Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Treatment For Cough
Drug Treatment For Cough
Uploaded by
Nadhirah Zulkifli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesCodeine and dextromethorphan are common antitussive drugs that work by suppressing the cough center in the brain. Codeine is converted to morphine which acts on opioid receptors, while dextromethorphan acts on sigma opioid receptors and as an NMDA antagonist. Guaifenesin is an expectorant that works by increasing fluid volume and decreasing viscosity of respiratory tract secretions. Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic agent that breaks down mucus viscosity through its sulfhydryl group, making mucus easier to cough up.
Original Description:
ggg
Original Title
Drug Treatment for Cough
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCodeine and dextromethorphan are common antitussive drugs that work by suppressing the cough center in the brain. Codeine is converted to morphine which acts on opioid receptors, while dextromethorphan acts on sigma opioid receptors and as an NMDA antagonist. Guaifenesin is an expectorant that works by increasing fluid volume and decreasing viscosity of respiratory tract secretions. Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic agent that breaks down mucus viscosity through its sulfhydryl group, making mucus easier to cough up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views4 pagesDrug Treatment For Cough
Drug Treatment For Cough
Uploaded by
Nadhirah ZulkifliCodeine and dextromethorphan are common antitussive drugs that work by suppressing the cough center in the brain. Codeine is converted to morphine which acts on opioid receptors, while dextromethorphan acts on sigma opioid receptors and as an NMDA antagonist. Guaifenesin is an expectorant that works by increasing fluid volume and decreasing viscosity of respiratory tract secretions. Acetylcysteine is a mucolytic agent that breaks down mucus viscosity through its sulfhydryl group, making mucus easier to cough up.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
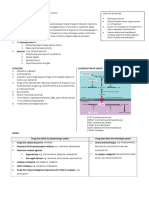
ANTITUSSIVES:
Suppress cough, produces symptomatic relief, useful for bothersome sleep, prevent restful sleep cough
MOA: suppress cough centre in medulla (central & peripheral effects) epithelial tissues heal themselves
Description Pharmacokinetics Adverse effect Drugs interaction
Codeine Low analgesic potency, Good oral bioavailability: 90% Abuse potential, but less than CYP450 inhibitors ↓ or
high antitussive activity Methylation of morphine at morphine completely block the
Suppress cough center carbon-3 ↓ hepatic pass effect Common: drowsiness, conversion of codeine to
as agonist at central μ Cytochrome P450 2D6 convert constipation morphine
opioid peptide codeine (10%) morphine Uncommon: addiction, CYP450 inducers
receptors Cytochrome P450 3A4 convert dependence, euphoria, (rifampicin &
Semi-synthetic opioid codeine norcodeine itching, nausea, vomiting, dry dexamethasone ↑
derived from codeine: Uridine diphosphate mouth, miosis, hypotension, conversion rate)
dihydrocodeine & glucuranosyl transferase depression Poor metabolisers
hydrocodeine (UDPGT) conjugates codeine, Rare: anaphylaxis, seizure, experience less
norcodeine & morphine to the respiratory depression morphine effects & side
corresponding 3- and 6- Codeine is metabolised to effects
glucuronides morphine passed through
breast milk fatally
depressing the respiration of a
breastfed baby
Withdrawal symptoms: drug
craving, runny nose, yawning
Dextromethropha Active ingredients in O-demethylation Pharmacokinetics only:
n many OTCs cold & dextrorphan by CYP3A4 Recommended doses: nausea, slight drowsiness, dizziness
cough medicines N-demethylation to 3- Recreational doses: euphoria, elevated mood, disorientation,
Suppress cough center methoxymorphinan by CYP3A4 confusion, altered time perception
at central & peripheral Partial conjugation with Acute OD: hallucinations, disturbance in thinking, senses &
sigma opioid peptide glucuronic acid and sulphate memory, impaired judgment
receptors & antagonist ions Could trigger histamine release allergic rxn
