Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Common Valvular Heart Disease (At A Glance)
Uploaded by
Tamim IshtiaqueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Valvular Heart Disease (At A Glance)
Uploaded by
Tamim IshtiaqueCopyright:
Available Formats
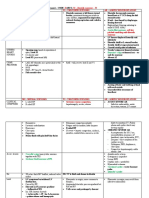
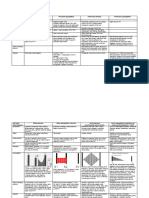
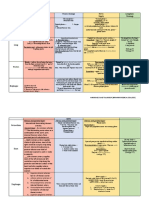
Common Valvular Heart Disease (at a glance)
Features /Points Mitral Stenosis Mitral Aortic Stenosis Aortic Regurgitation
Regurgitation
Peripheral Signs (Pulse) Low volume pulse, Normal Low volume slow High volume, Collapsing
normal in rhythm & Atrial rising pulse & Narrow pulse.
character or irregularly fibrillation/flutter pulse pressure Dancing Carotid pulse.
irregular (Atrial Quincke’s sign – Capillary
fibrillation) pulsation in nail beds.
Mitral facies (Malar de Musset’s sign – Head
flush) nodding with each pulse.
Duroziez’s sign – Pistol shot
murmur/bruit over femoral
artery.
Hills sign – Higher BP in legs
than arms.
Mueller’s sign – Pulsation in
uvula with heart beat.
Three BP – High systolic, Low
diastolic, Wide pulse pressure.
Palpation Apex Tapping Thrusting, active and Thrusting apex beat (LV Displaced, heaving apex beat
beat Others : RV heave, loud rocking (Volume pressure overload) (Volume overload)
P2 (pulmonary overload)
hypertension)
Thrill Diastolic apical thrill Systolic apical thrill Systolic apical thrill Diastolic apical thrill
Auscultation Heart Loud first heart sound Soft S1, apical S3 Soft second heart Fourth heart sound
sound and opening snap Sound 1st & 2nd heart sound normal
Murmur Low pitched, localized, Loud, blowing in Harsh, high pitched High pitch, blowing
rough, rumbling, character and musical Early diastolic murmur
Mid diastolic murmur Pansystolic murmur Ejection systolic Best heard in left lower para
Best heard with bell of Best heard at the apex murmur sternal area (3rd or 4th space)
stethoscope in left lateral that radiate to left Best heard in aortic with patient sitting and leaning
position and breathe hold axilla. area and radiate to right forward and breath hold after
after expiration. side of the neck. expiration.
Other murmur :
• Systolic murmur (increased
stroke volume)
• Austin Flint murmur (soft
mid-diastolic)
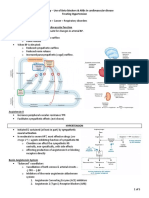
Symptoms • Breathlessness • Dyspnoea (pulmonary • Mild or moderate Mild to moderate aortic
• Fatigue venous congestion) stenosis: regurgitation
• Oedema, ascites • Fatigue (low cardiac usually asymptomatic • Often asymptomatic
• Palpitation output) • Exertional dyspnoea • Awareness of heart beat,
• Haemoptysis • Palpitation (atrial • Angina ‘palpitations’
• Cough fibrillation, increased • Exertional syncope Severe aortic regurgitation
• Chest pain stroke volume) • Sudden death • Breathlessness
• Thromboembolic • Oedema, ascites (right • Episodes of acute • Angina
complications (e.g. heart failure) pulmonary oedema
stroke, ischaemic limb)
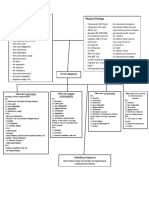
Investigations ECG • Right ventricular • Left atrial hypertrophy • Left ventricular • Initially normal, later left
hypertrophy: tall R waves (if not in atrial hypertrophy (usually) ventricular hypertrophy and T-
in V1–V3 fibrillation) • Left bundle branch wave inversion
• P mitrale or atrial • Left ventricular block
fibrillation hypertrophy
Chest X- • Enlarged LA & • Enlarged LA • May be normal; • Cardiac dilatation, maybe
ray Appendage • Enlarged LV sometimes enlarged LV aortic dilatation
(Straightening of Lt • Pulmonary venous and dilated • Features of left heart failure
border of heart, Double congestion ascending aorta on PA
shadow in Rt border of • Pulmonary oedema (if view, calcified valve on
heart) acute) lateral view
• Signs of pulmonary
venous congestion
(Kerley B line, Widening
of carina)
You might also like
- CAPE Biology Unit 2 ProjectDocument13 pagesCAPE Biology Unit 2 ProjectAudi Sweetangel0% (1)
- CARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditDocument2 pagesCARAS SCUTSHEET 2nd EditFrances Katrina Siruno100% (1)
