNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodiesDocument22 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid BodiesSpiro DourbalyNo ratings yet
- Statics ReviewDocument4 pagesStatics Reviewsamir_ssh7151No ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Motion and ElasticityDocument15 pagesSimple Harmonic Motion and ElasticitySubho BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- HeyaDocument46 pagesHeyaJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical PrinciplesDocument34 pagesMechanical PrinciplesJo okNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Design of Cotter JointsDocument21 pagesUnit2 - Design of Cotter JointsKunal AhiwaleNo ratings yet
- Lab Report of Modules (SP22-BCS-069)Document12 pagesLab Report of Modules (SP22-BCS-069)Tayyab Khan100% (1)
- Statics of Rigid Bodies Problem Set 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies Problem Set 1 SolutionsGillian AmbaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems With PulleysDocument30 pagesSolved Problems With PulleysAnonymous WNWk1h2No ratings yet
- The Copperbelt University School of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Department of Physics PH 110 Introductory PhysicsDocument3 pagesThe Copperbelt University School of Mathematics and Natural Sciences Department of Physics PH 110 Introductory PhysicsLazy BanditNo ratings yet
- 3 Eee Pe PDFDocument107 pages3 Eee Pe PDFjose19313922No ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis FundamentalsDocument20 pagesVibration Analysis FundamentalsVivek PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document57 pagesChap 4Mohamed AbdelsalamNo ratings yet
- Sma 2343 IntrodDocument34 pagesSma 2343 IntrodSammy OmbiroNo ratings yet
- PDF Ch3B Couple StaticDocument43 pagesPDF Ch3B Couple StaticHaiqal AzizNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document10 pagesExperiment 1Mary Tilt100% (2)
- Cable and ArchesDocument15 pagesCable and Archess k sharmaNo ratings yet
- Force Systems ProblemsDocument13 pagesForce Systems ProblemsClement KooNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law & Lenz's Law ProjectDocument2 pagesFaraday's Law & Lenz's Law ProjectHong J HuwuaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document2 pagesTutorial 5SiddarthanSrtNo ratings yet
- Past Exams Ens 161Document18 pagesPast Exams Ens 161MervinNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Problems Solved for Forces and ReactionsDocument15 pagesEquilibrium Problems Solved for Forces and ReactionsSivaprasad DusiNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNo ratings yet
- Mock Examination: For Mechanics of Rigid Bodies (Statics)Document3 pagesMock Examination: For Mechanics of Rigid Bodies (Statics)Lynne Dianne ParaonNo ratings yet
- 2nd PaperDocument2 pages2nd PaperKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Made Easy Work Book.Document29 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Made Easy Work Book.Krishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Sunday The Hindu Short Notes (As PDFDocument1 pageSunday The Hindu Short Notes (As PDFKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- 1st PaperDocument1 page1st PaperKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- TEST-18 (ME) Heat Transfer (HT02)Document19 pagesTEST-18 (ME) Heat Transfer (HT02)Krishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Solved IIFT 5th Dec 2021 Slot 1 Paper With SolutionsDocument41 pagesSolved IIFT 5th Dec 2021 Slot 1 Paper With SolutionsKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material-ME-ME (Gate2016.info) PDFDocument186 pagesStrength of Material-ME-ME (Gate2016.info) PDFjayendrakashyap01No ratings yet
- Representing and Drawing Curves with Parametric Equations and Bezier CurvesDocument35 pagesRepresenting and Drawing Curves with Parametric Equations and Bezier CurvesKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpsDocument29 pagesCentrifugal PumpsSteve CarwellNo ratings yet
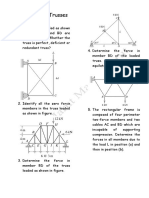
- Chapter 2: TrussesDocument2 pagesChapter 2: TrussesKrishna Vivek0% (1)
- Cover LetterDocument1 pageCover LetterKrishna VivekNo ratings yet
- Rectilinear Translation (Part I - Kinematics)Document2 pagesRectilinear Translation (Part I - Kinematics)Krishna VivekNo ratings yet