Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Fibrous Bands:: Case Illustration
Uploaded by
Fatma HandayaniOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Fibrous Bands:: Case Illustration
Uploaded by
Fatma HandayaniCopyright:
Available Formats
case illustration
J Neurosurg 124:186–187, 2016
Trigeminal neuralgia caused by fibrous bands:
case illustration
Yoshifumi Mizobuchi, MD, PhD, Kenji Shouno, MD, Kohei Nakajima, MD, PhD, and
Shinji Nagahiro, MD, PhD
Department of Neurosurgery, Institute of Health Biosciences, The University of Tokushima Graduate School,
Tokushima, Japan
http://thejns.org/doi/abs/10.3171/2014.12.JNS1463
Key Words trigeminal neuralgia; fibrous band; epidermoid tumor; peripheral nerve
W
e describe a rare case of trigeminal In conclusion, a fibrous band thus seems to be
neuralgia caused by a fibrous band an extremely rare cause of trigeminal neuralgia.
after epidermoid tumor resection. A Therefore, surgery to release the constricted
31-year-old woman presented with right-sided nerve should be considered even if MRI shows
facial pain. MRI showed an abnormal enhance- no apparent tumor recurrence or offending ar-
ment indicating a neoplasm in the right cerebel- tery around the trigeminal nerve.
lopontine cistern. Resection was performed,
and the tumor was completely removed (Fig. 1
left). The final diagnosis was epidermoid tumor. References
Two years after surgery, the patient experienced 1. Bathla G, Hegde AN: The trigeminal nerve: an
a gradual return of pain that became refractory illustrated review of its imaging anatomy and
pathology. Clin Radiol 68:203–213, 2013
to medication. She was referred to our hospital, 2. Kimura T, Sameshima T, Morita A: Trigeminal
where MRI revealed notches in the proximal and neuralgia caused by a fibrous ring around the
distal sides of the trigeminal nerve not seen on nerve. J Neurosurg 116:741–742, 2012
the immediate postoperative MR image (Fig. 1 3. Leclercq D, Thiebaut JB, Heran F: Trigeminal
right). On images obtained intraoperatively, we neuralgia. Diagn Interv Imaging 94:993–1001,
observed no offending artery that compressed a 2013
nerve or distortion of the trigeminal nerve. In- 4. Love S, Coakham HB: Trigeminal neuralgia: pa-
stead, we found fibrous bands constricting the thology and pathogenesis. Brain 124:2347–2360,
2001
trigeminal nerve at proximal and distal sites
(Fig. 2 left). After the fibrous bands were cut,
the patient’s neuralgia was relieved, and no oth-
er sensory deficit occurred (Fig. 2 right). Author Contributions
In patients presenting with typical trigeminal Conception and design: Mizobuchi. Acquisition of
neuralgia but with an MRI-documented notch data: Mizobuchi. Analysis and interpretation of data:
seen in the trigeminal nerve, the condition may Mizobuchi. Drafting the article: Mizobuchi. Critically
revising the article: all authors. Reviewed submitted
be caused by an unusual type of trigeminal version of manuscript: all authors. Approved the final
nerve constriction.1,3,4 To the best of our knowl- version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors:
edge, trigeminal neuralgia due to a fibrous band Mizobuchi. Administrative/technical/material support:
has been reported only once in the literature.2 Nagahiro. Study supervision: Nagahiro.
Submitted January 9, 2014. accepted December 18, 2014.
include when citing Published online June 26, 2015; DOI: 10.3171/2014.12.JNS1463.
Disclosure The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
Correspondence Yoshifumi Mizobuchi, Department of Neurosurgery, Institute of Health Biosciences, The University of Tokushima Graduate School, 3-18-15, Kuramo-
to-cho, Tokushima 770-8503, Japan. email: mizo@yj8.so-net.ne.jp.
186 J Neurosurg Volume 124 • January 2016 ©AANS, 2016
Trigeminal neuralgia caused by fibrous band
Fig. 1. Left: Postoperative 3D FIESTA image showing that the epidermoid tumor has been completely removed from the right
cerebellopontine cistern. Right: 3D FIESTA image obtained 2 years after surgery demonstrating no apparent tumor recurrence.
The arrows indicate notches in the right trigeminal nerve at the proximal and distal sites. The central part of the right trigeminal
nerve has become barrel shaped.
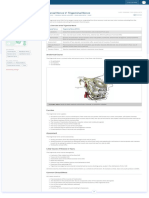
Fig. 2. Left: Illustration of the diseased trigeminal nerve, showing an absence of both distortion and arterial loops capable of
compressing the nerve. Close inspection revealed that the nerve was constricted by two fibrous circumferential bands. Right: Il-
lustration of the fibrous bands after they were cut using a microknife. Immediately after cutting, the constricted parts expanded
slightly. SCA = superior cerebellar artery. Copyright Yoshifumi Mizobuchi. Published with permission.