- Dr. Schussler's Biochemistry RemediesDocument6 pagesDr. Schussler's Biochemistry RemediesAndrewJohnsonJensson0% (1)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition Theresa KyleDocument13 pagesTest Bank For Essentials of Pediatric Nursing 2nd Edition Theresa KyleJamesJacksonjbpof100% (76)
- CARDIO - Valvular Heart Diseases Table DR BARTOLOMEDocument8 pagesCARDIO - Valvular Heart Diseases Table DR BARTOLOMEShams JailaniNo ratings yet
- CVS Heart MurmursDocument2 pagesCVS Heart MurmursIamTineshNo ratings yet
- Mitral, Aortic, Tricuspid Valve Disorders and Atrial Septal DefectDocument2 pagesMitral, Aortic, Tricuspid Valve Disorders and Atrial Septal Defectdanny_awwadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment Pocket Reference Card PDFDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Assessment Pocket Reference Card PDFerikaNo ratings yet
- Approach to Hypertension ManagementDocument11 pagesApproach to Hypertension ManagementNoreenNo ratings yet
- PE, Tamponade, Constrictive PericarditisDocument1 pagePE, Tamponade, Constrictive PericarditisKaylee HvezdaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument118 pagesDifferences Between Left and Right Heart Failure: Diagnosis and TreatmentMirza Thaariq HapsitoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Motility2Document46 pagesDisorders of Motility2valdomiroNo ratings yet
- GYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsDocument3 pagesGYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument9 pagesCardiovascular DisordersChristine Evan HoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDocument5 pagesPharmacology - Use of Beta-Blockers & Arbs in Cardiovascular Disease Treating HypertensionDana20SNo ratings yet
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 pagesPatent Ductus Arteriosus 6. Aortic Stenosis: Signs and Symptoms: Signs and SymptomsKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Classification of MurmursDocument2 pagesClassification of MurmursNazneen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMDocument8 pagesApproximate Equivalents:: 0.100 Gmn. 1.00 GMakane ryuNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideDocument32 pagesPneumothorax and Hemothorax GuideYan Sheng HoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PDFDocument182 pagesCardiovascular System PDFXochitl ZambranoNo ratings yet
- EAR First AidDocument4 pagesEAR First Aidr_lakshmi2722No ratings yet
- Afrisya Bimo Siwendro Marisha Yadian Putri Preceptor: DR - Liza Nursanty, Spb. FinacsDocument32 pagesAfrisya Bimo Siwendro Marisha Yadian Putri Preceptor: DR - Liza Nursanty, Spb. FinacsirmaNo ratings yet
- CardiomyopathyDocument8 pagesCardiomyopathyKarisaNo ratings yet
- IM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysDocument5 pagesIM - Heart Failure Concept Map - PathophysTrisNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument83 pagesInternal MedicineSumbul PNo ratings yet
- B4 DyspneaDocument100 pagesB4 DyspneaAnonymous HH3c17osNo ratings yet
- Acute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyDocument13 pagesAcute Hypertension-Hypertensive Urgency and Hypertensive EmergencyAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, ArrhythmiaDocument14 pagesWeek 10 - Hypertension, Atherosclerosis, Arrhythmiashivani patel100% (1)
- Basic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Document116 pagesBasic ECG For Refresher Course 2014Winz DolleteNo ratings yet
- Shock, Sirs & ModsDocument37 pagesShock, Sirs & ModsambitioustamannaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Resistant and Refractory HypertensionDocument21 pagesTreatment of Resistant and Refractory HypertensionLuis Rodriguez100% (1)
- Acute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ PerfusionDocument3 pagesAcute Medicine: Shock: Inadequate Tissue and Organ Perfusionmyat252No ratings yet
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- Medicine1 Grand PE ScriptDocument10 pagesMedicine1 Grand PE ScriptCarmeline Santi BeronillaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshDocument83 pagesApproach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Charting Examples For Physical AssessmentDocument16 pagesCharting Examples For Physical Assessmentim3in1No ratings yet
