Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sizing Hydropneumatic Tank
Uploaded by
mdzuljpi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views10 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views10 pagesSizing Hydropneumatic Tank
Uploaded by
mdzuljpiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
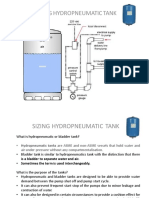
SIZING HYDROPNEUMATIC TANK
Eight steps to size hydropneumatic tank
1. Determine the flow rate requirement which is
normally the design flow rate of the pump system.
2. Determine the cut out pressure of the pump and
the cut in pressure. Normally the differential
between cut out pressure and cut in is about
10psig.
3. Determine the off time of the pump once it cuts
out says 15mins to 30mins.
4. Determine the type of use of the pump system.
5. Determine the acceptance volume for 30mins stop
time using table below.
6. Adjust the acceptance volume to the actual
required pump stop time if it differs from 30mins.
7. Tank size required is acceptance volume
(adjusted to pump stop time) divide by
draw down coefficient.
Determine the draw down coefficient from
table below.
8. Next select tank size from ASME table
below.
SETTING OF HYDROPNEUMATIC TANK AND WORKING OF TANK
1. The air charge pressure in the tank is typically set 2 PSI below
the pressure switch pump cut-in pressure or 10% to 20%
below the system pressure for surge applications.
2. Upon operation of the system, water is pumped into the
flexible bladder in the tank. As the bladder fills with water the
air cushion is compressed, causing a rise in the pressure in the
system. The pressure continues to rise until it reaches the
desired maximum system pressure (pump cut-out setting),
causing the pump to shut off.
3. Water remains in the system piping and the tank until
required. As water is drawn down from the system, the air
pressure in the tank decreases. When the system pressure
reaches the minimum pressure setting (pump cut-in setting),
the pump will turn on and start the cycle again.
SIZING OF HYDROPNEUMATIC TANK FOR
WATER CONTRACTION AND EXPANSION
SIZING OF HYDROPNEUMATIC TANK FOR
WATER CONTRACTION AND EXPANSION
• Obtain specific gravity of water at
maximum temperature.
• Obtain specific gravity of water at
minimum temperature.
• Obtain the volume of water in the pipe.
• Obtain the change in volume of water in
the pipe = volume of water in pipe multiply
by differential in specific gravity of water
You might also like
- How to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesFrom EverandHow to Select the Right Centrifugal Pump: A Brief Survey of Centrifugal Pump Selection Best PracticesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Booster PumpldhDocument40 pagesBooster PumpldhRishabh VermaNo ratings yet
- Sizing Pneumatic Tank 1659353147Document15 pagesSizing Pneumatic Tank 1659353147Engineering WavesNo ratings yet
- Hydro Pneumatic TankDocument15 pagesHydro Pneumatic TankChuck AnsphilNo ratings yet
- 09 Hydropneumatic Pressure Boosting SystemDocument64 pages09 Hydropneumatic Pressure Boosting SystemAnne Francoes NavarroNo ratings yet
- Wk11 - Chap9 Pumping FluidsDocument32 pagesWk11 - Chap9 Pumping Fluidsmohdyashfi mppNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Rotating EquipmentDocument32 pagesChapter 5 Rotating EquipmentAeffandii SamawiNo ratings yet
- AED Design Requirements - Jockey Pumps - Mar09Document5 pagesAED Design Requirements - Jockey Pumps - Mar09rogel_gana100% (1)
- The Proper Design Criteria For Selecting The Appropriate Pump - 2020-08-27 - Engineered Systems MagazineDocument3 pagesThe Proper Design Criteria For Selecting The Appropriate Pump - 2020-08-27 - Engineered Systems MagazineJhoNo ratings yet