J Neurosurg Volume 124 • January 2016 187
You might also like
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsDocument16 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Conventional AntipsychoticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior NCM 105 LectureDocument70 pagesCare of Clients With Maladaptive Pattern of Behavior NCM 105 LectureMay June100% (1)
- 1) A) List and Assess Each One of The Patient's ComplaintsDocument19 pages1) A) List and Assess Each One of The Patient's ComplaintsMuhammad HilmiNo ratings yet
- (Re-Work) Google's New Manager Training Slides PDFDocument121 pages(Re-Work) Google's New Manager Training Slides PDFAnca-Andreea HrițuleacNo ratings yet
- Body Mapping For Better Playing - Berklee College of MusicDocument11 pagesBody Mapping For Better Playing - Berklee College of MusicMax Gpsii100% (1)
- Sensory Images (English 9)Document45 pagesSensory Images (English 9)Shakira SonerNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Space Occupying Lesions of BrainDocument3 pagesDiagnosis of Space Occupying Lesions of BrainsarahNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation in Orthopedic SurgeryDocument132 pagesRehabilitation in Orthopedic Surgeryaminur rahman100% (1)
- Hydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectDocument7 pagesHydrocephalus AND Neural Tube DefectTherese ArellanoNo ratings yet
- BUKUDocument137 pagesBUKUFatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Thopaedic Science: JournalDocument16 pagesThopaedic Science: JournalCiro Madrid FloresNo ratings yet
- Matsui 2002Document5 pagesMatsui 2002Vishal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Calcified Pseudoneoplasm of The Neuraxis Capnon A Lesson Learnt From A Rare Entity PDFDocument3 pagesCalcified Pseudoneoplasm of The Neuraxis Capnon A Lesson Learnt From A Rare Entity PDFKisspetre PetreNo ratings yet
- Pure Trigeminal Motor Neuropathy: A Case Report: Clinical NoteDocument4 pagesPure Trigeminal Motor Neuropathy: A Case Report: Clinical Noteemilio9fernandez9gatNo ratings yet
- Acu Accident LumbarDocument2 pagesAcu Accident Lumbarrswongym449No ratings yet
- Cheesborough2014 PDFDocument5 pagesCheesborough2014 PDFGregorius Thomas PrasetiyoNo ratings yet
- Compression of The Posterior Interosseous Nerve Sec 2024 International JournDocument4 pagesCompression of The Posterior Interosseous Nerve Sec 2024 International JournRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument8 pages1 PBMahathir Harry PermanaNo ratings yet
- PIIS1526590013009358Document8 pagesPIIS1526590013009358intermediosamberesNo ratings yet
- Early Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmDocument3 pagesEarly Resolution of Third Nerve Palsy Following Endovascular Treatment of A Posterior Communicating Artery AneurysmZakiyul FuadNo ratings yet
- Post-Traumatic Neuroma After Hair Transplantation: LettersandcommunicationsDocument2 pagesPost-Traumatic Neuroma After Hair Transplantation: LettersandcommunicationsNishanthini AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- RsssDocument3 pagesRsssMuhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- 08 OccipitalDocument6 pages08 OccipitalFilippo FerrettiNo ratings yet
- Peroneal Nerve Palsy Following Acp TreatmentDocument3 pagesPeroneal Nerve Palsy Following Acp TreatmentLydwiNa JcNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue Mass and Electrical Discharge: Whats Involved?Document4 pagesSoft Tissue Mass and Electrical Discharge: Whats Involved?IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Jns 1988 68 3 0366Document12 pagesJns 1988 68 3 0366RomulopedrozaNo ratings yet
- Kakizawa 2008Document8 pagesKakizawa 2008Vasantha RajanNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus and Trigeminal Neuralgia: Exploring The Association and Management OptionsDocument5 pagesHydrocephalus and Trigeminal Neuralgia: Exploring The Association and Management Optionsakhmad ridhaniNo ratings yet
- TN 2Document5 pagesTN 2faty basalamahNo ratings yet
- Tumores en CuelloDocument6 pagesTumores en CuellokalixinNo ratings yet
- Fneur 12 661441Document17 pagesFneur 12 661441ChadiIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 00002.pdf JsessionidDocument8 pages00002.pdf JsessionidSeti Aji HNo ratings yet