- ECG - ACLS 2020 ModuleDocument68 pagesECG - ACLS 2020 ModuleRasheedAladdinNGuiomala100% (1)
- Thyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanDocument27 pagesThyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanMarrah Avila Acuin100% (1)
- IM-Module B Summarized Notes (IBD)Document69 pagesIM-Module B Summarized Notes (IBD)DeepbluexNo ratings yet
- Pre-op Evaluation SummaryDocument1 pagePre-op Evaluation Summarysabbo morsNo ratings yet
- (Warding) Guideline 1 - QCGH-HISTORY - PE - GUIDELINEDocument4 pages(Warding) Guideline 1 - QCGH-HISTORY - PE - GUIDELINEHynne Jhea Echavez100% (1)
- Stroke Signs, Risks, and Nursing CareDocument1 pageStroke Signs, Risks, and Nursing CareMariel Febreo MerlanNo ratings yet
- IMG EmpAposterDocument1 pageIMG EmpAposterChiu LeoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Main DrugsDocument14 pagesPharmacology Main DrugsSabir KhanNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretations GoodDocument104 pagesECG Interpretations GoodaymenNo ratings yet
- Treatment and Classification of Heart FailureDocument2 pagesTreatment and Classification of Heart FailureShannon RamsumairNo ratings yet
- Key AnatomyDocument12 pagesKey Anatomyjoedeegan_No ratings yet
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDocument1 pageGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentMuthia ArsilNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Emergencies PDFDocument57 pagesCardiac Emergencies PDFJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- ECG ReviewDocument146 pagesECG ReviewThea DinoNo ratings yet
- Notes ImDocument5 pagesNotes Imsharmee sarmientaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesApproach To Patient With Endocrine DisordersSeff CausapinNo ratings yet
- Medicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2Document4 pagesMedicine OSCE - Common Diseases Ver2TrisNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder PDFDocument22 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder PDFapi-545811586No ratings yet
- Common MedicationsDocument4 pagesCommon MedicationsFatima CarricoNo ratings yet
- History Taking and Physical ExaminationDocument53 pagesHistory Taking and Physical ExaminationBoruuf If GammachuuNo ratings yet
- Integumentry PDFDocument17 pagesIntegumentry PDFMehul RathoreNo ratings yet
- Abg InterpretationDocument1 pageAbg InterpretationPrincess EspadaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PathophysDocument1 pageRespiratory PathophysTori IkeharaNo ratings yet
- Physical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityDocument1 pagePhysical Inactivity: Aging Men Hypertension Smoker ObesityKEn PilapilNo ratings yet
- PEEP Positive End Expiratory Pressure and Its ConsequencesDocument2 pagesPEEP Positive End Expiratory Pressure and Its ConsequencesSadiq ZakariaNo ratings yet
- SoplosDocument1 pageSoplosMaría Fernanda Domínguez BojórquezNo ratings yet
- Copy of Mumurs Summary.pdfDocument6 pagesCopy of Mumurs Summary.pdfykteo323No ratings yet
- Artery, Vein, Nerve and Lymphatic Drainage of Thoracic OrgansDocument9 pagesArtery, Vein, Nerve and Lymphatic Drainage of Thoracic OrgansTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- A&P - 5. Neurobiology of Emotions (9p)Document9 pagesA&P - 5. Neurobiology of Emotions (9p)Tamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- MS MR As ArDocument21 pagesMS MR As ArTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Asd VSD TofDocument12 pagesAsd VSD TofTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - Pericardial Disease PDFDocument1 pageCardiology - Pericardial Disease PDFPshtiwan MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - ACLS Easy PDFDocument1 pageCardiology - ACLS Easy PDFViridianNo ratings yet
- OMedEd - Cardiology - CAD PDFDocument2 pagesOMedEd - Cardiology - CAD PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Cardiology - Hypertension PDFDocument2 pagesCardiology - Hypertension PDFCarlos RodriguesNo ratings yet