at NMDA receptors Traces of the unchanged drugs Potentiates activity of MAOIs & SSRIs hypotension &
Also acts as a are detectable in urine infrequently come
nonselective serotonin Poor metabolisers experience
reuptake inhitor ↑ effects, duration, & side
Half as potent as effects
codeine as an CYP450 inhibitor will effect this
antitussive drug
Noscapine General: Headache, loss of ↑ effects of centrally
Alkaloids from plants of the Papaveraceae family, w/o coordination, dizziness, sedating substances
significant analgesic properties drowsiness, tachycardia, such as alcohols &
Used for its antitussive effects nausea, vomiting hypnotics
Suppress cough center as agonist at central & peripheral May ↑ effect of
sigma opioid peptide receptors & antagonist at β2 receptors warfarin
Menthol General:
Organic compound derived from peppermint plant
Anti-irritant or anaesthetic cooling sensation produces by chemically triggering cold receptors
Has astringent & antibacterial properties that inhibit bacterial growth & help treat bad breath
Sore throat medication
ROA: oral
Suppress cough reflex & may be prescribed as menthol crystals or in the form of proprietary capsules
Cough suppression is acute and short-lived
Benzonatate Chemically related to Procaine, which is local anaesthetic Adverse effects:
Has both central & peripheral actions Headache, dizziness, pruritis, nasal congestion, burning of
MOA: exerts antitussive action on stretch or cough receptor in eyes, tightness of chess
lungs (local anaesthetic effect – also has some central effects)
DRUGS AFFECT THE RESPIRATORY TRACT FLUIDS (Expectorant, Mucolytic agents, Surfactants)
EXPECTORANTS
Description Pharmacokinetics Adverse effects Drug interaction
Guaifenesin OTC expectorant Rapidly metabolised Nausea, vomiting, formation of ↑ absorption &
Derived from guaiac tree used & excreted in the kidney stones, diarrhea, analgesic effect of
as remedy by American urine constipation paracetamol & aspirin
Indians, found when explorers Undergoes oxidation Nausea & vomiting can be ↓ by ↑ sedative effects of
reach North America in 16th to β-(2- taking guaifenesin w/ meals alcohol, tranquiliser,
century methoxyphenoxy) – Risk of forming kidney stones sleep-pills, & total
MOA: ↑ volume & ↓ viscosity lactic acid can be ↓ by maintaining good anaesthetics
of secretions in trachea & 40% of a dose is hydration & ↑ urine pH ↑ drug effects that ↓
bronchi; stimulates the flow of excreted as this Rare: severe allergic rxn may muscle tone
respiratory tract secretion metabolite in the occur, inc. rash or swelling of ↑ effects by lithium or
(allowing ciliary movement to urine w/I 3 hrs the lips or face magnesium
carry the loosened secretions t1/2 in plasma: 1hr Dry mouth ↑ dehydration effects of
upward toward the pharynx) diuretics & laxatives
Ammonium General: Irritant to gastric mucosa induce nausea & vomiting
chloride An electrolyte
Eg: Diphenhydramine expectorant syrup
MOA: irritate bronchial asthma production of excess
respiratory tract fluids
MUCOLYTIC AGENTS
Dissolves thick mucus & used to help relieve respiratory difficulties by dissolving various chemical bonds w/i secretions ↓ the viscosity
Inhalational: Acetylcysteine, Tyloxapol
Oral: Acetylcysteine, Bromohexine, Carbocysteine, Methylcysteine
Description Clinical uses Side effects
Acetylcysteine L-cysteine amino acid Asthma, emphysema, bronchitis, Stomatitis (inflammation of mouth &
MOA: contain reactive sulphydryl group ↓ mucus pneumonia, cystic fibrosis, lips), nausea, vomiting, rhinorrhoea
viscosity & liquefies it making it easier to cough up respiratory complication after (nasal cavity is filled with mucous
surgery fluid), bronchospasm
Bromhexine Synthetic derivative of vasicine Acute & chronic bronchitis CNS: Headache, tinnitus
MOA: acts at the formative stage of mucus formation in Bronchial asthma GIT: GI disturbances, gastric irritation
the glands w/i the mucus secreting cells by disrupting the
structure of acid mucopolysaccharide fibers easier to
expectorate
Ambroxol General: Occasional GIT side effects may
Synthesised from paracetamol & dibromobenzaldehyde occur but it is normally mild
MOA: stimulates synthesis & release of surfactant by type II pneumocytes promote mucus
clearance
MUCOPROTECTIVE AGENTS / ORAL DEMULCENT