- AsianJNeurosurg102126-4310714 115827 PDFDocument3 pagesAsianJNeurosurg102126-4310714 115827 PDFSucipto HartonoNo ratings yet
- Effect of The CO2 Milliwatt Laser On Neuroma Formation in RatsDocument5 pagesEffect of The CO2 Milliwatt Laser On Neuroma Formation in Ratsrnnr2159No ratings yet
- Abducens Nerve Palsy As Initial Symptom of Trigeminal SchwannomaDocument8 pagesAbducens Nerve Palsy As Initial Symptom of Trigeminal SchwannomaLinius CruzNo ratings yet
- Fneur 14 1138661Document2 pagesFneur 14 1138661ChadiIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Technical Notes & Surgical TechniquesDocument5 pagesInterdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Technical Notes & Surgical TechniquesYovanka Naryai ManuhutuNo ratings yet
- Case Series - A Radiological Spectrum of Cranial Nerve SchwannomasDocument11 pagesCase Series - A Radiological Spectrum of Cranial Nerve SchwannomasInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Neurocutaneous Vascular Hamartomas Mimicking Cobb Syndrome: Case ReportDocument4 pagesNeurocutaneous Vascular Hamartomas Mimicking Cobb Syndrome: Case ReportPam MoyolemaNo ratings yet
- Knee Pain and The Infrapatellar Branch of The Saphenous: NerveDocument3 pagesKnee Pain and The Infrapatellar Branch of The Saphenous: NervefostizzNo ratings yet
- Neuralgia Trigeminia 1Document7 pagesNeuralgia Trigeminia 1Nuni SukindarNo ratings yet
- Loukas Et Al-2013-Clinical AnatomyDocument3 pagesLoukas Et Al-2013-Clinical AnatomyChrissNo ratings yet
- Herniation of Uncus and Parahippocampal Gyrus: An Accidental Finding On Magnetic Resonance Imaging of CerebrumDocument3 pagesHerniation of Uncus and Parahippocampal Gyrus: An Accidental Finding On Magnetic Resonance Imaging of CerebrumDanaAmaranducaiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Removal of Spinal Tumors: Article by James Willey, Cst/Cfa, and Mark V. Iarkins, M DDocument8 pagesSurgical Removal of Spinal Tumors: Article by James Willey, Cst/Cfa, and Mark V. Iarkins, M DLuwiNo ratings yet
- Superficial Radial Nerve Compression Due To Fibrom 2019 Acta Orthopaedica EtDocument3 pagesSuperficial Radial Nerve Compression Due To Fibrom 2019 Acta Orthopaedica EtanggiNo ratings yet
- Jkns 45 57Document3 pagesJkns 45 57idelviceNo ratings yet
- Nerve Injuries of The NeckDocument12 pagesNerve Injuries of The NeckAndrés Faúndez TeránNo ratings yet
- 10 1056@NEJMra1914484Document9 pages10 1056@NEJMra1914484abhishekjha0082No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1878875018300159 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S1878875018300159 MainAlexandreNo ratings yet
- Uru Ingles ADocument7 pagesUru Ingles ASaurabh SatheNo ratings yet
- Intracranial Epidermoid CystDocument3 pagesIntracranial Epidermoid CystWildaHanimNo ratings yet
- Kishima 2007Document6 pagesKishima 2007moiNo ratings yet
- Fulltext - Smjo v3 1059Document3 pagesFulltext - Smjo v3 1059Rachell AchellNo ratings yet
- Chondrosarcoma of The Thoracic Spine A Rare CaseDocument21 pagesChondrosarcoma of The Thoracic Spine A Rare CaseTHESSNAVARRONo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument26 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptHippokampaNo ratings yet
- 127 - Case Report - Complicanza Iniezione Faccette CervicaliDocument3 pages127 - Case Report - Complicanza Iniezione Faccette CervicaliMarco PeroliNo ratings yet
- OrtoDocument4 pagesOrtoLuís CorreiaNo ratings yet
- Spinal Tuberculosis: Imaging Features On MRIDocument6 pagesSpinal Tuberculosis: Imaging Features On MRIEster JuanitaNo ratings yet
- Natrella Et Al. - 2012 - Rare Disease Supratentorial Neurenteric Cyst Associated With A Intraparenchymal SubependymomaDocument6 pagesNatrella Et Al. - 2012 - Rare Disease Supratentorial Neurenteric Cyst Associated With A Intraparenchymal SubependymomaflashjetNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve Trauma: Mechanisms of Injury and RecoveryDocument44 pagesPeripheral Nerve Trauma: Mechanisms of Injury and RecoveryJa NetNo ratings yet
- High Contrast High Resolution Imaging of PosttraumDocument10 pagesHigh Contrast High Resolution Imaging of PosttraumPaulo Ferreira OrtodontiaNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Approach For Extraforaminal Synovial Cyst L5-S1Document7 pagesMinimally Invasive Approach For Extraforaminal Synovial Cyst L5-S1Tatiana RoaNo ratings yet
