Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JC2 Chemistry Test P2
Uploaded by
Tesar DzikrullohCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JC2 Chemistry Test P2
Uploaded by
Tesar DzikrullohCopyright:
Available Formats
2
1 Aluminium is the most abundant Group 13 element and constitutes about 8%
of the Earth’s crust. The extraction of aluminium is done by processing
aluminium ore, bauxite to produce aluminium oxide also known as alumina.
A variety of aluminium compounds, for example aluminium chloride and
aluminium hydroxide, are used for different purposes such as food additives,
colouring and pharmaceuticals.
Aluminium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide are antacids. They are used to
treat symptoms of increased stomach acid, such as heartburn, upset stomach,
sour stomach, or acid indigestion. Once ingested, they react with the
hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
(a) Write down the electronic configuration of Al.
………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Why is the ionic radius of Al3+ far smaller than Al?
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… [2]
(c) Why is the ionic radius of Al3+ smaller than Mg2+?
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… [2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
3
(d) Explain why aluminium forms compounds with an oxidation state of +3
but not sodium.
……………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(e) Identify which antacid in the tablet is more effective in reacting with the
hydrochloric acid in the stomach? Show relevant working to support your
answer.
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… [2]
(f) Assuming that a typical adult has a body mass of 70 kg, determine the
maximum weekly intake of aluminium hydroxide in grams per kg of body
mass.
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………… [2]
(g) In the vapour phase, aluminium chloride forms a gaseous product with
molecular mass of 267. With an aid of a clearly labelled diagram, explain
how this product is formed from aluminium chloride.
Diagram :
Explanation :
……………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………….…………………………………………………[2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
4
(h) (i) Aluminium chloride is often describe as electron deficient.
Explain what is meant by electron deficient.
……………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………. [1]
(ii) State the angle of Cl-Al-Cl in AlCl3.
………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
[Total: 15]
2 Oxides of nitrogen such as NO2 are air pollutants that are present in the
exhaust of internal combustion engines. Modern cars are equipped with a
catalytic converter that reduces emissions of these harmful compounds. The
catalytic converter uses nanoparticles of platinum, palladium and rhodium,
which act as catalyst.
(a) (i) Write two equations for the reaction involving NO2 which occurs in
the catalytic converter.
………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
(ii) State the type of this catalyst.
……………………………………………………………………….…. [1]
(b) Nitrogen dioxide, NO2, is a brown gas while nitrogen tetroxide, N2O4, is a
colorless gas. The following equilibrium between these two gases was
set up.
2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4(g) ΔH < 0
Describe and explain, what you would see after the following changes
have been made and the system is allowed to reach equilibrium again.
(i) The temperature is decreased.
………………………………………………………………………..……
……………………………………………………………………...………
…………………………………………………………………...…………
……………………………………………..…………………………… [2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
5
(ii) The pressure is increased.
………………………………………………………………………..……
……………………………………………………………………...………
…………………………………………………………………...…………
……………………………………………..…………………………… [2]
(c) Nitrogen tetroxide is a strong oxidizing agent. It is liquefied and used as a
propellant in combination with a hydrazine-based rocket fuel.
2N2H4(l) + N2O4(l) → 3N2(g) + 4H2O(l)
(i) Suggest and explain a way to liquefy nitrogen tetroxide gas.
………………………………………………………………………..……
……………………………………………………………………...………
…………………………………………………………………...…………
……………………………………………..…………………………… [2]
(ii) Some average bond enthalpies are given below.
bond Bond enthalpy / kJ mol-1
N-O 201
N=O 607
Use the data in the table above, and relevant data from the Data
Booklet to calculate the enthalpy change of the reaction of
hydrazine with dinitrogen tetroxide.
[2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
6
(iii) The theoretical standard enthalpy change of reaction is found to be
–1258 kJ mol-1. Suggest another reason other than the bond
energies used are average values for the difference between your
calculated value in (ii) and the theoretical value.
……………………………………………..………………………...……
………………………………………………..…………………………[2]
(d) Hydrazine is also a strong reducing agent. Warming hydrazine with nitric
acid results in the production of gaseous nitrogen, N2, and nitrogen
monoxide, NO.