Protects mucous membrane tissues of the respiratory tract
MOA: coat the mucous membrane with soothing film relieve minor pain and inflammation
Used as common ingredient in cough syrup & throat lozenges
Example: Pectin, glycerine, honey, propylene glycol, methyl cellulose, herbs that have high content of mucilage
Throat lozenges
Small medicated tablets intended to dissolve in mouth
Have lubricating and soothing effect on irritated tissue of the throat
May contain benzocaine or dextromethorphan
BRONCHODILATORS
If cough is d/t bronchospasm, β2 agonists are given
Relieve cough in patients w/ bronchial hyper reactivity
Should be used only when an element of bronchoconstriction is present
Short-acting: albuterol, levalbuterol, ipratropium (inhaler or as a liquid added to a nebulizer)
o Side effects: dry mouth, blurred vision, cough, tremors
Long-acting bronchodilators: tiotropium, salmeterol, formoterol, arformoterol, indacaterol, aclidinium (inhaler or nebulizer)
o Side effects: dry mouth, dizziness, tremors, runny nose, irritated/scratchy throat, rashes, blurred vision, rapid heart rate
You might also like
- Opioids PDFDocument2 pagesOpioids PDFErica Hyeyeon LeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Testing I. Definition of TermsDocument7 pagesDrug Testing I. Definition of TermsMichael Salazar OcampoNo ratings yet
- CNS DrugsDocument15 pagesCNS Drugsrechelle mae legaspi100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDean Angelo BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Document5 pagesPhilippine College of Health Sciences Pharmacology 1Ric BarrosNo ratings yet
- Drugs in ICUDocument83 pagesDrugs in ICUJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Year 2 Drug ListDocument8 pagesYear 2 Drug ListRay100% (1)
- Psy Cwu 1Document18 pagesPsy Cwu 1Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Reading Option Chain Using VolumeDocument19 pagesReading Option Chain Using VolumeAjay RaiNo ratings yet
- Margin TradingDocument14 pagesMargin TradingNicholas Sudan100% (1)
- Liver Cleanse and Gallbladder Cleanse (Flush) No SurgeryDocument3 pagesLiver Cleanse and Gallbladder Cleanse (Flush) No SurgeryIulian CracanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, HypnoticsDocument32 pagesLecture 28 - 3rd Asessment - Sedatives, Hypnoticsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Uenr6908uenr6908-00 SisDocument2 pagesUenr6908uenr6908-00 SisHelar W. Cutipa Machaca100% (1)
- Short Cases in Clinical Exams of Internal Medicine (PDFDrive)Document185 pagesShort Cases in Clinical Exams of Internal Medicine (PDFDrive)Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Morphine SulfateDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Morphine SulfateShara Lailanie A. Azis100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMajo Coronel100% (1)
- Drug Study of OpioidDocument3 pagesDrug Study of OpioidGerrahNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Psy Cwu 2Document12 pagesPsy Cwu 2Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Case 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCase 5 - (Salimbagat) Drug StudyChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesName of Drug Dosage/Route Mechanism of Action/ Classification Indication/Contraindication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMonica Gagarin CortezNo ratings yet
- HALOPERIDOLDocument1 pageHALOPERIDOLAlyxen Pelingen75% (4)
- Drug Study AsDocument3 pagesDrug Study Askev mondaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01Document5 pagesPHARMACOLOGY Assisgnment 01muhammadhamza muhammadiqbalNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The CNSI: Unit 4 Week 5 Siti Ma'rufahDocument26 pagesDrugs Acting On The CNSI: Unit 4 Week 5 Siti Ma'rufahnur rachmad afandiNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-PtsdDocument4 pagesDrug Study-PtsdWILMARIE SAPANTANo ratings yet
- Antiparkinsonian DrugsDocument5 pagesAntiparkinsonian Drugsluq9fifNo ratings yet
- Dda DrugDocument18 pagesDda Drugfarrah hanimNo ratings yet
- Drug-Study 2eDocument10 pagesDrug-Study 2eaijelethdaldeavilaNo ratings yet
- Subiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsDocument15 pagesSubiaga Antiparkinsonismmuscle-RelaxantsNicole ObispoNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: TramadolDocument5 pagesDrug Study: TramadolOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Central Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesDrugs Affecting The Central Nervous SystemEeric AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document12 pagesUnit 2parmarkeval1610No ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyWTRNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of ParkinsonismDocument28 pagesDrug Therapy of ParkinsonismZobayer AhmedNo ratings yet
- MorphineDocument4 pagesMorphineXyries Manuel VillenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument186 pagesDrug StudyTheresa Sombilla FacunlaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The CNS - 2Document41 pagesDrugs Acting On The CNS - 2Daniel OkakaNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Document24 pagesAnxiolytic & Hypnotics Part 2Sarah ArkanNo ratings yet
- Medications NHBDocument40 pagesMedications NHBAnonymous 7hJgATNo ratings yet
- Typical Antipsychotic DrugsDocument4 pagesTypical Antipsychotic DrugsErika Blaire N. OlacaoNo ratings yet
- 2018-2019 Cns DepressantsDocument5 pages2018-2019 Cns DepressantsMary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Right-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichDocument47 pagesRight-Hand Tremor at Rest, WhichsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Central Nervous System StimulantsDocument33 pagesCentral Nervous System StimulantsShweta KateNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Course TaskDocument8 pagesWeek 7 - Course TaskCher Allain BellosilloNo ratings yet
- Sedative HypnoticsDocument39 pagesSedative HypnoticsFatima ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Nursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenDocument35 pagesNursing - 1 AntiParkinsonian Drug - MehreenKhubaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Sedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDocument29 pagesSedative/ Hypnotics: Silim, Miriam Grace DDeloria, Alma J.No ratings yet
- Drugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UDocument24 pagesDrugs That Cause and Drugs That Alleviate Parkinsonism: BY Prof. Mbah A.UtemitopeNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument18 pagesAnti ParkinsonRitika DasNo ratings yet
- Kappa Uptake of Choline: Pharmacology1-FinalsDocument8 pagesKappa Uptake of Choline: Pharmacology1-FinalsJered OlarveNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Document32 pagesPharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- Block I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsDocument41 pagesBlock I Posting, Pharmacology Lectures: Antiparkisonian DrugsOdiete EfeNo ratings yet
- 3 ParasympatholyticsDocument35 pages3 ParasympatholyticsSudhakar LakavathNo ratings yet
- 404T CNS StimulantsDocument19 pages404T CNS StimulantsRaja RajaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 CNSDocument106 pagesChap 5 CNSKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- And Other Movement DisordersDocument38 pagesAnd Other Movement DisordersshravaniNo ratings yet
- Pharma Do ADocument28 pagesPharma Do Achocoholic potchiNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument37 pagesAnti ParkinsonAkmal SafwanNo ratings yet
- MRCP - PART ONE - PassMedicine 2020 - EndocrinologyDocument676 pagesMRCP - PART ONE - PassMedicine 2020 - EndocrinologyNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- MRCP - PART ONE - PassMedicine 2020 - EndocrinologyDocument676 pagesMRCP - PART ONE - PassMedicine 2020 - EndocrinologyNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Syifaa'.Wani - Shera.Achik - Syaa.Alin - Anis.Fatin - Yaya. THE 9 X-VIBRANT2017Document23 pagesSyifaa'.Wani - Shera.Achik - Syaa.Alin - Anis.Fatin - Yaya. THE 9 X-VIBRANT2017Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 11th Teacher, 2nd EditionDocument213 pages11th Teacher, 2nd EditionNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- C. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Document26 pagesC. Liver Function Test (Child Pugh Criteria-To See Albumin and Bilirubin)Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- ST RD ST RD NDDocument13 pagesST RD ST RD NDNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- CNS MEQ Part 2Document2 pagesCNS MEQ Part 2Nadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- I-Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) /laparoscopic Dye Test Day 2/3 Serum FSH and LH or Day 21 Serum ProgesteroneDocument33 pagesI-Hysterosalpingogram (HSG) /laparoscopic Dye Test Day 2/3 Serum FSH and LH or Day 21 Serum ProgesteroneNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Doing Well: For: Doctor: Date: Doctor's Phone Number: Hospital/Emergency Department Phone NumberDocument2 pagesDoing Well: For: Doctor: Date: Doctor's Phone Number: Hospital/Emergency Department Phone NumberNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Approach To Anaemia & HaematuriaDocument2 pagesApproach To Anaemia & HaematuriaNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- PP Teaching RoundDocument2 pagesPP Teaching RoundNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- 5 Obstructive Jaundice EditedDocument33 pages5 Obstructive Jaundice EditedNadhirah ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- SAP Transaction Codes in Bill of MaterialDocument2 pagesSAP Transaction Codes in Bill of MaterialEseyin Rachael OnifadeNo ratings yet
- DR Estari Mamidala - AchievementsDocument15 pagesDR Estari Mamidala - AchievementsEstari Mamidala100% (1)
- Echocardiography PDFDocument4 pagesEchocardiography PDFDualaut AndiNo ratings yet
- GEN MATH MODULE Final PDFDocument103 pagesGEN MATH MODULE Final PDFDaniel Sigalat LoberizNo ratings yet
- PIC 16F84A TutorialDocument58 pagesPIC 16F84A TutorialEduardo LaRaa100% (1)
- What Is PRDocument8 pagesWhat Is PRLaura MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Educating For Deep Ecology: Dolores LachapelleDocument5 pagesEducating For Deep Ecology: Dolores LachapelleJeyver RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Bbi2421 - 6 Types of SentenceDocument22 pagesBbi2421 - 6 Types of SentenceFaizah AzizanNo ratings yet
- 10 Notable Members of The Bavarian Illuminati - Conspiracy ArchiveDocument43 pages10 Notable Members of The Bavarian Illuminati - Conspiracy Archivemkmd.meyymaNo ratings yet
- RRL Process Sheet 1Document4 pagesRRL Process Sheet 1Julia Martha QuindoNo ratings yet
- El Filibusterismo Kabanata 5Document10 pagesEl Filibusterismo Kabanata 5Rhainley Faith IllutNo ratings yet
- Xyz Limited: Audit Programme For Stock Taking ExerciseDocument7 pagesXyz Limited: Audit Programme For Stock Taking ExerciseSteven LukNo ratings yet
- Jian Liu: The Composite Theorem of Ternary Quadratic Inequalities and Its ApplicationsDocument11 pagesJian Liu: The Composite Theorem of Ternary Quadratic Inequalities and Its ApplicationsPanagiote LigourasNo ratings yet
- JBLNPairwayDocument39 pagesJBLNPairwayjmscribblerNo ratings yet
- Assignment On InflationDocument7 pagesAssignment On InflationKhalid Mahmood100% (4)
- The Forgotten Glory of Vijayanagara EmpireDocument12 pagesThe Forgotten Glory of Vijayanagara EmpireShravan Kumar CivilNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Constituents in CoalDocument8 pagesInorganic Constituents in CoalJEFY JEAN ANo ratings yet
- PDEA v. BrodettDocument11 pagesPDEA v. BrodettKevinNo ratings yet
- Igich Emergency CommiteeDocument46 pagesIgich Emergency CommiteeSultan QuranmalNo ratings yet
- AndroidDocument6 pagesAndroidnikunjpatel90No ratings yet
- The Story Elements of The Text 2: "Fluffy Bunny Rabbit" Orientation Events TwistDocument3 pagesThe Story Elements of The Text 2: "Fluffy Bunny Rabbit" Orientation Events TwistDenny WokerNo ratings yet
- Wbcs Mains Hist Geo 2022-1-51Document22 pagesWbcs Mains Hist Geo 2022-1-51Debosruti BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- Palatino Roxford Natl Artist EssayDocument3 pagesPalatino Roxford Natl Artist EssayPalatino Roxford Rodeth C.No ratings yet
- CH 9. Shear Zones and Progressive DeformationDocument37 pagesCH 9. Shear Zones and Progressive Deformationelias assefaNo ratings yet
- Arcserve Whitepaper - UDP TechnicalDocument24 pagesArcserve Whitepaper - UDP TechnicalApple PieNo ratings yet
- Under-12 Boys SchedulesDocument3 pagesUnder-12 Boys SchedulesDaniel ReddyNo ratings yet