- Lipoma Causing A Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Case ReportDocument3 pagesLipoma Causing A Posterior Interosseous Nerve Syndrome: Case ReportShashank SNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiologic Investigation of MandibularDocument3 pagesElectrophysiologic Investigation of MandibularlazacaixNo ratings yet
- 10.1055@s 0032 1313634Document8 pages10.1055@s 0032 1313634lucasnegromonte0001No ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: World NeurosurgeryDocument16 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: World Neurosurgerynegin.safari8227No ratings yet
- Isolated Hypertrophic Neuropathy of The Oculomotor NerveDocument4 pagesIsolated Hypertrophic Neuropathy of The Oculomotor NerveEvelin HarrizonNo ratings yet
- Surgery of the Cranio-Vertebral JunctionFrom EverandSurgery of the Cranio-Vertebral JunctionEnrico TessitoreNo ratings yet
- Preventive Resin Restorations: Review ArticlesDocument5 pagesPreventive Resin Restorations: Review ArticlesFatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Adj 12464Document3 pagesAdj 12464Fatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Crosstabs GTL Kualitas - Hidup: Lampiran Uji Chi SquareDocument3 pagesCrosstabs GTL Kualitas - Hidup: Lampiran Uji Chi SquareFatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Hospital Management and Health Policy-A South African PerspectiveDocument7 pagesHospital Management and Health Policy-A South African PerspectiveFatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- JIndianSocPeriodontol214326-4026404 010706Document3 pagesJIndianSocPeriodontol214326-4026404 010706Fatma HandayaniNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Pain: DR M Madhavi LathaDocument23 pagesPhysiology of Pain: DR M Madhavi Lathanico diangeloNo ratings yet
- Brain TumorDocument1 pageBrain TumorChase XerolfNo ratings yet
- Retrospective Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocument19 pagesRetrospective Post Traumatic AmnesiaIRSANCIPUTRANo ratings yet
- My Published Paper 6, AnesthesiaDocument5 pagesMy Published Paper 6, Anesthesiamir sahirNo ratings yet
- Speech AudiometryDocument5 pagesSpeech Audiometry354No ratings yet
- Alternate Loudness Balance TestDocument4 pagesAlternate Loudness Balance TestAnish RajNo ratings yet
- Example Wais-Iv-Iq-Sample-ReportDocument11 pagesExample Wais-Iv-Iq-Sample-ReportRachel100% (1)
- Telaah Jurnal Internasional 1Document3 pagesTelaah Jurnal Internasional 1Anonymous TwBnEVfzqNo ratings yet
- Nova Istrazivanja o AnksioznostiDocument6 pagesNova Istrazivanja o Anksioznostibarkley_gnarlsNo ratings yet
- Sample Preparation OutlineDocument2 pagesSample Preparation OutlineAtiqah NadirahNo ratings yet
- Final Notes-Biology For EngineersDocument146 pagesFinal Notes-Biology For EngineersMohammed FurqanNo ratings yet
- AIIMS Pharmacology May 2017 - 180517151700Document16 pagesAIIMS Pharmacology May 2017 - 180517151700SelvaArockiamNo ratings yet
- How Manipulation WorksDocument5 pagesHow Manipulation WorksRajeev TiwariNo ratings yet
- Kno Sys 9865Document57 pagesKno Sys 9865Tatiana BorisenkoNo ratings yet
- ABS Graduate Program GuideDocument199 pagesABS Graduate Program GuideJas MineNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve V - Trigeminal Nerve - FRCEM SuccessDocument1 pageCranial Nerve V - Trigeminal Nerve - FRCEM SuccessJohn CoxNo ratings yet
- Human ReflexesDocument13 pagesHuman ReflexesJörgen Puis50% (2)
- Praktikum FisiologiDocument49 pagesPraktikum FisiologiNurul Fadhilah Taniyo100% (1)
- EEG-based Emotion Perception During Music ListeningDocument5 pagesEEG-based Emotion Perception During Music ListeningSushrutha Bharadwaj. MNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: 1. General InformationDocument12 pagesSyllabus: 1. General InformationSpark LincolnNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Neurologic DisordersDocument78 pagesCare of Clients With Neurologic DisordersKatri ArasaNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic TransmissionDocument43 pagesCholinergic TransmissionAjay SinghNo ratings yet