Write a half-equation for the reduction of the nitrate ion, NO − to nitrogen
3
monoxide in acidic solution.
………………………………………………………………………………….[1]
[Total 13]
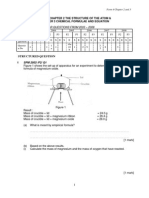
3 The bar chart below shows the third ionisation energy of nine consecutive
elements (J to R) in Periods 2 and 3 of the Periodic Table.
(a) Write an equation for the third ionization energy of element J.
………………………………………………………………………………… [1]
(b) Identify element K.
………………………………………………………………...………………. [1]
(c) On the axes provided, draw and label the orbital, which the third electron
is removed from element O.
[1]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
7
(d) With reference to the bar chart, your answer in (a) and (b) and the
electronic configuration of the species provided, explain:
(i) The higher 3rd ionization energy of N compare to O.
………………………………………………………………………..……
……………………………………………………………………...………
…………………………………………………………………...…………
……………………………………………..…………………………… [2]
(ii) The lower 3rd ionization energy Q than P.
………………………………………………………………………..……
……………………………………………………………………...………
…………………………………………………………………...…………
……………………………………………..…………………………… [2]
(e) The diagram below is an incomplete sketch showing the melting points of
some of the elements of the Period 3 (sodium to argon).
(i) Estimate and indicate on the graph, the melting points of the four
other elements: Mg, Al, S and Cl. [2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
8
(ii) Some reaction of magnesium and its compounds are shown below.
Mg + H2O(l) à D + H2
Mg + H2O(g) à E + H2
Identify compounds D and E.
D : ……………………………..
E : …………………………….. [2]
(f) Oxides of period 3 vary from basic, amphoteric, and acidic. In order for
the basic oxide to react with acidic oxide, it needs to be dissolved in
water first. Write the chemical equation for the basic oxides to react with
the acidic oxides with the help of water.
(i) Barium oxide and sulfur dioxide.
………………………………...……………………………………………
…………………….………………………………………....………… [1]
(ii) Sodium oxide and phosphorus (V) oxide.
…………………………………………………………………………...…
……………..………………………………………………………....... [1]
[Total 15]
4 But-1-ene reacts with hydrogen bromide to give 2-bromobutane as the major
product.
(a) Name and describe the mechanism for this reaction. Show all charges,
relevant lone pairs and the movement of electron pairs by using curly
arrows.
[3]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
9
(b) With reference to the mechanism you have drawn in (a)(i), explain why
the major product is 2-bromobutane rather than 1-bromobutane.
………………………………………………………………………..……………
……………………………………………….….………………...………………
…………………………………………….....…….………...……………………
………………………………………..…………..…………………………… [2]
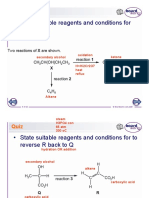
(c) The diagram below shows a reaction scheme involving 2-bromobutanone
a derivative product of 2-bromobutane.
2-bromobutanone M N
reaction 1 reaction 2
Compound M and N have the following properties:
§ Effervescence is seen when reacted with sodium metal.
§ No yellow precipitate is formed when mixed with alkaline aqueous
iodine.
§ A pale cream precipitate slowly forms when excess HNO3(aq) is
added followed by AgNO3(aq).
(i) Draw the structures for M and N.
M N
[2]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
10
(ii) Suggest the reagents and condition for reaction 1 and reaction 2.
reaction 1 …………………………………………………………….. [1]
reaction 2 …………………………………………………………….. [1]
(iii) State the mechanism in reaction 1.
………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(d) Ethanal is a flammable liquid with a fruity smell. It occurs naturally in ripe
fruit, coffee and fresh bread. A synthetic route involving ethanal is shown
below.
(i) Draw the structural formulae of compound B, C, and D in the
boxes below.
Reaction II
[3]
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
11
(iii) Suggest the reagents and conditions for.