- The Proper Design Criteria For Selecting The Appropriate Pump - 2020-08-27 - Engineered Systems MagazineDocument3 pagesThe Proper Design Criteria For Selecting The Appropriate Pump - 2020-08-27 - Engineered Systems MagazineJhoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic PumpsDocument6 pagesHydraulic PumpsSriram SastryNo ratings yet
- Proposed TIA 1229 NFPA1901Document3 pagesProposed TIA 1229 NFPA1901RJ MechNo ratings yet
- Controlled Circulation PumpDocument5 pagesControlled Circulation PumpLakshminarayanNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump InstallationDocument4 pagesCentrifugal Pump Installationjfisher2534No ratings yet
- Pump Head CalculationsDocument4 pagesPump Head CalculationsPrabhjot Singh SahiNo ratings yet
- Tank SizingDocument2 pagesTank SizingsamehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CompressorsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To CompressorsSriram SuryaNo ratings yet
- Ipe Plate 2 Fluid MachineriesDocument93 pagesIpe Plate 2 Fluid Machineriesjanuel borelaNo ratings yet
- 4VOL R01siDocument9 pages4VOL R01siNam Nguyen HoangNo ratings yet
- Why Bladder Tanks - 8!16!17Document10 pagesWhy Bladder Tanks - 8!16!17bla blaNo ratings yet
- Pump Head CalculationDocument15 pagesPump Head CalculationYashapuja100% (1)
- How To Size A Hydropneumatic Tank in A Pressure Booster SystemDocument3 pagesHow To Size A Hydropneumatic Tank in A Pressure Booster SystemAnonymous mNQq7ojNo ratings yet
- High Rise Water DistributionDocument2 pagesHigh Rise Water DistributionzueklateNo ratings yet
- Plant Layout-CompressorsDocument19 pagesPlant Layout-Compressorshalder_kalyan9216No ratings yet
- Minimum Thermal Flow in Centrifugal PumpsDocument3 pagesMinimum Thermal Flow in Centrifugal Pumpsmnt6176No ratings yet
- A W11-2011 GS-SV en XylemDocument128 pagesA W11-2011 GS-SV en XylemCristóbal ScheelNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Tuning of Pressure Switches and Hydropneumatic TanksDocument2 pagesSet Up and Tuning of Pressure Switches and Hydropneumatic TanksReza KhajeNo ratings yet
- Fire Nfpa 20Document25 pagesFire Nfpa 20BRANDON100% (2)
- Fluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)Document65 pagesFluid Machinery - Eng - Pump - Part2 (Compatibility Mode)ณัฐวัศ มั่นบุญสมNo ratings yet
- Pump HandbookDocument34 pagesPump Handbookamsc bNo ratings yet
- Hydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsDocument2 pagesHydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsBlancaNo ratings yet
- The Sizing Boiler Feed Pumps CalculationDocument3 pagesThe Sizing Boiler Feed Pumps CalculationArun Kumar DeyNo ratings yet
- 6 Boiler Feedwater PumpsDocument20 pages6 Boiler Feedwater PumpsCristhian Garcia VillarroelNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps: What Is A Centrifugal Pump?Document10 pagesCentrifugal Pumps: What Is A Centrifugal Pump?kenoly123No ratings yet
- PPSL3050 Manual 2 SpringDocument2 pagesPPSL3050 Manual 2 SpringLeAnn WysockiNo ratings yet
- How To Find Pump Size and Pump Head CalculationDocument8 pagesHow To Find Pump Size and Pump Head CalculationprosperNo ratings yet
- Subsea - Page 4Document79 pagesSubsea - Page 4lulalala8888100% (2)
- How To Size Hydropneumatic TankDocument3 pagesHow To Size Hydropneumatic TankfelipeNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Hydraulic PumpDocument22 pages3.1 Hydraulic PumpSiraj BusseNo ratings yet
- FOAM TANK (1/2) : Fire Fighting Equipment Data SheetDocument24 pagesFOAM TANK (1/2) : Fire Fighting Equipment Data SheetandinumailNo ratings yet