- InflammationDocument13 pagesInflammationTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- JNC 8 Guideline Algorithm for Treating HypertensionDocument2 pagesJNC 8 Guideline Algorithm for Treating HypertensionTaradifaNurInsi0% (1)
- FluidDocument6 pagesFluidTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Clostridium Tetani and BotulinumDocument12 pagesClostridium Tetani and BotulinumTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Management of SepsisDocument34 pagesManagement of SepsisTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology DrugsDocument16 pagesPharmacology DrugsTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument29 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument8 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisTamim IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- The British Zemu Gap Expedition 2008Document12 pagesThe British Zemu Gap Expedition 2008eccrkNo ratings yet
- Pharm Calcium Channel Blockers (Bahar&Amy) "Vera Dialed The Calcium Channel To Buy A Knife" Verapramil, Diltizaem, NifedipineDocument7 pagesPharm Calcium Channel Blockers (Bahar&Amy) "Vera Dialed The Calcium Channel To Buy A Knife" Verapramil, Diltizaem, Nifedipinecherrybombaz100% (4)
- Generalized Anxiety DisorderDocument14 pagesGeneralized Anxiety DisorderBarjees100% (2)
- CHN-Week 1Document4 pagesCHN-Week 1rich_dela_china100% (3)
- 21 Masterclass NLE Gapuz 2 - HANDOUTSDocument16 pages21 Masterclass NLE Gapuz 2 - HANDOUTSLimuel dale CaldezNo ratings yet
- Growing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyDocument2 pagesGrowing in Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) Market To Set New Business Opportunities For Start Up CompanyPR.comNo ratings yet
- 1st Half Book, EnglishDocument2 pages1st Half Book, EnglishFast Computers100% (2)
- Elstrott 2019Document9 pagesElstrott 2019Aurha Akmal GinarisNo ratings yet
- PHILOSOPHY and DISABILITYDocument21 pagesPHILOSOPHY and DISABILITYLuhan Albert YnarezNo ratings yet
- Defining Mental Illness' in Mental Health PolicyDocument13 pagesDefining Mental Illness' in Mental Health PolicyMohammad AfiefNo ratings yet
- Exfoliative Respiratory Cytology (Part 1 of 2)Document15 pagesExfoliative Respiratory Cytology (Part 1 of 2)Jenn100% (2)
- Infections AntibioticsDocument4 pagesInfections AntibioticsMatthieu FortinNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument11 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAlynna ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Testing and Medication ManagementDocument27 pagesPreoperative Testing and Medication ManagementWidya JelitaNo ratings yet
- Kansas Foodborne Illness ManualDocument186 pagesKansas Foodborne Illness ManualLeo M. Pedro Jr.No ratings yet
- Prodromal SchizophreniaDocument13 pagesProdromal SchizophreniadizhalfaNo ratings yet
- One Point Acupressure Treatment AllDocument23 pagesOne Point Acupressure Treatment AllPraveen Kumar100% (1)
- EnvMonitoringHygieneGuideforEHOs PDFDocument16 pagesEnvMonitoringHygieneGuideforEHOs PDFPramod SivanandanNo ratings yet
- Fluids and Electrolytes: Epidemiology/PathophysiologyDocument27 pagesFluids and Electrolytes: Epidemiology/PathophysiologyManna YankiNo ratings yet
- Decompensated HFDocument16 pagesDecompensated HFJessica GarletsNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Inflammatory Markers in HTNDocument6 pagesComparison of Inflammatory Markers in HTNDan JohnstonNo ratings yet
- Preventative Care Assignment 3 (1) ADocument9 pagesPreventative Care Assignment 3 (1) AOdia OaikhenaNo ratings yet
- The stellate ganglion is located anterior to the transverse processes of C7 and T1 vertebraeDocument287 pagesThe stellate ganglion is located anterior to the transverse processes of C7 and T1 vertebraeSAJID ALINo ratings yet
- Miopati - Referensi MiopatiDocument25 pagesMiopati - Referensi MiopatiKelvin Theandro GotamaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Diet GuideDocument6 pagesHospital Diet GuidejhelabooNo ratings yet
- The Reiki Power SymbolDocument23 pagesThe Reiki Power SymbolIuliana Rasaneanu100% (3)
- Daftar Kode BPJSDocument2 pagesDaftar Kode BPJSlilik agustinNo ratings yet