Reaction I …………………………………………………………….. [1]
Reaction II ……………………………………………………………. [1]
Reaction III …………………………………………………………… [1]
[Total 17]
End of Questions
Semester 2 Examinations /Grade 11/Chemistry/P2/Global Sevilla/2019-2020
You might also like
- INTERVIEW IUP - More DetailedDocument5 pagesINTERVIEW IUP - More DetailedRifkhi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Controlled AssessmentDocument9 pagesControlled AssessmentMe WhenNo ratings yet
- 09 JJ H2 Prelim P2Document15 pages09 JJ H2 Prelim P2etherfoxxNo ratings yet
- Test On Group II ElementsDocument5 pagesTest On Group II ElementsKoo Keung EngNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2Document8 pagesChemistry 5070 2023 Gce Question Paper 2andrew silungweNo ratings yet
- 2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth MetalsDocument37 pages2.04 - 2.06 Redox Reactions, Halogens and Alkali Earth Metalsgobod52280No ratings yet
- 16+ Chemistry Nov 2019Document18 pages16+ Chemistry Nov 2019Kitty chenNo ratings yet
- Example PTE Structured QuestionsDocument5 pagesExample PTE Structured Questions301 Dhia JaharahNo ratings yet
- 09 JJ H2 Prelim P2Document15 pages09 JJ H2 Prelim P2Gopi KupuchittyNo ratings yet
- RedOx SLDocument36 pagesRedOx SLrozalia.kozinskaNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Document12 pages1st Term Chemistry Paper - 42Krish PatelNo ratings yet
- 2019 Jc1 Myct H2chem Paper 2 QPDocument15 pages2019 Jc1 Myct H2chem Paper 2 QPcolNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Second Semester Final Paper 2Document11 pagesGrade 8 Second Semester Final Paper 2dodoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 QNDocument19 pagesPaper 2 QNchuasioklengNo ratings yet
- 2020 SAJC H2 Prelim Paper 3 (QP)Document37 pages2020 SAJC H2 Prelim Paper 3 (QP)clarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- S4 Chemistry Paper 2 Hes Mock Examinations 2020Document12 pagesS4 Chemistry Paper 2 Hes Mock Examinations 2020TwinomujuniNo ratings yet
- Anderson Serangoon Junior College: 2021 JC 2 Mid Year Common TestDocument24 pagesAnderson Serangoon Junior College: 2021 JC 2 Mid Year Common TestpianorificationNo ratings yet
- SCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetDocument11 pagesSCLP Samaj School Year 10 Chemistry Revision WorksheetHarshil PatelNo ratings yet
- STPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2Document13 pagesSTPM Percubaan 2008 Sabah Chemistry Paper 2ChinWynn.com100% (1)
- Chem F2Document8 pagesChem F2Festus NanokNo ratings yet
- Chemistry P1Document13 pagesChemistry P1zachaeusNo ratings yet
- Chem pp4Document8 pagesChem pp4antonettemosweu211No ratings yet
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Document27 pagesStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry P1 QSDocument14 pagesChemistry P1 QSbarakaminifarmNo ratings yet
- Chemi 401 QDocument13 pagesChemi 401 QPenang Home TuitionNo ratings yet
- pg10 12Document3 pagespg10 12Melor DihatiNo ratings yet
- 2021 CJC H2 CHEM Prelim P2 QPDocument20 pages2021 CJC H2 CHEM Prelim P2 QPclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- FORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - ADocument9 pagesFORM 1 2023 END T3 CHEMISTRY QN - TEACHER - CO - .KE - SET - AYussuf HirowNo ratings yet
- Latih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Document15 pagesLatih Tubi Menjelang SPM 2010Farah Aisyah AhmadNo ratings yet
- X Chemistry Holiday HomeworkDocument2 pagesX Chemistry Holiday HomeworkhsrA amrahSNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Set Three 2017 ExamsDocument13 pagesChemistry Set Three 2017 Examsmoggadavid480No ratings yet
- 2012 CJC CH h2 p2 PromoDocument12 pages2012 CJC CH h2 p2 PromoDaniel ChuNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionslNo ratings yet
- General Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPDocument10 pagesGeneral Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPaanammanaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Second Semester Final Paper 2Document10 pagesGrade 8 Second Semester Final Paper 2dodoNo ratings yet
- Maple Leaf International School: Half Yearly Examination 2021 Subject: CHEMISTRY Class: IX Total Marks: 60Document13 pagesMaple Leaf International School: Half Yearly Examination 2021 Subject: CHEMISTRY Class: IX Total Marks: 60SN EDUCATIONNo ratings yet
- 2012 C1 Promo Paper 2 QuestionsDocument11 pages2012 C1 Promo Paper 2 QuestionsJiadong YeNo ratings yet