- محمد 1Document10 pagesمحمد 1Osama EL-AbdNo ratings yet
- Cold Water Supply - Part2Document8 pagesCold Water Supply - Part2Derek YuNo ratings yet
- Ebae 161 92 Ram Pump JenningsDocument6 pagesEbae 161 92 Ram Pump JenningsGaguk Triosona PraditaNo ratings yet
- Fire Pump Design: NFPA 20: Standard For The Installation of Stationary Pumps For Fire ProtectionDocument43 pagesFire Pump Design: NFPA 20: Standard For The Installation of Stationary Pumps For Fire ProtectionISH-QUENo ratings yet
- Steam Jet Refrigeration SystemDocument9 pagesSteam Jet Refrigeration SystemHenok GhidayNo ratings yet
- Operation & Maintanance Manual For HVWS SystemDocument18 pagesOperation & Maintanance Manual For HVWS SystemVijay Patel100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pumps TipsDocument34 pagesCentrifugal Pumps TipsFaizan AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Calculating Pump HeadDocument8 pagesCalculating Pump HeadPascal SayahNo ratings yet
- Presentation Report-Converted 1Document11 pagesPresentation Report-Converted 1S.k. YadavNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 7 Pump Performance - Single Pump: MEHB221 Fluids Mechanics Lab 2016Document6 pagesExperiment No. 7 Pump Performance - Single Pump: MEHB221 Fluids Mechanics Lab 2016Syahmi ShahimanNo ratings yet
- B&G Sizing Cooling Tower Pumps and Piping TEH-275Document12 pagesB&G Sizing Cooling Tower Pumps and Piping TEH-275ChowKC03100% (3)
- UNIT-3 Compressors, Blowers, Vacuum Pumps and Their Performance CharacteristicsDocument15 pagesUNIT-3 Compressors, Blowers, Vacuum Pumps and Their Performance CharacteristicsDhruv JariwalaNo ratings yet
- chptr1 28b 29 HydrlcsystmDocument14 pageschptr1 28b 29 HydrlcsystmThiuyah A/p RajandranNo ratings yet
- Compressors: Reciprocating Compressors Centrifugal Compressors DrivesDocument14 pagesCompressors: Reciprocating Compressors Centrifugal Compressors Drivessteepa22No ratings yet
- Chapter 05 (Jet Pump)Document3 pagesChapter 05 (Jet Pump)Muhammad FahadNo ratings yet
- Vw1004 Control KosoDocument27 pagesVw1004 Control KosoAnup Mitra100% (1)
- How To Size A PumpDocument6 pagesHow To Size A PumpSoe T. HtunNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop SystemsDocument3 pagesClosed Loop SystemsRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Pump PresentationDocument47 pagesPump Presentationmdzuljpi100% (2)
- Motor Starting and Protection MethodsDocument38 pagesMotor Starting and Protection MethodsmdzuljpiNo ratings yet
- Pump PresentationDocument47 pagesPump Presentationmdzuljpi100% (2)
- Problems Encountered in Fire Design - WE15Sept20Document9 pagesProblems Encountered in Fire Design - WE15Sept20mdzuljpiNo ratings yet
- Choosing Right Air OutletsDocument6 pagesChoosing Right Air OutletsAnkit JainNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency - CommentsDocument10 pagesEnergy Efficiency - CommentsmdzuljpiNo ratings yet
- Code of Guidance For Storage of CylindersDocument19 pagesCode of Guidance For Storage of Cylinderscadvis2kNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE - WI - Displacement Ventilation - 14MAY10Document67 pagesASHRAE - WI - Displacement Ventilation - 14MAY10mdzuljpiNo ratings yet
- Critical Environments Engineering GuideDocument37 pagesCritical Environments Engineering GuideAnand NambiarNo ratings yet
- Pump PresentationDocument47 pagesPump Presentationmdzuljpi100% (2)
- Fans and ApplicationDocument49 pagesFans and ApplicationmdzuljpiNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Design HK STDDocument19 pagesEnergy Efficient Design HK STDmdzuljpiNo ratings yet