- Resourceful Mock Exam 1 2017 Uce Mocks Name . Index Number Signature 545/2 ChemistryDocument11 pagesResourceful Mock Exam 1 2017 Uce Mocks Name . Index Number Signature 545/2 ChemistryBaguma MichaelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper TWODocument12 pagesChemistry Paper TWOMBUGUA GRAPHICSNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document13 pagesChemistry Paper 2 Sabah STPM 2008 Excel Set 2 (Edu - Joshuatly.com)HaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Paper 2Document13 pagesForm 4 Paper 2gerald2.njoruNo ratings yet
- (Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1Document7 pages(Total 1 Mark) : IB Questionbank Chemistry 1DM0% (1)
- Chem Trial 2012Document14 pagesChem Trial 2012Han LingNo ratings yet
- Sda 3 Form 4Document13 pagesSda 3 Form 4Crystal MachipisaNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 32 MarksDocument6 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 32 Marksaya abdulfattahNo ratings yet
- 5th Form Exam ET 2014Document20 pages5th Form Exam ET 2014NIRVAN RAMESHNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: (S) 2 2 (Aq) 2 (G)Document30 pagesElectrochemistry: (S) 2 2 (Aq) 2 (G)Edon BediNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42taimurmalik5562100% (1)
- Oyani Mixed Secondary School: 233/1 Form Four Chemistry Paper 1 Theory MARCH 2020 Time: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesOyani Mixed Secondary School: 233/1 Form Four Chemistry Paper 1 Theory MARCH 2020 Time: 2 HoursAlmadiNo ratings yet
- Pahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)Document21 pagesPahang STPM Trial 2011 Chemistry Paper 2 (W Ans)plouffle100% (1)
- SMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Document16 pagesSMK Seri Perak, Parit Buntar Mid-Year Examination Form 5 2010Mohd Faizal Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Resource Mock Examinations, 2017: Paper 2Document9 pagesResource Mock Examinations, 2017: Paper 2Daniel MarkNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series Worksheet - 8B and 8CDocument6 pagesReactivity Series Worksheet - 8B and 8CHighlightNo ratings yet
- EdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 7 Paper Jan 2000Document8 pagesEdExcel A Level Chemistry Unit 7 Paper Jan 2000Nabeeha07No ratings yet
- SOALANnnDocument13 pagesSOALANnnKeertanaNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 32 MarksDocument7 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 32 MarksTasmiya BhyatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry F3 QNSDocument5 pagesChemistry F3 QNSangelinenyaboke360No ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Organic Reagent Practice - HWDocument14 pagesJC1 Chemistry Organic Reagent Practice - HWTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Enthalpy Change HWDocument2 pagesJC1 Chemistry Enthalpy Change HWTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Chemical EnergeticsDocument3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 6: Chemical EnergeticsTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Chemical Bonding HW3Document4 pagesJC1 Chemistry Chemical Bonding HW3Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Chemical Bonding HW2Document4 pagesJC1 Chemistry Chemical Bonding HW2Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Test1 Hydrocarbon (B)Document8 pagesJC1 Chemistry Test1 Hydrocarbon (B)Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- CarbonylDocument7 pagesCarbonylTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- JC1 Chemistry Test CarbonylDocument8 pagesJC1 Chemistry Test CarbonylTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- Thermal Decomposition (Strcture Questions)Document4 pagesThermal Decomposition (Strcture Questions)Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- Penjualan Tiket Drama 2019Document1 pagePenjualan Tiket Drama 2019Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- Jadwal AssemblyDocument2 pagesJadwal AssemblyTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- 5.1 NotesDocument10 pages5.1 NotesTasneemHudaNo ratings yet
- Reward Points Guidelines 2018-2019Document2 pagesReward Points Guidelines 2018-2019Tesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical Bonding PDFDocument16 pages3 Chemical Bonding PDFTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet
- 3 Chemical BondingDocument16 pages3 Chemical BondingTesar DzikrullohNo ratings yet